Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Osong Public Health Res Perspect > Volume 9(4); 2018 > Article
-
Original Article
Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors and Obesity Levels in Korean Adults: Results from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2007–2015 - Kwanjun Parka, Sunmi Limb, Yoonhyung Parkb, Woong Jua,c, Yoonhee Shina,d, Hansol Yeomb
-
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives 2018;9(4):150-159.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2018.9.4.03
Published online: August 31, 2018
aCenter for Public Health, Ewha Womans University Mokdong Hospital, Seoul, Korea
bDepartment of Preventive Medicine, Soonchunhyang University, Cheonan, Korea
cDepartment of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Ewha Womans University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
dDepartment of Medicine, Ewha Womans University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- *Corresponding author: Sunmi Lim, Department of Preventive Medicine, Soonchunhyang University, Cheonan, Korea, E-mail: sunmi7041@naver.com
Copyright ©2018, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/)
Abstract
-
Objectives
- The increase in the obesity rate in adult males in Korea is higher than countries in the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development and other Asian countries. We examined the trends and prevalence of major risk factors for cardiovascular disease by evaluating the weight status amongst adults from 2007 to 2015.
-
Methods
- The study included 37,402 adults, who participated in the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. The prevalence trends of cardiovascular disease risk factors were estimated for each body mass index group.
-
Results
- From 2007 to 2015, significant increases in the prevalence of hypertension, diabetes, and hypercholesterolemia were observed in normal weight adults (0.03 percentage point (%p), 0.06%p, and 0.13%p, respectively). Amongst the overweight and obese adults, a significant increase in the prevalence of hypercholesterolemia was observed, During this period, the prevalence of smoking decreased amongst obese adults and no significant changes in drinking habits and physical activity were noted across all body mass index groups.
-
Conclusion
- The prevalence of obesity in Korean adults is increasing, and it is necessary to implement interventions to prevent further weight gain and obesity-associated cardiovascular disease.
- Obesity is defined as an abnormal or excessive accumulation of fat that may impair health [1]. Upper-body obesity, especially with increased visceral fat is associated with hypertension, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, Type 2 diabetes, and premature death resulting from coronary disease [2]. In 2015, around a third (39.6% of males and 28.8% of females) of adults in Korea over the age of 19, were either overweight or obese [body mass index (BMI) ≥ 25 kg/m2 [3]. There is evidence that being overweight and obesity among adults is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) [4,5] and diabetes [6], respectively. Obesity not only increases the risk of coronary artery disease by 50%, but it also increases the risk of CVD and coronary artery disease mortality rate by 50% [7–9]. Analyses of National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey III (NHANES III) data from the United States, showed increased prevalence ratios when the severity of obesity and being overweight increased, for example high blood pressure (BP) [10]. It was also reported that higher prevalence ratios for high blood cholesterol were present amongst the overweight and the obese compared with people with a normal weight [10].
- The rate of increase in obesity among adult males in Korea is higher than those reported by the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) countries and other Asian countries [11], but it is unknown whether the health risks associated with a higher weight, will continue to rise. Although there have been previous studies examining the relationship between BMI and CVD risk factors, there have been an inadequate number of studies evaluating the changes in the CVD risk factors by weight status in Korean population. Therefore, this study analyzed data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES), 2007–2015, to examine trends in the prevalence of CVD risk factors by weight status amongst adults in Korea.
Introduction
- Data from the KNHANES, conducted by the Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (KCDC), was used in this study. The KNHANES data are open-source files released as de-identified data by the KCDC. The KNHANES was designed to provide nationally representative data to estimate the prevalence of major diseases, and nutritional disorders, and their potential risk factors. The sampling plan followed a complex, stratified, multistage, probability cluster design to produce estimates representative of the noninstitutionalized civilian population. The KNHANES collected data through interviews performed in participants’ homes and conducted medical examinations and laboratory assessments in a mobile examination center. Anthropometric data (i.e. height and weight) in the KNHANES were measured by trained nurses, using a standardized procedure. The health interview and health examination were conducted by trained staff members, including physicians, medical technicians and health interviewers, at a mobile examination center, and dieticians’ visits to the homes of the study participants were followed up. Data from the KNHANES between 2007–2015, with participants aged ≥ 19 years whose complete measurements of CVD risk factors and anthropometry data were available (n = 37,402), was used for analysis in this study.
- 1. BMI group
- BMI groups were defined according to the Asia-Pacific World Health Organization classification standard [12]. Participants were categorized based on their BMI and grouped as; normal weight (18.5 to < 23 kg/m2), overweight (23 to < 25 kg/m2), or obese (≥ 25 kg/m2). Participants who were morbidly obese (≥ 30 kg/m2) were included in the obese category. Underweight participants (BMI < 18.5 kg/m2) were excluded [n = 2,145; (100–350 annually)].
- 2. CVD risk factors
- Six CVD risk factors were evaluated in the analysis: hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia, smoking, drinking, and physical activity. Hypertension was defined as having a systolic BP ≥ 140 mmHg or diastolic BP ≥ 90 mmHg or use of antihypertensive medications. Diabetes was defined as having a fasting plasma glucose ≥ 126 mg/dL or diagnosis by a doctor. Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes were not distinguished. Dyslipidemia was defined as hypercholesterolemia (fasting total cholesterol ≥ 240 mg/dL or taking cholesterol medication), hypertriglyceridemia (fasting triglyceride > 200 mg/dL), low high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol (fasting < 40 mg/dL) or having been diagnosed by a physician.
- Current smokers were defined as those who had smoked > 5 packs (100 cigarettes) in their lifetime and currently smoke cigarettes. Monthly drinkers were defined as those who drank more than once a month over the previous year. High-risk drinkers were defined as those who drink more than twice a week, with an average of 7 glasses (5 glasses for women) per session. Physical activity was defined as having a mix of high and medium intensity exercise, with more than 2 hours and 30 minutes of medium-intensity physical activity, or 1 hour and 15 minutes of high-intensity physical activity per week.
- 3. Statistical analysis
- Sample design variables and weights were used to produce nationally representative estimates that accounted for the KNHANES complex survey design, including its stratified multistage cluster sampling. All statistical analyses were conducted using SAS 9.4 (SAS Inc., Cary, NC, USA). The level of statistical significance was set at p < 0.05 and the stability of the estimates reflected by 95% confidence intervals (CIs). The prevalence of each risk factor was calculated as the percentage change overall for each BMI group, while the trend analysis of risk factors for each group according to year, was analyzed. The prevalence of adults with 1, 2, or 3 or more risk factors within each BMI group was also calculated. Furthermore, a logistic regression model was used to compare the prevalence of CVD according to BMI group, to determine odds ratios (ORs) with 95% CIs. Adjusted ORs were calculated according to the percentage change after adjusting for gender, age, education, income, smoking status, alcohol consumption, and physical activity (ORs with 95% CIs).
Materials and Methods
- The general characteristics of the participants by year are reported in Table 1. Overall, there was little change in the demographics from 2007 to 2015. The male to female ratio did not vary greatly during the survey period. Regarding educational level, the ratio of elementary school, middle school, and high school decreased, while the ratio of college graduates increased. Overall, BMI group was higher in the order of normal, obese, and overweight during the survey period, and the prevalence of obese adults increased [33.1–35.8% (Table 1)].
- Table 2 shows trends in the prevalence of CVD risk factors by weight status group. From 2007 to 2015, there were increases in the prevalence of hypertension from 20.3% to 27.5%, diabetes from 8.1% to 9.7%, hypercholesterolemia from 9.0% to 20.4%, whilst low-HDL cholesterol, current smoking, and high-risk drinking were significantly decreased from 2007 to 2015.
- In the BMI group analysis, the prevalence of hypertension, diabetes, and hypercholesterolemia were significantly increased in the normal weight group, whilst in the low-HDL cholesterol and currently smoking rate, was significantly decreased (−0.09%p, −0.04%p, respectively). Amongst the overweight adults, the prevalence of each CVD risk factor (except for physical activity), was higher than among normal weight adults. In this group, from 2007 to 2015, there was a significant change showing a decrease in the prevalence of low-HDL cholesterol, currently smoking and high-risk drinking (−0.07%p, −0.03%p, −0.04%p, respectively), whilst hypercholesterolemia and physical activity was significantly increased (0.09%p, 0.02%p, respectively). Amongst the obese adults (except for high-risk drinking), physical activity had an even higher prevalence of CVD risk factor. In this group, there were significant increases in risk factors between 2007 and 2015 for hypercholesterolemia (0.08%p, 95% CI 0.06, 0.10), low-HDL cholesterol. The smoking rate was significantly decreased [−0.05%p, −0.02%p, respectively (Table 2)].
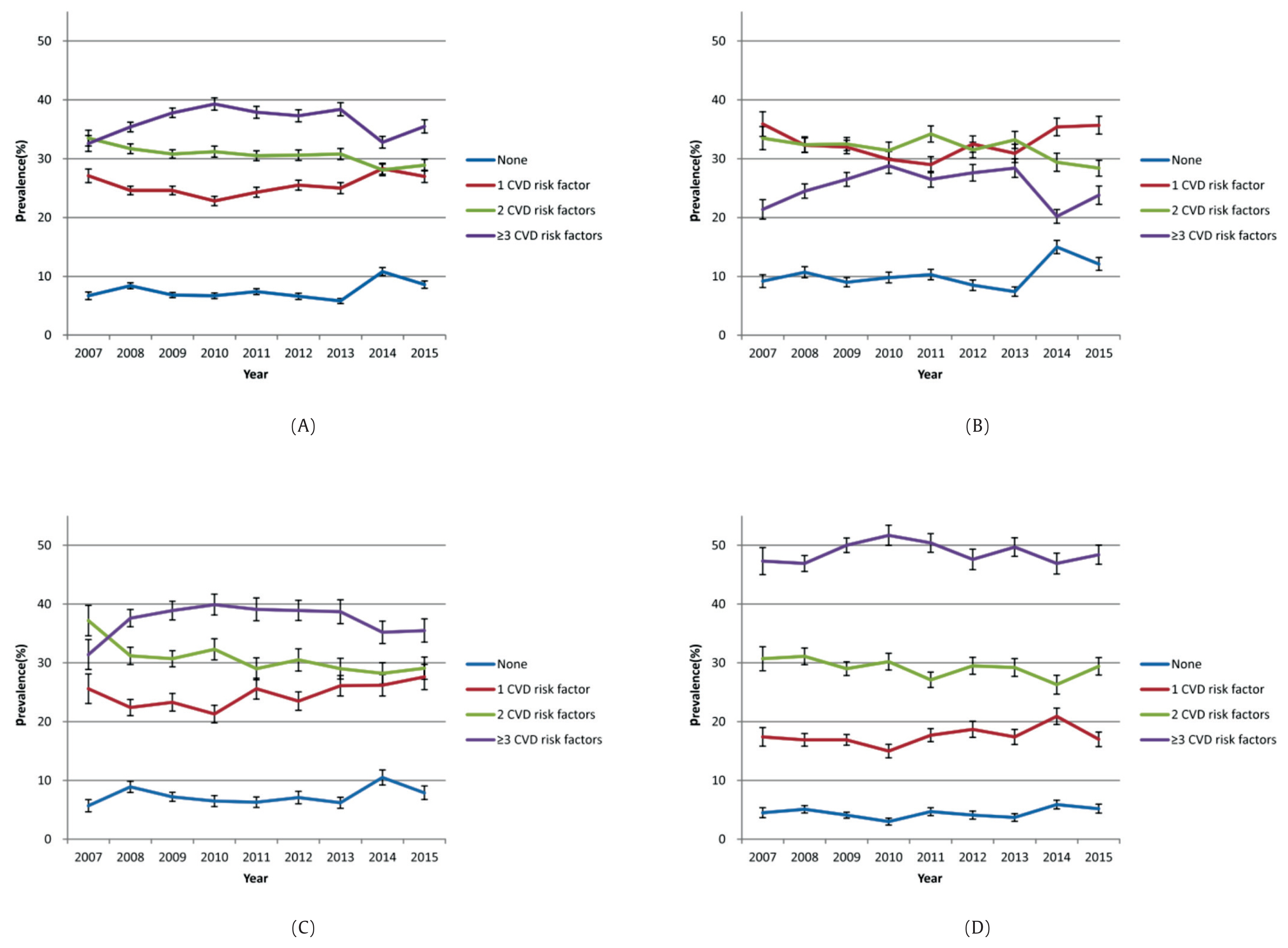
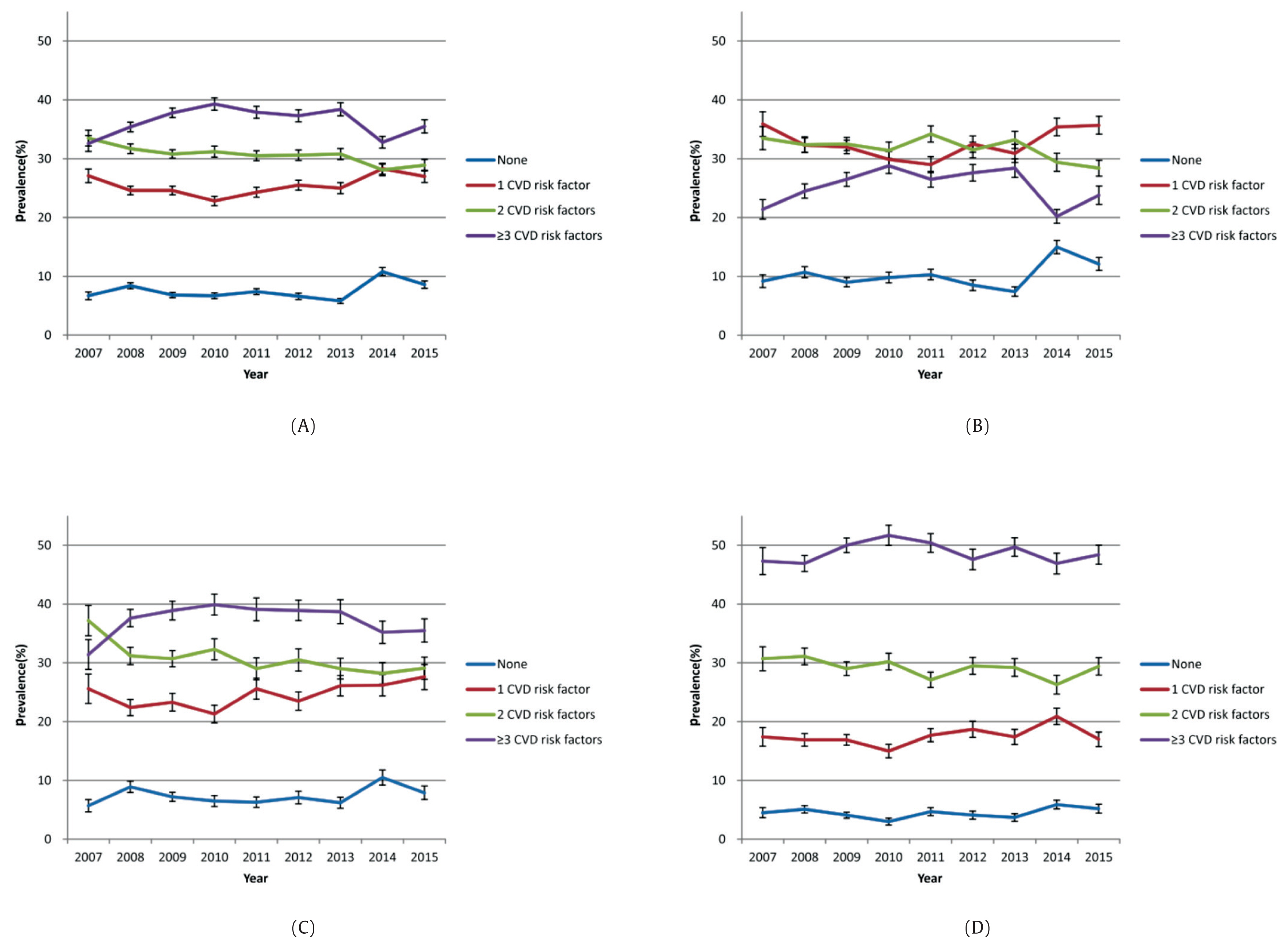
- Figure 1 presents the proportion of the number of risk factors for CVD according to BMI status. As the population is categorized according to BMI category, it is evident that in the overweight and obese categories, the number of CVD risk factors becomes more prevalent and delineated compared with the normal population.
- The number of individuals with 1 risk factor for CVD increased significantly, whereas the number of people with 2 risk factors for CVD decreased significantly (Figure 1).
- Table 3 presents the odd ratios of risk factors for CVD by BMI status. Unadjusted, the prevalence of hypertension was 1.9 times higher in the overweight group and 3.3 times higher in the obese group than in the normal weight group, and the prevalence of diabetes was also significantly higher in the overweight and obese groups compared to the normal weight group at 1.6 and 2.4 times, respectively. The prevalence of dyslipidemia was 2.2 times higher in the overweight group and 3.8 times higher in the obese group than in the normal weight group. Adjusted for the prevalence of hypertension, it was 1.7 times higher in the overweight group and 3.4 times higher in the obese group than in the normal weight. The prevalence of diabetes was also significantly higher in the overweight (1.3 times) and obese groups (2.4 times) compared to the normal weight group, and the prevalence of dyslipidemia was 2.1 times higher in the overweight group and 3.6 times higher in the obese group than in the normal weight group (Table 3).
Results
- Using data from the KNHANES 2007 to 2015, we found significant increases in the prevalence of hypertension, diabetes, hypercholesterolemia and significant decreases in the prevalence of low-HDL cholesterol, and smoking in normal weight adults. In overweight/obese adults, the prevalence of hypercholesterolemia increased, whereas the prevalence of low-HDL cholesterol and smoking significantly decreased.
- In recent times, South Korea has experienced lifestyle transitions such as eating a Westernized diet, and decreasing the amount of daily physical activity. It was found that Korean adult food intake has ever-increasing amounts of energy, fat and salt. Sodium daily intake as recommended by the WHO should be < 2,000 mg for adults [13]. A more Westernized diet is leading to an increased risk of high BP and diabetes as most people enjoy food containing more sodium and fat but do less exercise than before. Likewise, higher cholesterol levels due to this diet choice will tend to lead to hypercholesterolemia. Such consequences will be more predominant as obesity rises and the population ages [14]. Moreover, the “health life practicing status” from 2009 to 2013 [15], shows that obese adults do less “health life practice” for weight control generally, even though they have higher rate of chronic disease than those with a healthy, normal weight. This is consistent with the results in this study where the tendency for physical activity by obese people over the years was significantly reduced. This emphasizes the need for effective interventions to bring about lifestyle changes.
- In 2007–2015, the prevalence of obesity in Korean adults increased. Furthermore in 2015, > 42% of these obese adults had hypertension, 13% had diabetes, and 64% had dyslipidemia. The increased prevalence of obesity leads to an increase in various obesity-associated diseases and an increased socioeconomic burden for the country.
- In the United States, a reported 6%–9% of the national health expenditure was due to obesity versus 2%–3.5% in other countries [16–19]. In Korea in 2007, the prevalence of obesity was low and the related medical expenditures were lower than in Western developed countries. However, this study found that the prevalence of obesity in Korea was 2.7% higher in 2015 than in 2007. According to a study by Kang et al., the total socioeconomic cost of overweight people and obesity in Korea was 1.6 billion USD, which accounts for 3.7% of Korea’s total national health expenditure [20]. Obesity in Korea is continually increasing, and therefore medical expenditure due to obesity is expected to increase. Thus, the burden of disease caused by obesity is not limited to other countries, as it is a serious problem for Korea.
- The results of this study showed that the overweight and obese groups had the highest number of people with 3 or more CVD risk factors. The study by Saydah et al [21] also showed that the prevalence of obesity in adults with 3 or more CVD risk factors was significantly increased . The prevalence of CVD risk factors was reported to increase in overweight or obese adults compared to normal-weight adults [22,23]. Large prospective cohort studies have shown associations of adiposity at baseline and incidence of hypertension and dyslipidemia [24–29]. Associations between weight loss and lowering BPs and improving lipid values have been shown in clinical trials [30–33]. Must et al [34] found in the US National Health and Nutrition Survey that obesity-associated diseases in adults such as Type 2 diabetes, gallbladder disease, hypertension, and coronary artery disease increased with increasing BMI. CVD is a multifactorial disease that is not caused by a single risk factor but is caused by the interaction of many risk factors, such as socioeconomic level. Therefore, management to prevent CVD should consider the combination of all major risk factors.
- The current smoking rate in Korea had a steadily decreasing trend that dropped sharply from 2007 to 2015. This may reflect new pricing policies that were introduced after 2014 where tobacco tax was placed on cigarettes, with an 80% increase in cigarette prices by 2015, and non-smoking policies were introduced in restaurants from 2014 [35]. The current smoking rate showed a similar trend for each BMI group in this study. However, current smoking rates were still higher in the obese group compared with the normal weight and overweight groups. Previous studies have found that smoking was associated with weight loss and smoking cessation was associated with weight gain [36,37]. In contrast, a study by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) suggested that obese people were at a higher risk of smoking [38]. In addition, according to the risk factors of CVD, compared to the normal and overweight groups, the obesity group showed more CVD risk factors by smoking. These results have implications for public health interventions that aim to reduce the prevalence of these CVD risk factors.
- Physical activity was the 1 risk factor where the prevalence has not changed significantly in any BMI group from 2007 to 2015. However, epidemiological studies suggest that regular aerobic physical activity may be beneficial for both prevention and treatment of hypertension, and to lower CVD risk and mortality. The physical activity should be at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity dynamic aerobic exercise (walking, jogging, cycling or swimming) of 5–7 days per week [39–41].
- Previous studies have also reported that obese adults are at a higher risk for CVD than normal weight adults [42–44]. These results are consistent with the results of odds ratios according to the BMI group as shown in this study. The risk of diabetes, hypertension, and dyslipidemia was 1.4–2.1 times higher in overweight than in normal weight adults, and 2.4–3.6 times higher in obesity. Also, in previous studies, obesity had more than twice the population attributable risk compared with being overweight [20]. This implies that a positive relationship exists between BMI and CVD incidence in overweight and obese adults. Therefore, to prevent CVD caused by obesity, efforts should be made to reduce the proportion of overweight and obese adults in the population. However, in the short term, measures should be taken to prevent overweight and obese adults gaining more weight.
- In 2011–2015, amongst the normal weight adults, the number of people who had 1 risk factor for CVD increased significantly. Recently, increases in CVD mortality in South Korea have been documented. It was found that lifestyle choices are insufficiently managed, with a rapid rise in high-risk drinking, diabetes and hypercholesterolemia observed before CVD onset [45]. Many of these increases are likely to aggravate cardiovascular risk factors in the South Korean population. Along with an increase in the obese population, the normal weight population also showed increased risk of high BP and diabetes, which indicates preventive measures against the risk needs to be taken.
- CVD is 1 of the major causes of death in Korea and has a large disease burden. CVD and cerebrovascular disease have been the 2nd and 3rd highest causes of death in Korea over the past decade [46]. Moreover, the socioeconomic cost of CVD has been estimated at a cost of 12.2 billion USD [47]. This can only be prevented through sustainable management, and the state must intervene and manage it by considering individual health and socioeconomic benefits. CVD risk factors include obesity, reduced physical activity, smoking, and unhealthy meals, and changing these risk factors can delay or prevent CVD [48–50]. Therefore, preventing or carefully managing obesity can reduce the cost of related diseases as well as the health burden caused by CVD.
- The main strength of this study was the use of a nationally representative survey that measured weight and height and assessed CVD risk factors in a standardized method. However, this study has some limitations to consider. Firstly it could not be determined whether the change in prevalence of CVD risk factors was an actual increase or was due to a change in the age structure, because age-standardization for prevalence was not considered. Secondly, this is only representative of the noninstitutionalized civilian population that can attend in-person exations. Finally, we did not estimate at the subnational level to assess implications for particular population subgroups, such as those distinguished between urban and rural regions of South Korea.
- In conclusion, the prevalence of obesity in Korean adults is increasing, and it is necessary to implement interventions when considering the influence of obesity on the health of the nation. There is also a strong causal relationship between being overweight and obesity and the occurrence of CVD. Obesity management is very important for reducing the cost of medical treatments due to CVD and reducing the disease and economic burden. Obesity in particular is an important risk factor for hypertension, diabetes, and dyslipidemia, which are likely to progress to CVD. Therefore, it is necessary to focus more resources nationally on managing CVD.
Discussion
-
Acknowledgements
- This work was supported by the Soonchunhyang University Research Fund.
Acknowledgements
-
Conflicts of Interest
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Article information
- 1. Gray DS. Diagnosis and prevalence of obesity. Med Clin North Am 1989;73(1). 1−13. PMID: 10.1016/S0025-7125(16)30688-5. PMID: 2911222.ArticlePubMed
- 2. Jensen MD. Health consequences of fat distribution. Horm Res 1997;48(suppl 5). 88−92. PMID: 10.1159/000191335. PMID: 9434051.Article
- 3. Ministry of Health & Welfare, Korea Centers for Disease Control & Prevention. Health behavior and chronic disease statistics 2015: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES VI-3). Cheongju (Korea): Korea Centers for Disease Control & Prevention; 2015.
- 4. World Health Organization. Obesity and overweight. Geneva (Switzerland): World Health Organization; 2003.
- 5. Brown CD, Higgins M, Donato KA, et al. Body mass index and the prevalence of hypertension and dyslipidemia. Obes Res 2000;8(9). 605−19. PMID: 10.1038/oby.2000.79.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Abdullah A, Peeters A, Courten M, et al. The magnitude of association between overweight and obesity and the risk of diabetes: a meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2010;89(3). 309−19. PMID: 10.1016/j.diabres.2010.04.012. PMID: 20493574.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Lenz M, Richter T, Muhlhauser I. The morbidity and mortality associated with overweight and obesity in adulthood: a systematic review. Dtsch Arztebl Int 2009;106(40). 641−8. PMID: 19890430. PMID: 2770228.PubMedPMC
- 8. Guh DP, Zhang W, Bansback N, et al. The incidence of co-morbidities related to obesity and overweight: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Public Health 2009;9:88PMID: 10.1186/1471-2458-9-88. PMID: 19320986. PMID: 2667420.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 9. Tsigos C, Hainer V, Basdevant A, et al. Obesity Management Task Force of the European Association for the Study of Obesity. Management of obesity in adults: European clinical practice guidelines. Obes Facts 2008;1(2). 106−16. PMID: 10.1159/000126822. PMID: 20054170.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 10. Must A, Spadano J, Coakley EH, et al. The disease burden associated with overweight and obesity. JAMA 1999;282(16). 1523−9. PMID: 10.1001/jama.282.16.1523. PMID: 10546691.ArticlePubMed
- 11. World Health Organization [Internet]. Global database on body mass index. OECD Health Statistics. WHO infobase 2014 [cited 2017 May 30]. Available from: http://apps.who.int/bmi/index.jsp.
- 12. WHO/IASO/IOTF. The Asia-Pacific perspective: redefining obesity and its treatment Melbourne (Australia): Health communications; 2000.
- 13. World Health Organization [Internet]. Global strategy on diet. Physical Activity and Health Available from: http://www.who.int/dietphysicalactivity/background/en/.
- 14. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Korea health statistics 2013: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Seoul (Korea): Korea Ministry of Health and Welfare; 2015.
- 15. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Korea health statistics 2014 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES VI-1). Seoul (Korea): Korea Ministry of Health and Welfare; 2014.
- 16. Allison DB, Zannolli R, Narayan KMV. The direct health care costs of obesity in the United States. Am J Public Health 1999;89(8). 1194−9. PMID: 10.2105/AJPH.89.8.1194. PMID: 10432905. PMID: 1508703.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 17. Birmingham CL, Muller JL, Palepu A, et al. The cost of obesity in Canada. CMAJ 1999;160(4). 483−8. PMID: 10081464. PMID: 1230073.PubMedPMC
- 18. Wolf AM, Colditz GA. Current estimates of the economic cost of obesity in the United States. Obes Res 1998;6(2). 97−106. PMID: 10.1002/j.1550-8528.1998.tb00322.x. PMID: 9545015.ArticlePubMed
- 19. Colditz GA. Economic costs of obesity and inactivity. Med Sci Sports Exerc 1999;31(11 suppl). S663−7. PMID: 10.1097/00005768-199911001-00026. PMID: 10593542.ArticlePubMed
- 20. Kang JH, Jeong BG, Cho YG, et al. Medical expenditure attributable to overweight and obesity in adults with ischemic heart disease and stroke in Korea. Korean J Health Educ Promot 2010;27(4). 83−90.
- 21. Saydah S, Bullard KM, Cheng Y, et al. Trends in cardiovascular disease risk factors by obesity level in adults in the United States, NHANES 1999–2010. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2014;22(8). 1888−95. PMID: 10.1002/oby.20761.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 22. Bonow RO, Smaha LA, Smith SC Jr, et al. World Heart Day 2002: the international burden of cardiovascular disease: responding to the emerging global epidemic. Circulation 2002;106(13). 1602−5. PMID: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000035036.22612.2B. PMID: 12270848.ArticlePubMed
- 23. Wang G, Zheng ZJ, Heath G, et al. Economic burden of cardiovascular disease associated with excess body weight in U.S. adults. Am J Prev Med 2002;23(1). 1−6. PMID: 10.1016/S0749-3797(02)00448-8. PMID: 12093416.Article
- 24. Higgins M, Kannel W, Garrison R, et al. Hazards of obesity: the Framingham experience. Acta Med Scand Suppl 1988;723:23−36.ArticlePubMed
- 25. Manson JE, Willett WC, Stampfer MJ, et al. Body weight and mortality among women. N Engl J Med 1995;333(11). 677−85. PMID: 10.1056/NEJM199509143331101. PMID: 7637744.ArticlePubMed
- 26. Manson JE, Colditz GA, Stampfer MJ, et al. A prospective study of obesity and risk of coronary heart disease in women. N Engl J Med 1990;322(13). 882−9. PMID: 10.1056/NEJM199003293221303. PMID: 2314422.ArticlePubMed
- 27. Witteman JC, Willett WC, Stampfer MJ, et al. A prospective study of nutritional factors and hypertension among US women. Circulation 1989;80(5). 1320−7. PMID: 10.1161/01.CIR.80.5.1320. PMID: 2805268.ArticlePubMed
- 28. Gillum RF, Taylor HL, Brozek J, et al. Indices of obesity and blood pressure in young men followed 32 years. J Chronic Dis 1982;35(3). 211−9. PMID: 10.1016/0021-9681(82)90142-4. PMID: 7061678.ArticlePubMed
- 29. Willett WC, Manson JE, Stampfer MJ, et al. Weight, weight change, and coronary heart disease in women: risk within the “normal” weight range. JAMA 1995;273(6). 461−5. PMID: 10.1001/jama.1995.03520300035033. PMID: 7654270.ArticlePubMed
- 30. Trials of Hypertension Prevention Collaborative Group. The effects of nonpharmacologic interventions on blood pressure of persons with high normal levels. Results of the Trials of Hypertension Prevention, Phase I. JAMA 1992;267(9). 1213−20. PMID: 10.1001/jama.1992.03480090061028. PMID: 1586398.ArticlePubMed
- 31. Davis BR, Blauxfox MD, Oberman A, et al. Reduction in long-term antihypertensive medication requirements. Effects of weight reduction by dietary intervention in overweight persons with hypertension. Arch Intern Med 1993;153(15). 1773−82. PMID: 10.1001/archinte.1993.00410150051005. PMID: 8333814.ArticlePubMed
- 32. Dattilo AM, Kris-Etherton PM. Effects of weight reduction on blood lipids and lipoproteins: a meta-analysis. Am J Clin Nutr 1992;56(2). 320−8. PMID: 10.1093/ajcn/56.2.320. PMID: 1386186.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 33. Wood PD, Stefanick ML, Williams PT, et al. The effects on plasma lipoproteins of a prudent weight-reducing diet with or without exercise, in overweight men and women. N Engl J Med 1991;325(7). 461−6. PMID: 10.1056/NEJM199108153250703. PMID: 1852180.ArticlePubMed
- 34. Must A, Spadano J, Coakley EH, et al. The disease burden associated with overweight and obesity. JAMA 1999;282(16). 1523−9. PMID: 10.1001/jama.282.16.1523. PMID: 10546691.ArticlePubMed
- 35. Cho SH, Kim YJ, Oh KW. [Internet]. Tobacco control policy and smoking trends in Korea. Public Health Weekly Report Osong (Korea): Korea Centers for Disease Control & Prevention; 2017 10:530−3. Available from: http://www.cdc.go.kr/CDC/cms/content/mobile/41/74941_view.html.
- 36. Audrain-McGovern J, Benowitz NL. Cigarette smoking, nicotine, and body weight. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2011;90(1). 164−8. PMID: 10.1038/clpt.2011.105. PMID: 21633341. PMID: 3195407.ArticlePubMed
- 37. Williamson DF, Madans J, Anda RF, et al. Smoking cessation and severity of weight gain in a national cohort. N Engl J Med 1991;324(11). 739−45. PMID: 10.1056/NEJM199103143241106. PMID: 1997840.ArticlePubMed
- 38. Carreras-Torres R, Johansson M, Haycock PC, et al. Role of obesity in smoking behaviour: Mendelian randomization study in UK Biobank. BMJ 2018;361:k1767PMID: 10.1136/bmj.k1767.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 39. Aronow WS, Fleg JL, Pepine CJ, et al. ACCF/AHA 2011 Expert Consensus Document on Hypertension in the Elderly: A Report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Task Force on Clinical Expert Consensus Documents. Circulation 2011;123(21). 2434−506. PMID: 10.1161/CIR.0b013e31821daaf6. PMID: 21518977.ArticlePubMed
- 40. Mancia G, Fagard R, Narkiewicz K, et al. 2013 ESH/ESC guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J 2013;34(28). 2159−219. PMID: 10.1093/eurheartj/eht151. PMID: 23771844.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 41. Korean Academy of Medical Sciences. 2014 Evidence-based recommendations for hypertension in primary care. Seoul (Korea): 2014.
- 42. Brown CD, Higgins M, Donato KA, et al. Body mass index and the prevalence of hypertension and dyslipidemia. Obes Res 2000;8(9). 605−19. PMID: 10.1038/oby.2000.79.ArticlePubMed
- 43. Wilson PW, D’Agostino RB, Sullivan L, et al. Overweight and obesity as determinants of cardiovascular risk: the Framingham experience. Arch Intern Med 2002;162(16). 1867−72. PMID: 10.1001/archinte.162.16.1867. PMID: 12196085.ArticlePubMed
- 44. Abdullah A, Peeters A, de Courten M, et al. The magnitude of association between overweight and obesity and the risk of diabetes: a meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2010;89(3). 309−19. PMID: 10.1016/j.diabres.2010.04.012. PMID: 20493574.ArticlePubMed
- 45. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Factbook of non-communicable disease. Cheongju (Korea): Korea Centers for Disease Control & Prevention; 2015.
- 46. Statistics Korea [Internet]. Causes of death statistics 2014 Daejeon (Korea): Statistics Korea; 2014 [cited 2017 Jul 10]. Available from: http://kosis.kr/ups/ups_01List.jsp.
- 47. Yun SJ, Kim EJ, Kim HJ, et al. A study on measuring the economic burden of cardio-cerebrovascular disease in Korea. Cheongju (Korea): Korea Centers for Disease Control & Prevention; 2010.
- 48. Reaven GM. Pathophysiology of insulin resistance in human disease. Physiol Rev 1995;75(3). 473−86. PMID: 10.1152/physrev.1995.75.3.473. PMID: 7624391.ArticlePubMed
- 49. Yusuf S, Hawken S, Ounpuu S, et al. Effect of potentially modifiable risk factors associated with myocardial infarction in 52 countries (the INTERHEART study): case-control study. Lancet 2004;364(9438). 937−52. PMID: 10.1016/S0140-6736(04)17018-9. PMID: 15364185.ArticlePubMed
- 50. Willi C, Bodenmann P, Ghali WA, et al. Active smoking and the risk of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 2007;298(22). 2654−64. PMID: 10.1001/jama.298.22.2654. PMID: 18073361.ArticlePubMed
References
| 2007 (N=2,282) | 2008 (N=4,830) | 2009 (N=5,632) | 2010 (N=4,694) | 2011 (N=4,716) | 2012 (N=4,376) | 2013 (N=3,548) | 2014 (N=3,563) | 2015 (N=3,761) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender, % (SE) | |||||||||
|
|
|||||||||
| Male | 49.8 (1.17) | 49.5 (0.79) | 50 (0.62) | 49.6 (0.81) | 49.8 (0.78) | 50.1 (0.85) | 49.7 (0.81) | 49.9 (0.79) | 50 (0.86) |
| Female | 50.2 (1.17) | 50.5 (0.79) | 50 (0.62) | 50.4 (0.81) | 50.2 (0.78) | 49.9 (0.85) | 50.3 (0.81) | 50.1 (0.79) | 50 (0.86) |
|
|
|||||||||
| Age group (y), % (SE) | |||||||||
|
|
|||||||||
| 19–64 | 88.7 (0.98) | 86.1 (0.80) | 86.1 (0.77) | 86.3 (0.80) | 85.5 (0.80) | 85.4 (0.87) | 85 (0.87) | 85.8 (0.87) | 83.8 (0.89) |
| ≥ 65 | 11.3 (0.98) | 13.9 (0.80) | 13.9 (0.77) | 13.7 (0.80) | 14.5 (0.80) | 14.6 (0.87) | 15 (0.87) | 14.2 (0.87) | 16.2 (0.89) |
| Mean age (SE) | 44.0 (0.54) | 45.3 (0.42) | 45.8 (0.40) | 45.8 (0.48) | 46.4 (0.46) | 46.2 (0.44) | 46.7 (0.46) | 46.3 (0.50) | 47.4 (0.45) |
|
|
|||||||||
| Educational level, % (SE) | |||||||||
|
|
|||||||||
| < Elementary school | 19.2 (1.59) | 20.7 (1.05) | 20.5 (1.07) | 20.3 (1.27) | 19.1 (1.14) | 18.6 (1.09) | 19.0 (1.2) | 16.0 (1.09) | 16.4 (1.01) |
| Middleschool | 11.2 (1.06) | 10.8 (0.62) | 10.7 (0.54) | 10.3 (0.59) | 11.3 (0.60) | 9.8 (0.63) | 9.7 (0.63) | 9.8 (0.67) | 9.2 (0.67) |
| High school | 40.3 (1.67) | 39.2 (1.15) | 39.0 (1.12) | 36.6 (1.12) | 37.9 (1.22) | 40.5 (1.23) | 38.2 (1.21) | 39.0 (1.27) | 36.6 (1.11) |
| ≥ College | 29.3 (1.87) | 29.3 (1.49) | 29.8 (1.50) | 32.8 (1.40) | 31.7 (1.44) | 31.0 (1.54) | 33.2 (1.37) | 35.3 (1.58) | 37.8 (1.54) |
|
|
|||||||||
| Household monthly income, % (SE) | |||||||||
|
|
|||||||||
| 1st quintile (lowest) | 15.7 (1.60) | 15.9 (1.10) | 16.7 (0.94) | 17.5 (1.11) | 15.5 (0.94) | 14.2 (1.08) | 16.7 (1.26) | 13.6 (1.04) | 14.8 (1.06) |
| 2nd quintile | 25.7 (1.84) | 26.6 (1.23) | 22.8 (1.05) | 26.8 (1.24) | 28.6 (1.23) | 26.8 (1.48) | 26.0 (1.25) | 25.2 (1.36) | 23.4 (1.30) |
| 3rd quintile | 28.5 (1.62) | 27.7 (0.97) | 29.9 (1.17) | 28.8 (1.13) | 29.1 (1.18) | 29.0 (1.18) | 28.2 (1.19) | 32.0 (1.52) | 30.3 (1.48) |
| 4th quintile | 30.1 (2.38) | 29.7 (1.77) | 30.6 (1.72) | 26.9 (1.35) | 26.9 (1.36) | 30.0 (1.57) | 29.1 (1.64) | 29.2 (1.88) | 31.5 (1.77) |
|
|
|||||||||
| BMI group, % (SE)* | |||||||||
|
|
|||||||||
| Normal | 41.0 (1.29) | 41.1 (0.87) | 40.1 (0.83) | 41.7 (0.89) | 40.7 (0.94) | 41.2 (1.12) | 40.2 (1.09) | 42.2 (1.03) | 39.8 (0.99) |
| Overweight | 25.9 (1.13) | 25.0 (0.75) | 25.0 (0.66) | 23.9 (0.81) | 24.6 (0.68) | 23.3 (0.81) | 24.7 (0.87) | 24.1 (0.87) | 24.4 (0.79) |
| Obese | 33.1 (1.22) | 33.8 (0.90) | 34.9 (0.85) | 34.4 (0.94) | 34.8 (0.94) | 35.5 (1.04) | 35.1 (0.89) | 33.7 (1.03) | 35.8 (0.92) |
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | Percentage point change‡, 2007–2015, % (95% CI) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total population | |||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||
| Disease | Hypertension | 20.5 (1.31) | 24.2 (0.88) | 31.3 (0.96) | 31.0 (0.97) | 27.9 (0.90) | 27.9 (1.13) | 28.2 (1.09) | 24.1 (0.95) | 27.5 (1.03) | 0.02 (0.01, 0.03) |
| Diabetes | 8.1 (0.80) | 8.7 (0.44) | 8.9 (0.52) | 9.3 (0.52) | 9.8 (0.62) | 8.6 (0.53) | 11.4 (0.72) | 9.9 (0.58) | 9.7 (0.63) | 0.03 (0.01, 0.05) | |
| Dyslipidemia | 39.0 (1.18) | 46.1 (0.95) | 46.6 (0.80) | 46.0 (0.96) | 42.1 (0.93) | 40.5 (0.97) | 42.3 (1.03) | 42.1 (0.98) | 45.9 (0.98) | 0.002 (−0.01, 0.01) | |
| Hypercholesterolemia | 9.0 (0.77) | 11.5 (0.51) | 12.3 (0.52) | 14.0 (0.60) | 14.6 (0.58) | 15.4 (0.72) | 16.9 (0.71) | 16.0 (0.76) | 20.4 (0.79) | 0.1 (0.08, 0.11) | |
| Hypertriglyceridemia | 16.8 (0.94) | 15.7 (0.74) | 15.7 (0.63) | 16.0 (0.68) | 15.5 (0.72) | 15.9 (0.78) | 16.2 (0.77) | 16.6 (0.80) | 15.3 (0.71) | −0.004 (−0.02, 0.01) | |
| Low HDL-cholesterol | 24.4 (1.16) | 30.8 (1.00) | 31.2 (0.81) | 29.3 (0.94) | 23.6 (0.88) | 21.1 (0.87) | 19.8 (0.77) | 19.7 (0.78) | 22.6 (0.88) | −0.06 (−0.08, −0.05) | |
|
|
|||||||||||
| Smoking | Current smoking | 24.3 (1.26) | 25.1 (0.78) | 26.3 (0.75) | 26.1 (0.88) | 25.8 (0.95) | 24.6 (0.92) | 23.1 (0.95) | 22.9 (0.87) | 19.2 (0.89) | −0.03 (−0.05, −0.02) |
|
|
|||||||||||
| Drinking | Monthly drinking | 58.7 (1.38) | 58.1 (0.90) | 57.5 (0.86) | 59.2 (1.08) | 57.9 (1.02) | 56.5 (1.04) | 57.7 (1.13) | 58.2 (1.04) | 57.8 (1.02) | −0.004 (−0.02, 0.01) |
| High-risk drinking | 16.9 (1.14) | 19.0 (0.83) | 17.9 (0.79) | 16.8 (0.90) | 17.4 (0.8) | 17.3 (0.90) | 15.3 (0.85) | 17.0 (0.98) | 15.4 (0.92) | −0.02 (−0.04, −0.01) | |
|
|
|||||||||||
| Physical activity | 45.0 (1.63) | 52.6 (1.26) | 53.8 (1.09) | 49.0 (1.21) | 45.5 (1.03) | 41.8 (1.22) | 41.6 (1.05) | 58.3 (1.16) | 51.3 (1.20) | 0.01 (−0.01, 0.02) | |
|
|
|||||||||||
| Normal weight | |||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||
| Disease | Hypertension | 10.8 (1.03) | 14.1 (0.94) | 19.3 (1.25) | 19.1 (1.07) | 17.8 (1.13) | 17.3 (1.15) | 18.1 (1.24) | 14.6 (1.13) | 16.6 (1.07) | 0.03 (0.01, 0.05) |
| Diabetes | 3.4 (0.64) | 5.7 (0.54) | 5.4 (0.68) | 5.8 (0.61) | 7.1 (0.87) | 6.1 (0.69) | 7.5 (0.90) | 6.6 (0.70) | 6.8 (0.74) | 0.06 (0.03, 0.09) | |
| Dyslipidemia | 23.2 (1.80) | 32.3 (1.22) | 30.5 (1.05) | 29.4 (1.28) | 27.1 (1.36) | 26.7 (1.33) | 28.1 (1.42) | 25.0 (1.32) | 29.8 (1.34) | −0.002 (−0.02, 0.02) | |
| Hypercholesterolemia | 4.2 (0.68) | 7.7 (0.64) | 6.7 (0.57) | 7.8 (0.72) | 8.7 (0.71) | 11.0 (1.11) | 12.1 (1.02) | 10.0 (0.87) | 14.2 (1.10) | 0.13 (0.10, 0.15) | |
| Hypertriglyceridemia | 6.9 (0.93) | 9.1 (0.86) | 7.7 (0.69) | 7.9 (0.83) | 7.2 (0.76) | 7.0 (0.81) | 8.3 (0.89) | 7.8 (0.90) | 7.2 (0.79) | −0.004 (−0.03, 0.03) | |
| Low HDL-cholesterol | 15.7 (1.61) | 21.0 (1.24) | 20.5 (1.02) | 18.3 (1.15) | 15.0 (1.13) | 13.7 (0.94) | 10.7 (0.94) | 10.0 (0.97) | 12.2 (1.06) | −0.09 (−0.12, −0.07) | |
|
|
|||||||||||
| Smoking | Current smoking | 21.2 (1.65) | 22.4 (1.14) | 25.5 (1.11) | 24.9 (1.35) | 23.7 (1.42) | 22.1 (1.40) | 20.4 (1.48) | 19.5 (1.12) | 15.7 (1.25) | −0.04 (−0.06, −0.02) |
|
|
|||||||||||
| Drinking | Monthly drinking | 57.1 (1.82) | 55.9 (1.32) | 56.6 (1.27) | 57.6 (1.60) | 55.1 (1.61) | 54.9 (1.60) | 59.8 (1.59) | 56.7 (1.65) | 57.2 (1.67) | 0.004 (−0.01, 0.02) |
| High-risk drinking | 10.8 (1.46) | 14.7 (1.31) | 14.9 (1.22) | 12.0 (1.14) | 13.1 (1.06) | 13.9 (1.32) | 11.5 (1.17) | 12.8 (1.24) | 11.3 (1.34) | −0.01 (−0.04, 0.02) | |
|
|
|||||||||||
| Physical activity | 42.9 (2.25) | 50.7 (1.49) | 50.8 (1.38) | 45.4 (1.64) | 43.0 (1.55) | 39.1 (1.71) | 40.3 (1.66) | 59.2 (1.55) | 52.5 (1.69) | 0.01 (−0.02, 0.03) | |
|
|
|||||||||||
| Overweight | |||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||
| Disease | Hypertension | 19.3 (1.74) | 24.5 (1.41) | 31.7 (1.41) | 33.7 (1.9) | 28.4 (1.58) | 30.0 (1.64) | 26.7 (1.84) | 23.2 (1.61) | 24.4 (1.59) | 0.005 (−0.02, 0.03) |
| Diabetes | 9.2 (1.43) | 8.5 (0.89) | 7.6 (0.76) | 9.3 (1.00) | 9.2 (1.09) | 8.6 (0.85) | 10.9 (1.24) | 8.9 (1.03) | 10.0 (1.01) | 0.02 (−0.01, 0.06) | |
| Dyslipidemia | 42.7 (1.97) | 48.7 (1.61) | 50.1 (1.44) | 49.2 (1.78) | 42.5 (1.90) | 43.6 (1.89) | 46.9 (2.02) | 47.7 (1.97) | 46.1 (1.95) | −0.0002 (−0.02, 0.02) | |
| Hypercholesterolemia | 10.0 (1.20) | 11.7 (0.92) | 14.3 (0.98) | 14.1 (1.13) | 13.4 (1.15) | 15.9 (1.30) | 19.0 (1.39) | 15.8 (1.41) | 21.8 (1.51) | 0.09 (0.07, 0.12) | |
| Hypertriglyceridemia | 18.3 (1.94) | 14.9 (1.27) | 18.4 (1.20) | 17.7 (1.59) | 16.9 (1.51) | 16.0 (1.54) | 17.1 (1.45) | 17.6 (1.60) | 12.6 (1.33) | −0.02 (−0.05, 0.01) | |
| Low HDL-cholesterol | 26.8 (2.06) | 33.5 (1.62) | 31.1 (1.49) | 31.8 (1.70) | 23.9 (1.69) | 22.2 (1.71) | 22.2 (1.60) | 23.0 (1.60) | 22.1 (1.65) | −0.07 (−0.09, −0.04) | |
|
|
|||||||||||
| Smoking | Current smoking | 22.7 (2.35) | 25.8 (1.65) | 25.5 (1.36) | 25.2 (1.78) | 27.3 (1.81) | 24.5 (1.70) | 21.8 (1.66) | 23.2 (1.82) | 18.8 (1.77) | −0.03 (−0.05, −0.01) |
|
|
|||||||||||
| Drinking | Monthly drinking | 61.3 (2.42) | 60.2 (1.72) | 57.8 (1.39) | 58.4 (1.87) | 61.6 (1.66) | 55.6 (1.81) | 56.5 (1.94) | 57.9 (1.9) | 57.6 (1.84) | −0.02 (−0.04, 0.01) |
|
|
|||||||||||
| High-risk drinking | 20.8 (2.27) | 21.2 (1.60) | 18.2 (1.50) | 18.5 (1.60) | 18.1 (1.72) | 14.8 (1.84) | 13.6 (1.56) | 16.9 (1.9) | 18.7 (1.92) | −0.04 (−0.07, −0.01) | |
|
|
|||||||||||
| Physical activity | 44.1 (2.46) | 54.6 (2.03) | 54.6 (1.82) | 49.8 (1.94) | 48.6 (1.79) | 44.8 (1.96) | 42.6 (2.18) | 58.3 (2.01) | 50.7 (2.12) | 0.02 (0.01, 0.04) | |
|
|
|||||||||||
| Obese | |||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||
| Disease | Hypertension | 33.3 (2.45) | 36.3 (1.45) | 44.9 (1.39) | 43.5 (1.73) | 39.4 (1.50) | 38.9 (1.89) | 41.0 (1.74) | 36.6 (1.61) | 41.7 (1.89) | 0.02 (−0.01, 0.04) |
| Diabetes | 13.1 (1.68) | 12.6 (0.84) | 13.9 (0.86) | 13.6 (1.08) | 13.4 (1.04) | 11.6 (1.00) | 16.3 (1.21) | 14.7 (1.15) | 12.8 (1.08) | 0.01 (−0.02, 0.04) | |
| Dyslipidemia | 55.7 (2.23) | 61 (1.45) | 62.7 (1.24) | 63.7 (1.71) | 59.5 (1.53) | 54.6 (1.55) | 55.2 (1.69) | 59.5 (1.73) | 63.6 (1.46) | 0.003 (−0.02,0.02) | |
| Hypercholesterolemia | 14.1 (1.59) | 15.9 (1.01) | 17.3 (0.93) | 21.5 (1.28) | 22.4 (1.32) | 20.3 (1.27) | 20.9 (1.27) | 23.6 (1.44) | 26.3 (1.36) | 0.08 (0.06, 0.10) | |
| Hypertriglyceridemia | 27.8 (2.19) | 25.4 (1.40) | 23.7 (1.17) | 25.3 (1.20) | 24.8 (1.38) | 26.7 (1.61) | 24.9 (1.52) | 27.6 (1.62) | 27.0 (1.46) | 0.01 (−0.02, 0.03) | |
| Low HDL-cholesterol | 33.3 (2.14) | 40.6 (1.62) | 43.4 (1.27) | 40.8 (1.78) | 33.4 (1.37) | 28.8 (1.48) | 28.5 (1.46) | 29.6 (1.60) | 34.4 (1.59) | −0.05 (−0.07, −0.03) | |
|
|
|||||||||||
| Smoking | Current smoking | 29.3 (2.03) | 27.9 (1.38) | 27.9 (1.31) | 28.1 (1.41) | 27.3 (1.44) | 27.7 (1.79) | 27.2 (1.54) | 26.9 (1.57) | 23.4 (1.52) | −0.02 (−0.05, −0.01) |
|
|
|||||||||||
| Drinking | Monthly drinking | 58.6 (2.25) | 59.1 (1.50) | 58.3 (1.34) | 61.9 (1.43) | 58.7 (1.53) | 59.0 (1.64) | 56.0 (1.71) | 60.3 (1.70) | 58.7 (1.68) | −0.002 (−0.02, 0.02) |
| High-risk drinking | 21.3 (2.07) | 22.5 (1.47) | 21.1 (1.18) | 21.5 (1.73) | 22.0 (1.51) | 22.9 (1.75) | 20.9 (1.51) | 22.2 (1.80) | 17.9 (1.58) | −0.01 (−0.04, 0.01) | |
|
|
|||||||||||
| Physical activity | 48.4 (2.52) | 53.3 (1.77) | 56.8 (1.43) | 52.8 (1.82) | 46.4 (1.60) | 43.0 (1.94) | 42.4 (1.55) | 57.0 (1.87) | 50.5 (1.97) | −0.01 (−0.03, 0.01) | |
* CVD risk factors included: hypertension (systolic BP ≥ 140 mmHg, diastolic BP ≥ 90 mmHg, or use of antihypertensive medications); diabetes (fasting plasma glucose ≥ 126 mg/dL or diagnosed by a doctor); dyslipidemia (at least 1 of the following: hypercholesterolemia, hypertriglyceridemia, low HDL-cholesterol), or diagnosed by a physician); hypercholesterolemia (fasting total cholesterol ≥ 240 mg/dL or taking cholesterol medication), hypertriglyceridemia (fasting triglyceride > 200 mg/dL), low HDL-cholesterol (fasting < 40 mg/dL); self-reported current smoking (more than 5 packs [100 cigarettes] in their lifetime and currently smoking cigarettes); monthly drinking (drinking more than once a month for the previous year); high-risk drinking (drinking more than twice a week a mean 7 glasses [5 glasses for women] per session); physical activity (exercise a time equivalent to each activity by mixing physical strength activities (high intensity, 1 minute; medium intensity, 2 minutes) of medium and high intensity for more than 2 hours and 30 minutes of medium-intensity physical activity or 1 hour and 15 minutes of high-intensity physical activity per week).
† BMI group (kg/m2): normal weight, 18.5 to < 23; overweight, 23 to < 25; obese, ≥ 25.
‡ A percentage point change is the unit for the arithmetic difference of annual percentages.
CVD = cardiovascular disease; BMI = body mass index; SE = standard error; CI = confidence interval; BP = blood pressure; HDL = high-density lipoprotein.
| Unadjusted | Adjusted‡ | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | OR (95% CI) | ||
| Hypertension | Overweight vs normal weight (ref.) | 1.87 (1.75–2.01) | 1.65 (1.50–1.82) |
| Obesity vs normal weight (ref.) | 3.34 (3.13–3.56) | 3.38 (3.08–3.70) | |
|
|
|||
| Diabetes | Overweight vs normal weight (ref.) | 1.57 (1.40–1.75) | 1.34 (1.15–1.56) |
| Obesity vs normal weight (ref.) | 2.44 (2.21–2.70) | 2.37 (2.07–2.72) | |
|
|
|||
| Dyslipidemia | Overweight vs normal weight (ref.) | 2.22 (2.08–2.37) | 2.07 (1.91–2.24) |
| Obesity vs normal weight (ref.) | 3.79 (3.55–4.04) | 3.61 (3.34–3.91) | |
* CVD risk factors included: hypertension (systolic BP ≥ 140 mmHg, diastolic BP ≥ 90 mmHg, or use of antihypertensive medications); diabetes (fasting plasma glucose ≥ 126 mg/dL or diagnosed by a doctor); dyslipidemia [at least 1 of the following: hypercholesterolemia (fasting total cholesterol ≥ 240 mg/dL or taking cholesterol medication)].
† BMI group (kg/m2): normal weight, 18.5 to < 23; overweight, 23 to < 25; obese, ≥ 25.
‡ Adjusted for gender, age, education, household monthly income, current smoking, monthly drinking, high-risk drinking, and physical activity.
CVD = cardiovascular disease; BMI = body mass index; CI = confidence interval.
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors in middle-aged Lithuanian women in different body mass index and waist circumference groups
Egidija Rinkūnienė, Emilija Petrulionytė, Vilma Dženkevičiūtė, Žaneta Petrulionienė, Augustė Senulytė, Roma Puronaitė, Aleksandras Laucevičius
Primary Care Diabetes.2023; 17(1): 27. CrossRef - The effect of a nutrition program based on the Health Behavior Interaction Model on primary school students’ nutritional attitudes and behaviors
Ayşe Burcu Başçı, Oya Nuran Emiroğlu, Bilge Kalanlar
Journal of Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Thirty-six Year Trends in Mortality from Diseases of Circulatory System in Korea
Jongmin Baek, Hokyou Lee, Hyeok-Hee Lee, Ji Eun Heo, So Mi Jemma Cho, Hyeon Chang Kim
Korean Circulation Journal.2021; 51(4): 320. CrossRef - The identification of established modifiable mid-life risk factors for cardiovascular disease which contribute to cognitive decline: Korean Longitudinal Study of Aging (KLoSA)
Yebeen Ysabelle Boo, Otto-Emil Jutila, Meghan A. Cupp, Logan Manikam, Sung-Il Cho
Aging Clinical and Experimental Research.2021; 33(9): 2573. CrossRef - A Healthy Diet Rich in Calcium and Vitamin C Is Inversely Associated with Metabolic Syndrome Risk in Korean Adults from the KNHANES 2013–2017
Sunmin Park, Kyungjin Kim, Byung-Kook Lee, Jaeouk Ahn
Nutrients.2021; 13(4): 1312. CrossRef - Classification and Prediction on the Effects of Nutritional Intake on Overweight/Obesity, Dyslipidemia, Hypertension and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Using Deep Learning Model: 4–7th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Hyerim Kim, Dong Hoon Lim, Yoona Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2021; 18(11): 5597. CrossRef - Trends in cardiovascular disease risk factors by BMI category among adults in England, 2003‐2018
Shaun Scholes, Linda Ng Fat, Jennifer S. Mindell
Obesity.2021; 29(8): 1347. CrossRef - Precision Medicine and Cardiovascular Health: Insights from Mendelian Randomization Analyses
Wes Spiller, Keum Ji Jung, Ji-Young Lee, Sun Ha Jee
Korean Circulation Journal.2020; 50(2): 91. CrossRef - Association of the Healthy Eating Index with Estimated Cardiovascular Age in Adults from the KNHANES 2013–2017
Sunmin Park, Kyungjin Kim, Byung-Kook Lee, Jaeouk Ahn
Nutrients.2020; 12(10): 2912. CrossRef


 PubReader
PubReader Cite
Cite