Most view
- Page Path
- HOME > Articles and issues > Most view
Most-read articles are from the articles published in 2022 during the last three month.
Original Articles
- Risk factors for SARS-CoV-2 transmission during a movie theater outbreak in Incheon in the Republic of Korea, November 2021: a retrospective study
- Hye Young Lee, Young-Joon Park, Sang-Eun Lee, Han-Na Yoo, Il-Hwan Kim, Jin Sun No, Eun-Jin Kim, Jungyeon Yu, Sanghwan Bae, Mi Yu
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2024;15(1):45-55. Published online January 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0269
- 10,580 View
- 325 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 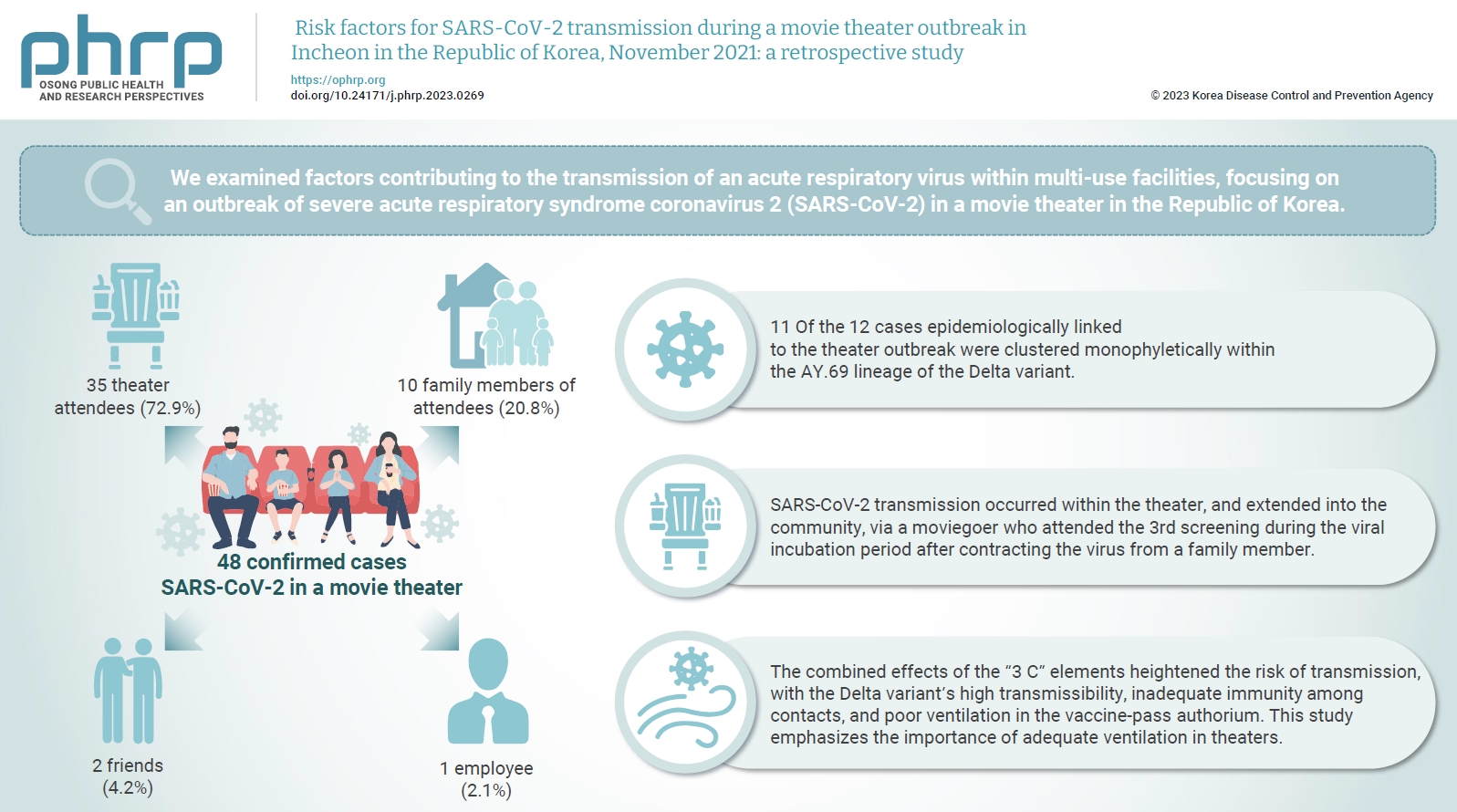
- Objectives
We examined factors contributing to the transmission of an acute respiratory virus within multi-use facilities, focusing on an outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in a movie theater in the Republic of Korea. Methods: This retrospective cohort study involved a descriptive analysis of 48 confirmed cases. Logistic regression was applied to a cohort of 80 theater attendees to identify risk factors for infection. The infection source and transmission route were determined through gene sequencing data analysis. Results: Of the 48 confirmed cases, 35 were theater attendees (72.9%), 10 were family members of attendees (20.8%), 2 were friends (4.2%), and 1 was an employee (2.1%). Among the 80 individuals who attended the 3rd to 5th screenings of the day, 35 became infected, representing a 43.8% attack rate. Specifically, 28 of the 33 third-screening attendees developed confirmed SARSCoV-2, constituting an 84.8% attack rate. Furthermore, 11 of the 12 cases epidemiologically linked to the theater outbreak were clustered monophyletically within the AY.69 lineage. At the time of the screening, 35 individuals (72.9%) had received 2 vaccine doses. However, vaccination status did not significantly influence infection risk. Multivariate analysis revealed that close contacts had a 15.9-fold higher risk of infection (95% confidence interval, 4.37–78.39) than casual contacts. Conclusion: SARS-CoV-2 transmission occurred within the theater, and extended into the community, via a moviegoer who attended the 3rd screening during the viral incubation period after contracting the virus from a family member. This study emphasizes the importance of adequate ventilation in theaters.
- Estimating the prevalence of oral manifestations in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review
- Ankita Gupta, Kriti Shrivastav, Amit Agrawal, Abhishek Purohit, Roshan Chanchlani
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(5):388-417. Published online September 19, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0033
- 2,813 View
- 94 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 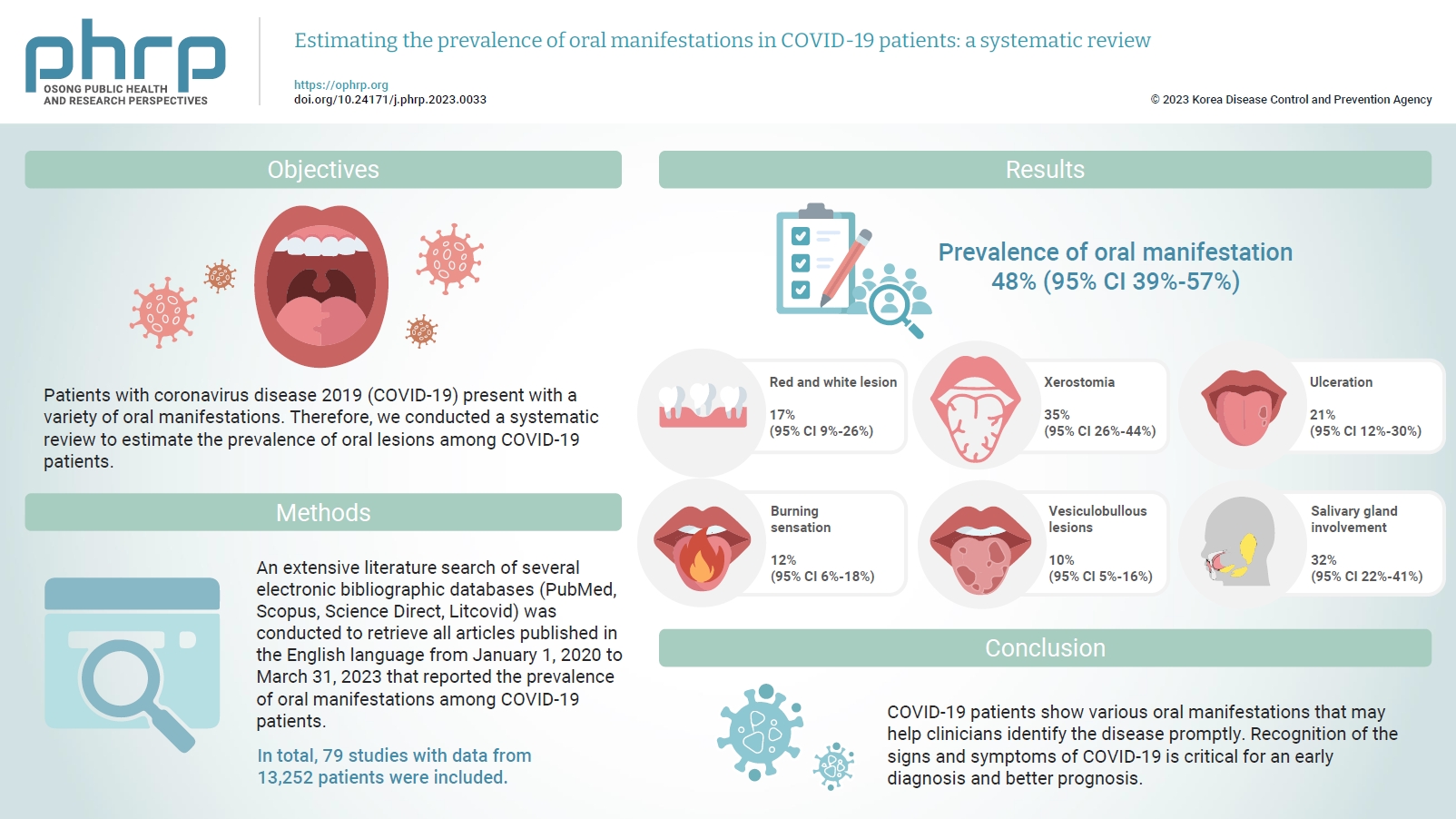
- Objectives
Patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) present with a variety of oral manifestations. Therefore, we conducted a systematic review to estimate the prevalence of oral lesions among COVID-19 patients. Methods: An extensive literature search of several electronic bibliographic databases (PubMed, Scopus, Science Direct, Litcovid) was conducted to retrieve all articles published in the English language from January 1, 2020 to March 31, 2023 that reported the prevalence of oral manifestations among COVID-19 patients. A meta-analysis of pooled prevalence was performed using Jamovi ver. 2.3 (2022). The I2 and Q statistics were used to assess heterogeneity between studies, and p-values <0.01 were considered statistically significant. Results: In total, 79 studies with data from 13,252 patients were included. The articles were predominantly published in 2020 (n=33), and Italy was the most common country (n=14). Most of the affected patients more than 50 years old and women (56.6%). The most common sites of involvement were the tongue (n=65), followed by the oral mucosa (n=37) and lips (n=19). High heterogeneity was found between studies. The most common oral manifestation was taste alteration, followed by xerostomia and ulceration, showing pooled prevalence rates of 48%, 35%, and 21%, respectively. Conclusion: COVID-19 patients show various oral manifestations that may help clinicians identify the disease promptly. Recognition of the signs and symptoms of COVID-19 is critical for an early diagnosis and better prognosis.
Review Article
- Yersinia pestis antibiotic resistance: a systematic review
- Chen Lei, Suresh Kumar
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(1):24-36. Published online February 18, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.0288
- 7,274 View
- 248 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Yersinia pestis, the cause of plague and a potential biological weapon, has always been a threatening pathogen. Some strains of Y. pestis have varying degrees of antibiotic resistance. Thus, this systematic review was conducted to alert clinicians to this pathogen’s potential antimicrobial resistance. A review of the literature was conducted for experimental reports and systematic reviews on the topics of plague, Y. pestis, and antibiotic resistance. From 1995 to 2021, 7 Y. pestis isolates with 4 antibiotic resistance mechanisms were reported. In Y. pestis 17/95, 16/95, and 2180H, resistance was mediated by transferable plasmids. Each plasmid contained resistance genes encoded within specific transposons. Strain 17/95 presented multiple drug resistance, since plasmid 1202 contained 10 resistance determinants. Strains 16/95 and 2180H showed single antibiotic resistance because both additional plasmids in these strains carried only 1 antimicrobial determinant. Strains 12/87, S19960127, 56/13, and 59/13 exhibited streptomycin resistance due to an rpsl gene mutation, a novel mechanism that was discovered recently. Y. pestis can acquire antibiotic resistance in nature not only via conjugative transfer of antimicrobial-resistant plasmids from other bacteria, but also by gene point mutations. Global surveillance should be strengthened to identify antibiotic-resistant Y. pestis strains by whole-genome sequencing and drug susceptibility testing.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Seek and you shall find: Yersinia enterocolitica in Ireland’s drinking water
James Powell, Maureen Daly, Nuala H. O’Connell, Colum P. Dunne
Irish Journal of Medical Science (1971 -).2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A novel sORF gene mutant strain of Yersinia pestis vaccine EV76 offers enhanced safety and improved protection against plague
Xiao Guo, Youquan Xin, Zehui Tong, Shiyang Cao, Yuan Zhang, Gengshan Wu, Hongyan Chen, Tong Wang, Yajun Song, Qingwen Zhang, Ruifu Yang, Zongmin Du, Gregory P. Priebe
PLOS Pathogens.2024; 20(3): e1012129. CrossRef - Rapid Induction of Protective Immunity against Pneumonic Plague by Yersinia pestis Polymeric F1 and LcrV Antigens
Moshe Aftalion, Avital Tidhar, Yaron Vagima, David Gur, Ayelet Zauberman, Tzvi Holtzman, Arik Makovitzki, Theodor Chitlaru, Emanuelle Mamroud, Yinon Levy
Vaccines.2023; 11(3): 581. CrossRef - Antibiotic resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae: broad-spectrum drug target identification using subtractive genomics
Umairah Natasya Mohd Omeershffudin, Suresh Kumar
Genomics & Informatics.2023; 21(1): e5. CrossRef - Polyclonal Antibodies Derived from Transchromosomic Bovines Vaccinated with the Recombinant F1-V Vaccine Increase Bacterial Opsonization In Vitro and Protect Mice from Pneumonic Plague
Sergei S. Biryukov, Hua Wu, Jennifer L. Dankmeyer, Nathaniel O. Rill, Christopher P. Klimko, Kristi A. Egland, Jennifer L. Shoe, Melissa Hunter, David P. Fetterer, Ju Qiu, Michael L. Davies, Christoph L. Bausch, Eddie J. Sullivan, Thomas Luke, Christopher
Antibodies.2023; 12(2): 33. CrossRef - New Bacteriophages with Podoviridal Morphotypes Active against Yersinia pestis: Characterization and Application Potential
Tamar Suladze, Ekaterine Jaiani, Marina Darsavelidze, Maia Elizbarashvili, Olivier Gorge, Ia Kusradze, Tamar Kokashvili, Nino Lashkhi, George Tsertsvadze, Nino Janelidze, Svetlana Chubinidze, Marina Grdzelidze, Shota Tsanava, Eric Valade, Marina Tediashvi
Viruses.2023; 15(7): 1484. CrossRef -
Characterization of Mu-Like
Yersinia
Phages Exhibiting Temperature Dependent Infection
Biao Meng, Zhizhen Qi, Xiang Li, Hong Peng, Shanzheng Bi, Xiao Wei, Yan Li, Qi Zhang, Xiaoqing Xu, Haihong Zhao, Xiaoyan Yang, Changjun Wang, Xiangna Zhao, Olaya Rendueles
Microbiology Spectrum.2023;[Epub] CrossRef -
Ancient
Yersinia pestis
genomes lack the virulence-associated Ypf
Φ
prophage present in modern pandemic strains
Joanna H. Bonczarowska, Julian Susat, Ben Krause-Kyora, Dorthe Dangvard Pedersen, Jesper Boldsen, Lars Agersnap Larsen, Lone Seeberg, Almut Nebel, Daniel Unterweger
Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sci.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A situation analysis of the current plague outbreak in the Demographic Republic of Congo and counteracting strategies – Correspondence
Ranjit Sah, Abdullah Reda, Rachana Mehta, Ranjan K. Mohapatra, Kuldeep Dhama
International Journal of Surgery.2022; 105: 106885. CrossRef - Antimicrobial resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae: identification of bacterial DNA adenine methyltransferase as a novel drug target from hypothetical proteins using subtractive genomics
Umairah Natasya Mohd Omeershffudin, Suresh Kumar
Genomics & Informatics.2022; 20(4): e47. CrossRef
- Seek and you shall find: Yersinia enterocolitica in Ireland’s drinking water
Brief Report
- Isolation and identification of monkeypox virus MPXV-ROK-P1-2022 from the first case in the Republic of Korea
- Jin-Won Kim, Minji Lee, Hwachul Shin, Chi-Hwan Choi, Myung-Min Choi, Jee Woong Kim, Hwajung Yi, Cheon-Kwon Yoo, Gi-Eun Rhie
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(4):308-311. Published online August 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0232
- 5,277 View
- 136 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 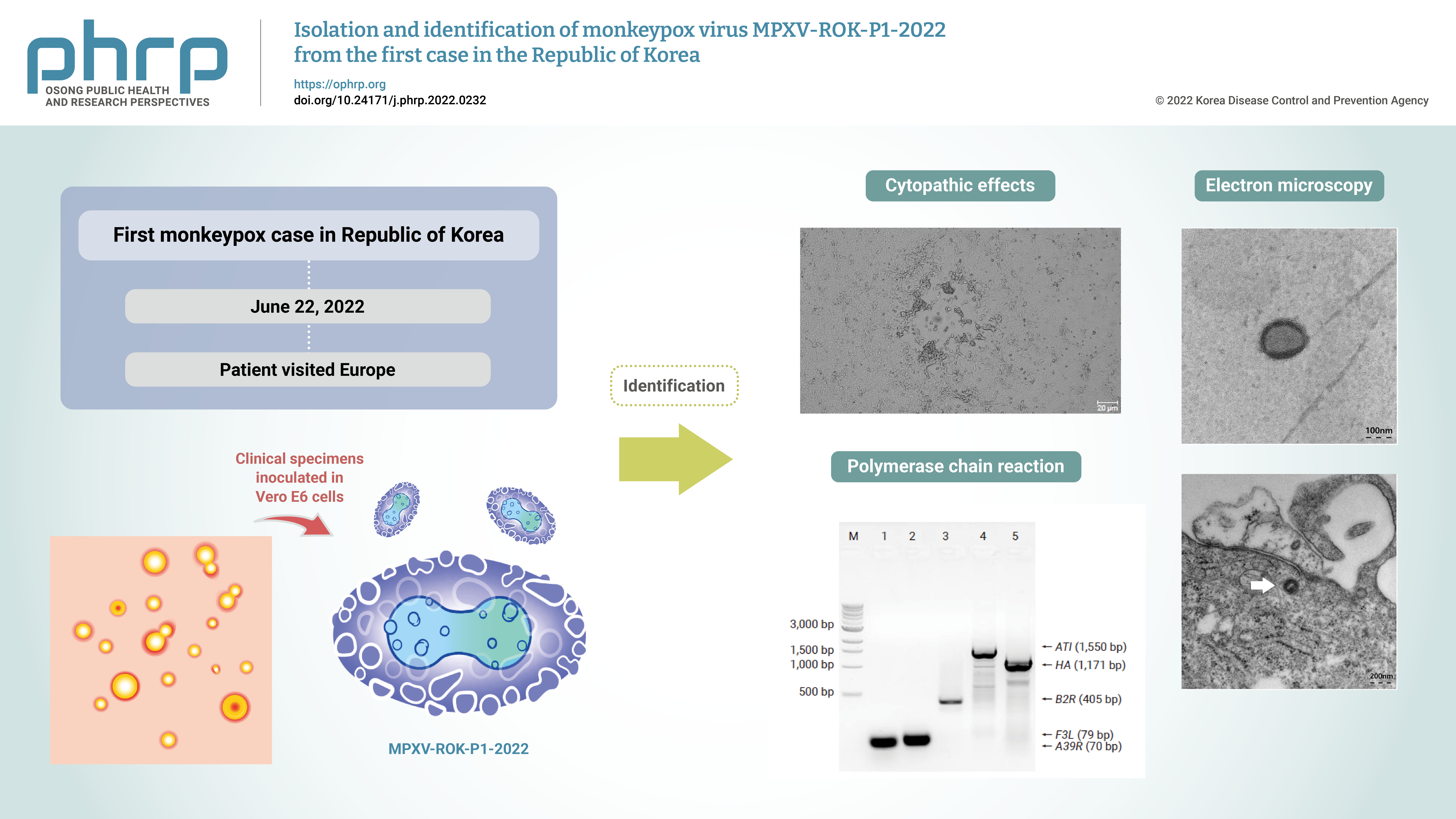
- Objectives
Monkeypox outbreaks in nonendemic countries have been reported since early May 2022. The first case of monkeypox in the Republic of Korea was confirmed in a patient who traveled to Europe in June 2022, and an attempt was made to isolate and identify the monkeypox virus (MPXV) from the patient’s specimens.
Methods
Clinical specimens from the patient were inoculated in Vero E6 cells. The isolated virus was identified as MPXV by the observation of cytopathic effects on Vero E6 cells, transmission electron microscopy, conventional polymerase chain reaction (PCR), and sequencing of PCR products.
Results
Cytopathic effects were observed in Vero E6 cells that were inoculated with skin lesion swab eluates. After multiple passages from the primary culture, orthopoxvirus morphology was observed using transmission electron microscopy. In addition, both MPXV-specific (F3L and ATI) and orthopoxvirus-specific genes (A39R, B2R, and HA) were confirmed by conventional PCR and Sanger sequencing.
Conclusion
These results indicate the successful isolation and identification of MPXV from the first patient in the Republic of Korea. The isolated virus was named MPXV-ROK-P1-2022. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ultrasensitive one-pot detection of monkeypox virus with RPA and CRISPR in a sucrose-aided multiphase aqueous system
Yue Wang, Yixin Tang, Yukang Chen, Guangxi Yu, Xue Zhang, Lihong Yang, Chenjie Zhao, Pei Wang, Song Gao, Frederick S. B. Kibenge, Ruijie Deng, Wei Chen, Shuang Yang
Microbiology Spectrum.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Epidemiological, Clinical, and Virological Investigation of the First Four Cases of Monkeypox in Cartagena during the 2022 Outbreak
Steev Loyola, Mashiel Fernández-Ruiz, Doris Gómez-Camargo
Pathogens.2023; 12(2): 159. CrossRef - 원숭이두창바이러스의 분리 배양과 전장유전체 정보 분석
민지 이, 진원 김, 치환 최, 화철 신, 명민 최, 상은 이, 화중 이, 윤석 정
Public Health Weekly Report.2023; 16(15): 464. CrossRef - Overview of Diagnostic Methods, Disease Prevalence and Transmission of Mpox (Formerly Monkeypox) in Humans and Animal Reservoirs
Ravendra P. Chauhan, Ronen Fogel, Janice Limson
Microorganisms.2023; 11(5): 1186. CrossRef - How to cope with suspected mpox patients in the outpatient clinic
Nam Joong Kim, Sun Huh
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2023; 66(5): 325. CrossRef - An Updated Review on Monkeypox Viral Disease: Emphasis on Genomic Diversity
Ali A. Rabaan, Nada A. Alasiri, Mohammed Aljeldah, Abeer N. Alshukairiis, Zainab AlMusa, Wadha A. Alfouzan, Abdulmonem A. Abuzaid, Aref A. Alamri, Hani M. Al-Afghani, Nadira Al-baghli, Nawal Alqahtani, Nadia Al-baghli, Mashahed Y. Almoutawa, Maha Mahmoud
Biomedicines.2023; 11(7): 1832. CrossRef - Monkeypox (Mpox) virus isolation and ultrastructural characterisation from a Brazilian human sample case
Milene Dias Miranda, Gabriela Cardoso Caldas, Vivian Neuza Ferreira, Ortrud Monika Barth, Aline de Paula Dias da Silva, Mayara Secco Torres Silva, Beatriz Grinsztejn, Valdiléa Gonçalves Veloso, Thiago Moreno Souza, Edson Elias da Silva, Debora Ferreira Ba
Memórias do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Isolation and Characterization of Monkeypox Virus from the First Case of Monkeypox — Chongqing Municipality, China, 2022
Baoying Huang, Hua Zhao, Jingdong Song, Li Zhao, Yao Deng, Wen Wang, Roujian Lu, Wenling Wang, Jiao Ren, Fei Ye, Houwen Tian, Guizhen Wu, Hua Ling, Wenjie Tan
China CDC Weekly.2022; 4(46): 1019. CrossRef
- Ultrasensitive one-pot detection of monkeypox virus with RPA and CRISPR in a sucrose-aided multiphase aqueous system
Original Article
- The incidence and clinical characteristics of myocarditis and pericarditis following mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccination in Republic of Korea adolescents from July 2021 to September 2022
- Ju-Young Sim, Seung-Yun Kim, Eun-Kyoung Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(2):76-88. Published online April 18, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0032
- 3,984 View
- 231 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 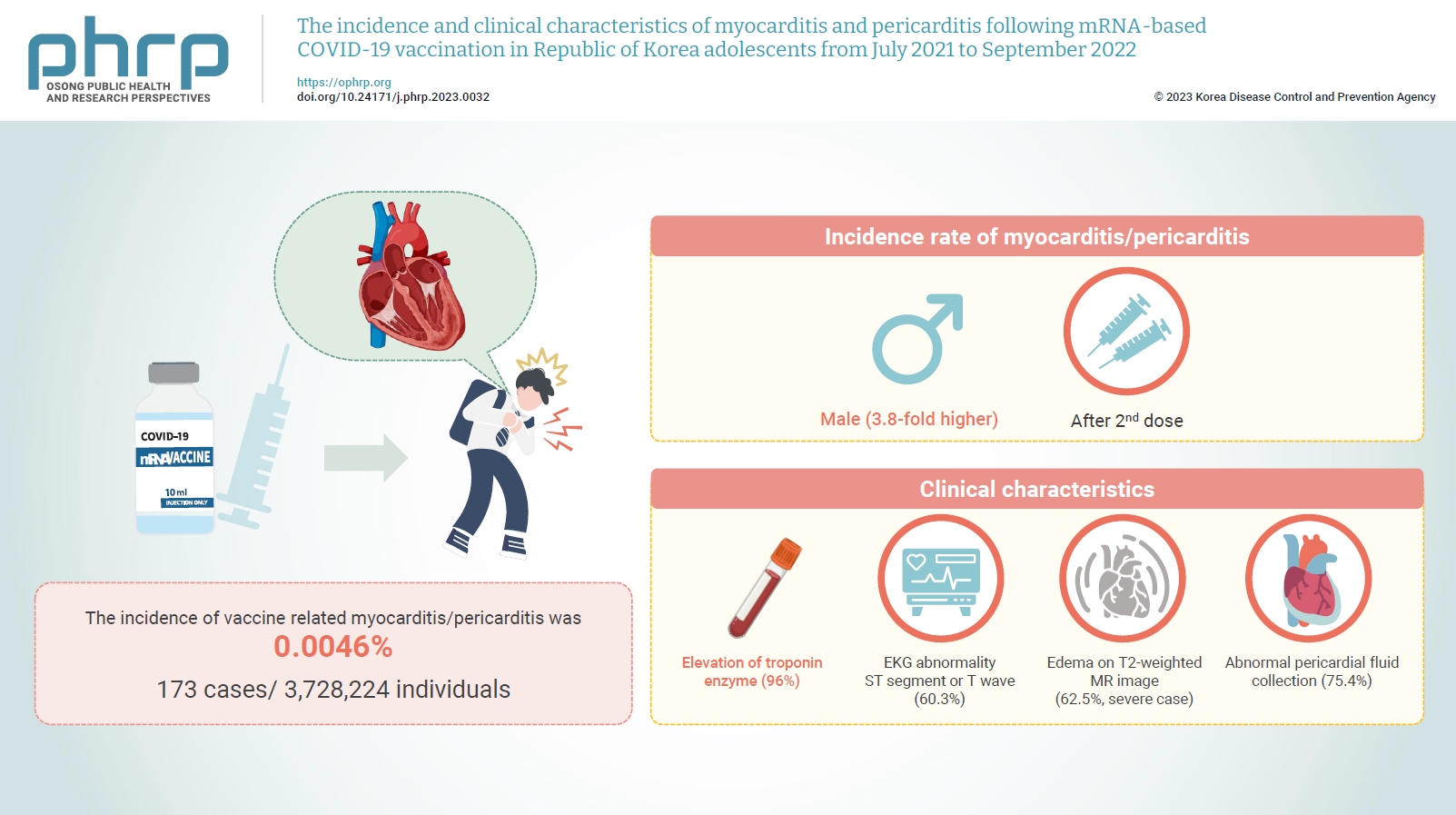
- Objectives
Age-specific information regarding myocarditis/pericarditis in adolescents following mRNA-based coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccination in Asia remains insufficient. This study investigated the incidence and clinical characteristics of myocarditis/pericarditis in Republic of Korea adolescents after mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccination.
Methods
This retrospective descriptive study utilized patient data from the Korea Immunization Management System. Incidence rates were calculated according to age and sex. Clinical characteristics (symptoms/signs, laboratory values, and imaging results) were compared between mild and severe cases.
Results
Between July 19, 2021 and September 30, 2022, 3,728,224 individuals aged 12 to 19 years received 6,484,165 mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines, and 173 cases met the case definition for myocarditis/pericarditis: 151 mild (87.3%) and 22 severe (12.7%). The incidence was 3.8-fold higher in males than in females. Troponin I/ troponin T was elevated in 96% of myocarditis cases, demonstrating higher sensitivity than creatine kinase-myocardial band (67.6%) or C-reactive protein (75.2%). ST-segment or Twave on electrography abnormalities were found in 60.3% (85/141). Paroxysmal/sustained atrial/ventricular arrhythmias were more common in severe than in mild cases (45.5% vs. 16.8%, p=0.008). Edema on T2-weighted magnetic imaging occurred in 21.6% (8/37) and 62.5% (5/8) of mild and severe cases, respectively (p=0.03). Abnormal pericardial fluid collection or pericardial inflammation was found in 75.4% of pericarditis cases (49/65).
Conclusion
Myocarditis/pericarditis occurred in rare cases following mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccination. Most cases were mild, but the incidence was higher in adolescent males and after the second dose. As bivalent severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 mRNA vaccination started in Republic of Korea in October 2022, the post-vaccination incidence of myocarditis/pericarditis should be closely monitored, considering clinical characteristics. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Responses to Common Misconceptions Relating to COVID-19 Variant-Adapted mRNA Vaccines
George Kassianos, Pauline MacDonald, Ivan Aloysius, Shanti Pather
Vaccines.2024; 12(1): 57. CrossRef - To become a more stronger and safer country
Jong-Koo Lee
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2023; 14(2): 67. CrossRef
- Responses to Common Misconceptions Relating to COVID-19 Variant-Adapted mRNA Vaccines
Review Article
- Predictors of outcomes 3 to 12 months after traumatic brain injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Younes Iderdar, Maryem Arraji, Nadia Al Wachami, Morad Guennouni, Karima Boumendil, Yassmine Mourajid, Noureddine Elkhoudri, Elmadani Saad, Mohamed Chahboune
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2024;15(1):3-17. Published online February 5, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0288
- 1,044 View
- 72 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 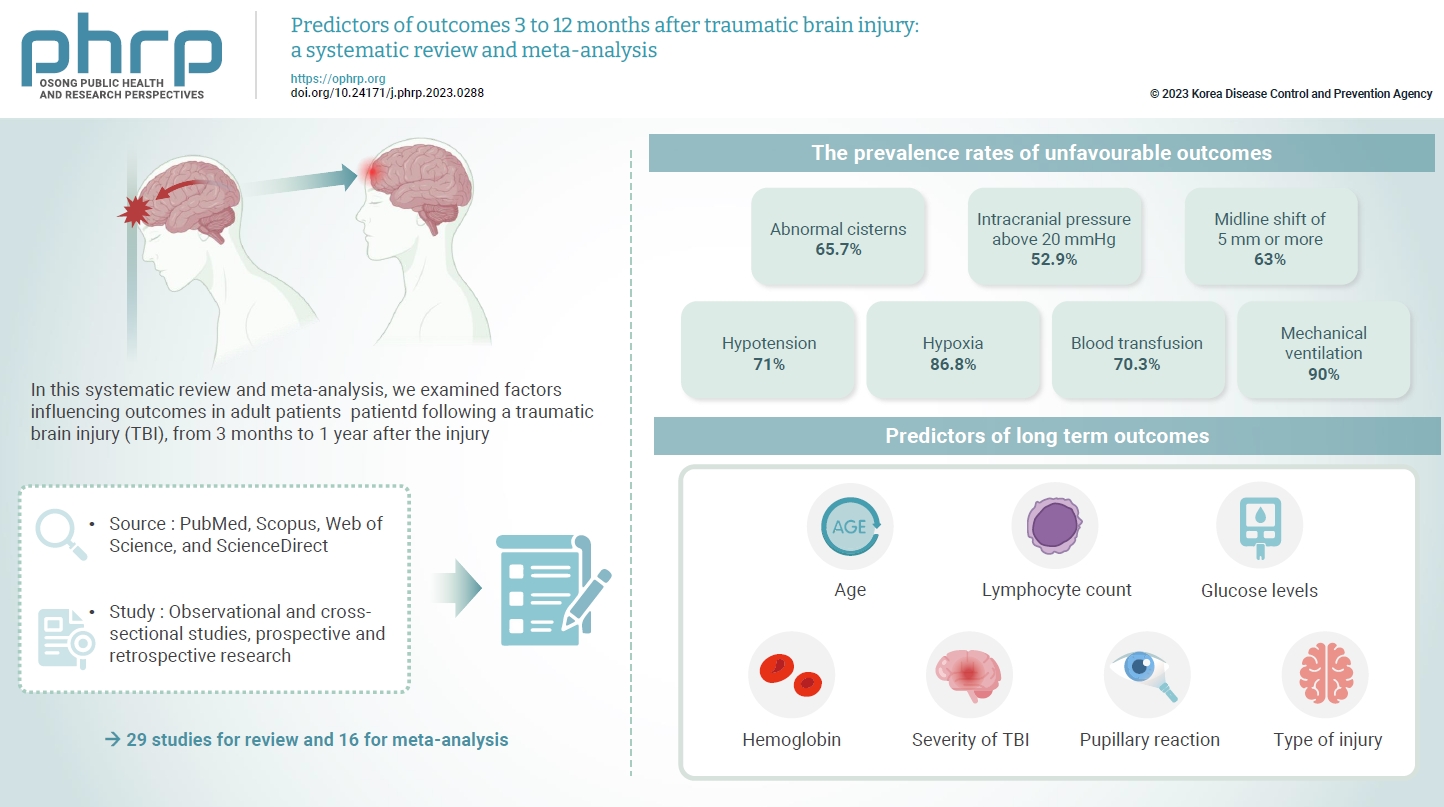
- The exact factors predicting outcomes following traumatic brain injury (TBI) remain elusive. In this systematic review and meta-analysis, we examined factors influencing outcomes in adult patients with TBI, from 3 months to 1 year after injury. A search of four electronic databases—PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and ScienceDirect—yielded 29 studies for review and 16 for meta-analysis, in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis guidelines. In patients with TBI of any severity, mean differences were observed in age (8.72 years; 95% confidence interval [CI], 4.77–12.66 years), lymphocyte count (−0.15 109/L; 95% CI, −0.18 to −0.11), glucose levels (1.20 mmol/L; 95% CI, 0.73–1.68), and haemoglobin levels (−0.91 g/dL; 95% CI, −1.49 to −0.33) between those with favourable and unfavourable outcomes. The prevalence rates of unfavourable outcomes were as follows: abnormal cisterns, 65.7%; intracranial pressure above 20 mmHg, 52.9%; midline shift of 5 mm or more, 63%; hypotension, 71%; hypoxia, 86.8%; blood transfusion, 70.3%; and mechanical ventilation, 90%. Several predictors were strongly associated with outcome. Specifically, age, lymphocyte count, glucose level, haemoglobin level, severity of TBI, pupillary reaction, and type of injury were identified as potential predictors of long-term outcomes.
Original Articles
- Epidemiological analysis and prevention strategies in response to a shigellosis cluster outbreak: a retrospective case series in an alternative school in the Republic of Korea, 2023
- Yeongseo Ahn, Sunmi Jin, Gemma Park, Hye Young Lee, Hyungyong Lee, Eunkyung Shin, Junyoung Kim, Jaeil Yoo, Yuna Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2024;15(1):68-76. Published online February 7, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0298
- 975 View
- 51 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 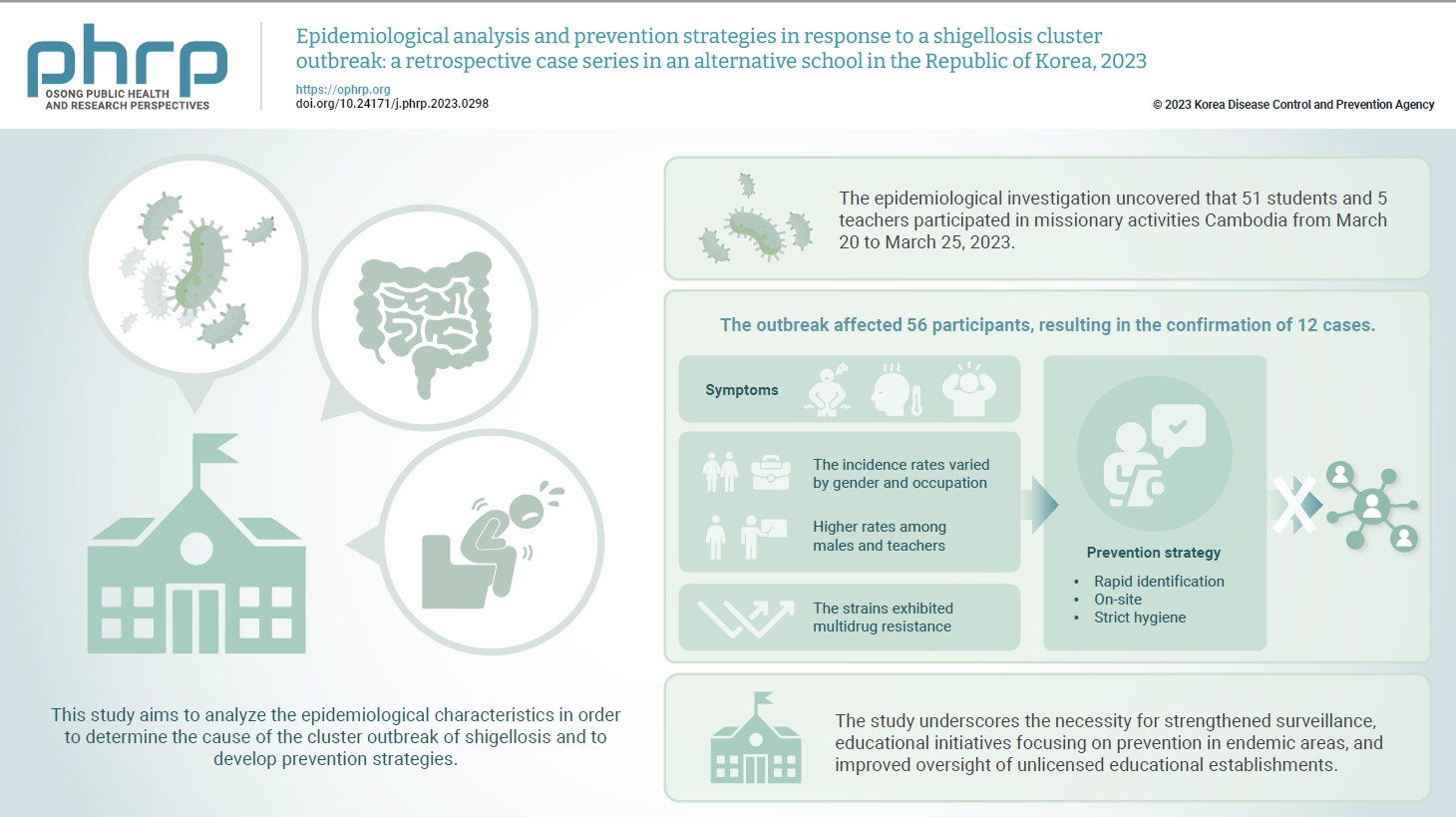
- Objectives
In March 2023, an alternative school in the Republic of Korea reported 12 cases of shigellosis. This study aims to analyze the epidemiological characteristics in order to determine the cause of the cluster outbreak of shigellosis and to develop prevention strategies. Methods: This study focused on 12 patients with confirmed Shigella infection and investigated their demographics, clinical features, epidemiology, diagnostics, and antimicrobial susceptibility. Following the identification of Shigella, we conducted follow-up rectal smear cultures to manage patients, implementing isolation and control measures. Results: This study investigated the emergence of multidrug-resistant Shigella following missionary activities in Cambodia, documenting a cluster infection within an alternative school in Daejeon, the Republic of Korea. The outbreak affected 56 participants, resulting in the confirmation of 12 cases. The incidence rates varied by gender and occupation, with higher rates among males and teachers. All 12 cases demonstrated multidrug resistance. Challenges included delayed pathogen confirmation and suboptimal adherence to isolation criteria. The incident prompted revisions in the criteria for isolation release, focusing on symptom resolution. The study underscores the necessity for strengthened surveillance, educational initiatives focusing on prevention in endemic areas, and improved oversight of unlicensed educational establishments. Conclusion: Successful response strategies included swift situation assessment, collaborative efforts, effective infection control measures, and modified criteria for isolation release. Continued surveillance of multidrug-resistant strains is recommended, especially in regions with a high prevalence.
- Developing a national surveillance system for stroke and acute myocardial infarction using claims data in the Republic of Korea: a retrospective study
- Tae Jung Kim, Hak Seung Lee, Seong-Eun Kim, Jinju Park, Jun Yup Kim, Jiyoon Lee, Ji Eun Song, Jin-Hyuk Hong, Joongyub Lee, Joong-Hwa Chung, Hyeon Chang Kim, Dong-Ho Shin, Hae-Young Lee, Bum Joon Kim, Woo-Keun Seo, Jong-Moo Park, Soo Joo Lee, Keun-Hwa Jung, Sun U. Kwon, Yun-Chul Hong, Hyo-Soo Kim, Hyun-Jae Kang, Juneyoung Lee, Hee-Joon Bae
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2024;15(1):18-32. Published online January 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0248
- 927 View
- 58 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 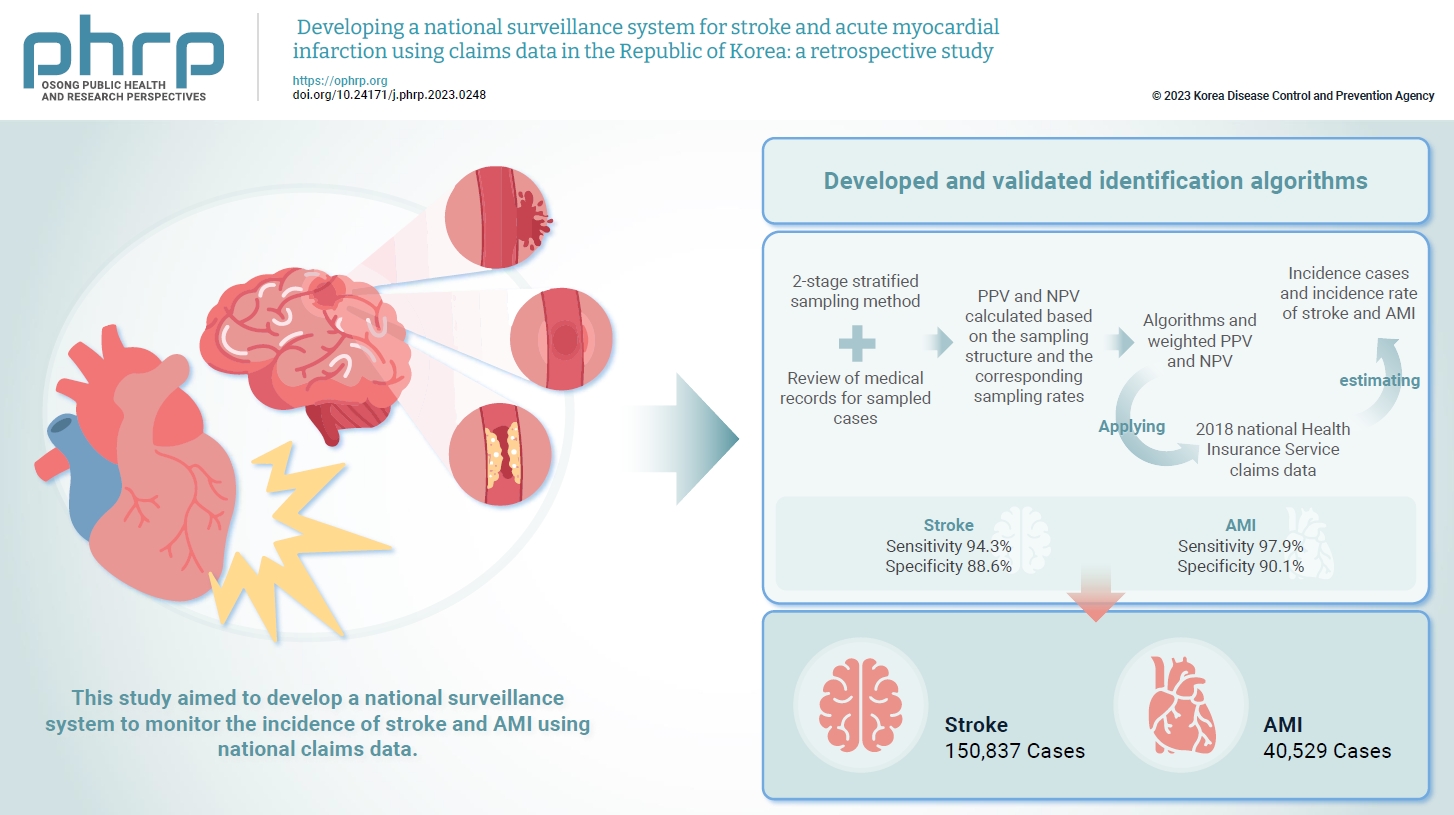
- Objectives
Limited information is available concerning the epidemiology of stroke and acute myocardial infarction (AMI) in the Republic of Korea. This study aimed to develop a national surveillance system to monitor the incidence of stroke and AMI using national claims data. Methods: We developed and validated identification algorithms for stroke and AMI using claims data. This validation involved a 2-stage stratified sampling method with a review of medical records for sampled cases. The weighted positive predictive value (PPV) and negative predictive value (NPV) were calculated based on the sampling structure and the corresponding sampling rates. Incident cases and the incidence rates of stroke and AMI in the Republic of Korea were estimated by applying the algorithms and weighted PPV and NPV to the 2018 National Health Insurance Service claims data. Results: In total, 2,200 cases (1,086 stroke cases and 1,114 AMI cases) were sampled from the 2018 claims database. The sensitivity and specificity of the algorithms were 94.3% and 88.6% for stroke and 97.9% and 90.1% for AMI, respectively. The estimated number of cases, including recurrent events, was 150,837 for stroke and 40,529 for AMI in 2018. The age- and sex-standardized incidence rate for stroke and AMI was 180.2 and 46.1 cases per 100,000 person-years, respectively, in 2018. Conclusion: This study demonstrates the feasibility of developing a national surveillance system based on claims data and identification algorithms for stroke and AMI to monitor their incidence rates.
Review Article
- Strategies to combat Gram-negative bacterial resistance to conventional antibacterial drugs: a review
- Priyanka Bhowmik, Barkha Modi, Parijat Roy, Antarika Chowdhury
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(5):333-346. Published online October 18, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0323
- 2,157 View
- 173 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 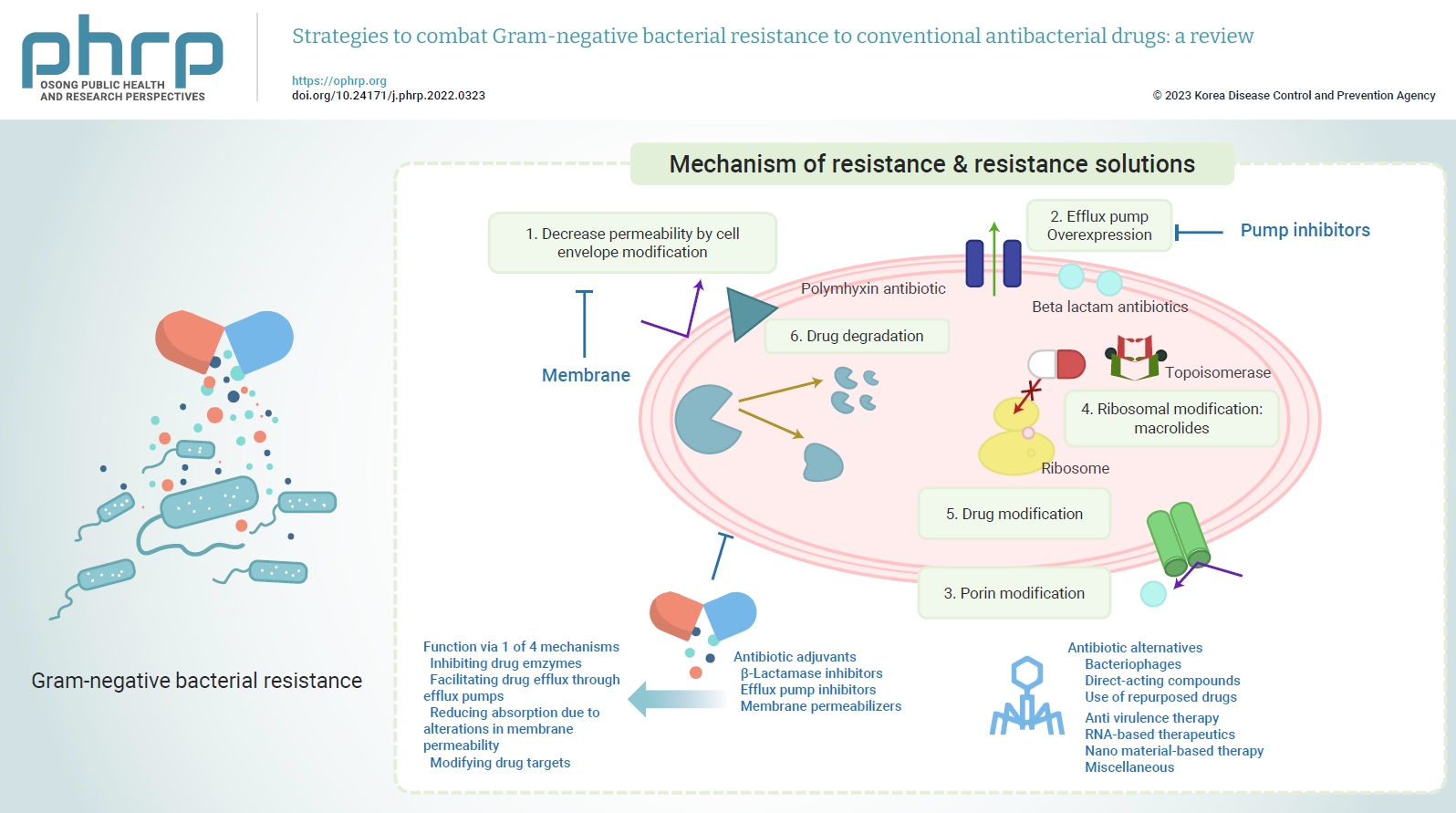
- The emergence of antimicrobial resistance raises the fear of untreatable diseases. Antimicrobial resistance is a multifaceted and dynamic phenomenon that is the cumulative result of different factors. While Gram-positive pathogens, such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Clostridium difficile, were previously the most concerning issues in the field of public health, Gram-negative pathogens are now of prime importance. The World Health Organization’s priority list of pathogens mostly includes multidrug-resistant Gram-negative organisms particularly carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales, carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and extensively drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. The spread of Gram-negative bacterial resistance is a global issue, involving a variety of mechanisms. Several strategies have been proposed to control resistant Gram-negative bacteria, such as the development of antimicrobial auxiliary agents and research into chemical compounds with new modes of action. Another emerging trend is the development of naturally derived antibacterial compounds that aim for targets novel areas, including engineered bacteriophages, probiotics, metal-based antibacterial agents, odilorhabdins, quorum sensing inhibitors, and microbiome-modifying agents. This review focuses on the current status of alternative treatment regimens against multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria, aiming to provide a snapshot of the situation and some information on the broader context.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficacy of new generation biosorbents for the sustainable treatment of antibiotic residues and antibiotic resistance genes from polluted waste effluent
Barkha Madhogaria, Sangeeta Banerjee, Atreyee Kundu, Prasanta Dhak
Infectious Medicine.2024; 3(1): 100092. CrossRef - Evaluation of Plant-Based Silver Nanoparticles for Antioxidant Activity and Promising Wound-Healing Applications
Maria Qubtia, Shazia Akram Ghumman, Sobia Noreen, Huma Hameed, Shazia Noureen, Rizwana Kausar, Ali Irfan, Pervaiz Akhtar Shah, Hafsa Afzal, Misbah Hameed, Mohammad Raish, Maria Rana, Ajaz Ahmad, Katarzyna Kotwica-Mojzych, Yousef A. Bin Jardan
ACS Omega.2024; 9(10): 12146. CrossRef
- Efficacy of new generation biosorbents for the sustainable treatment of antibiotic residues and antibiotic resistance genes from polluted waste effluent
Short Communication
- Characteristics of a large outbreak arising from a school field trip after COVID-19 restrictions were eased in 2022
- Sueng-Jin Kim, Eun-Young Kim, Jeonghee Yu
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2024;15(1):83-89. Published online February 5, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0264
- 875 View
- 22 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 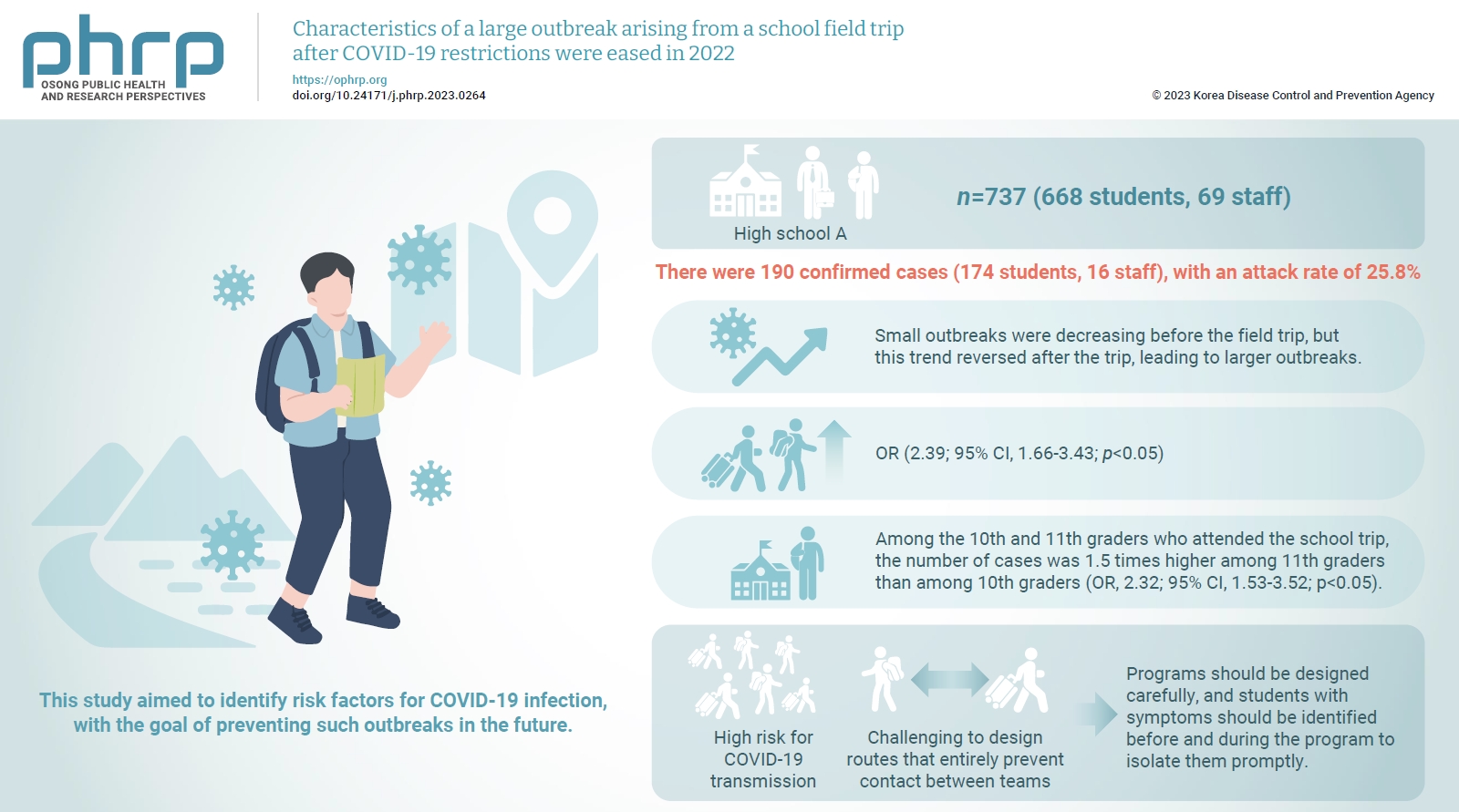
- Objectives
This study analyzed a large outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) that occurred during a high school field trip in the Jeonbuk region and aimed to identify risk factors for COVID-19 infection, with the goal of preventing such outbreaks in the future. Methods: A retrospective cohort study of 737 participants, including 668 students and 69 staff at High School A, was designed to describe the epidemiological characteristics of this large COVID-19 outbreak. Logistic regression analysis was performed to calculate relative risks (odds ratios [ORs]) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Results: There were 190 confirmed cases (174 students, 16 staff), with an attack rate of 25.8%. Small outbreaks were decreasing before the field trip, but this trend reversed after the trip, leading to larger outbreaks. Logistic regression showed an OR of 2.39 (95% CI, 1.66–3.43; p<0.05) for COVID-19 infection among field trip participants. Among them, 11th graders had an OR of 2.32 (95% CI, 1.53–3.52; p<0.05) compared to 10th graders, while no significant risk difference was found within same-grade teams. Conclusion: There was a high risk for COVID-19 transmission during extracurricular activities with a large number of participants, such as field trips, even after the nationwide Omicron variant epidemic subsided. Even when students are separated into teams and follow different routes, it is challenging to design routes that entirely prevent contact between teams. Thus, programs should be designed carefully, and students with symptoms should be identified before and during the program to isolate them promptly.
Original Articles
- Prevalence, multidrug resistance, and biofilm formation of Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from fish mariculture environments in Cat Ba Island, Vietnam
- Kim Cuc Thi Nguyen, Phuc Hung Truong, Hoa Truong Thi, Xuan Tuy Ho, Phu Van Nguyen
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2024;15(1):56-67. Published online February 19, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0181
- 805 View
- 49 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 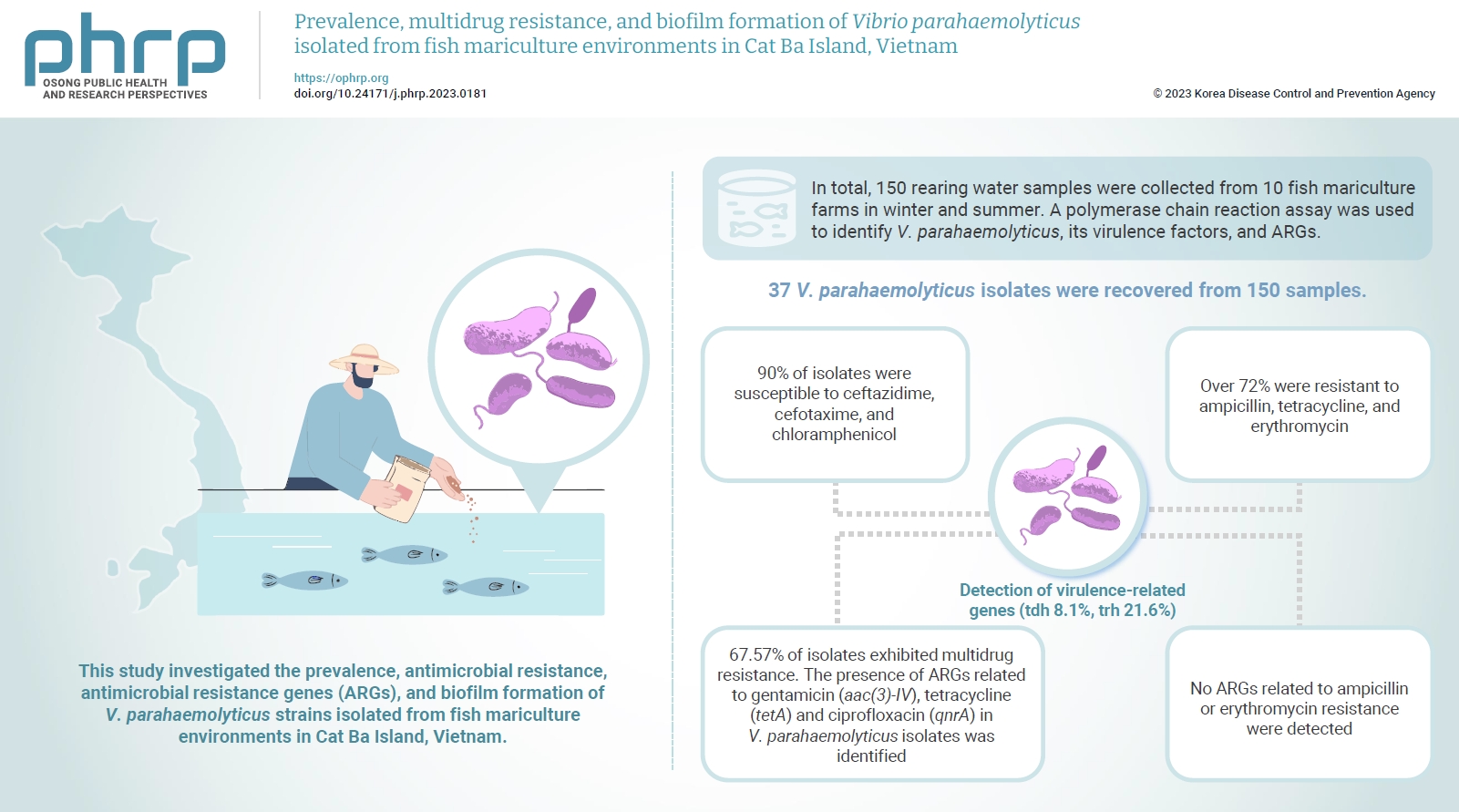
- Objectives
Vibrio parahaemolyticus is a major foodborne pathogen in aquatic animals and a threat to human health worldwide. This study investigated the prevalence, antimicrobial resistance, antimicrobial resistance genes (ARGs), and biofilm formation of V. parahaemolyticus strains isolated from fish mariculture environments in Cat Ba Island, Vietnam. Methods: In total, 150 rearing water samples were collected from 10 fish mariculture farms in winter and summer. A polymerase chain reaction assay was used to identify V. parahaemolyticus, its virulence factors, and ARGs. The antimicrobial resistance patterns and biofilm formation ability of V. parahaemolyticus strains were investigated using the disk diffusion test and a microtiter plate-based crystal violet method, respectively. Results: Thirty-seven V. parahaemolyticus isolates were recovered from 150 samples. The frequencies of the tdh and trh genes among V. parahaemolyticus isolates were 8.1% and 21.6%, respectively. More than 90% of isolates were susceptible to ceftazidime, cefotaxime, and chloramphenicol, but over 72% were resistant to ampicillin, tetracycline, and erythromycin. Furthermore, 67.57% of isolates exhibited multidrug resistance. The presence of ARGs related to gentamicin (aac(3)-IV), tetracycline (tetA) and ciprofloxacin (qnrA) in V. parahaemolyticus isolates was identified. Conversely, no ARGs related to ampicillin or erythromycin resistance were detected. Biofilm formation capacity was detected in significantly more multidrug-resistant isolates (64.9%) than non-multidrug-resistant isolates (18.9%). Conclusion: Mariculture environments are a potential source of antibiotic-resistant V. parahaemolyticus and a hotspot for virulence genes and ARGs diffusing to aquatic environments. Thus, the prevention of antibiotic-resistant foodborne vibriosis in aquatic animals and humans requires continuous monitoring.
- Impact of long COVID-19 on posttraumatic stress disorder as modified by health literacy: an observational study in Vietnam
- Han Thi Vo, Tien Duc Dao, Tuyen Van Duong, Tan Thanh Nguyen, Binh Nhu Do, Tinh Xuan Do, Khue Minh Pham, Vinh Hai Vu, Linh Van Pham, Lien Thi Hong Nguyen, Lan Thi Huong Le, Hoang Cong Nguyen, Nga Hoang Dang, Trung Huu Nguyen, Anh The Nguyen, Hoan Van Nguyen, Phuoc Ba Nguyen, Hoai Thi Thanh Nguyen, Thu Thi Minh Pham, Thuy Thi Le, Thao Thi Phuong Nguyen, Cuong Quoc Tran, Kien Trung Nguyen
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2024;15(1):33-44. Published online February 19, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0261
- 766 View
- 55 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 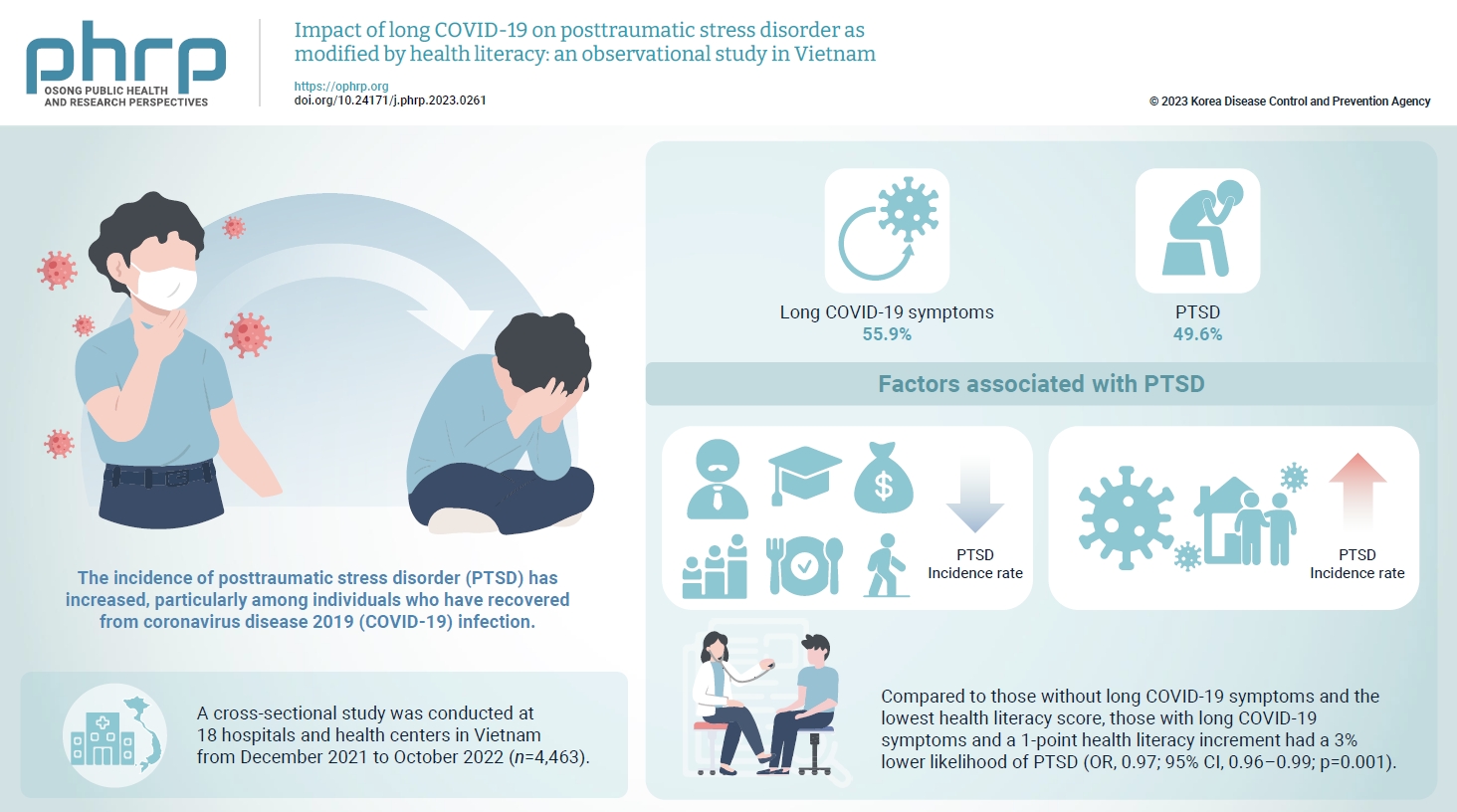
- Objectives
The prevalence of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) has increased, particularly among individuals who have recovered from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection. Health literacy is considered a “social vaccine” that helps people respond effectively to the pandemic. We aimed to investigate the association between long COVID-19 and PTSD, and to examine the modifying role of health literacy in this association. Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted at 18 hospitals and health centers in Vietnam from December 2021 to October 2022. We recruited 4,463 individuals who had recovered from COVID-19 infection for at least 4 weeks. Participants provided information about their sociodemographics, clinical parameters, health-related behaviors, health literacy (using the 12-item short-form health literacy scale), long COVID-19 symptoms and PTSD (Impact Event Scale-Revised score of 33 or higher). Logistic regression models were used to examine associations and interactions. Results: Out of the study sample, 55.9% had long COVID-19 symptoms, and 49.6% had PTSD. Individuals with long COVID-19 symptoms had a higher likelihood of PTSD (odds ratio [OR], 1.86; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.63–2.12; p<0.001). Higher health literacy was associated with a lower likelihood of PTSD (OR, 0.98; 95% CI, 0.97–0.99; p=0.001). Compared to those without long COVID-19 symptoms and the lowest health literacy score, those with long COVID-19 symptoms and a 1-point health literacy increment had a 3% lower likelihood of PTSD (OR, 0.97; 95% CI, 0.96–0.99; p=0.001). Conclusion: Health literacy was found to be a protective factor against PTSD and modified the negative impact of long COVID-19 symptoms on PTSD.
Review Article
- India’s efforts to achieve 1.5 billion COVID-19 vaccinations: a narrative review
- Kapil Singh, Ashwani Verma, Monisha Lakshminarayan
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(5):316-327. Published online October 14, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0104
- 3,676 View
- 91 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 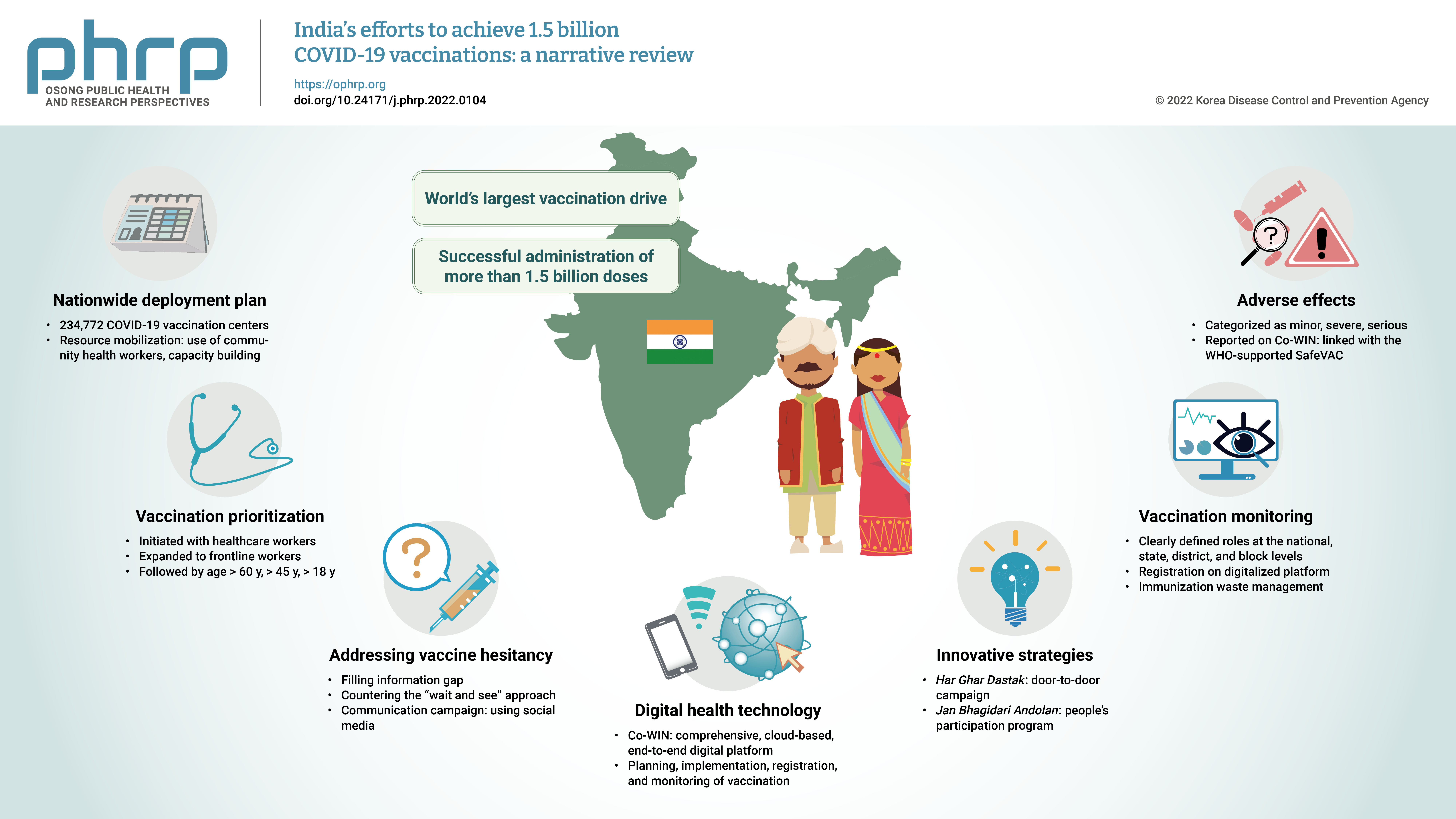
- The initial case of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in India was reported on January 30, 2020, and subsequently, the number of COVID-19-infected patients surged during the first wave of April 2020 and the second wave in the same month of 2021. The government of India imposed a strict nationwide lockdown in April 2020 and extended it until May 2020. The second wave of COVID-19 in India overwhelmed the country’s health facilities and exhausted its medical and paramedical workforce. This narrative review was conducted with the aim of summarizing the evidence drawn from policy documents of governmental and non-governmental organizations, as well as capturing India's COVID-19 vaccination efforts. The findings from this review cover the Indian government's vaccination initiatives, which ranged from steps taken to combat vaccine hesitancy to vaccination roadmaps, deployment plans, the use of digital health technology, vaccination monitoring, adverse effects, and innovative strategies such as Har Ghar Dastak and Jan Bhagidari Andolan (people’s participation). These efforts collectively culminated in the successful administration of more than 1.8 billion doses of COVID-19 vaccines in India. This review also provides insights into other countries’ responses to COVID-19 and guidance for future pandemics.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Digital health technology used in emergency large-scale vaccination campaigns in low- and middle-income countries: a narrative review for improved pandemic preparedness
Paula Mc Kenna, Lindsay A. Broadfield, Annik Willems, Serge Masyn, Theresa Pattery, Ruxandra Draghia-Akli
Expert Review of Vaccines.2023; 22(1): 243. CrossRef - Media Reporting Relating to COVID-19 Vaccination as a Driver of Vaccine Hesitancy Prior to the Second Wave of the COVID-19 Pandemic in India: A Content Analysis of Newspaper and Digital Media Reports
Saurav Basu, Himanshi Sharma
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - An assessment of the strategy and status of COVID-19 vaccination in India
Sneh Lata Gupta, Surbhi Goswami, Ananya Anand, Namrata Naman, Priya Kumari, Priyanka Sharma, Rishi K. Jaiswal
Immunologic Research.2023; 71(4): 565. CrossRef - Development of a Choice-framework for Covid vaccines in India using a multi-criteria decision analysis approach
Tarun K. George, Nayana P. Nair, Awnish Kumar Singh, A. Dilesh Kumar, Arup Deb Roy, Varshini Neethi Mohan, Gagandeep Kang
Vaccine.2023; 41(25): 3755. CrossRef - COVID-19 Booster Dose Coverage and Hesitancy among Older Adults in an Urban Slum and Resettlement Colony in Delhi, India
Nandini Sharma, Saurav Basu, Heena Lalwani, Shivani Rao, Mansi Malik, Sandeep Garg, Rahul Shrivastava, Mongjam Meghachandra Singh
Vaccines.2023; 11(7): 1177. CrossRef - Review of the unmet medical need for vaccination in adults with immunocompromising conditions: An Indian perspective
Ashok Vaid, Neha Rastogi, T. Mark Doherty, Peter San Martin, Yashpal Chugh
Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Translating the COVID-19 experience in widening the HPV vaccination campaign for cervical cancer in India
Aruni Ghose, Anisha Agarwal, Bhawna Sirohi, Shona Nag, Linus Chuang, Swarupa Mitra
Gynecologic Oncology Reports.2023; 48: 101247. CrossRef - Symptomatic prevalence of covid-19 in vaccinated and non-vaccinated population
Jay Bhupesh Pandya, Nirali Milind Shethia, Divya Bangera, Shailaja Gada Saxena
IP International Journal of Medical Microbiology a.2023; 9(2): 110. CrossRef - Active surveillance of adverse events following COVID-19 vaccines in a tertiary care hospital
Naveena Mary Cherian, Dravya Anna Durai, Muhammed Jaisel, Divyansh Sharma, Juny Sebastian, Chetak Kadabasal Basavaraja, Merrin Mathew
Therapeutic Advances in Vaccines and Immunotherapy.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of ayurvedic formulation, NAOQ19 along with standard care in the treatment of mild-moderate COVID-19 patients: A double blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, multicentric trial
Pankaj Bhardwaj, Kalaiselvan Ganapathy, Monika Pathania, K.H. Naveen, Jaykaran Charan, Siddhartha Dutta, Ravisekhar Gadepalli, Srikanth Srinivasan, Manoj Kumar Gupta, Akhil D. Goel, Naresh Midha, Bharat Kumar, Meenakshi Sharma, Praveen Sharma, Mithu Baner
Journal of Ayurveda and Integrative Medicine.2023; 14(6): 100778. CrossRef - Balancing Routine and Pandemic: The Synergy of India’s Universal Immunization Program and COVID-19 Vaccination Program
Pawan Kumar, Ashish Birendra Chakraborty, Suhas Dhandore, Pritu Dhalaria, Ajeet Kumar Singh, Disha Agarwal, Kapil Singh, Pretty Priyadarshini, Paras Jain, Vidushi Bahl, Gunjan Taneja
Vaccines.2023; 11(12): 1776. CrossRef - Unveiling vaccine safety: a narrative review of pharmacovigilance in India's COVID-19 vaccination
Megha Hegde, Saurav Raj, Dhananjay Tikadar, Sanatkumar B Nyamagoud
Monaldi Archives for Chest Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Digital health technology used in emergency large-scale vaccination campaigns in low- and middle-income countries: a narrative review for improved pandemic preparedness
Original Articles
- The associations of health behaviors and working hours with high-sensitivity C-reactive protein levels in Korean wage workers: a cross-sectional study
- Choong-Won Seo, Eun-A Park, Tae-Hyung Yoon
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(5):356-367. Published online September 21, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0052
- 1,604 View
- 47 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 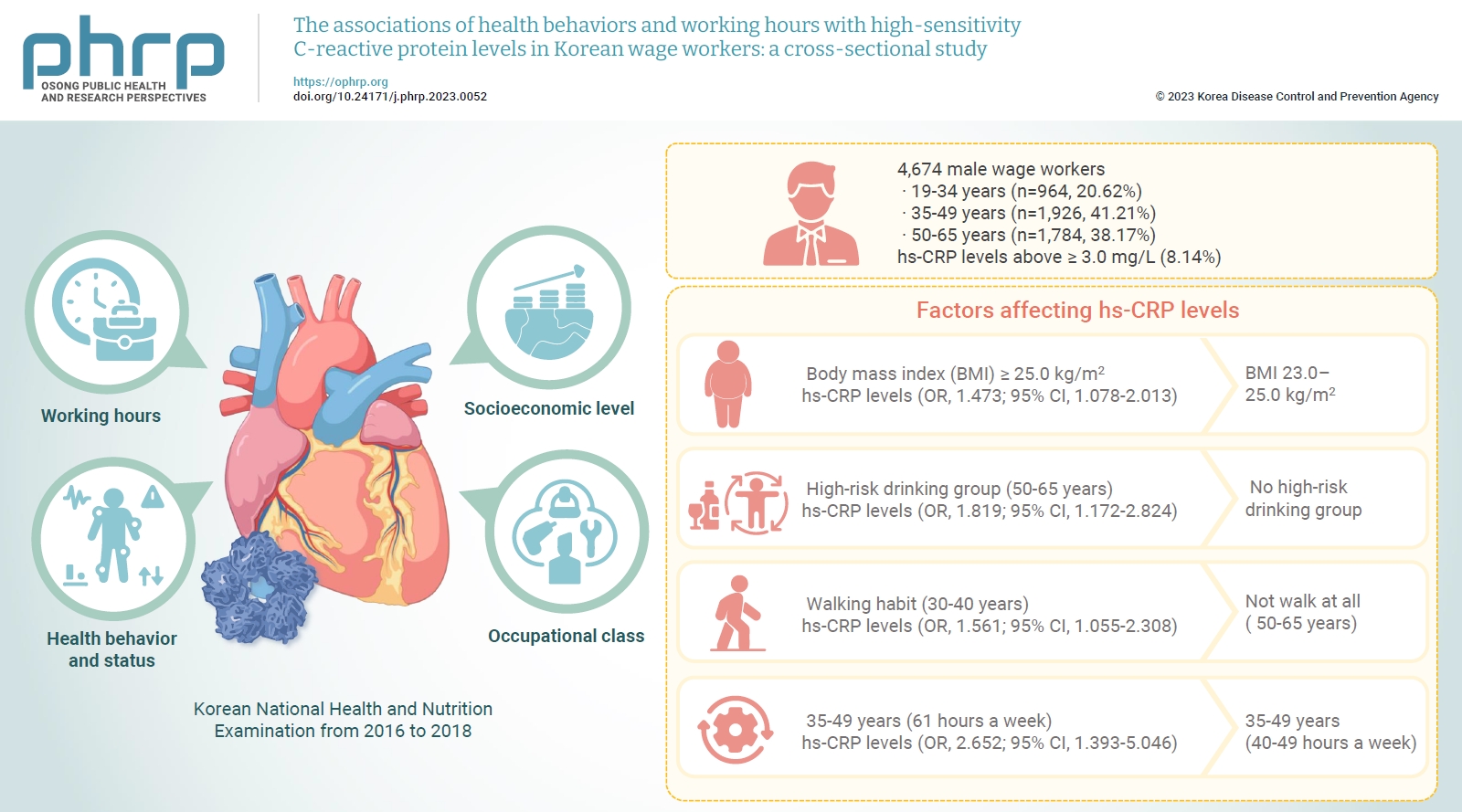
- Objectives
We investigated differences in high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) levels by age group according to working hours, socioeconomic level, health behavior and status, and occupational class, and aimed to identify factors affecting hs-CRP levels in various age groups using data from the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination from 2016 to 2018. Methods: The study included a total of 4,786 male wage workers across the nation, aged between 19 and 65. Data from 4,674 workers were analyzed using multiple logistic regression analysis. Results: Obesity, metabolic syndrome, and weekly working hours were associated with hs-CRP, a biomarker of inflammation. Participants with a body mass index (BMI) ≥25.0 kg/m2 showed significantly higher hs-CRP levels than those with a BMI 23.0 to 25.0 kg/m2. Workers with high-risk drinking and metabolic syndrome showed significantly higher hs-CRP levels in the 50 to 65 years group. Obesity, walking 0 to 149 min/wk, and working ≥61 hours a week were associated with significantly higher hs-CRP levels in the 35 to 49 years group. The factors that significantly affected hs-CRP levels were different among age groups. Conclusion: Plans to adjust working hours should be considered health behaviors, such as drinking and physical activity, and health conditions, such as metabolic syndrome and obesity, according to workers’ age.
- Chronic kidney disease in Indonesia: evidence from a national health survey
- Puti Sari Hidayangsih, Dwi Hapsari Tjandrarini, Noor Edi Widya Sukoco, Nikson Sitorus, Ika Dharmayanti, Feri Ahmadi
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(1):23-30. Published online February 14, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0290
- 3,234 View
- 233 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 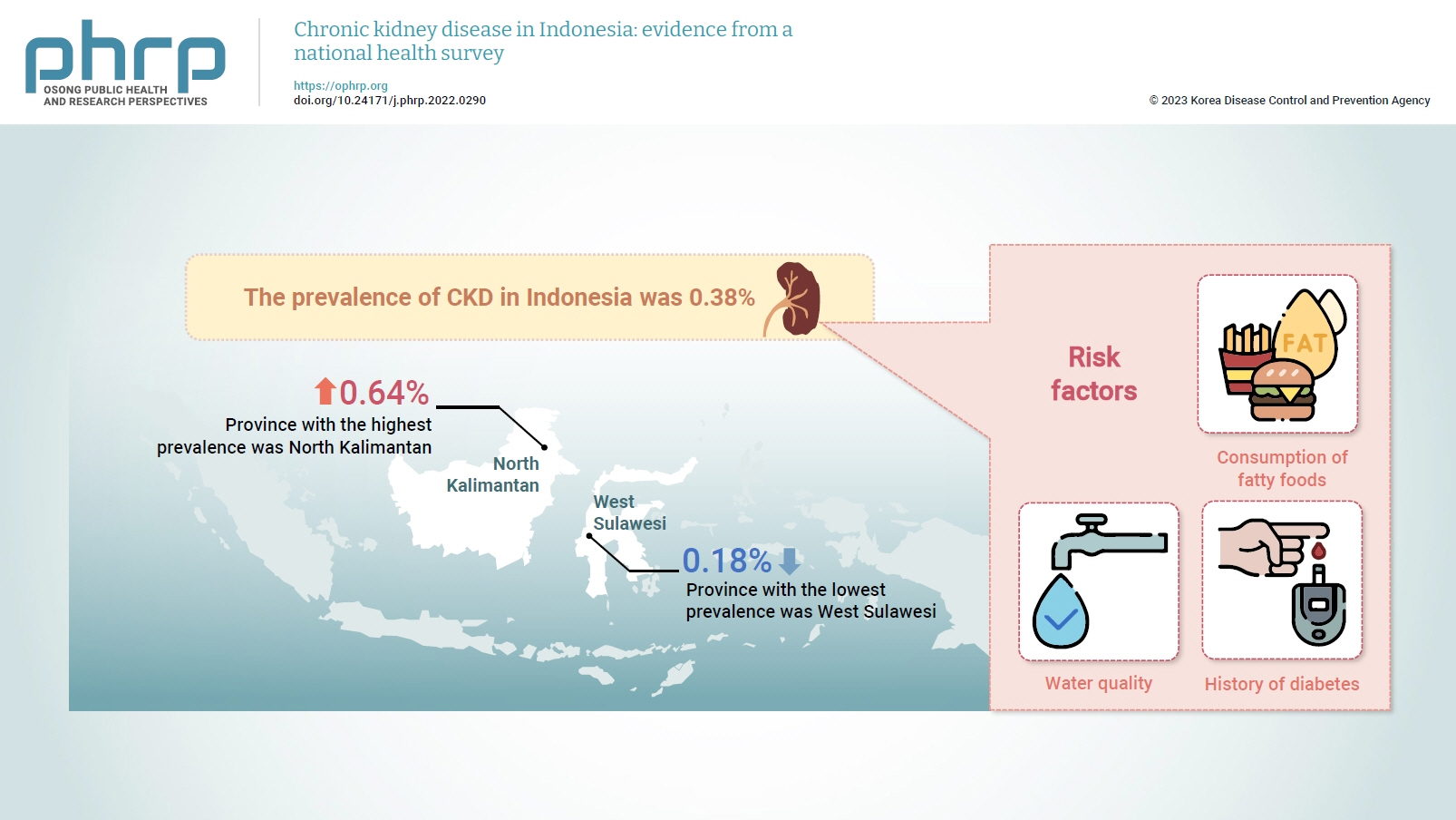
- Objectives
Several previous studies have stated that consuming certain foods and beverages might increase the risk of chronic kidney disease (CKD). This study aimed to examine the relationships of food and beverage consumption with other risk factors for CKD. Methods: Data sources included the 2018 Basic Health Research (Riskesdas) and the National Socio-Economic Survey (Susenas), which were analyzed using a cross-sectional design. The study samples were households from 34 provinces in Indonesia, and the analysis was performed with provincial aggregates. Data were analyzed using risk factor analysis followed by linear regression to identify relationships with CKD. Results: The prevalence of CKD in Indonesia was 0.38%. The province with the highest prevalence was North Kalimantan (0.64%), while the lowest was found in West Sulawesi (0.18%). Five major groups were formed from 15 identified risk factors using factor analysis. A linear regression model presented 1 significant selected factor (p=0.006, R2 =31%). The final model of risk factors included water quality, consumption of fatty foods, and a history of diabetes. Conclusion: Drinking water quality, fatty food consumption, and diabetes are associated with CKD. There is a need to monitor drinking water, as well as to promote health education and provide comprehensive services for people with diabetes, to prevent CKD.



 First
First Prev
Prev


