Funded articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Articles and issues > Funded articles
Original Articles
- The value of CDC42 effector protein 2 as a novel prognostic biomarker in liver hepatocellular carcinoma: a comprehensive data analysis
- Hye-Ran Kim, Choong Won Seo, Jongwan Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(6):451-467. Published online December 15, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0229
- Funded: National Research Foundation of Korea
- 857 View
- 38 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Objectives
The prognostic significance of CDC42 effector protein 2 (CDC42EP2) and its association with tumor-infiltrating immune cells (TIICs) have not been explored in liver hepatocellular carcinoma (LIHC). This study aims to assess the potential prognostic value of CDC42EP2 by conducting a comprehensive analysis of online databases pertaining to LIHC. Methods: We evaluated the potential of CDC42EP2 as a prognostic biomarker by utilizing online databases such as TIMER, GEPIA2, KM, OSlihc, HPA, and LinkedOmics. Results: In LIHC, we observed that the mRNA and protein expression of CDC42EP2 were upregulated compared to normal tissues. Upregulated CDC42EP2 expression was associated with a worse prognosis based on the clinicopathological characteristics of patients with LIHC. Furthermore, CDC42EP2 was positively associated with TIICs. In the co-expression and functional enrichment analyses of CDC42EP2, 11,416 genes showed positive associations with CDC42EP2 while 8,008 genes showed negative associations. CDC42EP2-related co-expression genes were involved in protein localization to the endoplasmic reticulum, translational initiation, and RNA catabolic processes in gene set enrichment analysis-Gene Ontology (GSEAGO), and regulated the ribosome, spliceosome, and primary immune deficiency in the GSEAKyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway. In a survival map, 23 and 17 genes that exhibited positive associations with CDC42EP2 showed a significant hazard ratio (HR) for overall survival and disease-free survival, respectively. Conclusion: Our findings demonstrated that CDC42EP2 is a novel prognostic biomarker and a potential tumor immune therapeutic target in patients with LIHC.
- Risk factors for transmission in a COVID-19 cluster infection in a high school in the Republic of Korea
- Jin-Hwan Jeon, Su Jin Kang, Se-Jin Jeong, Hyeon-Cheol Jang, Young-Joon Park, Sang-Eun Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(4):252-262. Published online July 27, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0125
- Funded: Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency
- 3,450 View
- 192 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 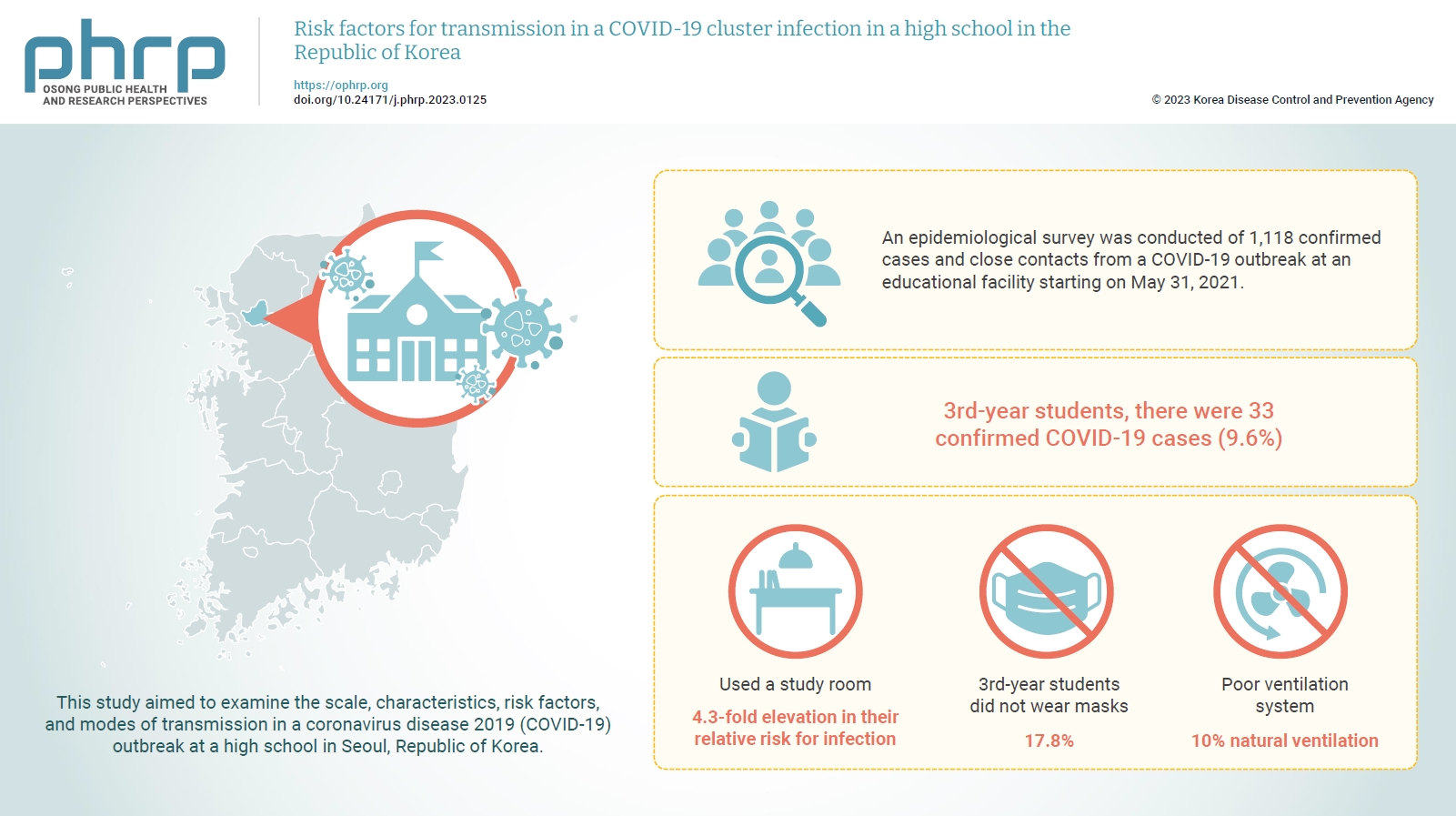
- Objectives
This study aimed to examine the scale, characteristics, risk factors, and modes of transmission in a coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak at a high school in Seoul, Republic of Korea.
Methods
An epidemiological survey was conducted of 1,118 confirmed cases and close contacts from a COVID-19 outbreak at an educational facility starting on May 31, 2021. In-depth interviews, online questionnaires, flow evaluations, and CCTV analyses were used to devise infection prevention measures. Behavioral and spatial risk factors were identified, and statistical significance was tested.
Results
Among 3rd-year students, there were 33 confirmed COVID-19 cases (9.6%). Students who used a study room in the annex building showed a statistically significant 4.3-fold elevation in their relative risk for infection compared to those who did not use the study room. Moreover, CCTV facial recognition analysis confirmed that 17.8% of 3rd-year students did not wear masks and had the lowest percentage of mask-wearers by grade. The air epidemiological survey conducted in the study room in the annex, which met the 3 criteria for a closed space, confirmed that there was only 10% natural ventilation due to the poor ventilation system.
Conclusion
To prevent and manage the spread of COVID-19 in educational facilities, advance measures that consider the size, operation, and resources of each school are crucial. In addition, various survey methodologies should be used in future studies to quickly analyze a wider range of data that can inform an evidence-based quarantine response. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Detection of a cluster of Omicron's BA.4 sublineage in Northern Senegal and identification of the first XAS recombinant variant in Senegal
Martin Faye, Modeste Name Faye, Babacar Ndiaye, Moussa Moïse Diagne, Safietou Sankhe, Ndeye Marième Top, Amadou Diallo, Cheikh Loucoubar, Ndongo Dia, Amadou Alpha Sall, Ousmane Faye
Virus Research.2024; 339: 199259. CrossRef
- Detection of a cluster of Omicron's BA.4 sublineage in Northern Senegal and identification of the first XAS recombinant variant in Senegal
- Increased viral load in patients infected with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 Omicron variant in the Republic of Korea
- Jeong-Min Kim, Dongju Kim, Nam-Joo Lee, Sang Hee Woo, Jaehee Lee, Hyeokjin Lee, Ae Kyung Park, Jeong-Ah Kim, Chae Young Lee, Il-Hwan Kim, Cheon Kwon Yoo, Eun-Jin Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(4):272-278. Published online July 27, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0024
- Funded: Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency
- 1,328 View
- 108 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Objectives
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has been declared a global pandemic owing to the rapid spread of the causative agent, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. Its Delta and Omicron variants are more transmissible and pathogenic than other variants. Some debates have emerged on the mechanism of variants of concern. In the COVID-19 wave that began in December 2021, the Omicron variant, first reported in South Africa, became identifiable in most cases globally. The aim of this study was to provide data to inform effective responses to the transmission of the Omicron variant.
Methods
The Delta variant and the spike protein D614G mutant were compared with the Omicron variant. Viral loads from 5 days after symptom onset were compared using epidemiological data collected at the time of diagnosis.
Results
The Omicron variant exhibited a higher viral load than other variants, resulting in greater transmissibility within 5 days of symptom onset.
Conclusion
Future research should focus on vaccine efficacy against the Omicron variant and compare trends in disease severity associated with its high viral load.
- Mental health and its determinants among adolescents living in families with separated or divorced parents in an urban area of Vietnam
- Binh Thang Tran, Minh Tu Nguyen, Minh Tam Nguyen, Thanh Gia Nguyen, Vo Nu Hong Duc, Thi Tra My Tran
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(4):300-311. Published online August 9, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0110
- Funded: Hue University
- 2,200 View
- 171 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Objectives
We assessed the prevalence of stress, anxiety, and depression among adolescents living in families with separated or divorced parents in Hue City, Vietnam and identified factors associated with these conditions.
Methods
This cross-sectional study enrolled 309 adolescents, aged 12 to 17 years, living in families with separated or divorced parents in Hue City, Vietnam. The depression anxiety stress scale-21 (DASS-21) was used to measure stress, anxiety, and depression. Predictors of overall and individual mental health problems were identified using ordered and binary logistic regression, respectively.
Results
The DASS-21 scale revealed a 49.2% prevalence of stress, while anxiety and depression had s prevalence rates of 61.5%. Among participants, 42.4% experienced all 3 mental health issues. Several factors were identified as significant predictors of mental health problems, including poor to average economic status (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 2.00; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.21–3.31; p=0.007); being in high school (aOR, 5.02; 95% CI, 2.93–8.60; p<0.001); maternal occupation of teacher, healthcare professional, or official (aOR, 2.39; 95% CI, 1.13–5.03; p=0.022); longer duration of family separation or divorce (aOR, 1.24; 95% CI, 1.05–1.45; p=0.009); living with one’s mother (aOR, 1.69; 95% CI, 1.03–2.76; p=0.04); alcohol consumption (aOR, 1.70; 95% CI, 0.99–2.92; p=0.050); and being bullied (aOR, 5.33; 95% CI, 1.10–25.69; p=0.037). Most of these factors were associated with stress, anxiety, and depression. Additionally, smoking was associated with stress.
Conclusion
Adolescents with separated or divorced parents were at increased risk of stress, anxiety, and depression. The findings of this study provide important implications for prevention programs.
Short Communication
- Trends of legionellosis reported in Jeju Province, Republic of Korea, 2015–2022
- Juyoung Park, Jong-Myon Bae
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(4):321-327. Published online August 21, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0145
- Funded: Jeju National University
- 1,195 View
- 98 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Objectives
The number of reported cases of Legionnaires’ disease (LD) in the Republic of Korea surged nationally in 2016; however, in 2022, this number was higher in Jeju Province than the previous national peak. A descriptive epidemiological study was conducted to analyze trends in the incidence of reported LD cases in Jeju Island from 2015 to 2022.
Methods
The data for this study were obtained from case reports submitted to the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency through its Disease and Health Integrated Management System. The selection criteria were cases or suspected cases of LD reported among Jeju residents between 2015 and 2022. The 95% confidence interval of the crude incidence rate was calculated using the Poisson distribution.
Results
Since 2020, the incidence rate of LD in Jeju has risen sharply, showing a statistically significant difference from the national incidence rate. A particular medical institution in Jeju reported a significant number of LD cases. Screening with the urine antigen test (UAT) also increased significantly.
Conclusion
Our findings indicate that the rapid increase in cases of LD in Jeju Province since 2020 was due to the characteristics of medical-care use among Jeju residents, which were focused on a specific medical institution. According to their clinical practice guidelines, this medical institution conducted UATs to screen patients suspected of pneumonia.
Original Article
- The COVID-19 pandemic and healthcare utilization in Iran: evidence from an interrupted time series analysis
- Monireh Mahmoodpour-Azari, Satar Rezaei, Nasim Badiee, Mohammad Hajizadeh, Ali Mohammadi, Ali Kazemi-Karyani, Shahin Soltani, Mehdi Khezeli
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(3):180-187. Published online June 22, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0041
- Funded: Kermanshah University of Medical Sciences
- 1,371 View
- 66 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 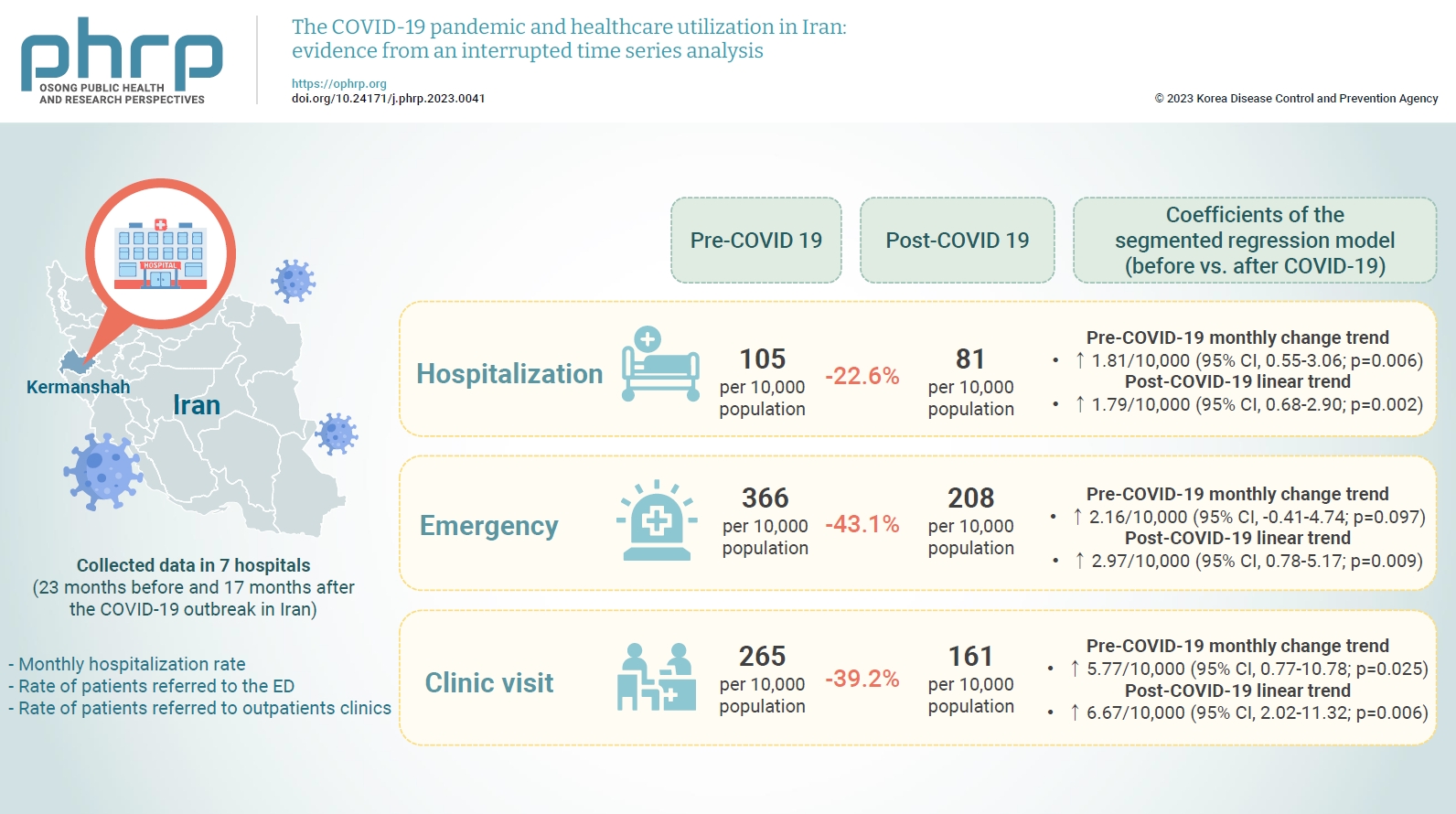
- Objectives
This study aimed to examine the effect of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak on the hospitalization rate, emergency department (ED) visits, and outpatient clinic visits in western Iran.
Methods
We collected data on the monthly hospitalization rate, rate of patients referred to the ED, and rate of patients referred to outpatient clinics for a period of 40 months (23 months before and 17 months after the COVID-19 outbreak in Iran) from all 7 public hospitals in the city of Kermanshah. An interrupted time series analysis was conducted to examine the impact of COVID-19 on the outcome variables in this study.
Results
A statistically significant decrease of 38.11 hospitalizations per 10,000 population (95% confidence interval [CI], 24.93–51.29) was observed in the first month of the COVID-19 outbreak. The corresponding reductions in ED visits and outpatient visits per 10,000 population were 191.65 (95% CI, 166.63–216.66) and 168.57 (95% CI, 126.41–210.73), respectively. After the initial reduction, significant monthly increases in the hospitalization rate (an increase of 1.81 per 10,000 population), ED visits (an increase of 2.16 per 10,000 population), and outpatient clinic visits (an increase of 5.77 per 10,000 population) were observed during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Conclusion
Our study showed that the utilization of outpatient and inpatient services in hospitals and clinics significantly declined after the COVID-19 outbreak, and use of these services did not return to pre-outbreak levels as of June 2021.
Brief Report
- Early countermeasures to COVID-19 at long-term care facilities in Gwangju Metropolitan City, Republic of Korea
- Hye-Jin Kim, Jieun Kim, Yoon Suk Jang, Hanul Park, Jong Mu Kim, Young Joon Park, So-Yeon Ryu, Jun Hwi Cho, So Yeong Park, Sang-Eun Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(1):59-65. Published online February 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0293
- Funded: Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency
- 1,881 View
- 79 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 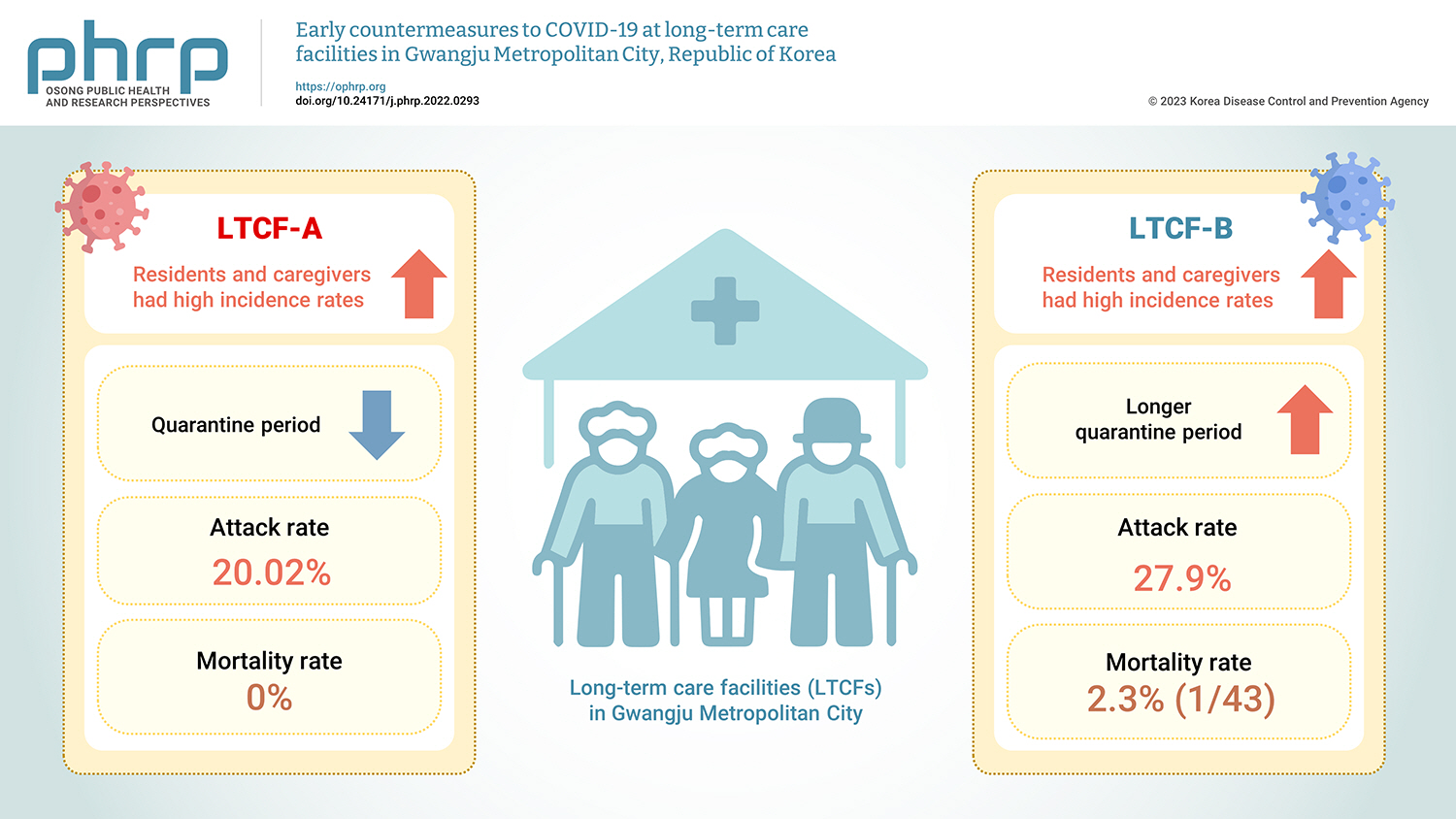
- Objectives
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has continued since its first detection in the Republic of Korea on January 20, 2020. This study describes the early countermeasures used to minimize the risk of COVID-19 outbreaks during cohort quarantine and compares the epidemiological characteristics of 2 outbreaks in long-term care facilities (LTCFs) in Gwangju Metropolitan City in summer 2020. Methods: An epidemiological investigation was conducted via direct visits. We investigated epidemiological characteristics, including incidence, morbidity, and mortality rates, for all residents and staff members. Demographic characteristics were analyzed using a statistical program. Additionally, the method of managing infection in LTCFs is described. Results: Residents and caregivers had high incidence rates in LTCF-A and LTCF-B, respectively. LTCF-B had a longer quarantine period than LTCF-A. The attack rate was 20.02% in LTCF-A and 27.9% in LTCF-B. The mortality rate was 2.3% (1/43) in LTCF-B, the only facility in which a COVID-19 death occurred. Conclusion: Extensive management requires contact minimization, which involves testing all contacts to mitigate further transmission in the early stages of LTCF outbreaks. The findings of this study can help inform and prepare public health authorities for COVID-19 outbreaks, particularly for early control in vulnerable facilities.
Special Article
- A framework for nationwide COVID-19 vaccine safety research in the Republic of Korea: the COVID-19 Vaccine Safety Research Committee
- Na-Young Jeong, Hyesook Park, Sanghoon Oh, Seung Eun Jung, Dong-Hyun Kim, Hyoung-Shik Shin, Hee Chul Han, Jong-Koo Lee, Jun Hee Woo, Byung-Joo Park, Nam-Kyong Choi
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(1):5-14. Published online February 28, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0026
- Funded: Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency
- 3,028 View
- 153 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- With the introduction of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccines, the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency (KDCA) commissioned the National Academy of Medicine of Korea to gather experts to independently assess post-vaccination adverse events. Accordingly, the COVID-19 Vaccine Safety Research Committee (CoVaSC) was launched in November 2021 to perform safety studies and establish evidence for policy guidance. The CoVaSC established 3 committees for epidemiology, clinical research, and communication. The CoVaSC mainly utilizes pseudonymized data linking KDCA’s COVID-19 vaccination data and the National Health Insurance Service’s claims data. The CoVaSC’s 5-step research process involves defining the target diseases and organizing ad-hoc committees, developing research protocols, performing analyses, assessing causal relationships, and announcing research findings and utilizing them to guide compensation policies. As of 2022, the CoVaSC completed this research process for 15 adverse events. The CoVaSC launched the COVID-19 Vaccine Safety Research Center in September 2022 and has been reorganized into 4 divisions to promote research including international collaborative studies, long-/short-term follow-up studies, and education programs. Through these enhancements, the CoVaSC will continue to swiftly provide scientific evidence for COVID-19 vaccine research and compensation and may serve as a model for preparing for future epidemics of new diseases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk of encephalitis and meningitis after COVID-19 vaccination in South Korea: a self-controlled case series analysis
Ju Hwan Kim, Dongwon Yoon, Hwa Yeon Ko, Kyungyeon Jung, Jun-Sang Sunwoo, Won Chul Shin, Jung-Ick Byun, Ju-Young Shin
BMC Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - To become a more stronger and safer country
Jong-Koo Lee
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2023; 14(2): 67. CrossRef - Risk of lymphadenopathy from SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in Korea: a self-controlled case series analysis
Mi-Sook Kim, Bongyoung Kim, Jeong Pil Choi, Nam-Kyong Choi, Jung Yeon Heo, Jun Yong Choi, Joongyub Lee, Sang Il Kim
Epidemiology and Health.2023; 45: e2023090. CrossRef
- Risk of encephalitis and meningitis after COVID-19 vaccination in South Korea: a self-controlled case series analysis
Original Articles
- Investigation of SARS-CoV-2 lineages and mutations circulating in a university-affiliated hospital in South Korea analyzed using Oxford Nanopore MinION sequencing
- Hyaekang Kim, Sung Hee Chung, Hyun Soo Kim, Han-Sung Kim, Wonkeun Song, Ki Ho Hong, Jae-Seok Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(5):360-369. Published online October 11, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0183
- Funded: Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, Ministry of Health and Welfare
- 3,082 View
- 76 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Objectives
Despite the introduction of vaccines, treatments, and massive diagnostic testing, the evolution of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has continued to overcome barriers that had slowed its previous spread. As the virus evolves towards increasing fitness, it is critical to continue monitoring the occurrence of new mutations that could evade human efforts to control them. Methods: We performed whole-genome sequencing using Oxford Nanopore MinION sequencing on 58 SARS-CoV-2 isolates collected during the ongoing coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic at a tertiary hospital in South Korea and tracked the emergence of mutations responsible for massive spikes in South Korea. Results: The differences among lineages were more pronounced in the spike gene, especially in the receptor-binding domain (RBD), than in other genes. Those RBD mutations could compromise neutralization by antibodies elicited by vaccination or previous infections. We also reported multiple incidences of Omicron variants carrying mutations that could impair the diagnostic sensitivity of reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction-based testing. Conclusion: These results provide an understanding of the temporal changes of variants and mutations that have been circulating in South Korea and their potential impacts on antigenicity, therapeutics, and diagnostic escape of the virus. We also showed that the utilization of the nanopore sequencing platform and the ARTIC workf low can provide convenient and accurate SARS-CoV-2 genomic surveillance even at a single hospital. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Understanding large scale sequencing datasets through changes to protein folding
David Shorthouse, Harris Lister, Gemma S Freeman, Benjamin A Hall
Briefings in Functional Genomics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Molecular epidemiology of SARS‐CoV‐2 in Mongolia, first experience with nanopore sequencing in lower‐ and middle‐income countries setting
Munkhtuya Erendereg, Suvd Tumurbaatar, Otgonjargal Byambaa, Gerelmaa Enebish, Natsagdorj Burged, Tungalag Khurelsukh, Nomin‐Erdene Baatar, Badmaarag Munkhjin, Jargaltulga Ulziijargal, Anuujin Gantumur, Oyunbaatar Altanbayar, Ochbadrakh Batjargal, Delgermu
Immunity, Inflammation and Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Understanding large scale sequencing datasets through changes to protein folding
- A case-control study of acute hepatitis A in South Korea, 2019
- Jung Hee Hyun, Ju Young Yoon, Sang Hyuk Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(5):352-359. Published online October 12, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0141
- Funded: Ministry of Education, National Research Foundation of Korea
- 2,909 View
- 117 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Objectives
We aimed to reconfirm the source of hepatitis A virus (HAV) infection through epidemiological and genotype investigations of individual cases in a 2019 outbreak in South Korea. Methods: We investigated food intake histories, associations with hepatitis A, and genotypes of HAV in 31 patients with hepatitis aged 20 to 49 years registered in the integrated disease and health management system during December 1–7, 2019 (case group) and in 35 sex- and agematched people without a history of HAV vaccination or infection among patients’ families and colleagues (control group). Results: The consumption of salted clams was a significant factor (odds ratio, 4.33; 95% confidence interval, 1.32–14.18) in the risk factor analysis of food intake history. HAV genotypes were analyzed in 24 of 31 patients. Type IA and type IIIA were found in 23 and 1 cases, respectively. Conclusion: Salted clams are considered to have been the source of HAV infection at 49 weeks of the HAV outbreak in 2019; this result was consistent with that of a previous epidemiological investigation conducted by the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency in September 2019. Therefore, monitoring of the production and distribution of salted clams needs to be continued. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Monitoring viruses and beta-lactam resistance genes through wastewater surveillance during a COVID-19 surge in Suwon, South Korea
Rajendra Singh, Jaewon Ryu, Sung Soo Park, Sungpyo Kim, Keugtae Kim
Science of The Total Environment.2024; 922: 171223. CrossRef - Prevalence of foodborne viruses and influenza A virus from poultry processing plants to retailed chickens
Daseul Yeo, Mengxiao Song, Md. Iqbal Hossain, Soontag Jung, Zhaoqi Wang, Dong Joo Seo, Min Suk Rhee, Changsun Choi
Frontiers in Sustainable Food Systems.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A Study on the Detection Rate of Hepatitis A from Gastroenteritis Patients and the Genotype Analysis of Hepatitis A Virus in Busan
Sun Hee Park, Chanhee Kim, Summi Lee, Jihye Jeong, Junghye Choi, Seung Ju Lee
Journal of Bacteriology and Virology.2023; 53(2): 74. CrossRef - A Study on the Detection Rate of Hepatitis A from Gastroenteritis Patients and the Genotype Analysis of Hepatitis A Virus in Busan
Sun Hee Park, Chanhee Kim, Summi Lee, Jihye Jeong, Junghye Choi, Seung Ju Lee
Journal of Bacteriology and Virology.2023; 53(2): 74. CrossRef
- Monitoring viruses and beta-lactam resistance genes through wastewater surveillance during a COVID-19 surge in Suwon, South Korea
Review Article
- Effects of medication adherence interventions for older adults with chronic illnesses: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Hae Ok Jeon, Myung-Ock Chae, Ahrin Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(5):328-340. Published online October 12, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0168
- Funded: National Research Foundation of Korea
- 3,580 View
- 170 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to understand the characteristics of medication adherence interventions for older adults with chronic illnesses, and to investigate the average effect size by combining the individual effects of these interventions. Data from studies meeting the inclusion criteria were systematically collected in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis guidelines. The results showed that the average effect size (Hedges’ g) of the finally selected medication adherence interventions for older adults with chronic illnesses calculated using a random-effects model was 0.500 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.342−0.659). Of the medication adherence interventions, an implementation intention intervention (using face-to-face meetings and telephone monitoring with personalized behavioral strategies) and a health belief model–based educational program were found to be highly effective. Face-to-face counseling was a significantly effective method of implementing medication adherence interventions for older adults with chronic illnesses (Hedges’ g=0.531, 95% CI, 0.186−0.877), while medication adherence interventions through education and telehealth counseling were not effective. This study verified the effectiveness of personalized behavioral change strategies and cognitive behavioral therapy based on the health belief model, as well as face-to-face meetings, as medication adherence interventions for older adults with chronic illnesses.
Original Articles
- The effect of photodynamic therapy using Radachlorin on biofilm-forming multidrug-resistant bacteria
- Choong-Won Seo, Young-Kwon Kim, Jeong-Lib An, Jong-Sook Kim, Pil-Seung Kwon, Young-Bin Yu
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(4):290-297. Published online August 10, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0150
- Funded: Konyang University
- 2,098 View
- 45 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to test the effect of photodynamic therapy (PDT) on the inhibition and removal of biofilms containing multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii.
Methods
Using multidrug-resistant A. baumannii strains, an antibiotic susceptibility test was performed using the Gram-negative identification card of the Vitek 2 system (bioMérieux Inc., France), as well as an analysis of resistance genes, the effects of treatment with a light-emitting diode (LED) array using Radachlorin (RADA-PHARMA Co., Ltd., Russia), and transmission and scanning electron microscopy to confirm the biofilm-inhibitory effect of PDT.
Results
The antibiotic susceptibility test revealed multiple resistance to the antibiotics imipenem and meropenem in the carbapenem class. A class-D–type β-lactamase was found, and OXA-23 and OXA-51 were found in 100% of 15 A. baumannii strains. After PDT using Radachlorin, morphological observations revealed an abnormal structure due to the loss of the cell membrane and extensive morphological changes, including low intracellular visibility and small vacuoles attached to the cell membrane.
Conclusion
PDT involving a combination of LED and Radachlorin significantly eliminated the biofilm of multidrug-resistant A. baumannii. Observations made using electron microscopy showed that PDT combining LED and Radachlorin was effective. Additional studies on the effective elimination of biofilms containing multidrug-resistant bacteria are necessary, and we hope that a treatment method superior to sterilization with antibiotics will be developed in the future. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Photophysical properties of Radachlorin photosensitizer in solutions of different pH, viscosity and polarity
A.V. Belashov, A.A. Zhikhoreva, I.A. Gorbunova, M.E. Sasin, Sh.S. Shayakhmedov, I.V. Semenova
Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolec.2024; 305: 123480. CrossRef - Applications of Antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy in Aquaculture: Effect on Fish Pathogenic Bacteria
Edith Dube, Grace Emily Okuthe
Fishes.2024; 9(3): 99. CrossRef - Understanding the biofilm development of Acinetobacter baumannii and novel strategies to combat infection
Naji Naseef Pathoor, Akshaya Viswanathan, Gulshan Wadhwa, Pitchaipillai Sankar Ganesh
APMIS.2024; 132(5): 317. CrossRef - PDT-Induced Variations of Radachlorin Fluorescence Lifetime in Living Cells In Vitro
Andrey V. Belashov, Anna A. Zhikhoreva, Anna V. Salova, Tatiana N. Belyaeva, Ilia K. Litvinov, Elena S. Kornilova, Irina V. Semenova
Photonics.2023; 10(11): 1262. CrossRef
- Photophysical properties of Radachlorin photosensitizer in solutions of different pH, viscosity and polarity
- Insufficient weight management in pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus
- Kyunghee Han, Dong Wook Kwak, Hyun Mee Ryu, Hyun-Young Park
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(4):242-251. Published online August 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0182
- Funded: Korea National Institute of Health
- 2,461 View
- 93 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Objectives
This study investigated whether weight was managed appropriately in pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) and examined the association between insufficient gestational weight gain (GWG) and adverse pregnancy outcomes.
Methods
The study included 235 pregnant women with GDM from the Korean Pregnancy Outcome Study. GWG from the second to the third trimester (kg/wk) and total GWG (kg) were classified as insufficient, appropriate, or excessive according to the 2009 Institute of Medicine guidelines. Adverse pregnancy outcomes included maternal (hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, preterm birth, cesarean delivery, and delivery complications) and infant (low birth weight, high birth weight, neonatal intensive care unit admission, and congenital anomalies) outcomes.
Results
The proportion of pregnant women with GDM who had insufficient GWG from the second to the third trimester was 52.3%, and that of participants with total insufficient GWG was 48.1%. There were no significant associations between insufficient GWG from the second to the third trimester and adverse pregnancy outcomes. Participants with total insufficient GWG had a significantly lower risk of preterm birth (odds ratio [OR], 0.17; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.05–0.60) and high birth weight (OR, 0.23; 95% CI, 0.07–0.80).
Conclusion
Our findings suggest the importance of appropriate weight management and the need for GWG guidelines for pregnant women with GDM.
- The role of risk perception, risk communication, and demographic factors in COVID-19 preventive behaviors: an online survey in Iran
- Mansour Rezaei, Nader Rajabi Gilan, Ali Almasi, Mehdi Khezeli, Fatemeh Jamshidi Nazar, Zahra Jorjoran Shushtari, Yahya Salimi, Farid Najafi, Neda Sarabi, Shahram Saeidi, Saeid Saeidi
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(4):282-289. Published online August 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.0345
- Funded: Kermanshah University of Medical Sciences Research
- 2,850 View
- 57 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study investigated preventive behaviors toward coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and related factors in a Kurdish Iranian sample.
Methods
This online survey was conducted among the population aged 18 and above in Kermanshah Province, in western Iran, in April 2020. Samples were invited and recruited through social media. Data were collected using a questionnaire consisting of 4 sections (questions on demographic variables, risk perception, risk communication, and COVID-19 preventive behaviors) and analyzed using Stata ver. 8.
Results
The Pearson correlation test showed that risk communication was significantly correlated with COVID-19 preventive behaviors (r=0.320, p<0.01). In the final model, where the explanatory power increased with the entry of the risk communication variable, the variables explained a total of 14% of variance in COVID-19 preventive behaviors. Sex (β=−0.482), risk perception (β=0.047), and risk communication (β=0.662) were significant determinants.
Conclusion
Risk communication and risk perception related to COVID-19, as well as being a woman, were determinants of COVID-19 preventive behaviors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Understanding Australian Government Risk Communication Early in the COVID-19 Pandemic: Sociodemographics, Risk Attitudes and Media Consumption
Yiyun Shou, Louise M. Farrer, Amelia Gulliver, Eryn Newman, Philip J. Batterham, Michael Smithson
Journal of Health Communication.2023; 28(4): 254. CrossRef - Risk perception and avoidance of preventive behavior on the COVID‐19 among cancer patients
Mehdi Khezeli, Asghar Tavan, Sajjad Narimani, Vahideh Hoseini, Elham Zare Hosseinzadeh, Parisa Motamedi
Health Science Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Role of Risk Communication in Shaping Health-Protective Behavior Amid the COVID-19 Pandemic in Thailand
Suphunnika Termmee, Bing Wang
Social Sciences.2023; 12(10): 551. CrossRef
- Understanding Australian Government Risk Communication Early in the COVID-19 Pandemic: Sociodemographics, Risk Attitudes and Media Consumption
- Menstrual hygiene management and its determinants among adolescent girls in low-income urban areas of Delhi, India: a community-based study
- Suneela Garg, Nidhi Bhatnagar, Mongjam Meghachandra Singh, Saurav Basu, Amod Borle, Yamini Marimuthu, Falak Azmi, Yomri Dabi, Indu Bala
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(4):273-281. Published online August 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0127
- Funded: Delhi State Health Mission
- 3,493 View
- 253 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Menstrual hygiene management (MHM) in developing countries is linked to human rights, social justice, and the education and empowerment of young girls. The objective of this study was to assess menstrual hygiene practices and their determinants among adolescent girls, including school dropouts, and the effects of pad distribution programs in urban resettlement areas of Delhi, India.
Methods
A cross-sectional study was conducted from March 2019 to February 2020 in urban resettlement colonies and 2 villages of Delhi among 1,130 adolescent girls aged 10 to 19 years, who were interviewed face to face.
Results
In total, 954 participants (84.4%) used only disposable sanitary pads, 150 (13.3%) used both sanitary pads and cloths, and 26 (2.3%) used only cloths (n=1,130). Most school-going girls utilized the scheme for pad distribution, but only two-thirds of the girls who were out of school utilized the scheme. In the adjusted analysis, girls with lower educational status, those who had dropped out of school, and those from the Muslim religious community were more likely to use cloths for MHM.
Conclusion
More than 4 out of 5 adolescent girls in Delhi in low-income neighborhoods preferred sanitary pads for MHM. The government free pad scheme reached near-universal utilization among school-going girls (97%), but the subsidized pad scheme for girls who did not attend school was insufficiently utilized (75%). -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Associated with Exclusive Use of Hygienic Methods during Menstruation among Adolescent Girls (15–19 Years) in Urban India: Evidence from NFHS-5
Doli Roy, Nuruzzaman Kasemi, Manik Halder, Malasree Majumder
Heliyon.2024; 10(8): e29731. CrossRef - Menstrual Hygiene Problems and Challenges Faced by Adolescent Females in Rural Areas: A Narrative Review
Vijiya Kashyap, Sonali G Choudhari
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Perceived difficulties in maintaining menstrual hygiene practices among indigenous adolescents during seasonal water scarcity periods in Bandarban hill district of Bangladesh: A cross-sectional study
Imdadul Haque Talukdar, M.A. Rifat, Plabon Sarkar, Nobonita Saha, Mesfin Kassaye Tessma, Md. Ibrahim Miah
International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental.2023; 254: 114268. CrossRef - Menstrual hygiene practices among adolescent women in rural India: a cross-sectional study
Aditya Singh, Mahashweta Chakrabarty, Shivani Singh, Rakesh Chandra, Sourav Chowdhury, Anshika Singh
BMC Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Factors Associated with Exclusive Use of Hygienic Methods during Menstruation among Adolescent Girls (15–19 Years) in Urban India: Evidence from NFHS-5



 First
First Prev
Prev


