Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Osong Public Health Res Perspect > Volume 14(5); 2023 > Article
-
Original Article
Factors associated with the combination of general and abdominal obesity in middle-aged and older Korean women: a cross-sectional study -
Jin Suk Ra

-
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives 2023;14(5):379-387.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0089
Published online: September 20, 2023
College of Nursing, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Republic of Korea
- Corresponding author: Jin Suk Ra College of Nursing, Chungnam National University, 266 Munhwa-ro, Jung-gu, Daejeon 35015, Republic of Korea E-mail: jinsukra@cnu.ac.kr
© 2023 Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency.
This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
- 1,064 Views
- 39 Download
Abstract
-
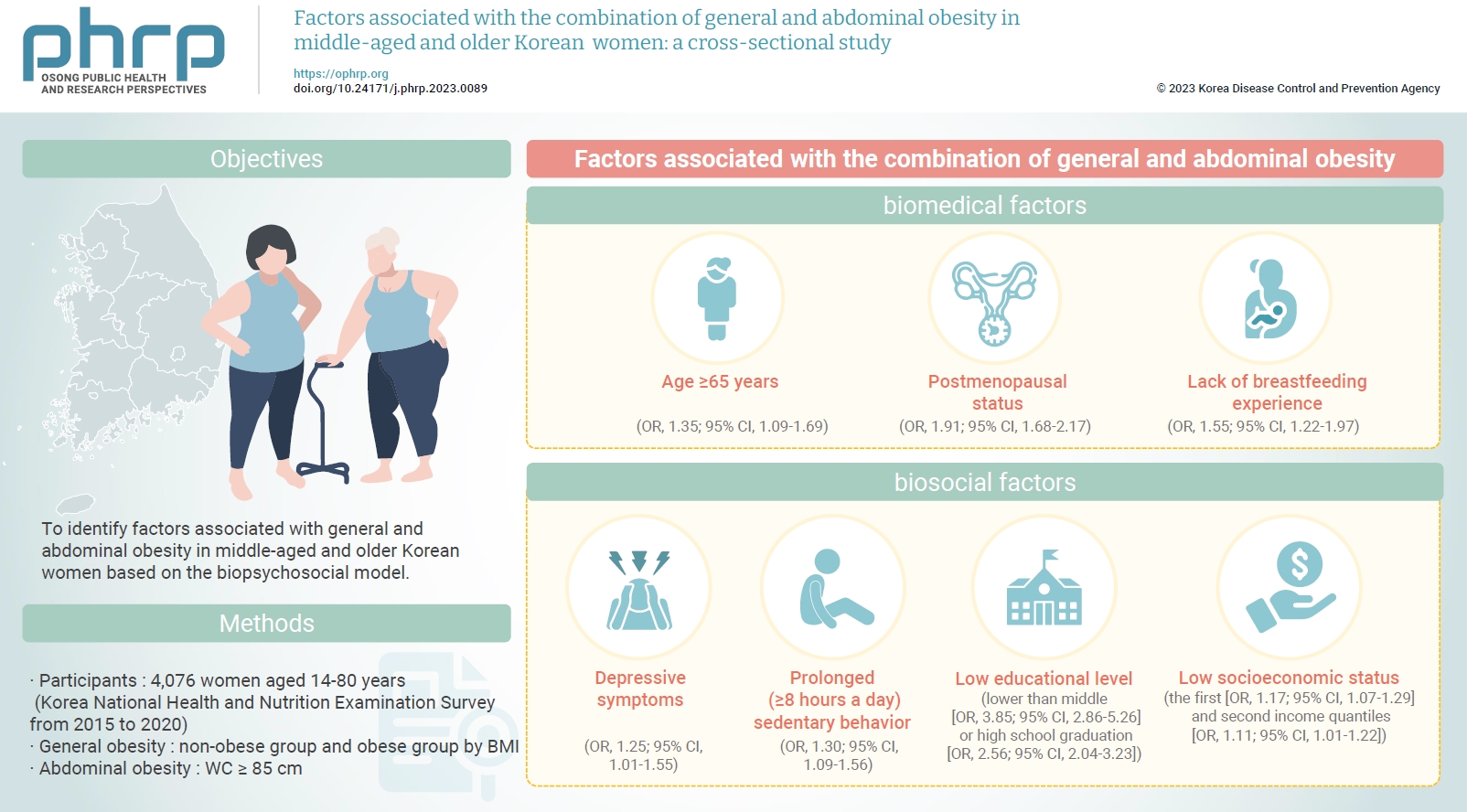
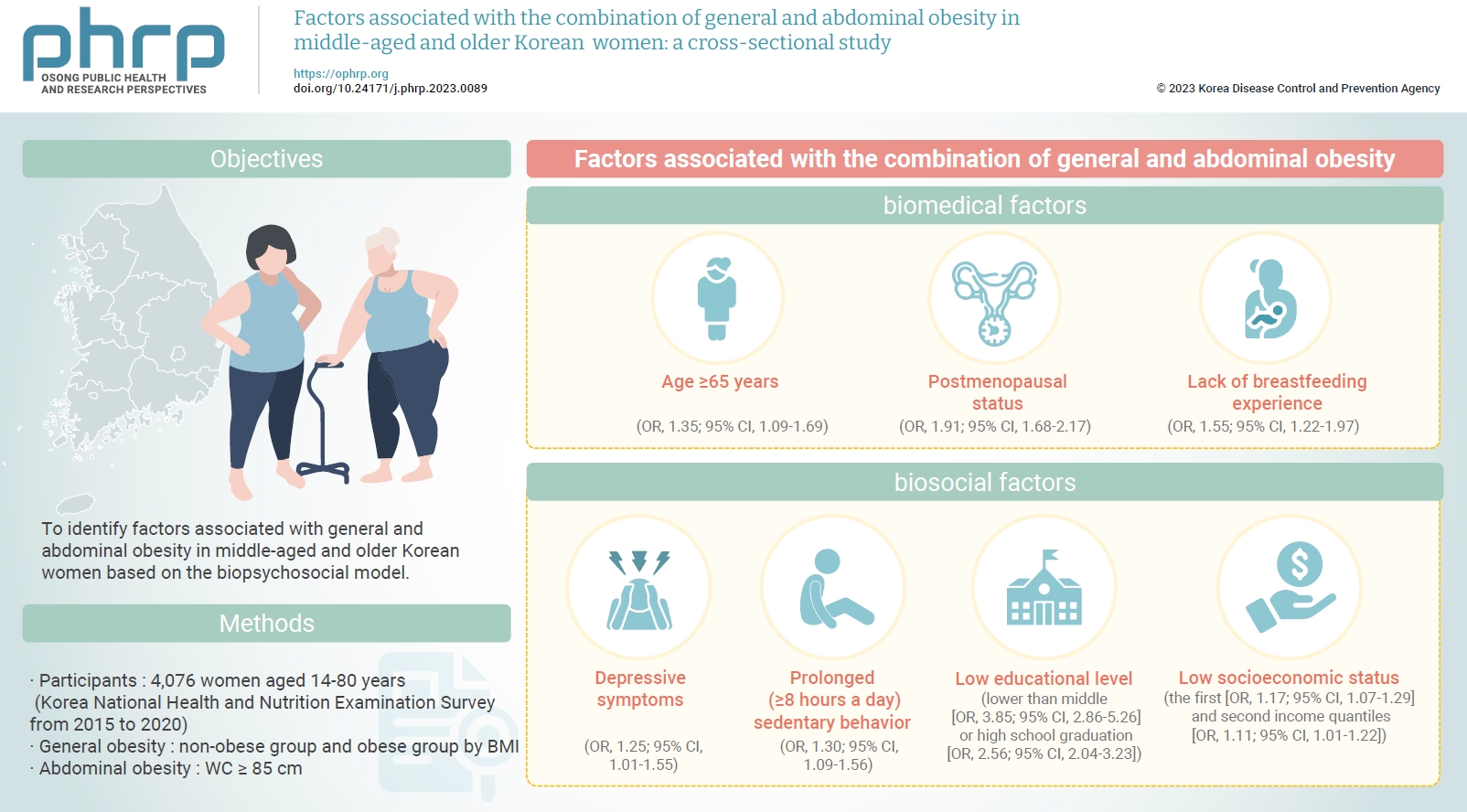
Objectives
- To identify factors associated with general and abdominal obesity in middle-aged and older Korean women based on the biopsychosocial model.
-
Methods
- Data from 4,076 women aged ≥45 years who participated in the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey from 2015 to 2020 were analyzed. Complex sampling analysis was performed using IBM SPSS ver. 26.0.
-
Results
- The combination of general and abdominal obesity was positively associated with age ≥65 years, postmenopausal status, and without breastfeeding experience among biomedical factors; depressive symptoms and prolonged (≥8 hours a day) sedentary behavior among psychosocial factors; and an educational level lower than middle or high school graduation and the first and second income quantiles among biosocial factors.
-
Conclusion
- Healthcare providers in communities and public societies should screen for risk factors for the combination of general and abdominal obesity while considering non-modifiable biomedical (e.g., age) and biosocial factors (e.g., educational level). In addition, intervention strategies should be developed by considering modifiable psychosocial factors such as sedentary behavior.
- Obesity is a major health problem. The prevalence rates of general obesity based on body mass index (BMI) and abdominal obesity based on waist circumference (WC) have steadily increased over time [1]. According to a report on Korean national trends, the prevalence of general obesity in adults increased from 29.7% in 2009 to 36.3% in 2019, and that of abdominal obesity in adults increased from 19.0% in 2009 to 23.9% in 2019 [2]. Furthermore, middle-aged and older women aged >50 years may have higher risks than men of developing general and abdominal obesity, owing to menopause with decreased ovarian function and related aging processes [2]. According to previous studies, in middle-aged and older Korean women aged >45 years, 37.3% of those aged between 45 and 80 years were obese (BMI ≥25 kg/m2) [3], and 28.9% of those aged between 45 and 65 years had abdominal obesity with (WC ≥85 cm) [4]. Additionally, a study of Brazilian middle-aged women aged 45 to 64 years reported the prevalence rates of general obesity and abdominal obesity as 68.2% to 73.8% and 56.4% to 63.1%, respectively [5]. Thus, general and abdominal obesity may present major health problems for middle-aged and older women.
- General obesity is independently associated with metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular disease (CVD), and cancer in adults, including middle-aged and older women [6,7]. Abdominal obesity is also strongly associated with a high risk of developing metabolic abnormalities (e.g., dyslipidemia, hypertension, and diabetes), CVD, cancer, and all-cause mortality [6–10]. However, previous studies have reported that the development of diabetes and CVD was associated with the combination of general and abdominal obesity [11,12]. Considering their individual effects, this combination might have synergetic effects on health, such as the development of diabetes [12]. Additionally, the risk of developing diabetes increased significantly only with the combination of general and abdominal obesity, but not with other patterns such as general obesity without abdominal obesity and vice versa [12]. Individuals with both general and abdominal obesity have a higher risk of cancer and stroke than those with other obesity patterns [7,13]. Particularly in women, the combination of general and abdominal obesity, and not other patterns of obesity alone, is significantly associated with an elevated risk of stroke [13]. Furthermore, in individuals aged >50 years, the combination of general and abdominal obesity is associated with a high risk of CVD [13]. Similarly, postmenopausal women with the combination of general and abdominal obesity have a notably higher risk of cancer (e.g., breast and endometrial cancer) than postmenopausal women with other patterns of obesity (general obesity without abdominal obesity) and premenopausal women with the combination of general and abdominal obesity [7]. Thus, the combination of general and abdominal obesity is considered a better predictor of CVD and cancer in middle-aged women [7,13]. Considering that this combination is the most common pattern of obesity in adults [13], preventing it may be important for promoting good health in middle-aged and older women. To prevent this combination, the identification of associated factors at multiple levels may be the first step in the development of health promotion strategies. However, awareness of the factors associated with the combination of general and abdominal obesity is limited, although they differ according to obesity patterns [12]. Middle-aged and older Korean women grew up in a Confucian culture that imposed stricter social norms on women than men and attributes superiority to men [14]. Thus, these women might have lower smoking and alcohol consumption than same-aged Korean men [14]. They might also be less educated than same-aged Korean men, resulting in low information about how to engage in a healthy lifestyle [15]. Therefore, the factors associated with the combination of general and abdominal obesity in middle-aged and older Korean women are different from those in same-aged Korean men and same-aged women in other countries with different cultural norms.
- Several factors contribute to the development of obesity, with various underlying mechanisms. Straub [16] proposed that obesity as a complex phenomenon is influenced by biological, social, and psychological factors. According to Hoffman and Driscoll [17], the biopsychosocial model might be an appropriate framework to evaluate the effects of multivariate factors on metabolic health (e.g., abdominal obesity). Thus, the biopsychosocial model can provide a framework for a comprehensive understanding of distinctive individual characteristics associated with health status, including obesity [18].
- According to the biopsychosocial model, biomedical (e.g., age and sex), psychosocial (e.g., mood and health-related behaviors), and biosocial factors (e.g., educational level and socioeconomic household status) interact to influence people’s health. Biomedical factors associated with general and abdominal obesity include age [10,19], postmenopausal status, and breastfeeding experience [20]. Psychosocial factors include depressive symptoms [21], skipping breakfast [22], eating out [22], sedentary behavior [22], physical activity (days of walking per week) [22–24], current and past smoking [10,19], and current alcohol consumption [19,25]. Among biosocial factors, educational level [10], employment [26], and household socioeconomic status [10] have been associated with abdominal obesity. Therefore, this study aimed to identify factors associated with the combination of general and abdominal obesity in middle-aged and older Korean women based on the biopsychosocial model.
Introduction
- Study Design and Samples
- Using a cross-sectional design, secondary data analysis was conducted using the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) data of 44,951 Korean individuals (20,473 men and 24,478 women) 1 to 80 years old who participated in the survey from 2015 to 2020. Of 20,176 Korean women aged ≥20 years old, 13,725 middle-aged and older women aged 45 to 80 years were selected. Finally, after excluding individuals who did not complete the questionnaires and physical examinations (height, body weight, and WC), data from 4,076 women aged 45 to 80 years old were analyzed (Figure 1).
- Measurements
- To evaluate the combination of general and abdominal obesity, BMI and WC were measured. Obesity patterns were categorized into 4 groups: combination of general and abdominal obesity, general obesity without abdominal obesity, abdominal obesity without general obesity, and neither general nor abdominal obesity.
- To evaluate adiposity, BMI was calculated by dividing weight (kg) by height squared (m2). BMI was classified into the following categories: underweight (<18.5 kg/m2), normal weight (≥18.5 kg/m2 and <23 kg/m2), overweight (≥23 kg/m2 and <25 kg/m2), or obese (≥25 kg/m2) [27]. Regarding adiposity, participants were classified into non-obese (underweight and normal weight) and obese (overweight and obese) groups.
- Abdominal obesity was assessed using WC. A WC ≥85 cm in women indicates abdominal obesity [28].
- Independent variables and measurements are described in Table 1 [29,30].
- Data Analyses
- Following the guidelines for the statistical analysis of the KNHANES data, a complex sampling analysis was applied using IBM SPSS ver. 26.0 (IBM Corp.). The prevalence of obesity according to the patterns and variables of biomedical, psychosocial, and biosocial factors was analyzed using frequencies and percentages. Logistic regression analysis was applied for identification of the factors associated with the combination of general and abdominal obesity.
- IRB/IACUC Approval
- Since this study used the KNHANES results for secondary data analysis, the institutional review board of Chungnam National University approved the exemption of review (202210-SB-147-01). It was performed in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Materials and Methods
Dependent variables
General obesity
Abdominal obesity
Independent variables
- Prevalence of Obesity by Patterns and Biomedical, Psychosocial, and Biosocial Factors
- Table 2 shows that 33.1% of the participants had the combination of general and abdominal obesity. Regarding biomedical factors, 71.7% of the participants were aged 45 to 64 years old, 76.7% were postmenopausal, and 83.5% had breastfeeding experience. Regarding psychological factors, 14.7% had depressive symptoms; 75.2% and 9.1% skipped breakfast <2 days a week and 7 days a week (daily), respectively; 51.2% and 10.9% ate out 1 to 6 times a week and >1 time a day; 49.8% had prolonged (>8 hours a day) sedentary behavior, 45.4% walked >10 minutes 5 to 7 days a week, and 17.6% did not walk at all in a week; 4.9% and 4.2% were current and past smokers, respectively; and 57.5% currently consumed alcohol <1 time a month. Regarding biosocial factors, 41.6% of the participants graduated from middle school, and 51.5% were employed; regarding socioeconomic status, 22.3% reported that their monthly income was in the first quantile (lowest).
- Factors Associated with the Combination of General and Abdominal Obesity
- The associated factors included age and postmenopausal status, depressive symptoms and sedentary behavior, educational level, and household socioeconomic status (Table 3).
- Regarding biomedical factors, participants aged ≥65 years had a 1.35-fold higher likelihood of developing the combination of general and abdominal obesity than 45- to 64-year-olds (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.09–1.69; p=0.01). In addition, women aged >65 years had a higher likelihood of developing general obesity without abdominal obesity and vice versa than women aged 45 to 64 years. Postmenopausal status was associated with a 1.91-fold increased likelihood of developing the combination of general and abdominal obesity, compared with premenopausal status (95% CI, 1.68–2.17; p<0.001). A lack of breastfeeding experience was associated with a 1.55-fold increased likelihood of developing the combination of general and abdominal obesity, compared with having breastfed (95% CI, 1.22–1.97; p<0.001) (Table 3).
- Regarding psychosocial factors, depressive symptoms were associated with a 1.25-fold increased likelihood of developing the combination of general and abdominal obesity, compared with the absence of depressive symptoms (95% CI, 1.01–1.55; p=0.04). In addition, prolonged (≥8 hours a day) sedentary behavior was associated with a 1.30-fold increased likelihood of developing the combination of general and abdominal obesity, compared with appropriate (<8 hours a day) sedentary behavior (95% CI, 1.09–1.56; p=0.003) (Table 3).
- Regarding biosocial factors, having an educational level lower than middle school and high school graduation was associated, respectively, with 3.85-fold (95% CI, 2.86–5.26, p<0.001) and 2.56-fold (95% CI, 2.04–3.23; p<0.001) increased likelihoods of developing the combination of general and abdominal obesity, compared with college graduation. Regarding household socioeconomic status, the first and second quantiles of monthly income were associated with 1.17-fold (95% CI, 1.07–1.29; p=0.001) and 1.11-fold (95% CI, 1.01–1.22; p=0.03) increased likelihoods of developing the combination of general and abdominal obesity, respectively, compared with the fourth quantile (Table 3).
Results
- This study was conducted to identify factors associated with the combination of general and abdominal obesity among middle-aged and older Korean women. According to the results of this study, age, postmenopausal status, and breastfeeding experience were positively associated with the combination of general and abdominal obesity. A previous study on Norwegian and Russian individuals aged 40 to 69 years showed that older women had a higher likelihood of developing general and abdominal obesity [19]. This may be linked to metabolic changes associated with aging and hormonal changes during menopause in women [31,32]. During normal aging, white adipose tissue in the abdominal cavity and fat deposition in skeletal muscle increase [33,34]. In addition, middle-aged and older women gain weight with decreased energy expenditure via increased sedentary behavior and decreased physical activity due to reduced muscle strength and physical endurance [31,35]. Lower postmenopausal estrogen levels also result in increased accumulation of adipose tissue in the abdominal cavity [32]. Thus, middle-aged and older women may be at risk of increased weight gain and WC.
- In addition, middle-aged women who experienced 1–6 months of breastfeeding have shown lower general and abdominal obesity rates [36,37]. A total breastfeeding duration >3 months has been associated with a lower abdominal obesity rate in postmenopausal Korean women aged >40 years [38]. Bobrow et al. [39] reported that every 6 months of breastfeeding was associated with a 1% decrease in the mean BMI. Furthermore, a longer duration of breastfeeding was associated with a lower BMI among women with obesity 6 years postpartum [40]. In a previous study on Filipino, Caucasian, and African-American women aged 55 to 80 years [41], breastfeeding duration >3 months was associated with less visceral fat than in women with no history of breastfeeding. Since breastfeeding improves lipid metabolism [42], adipose tissue deposition in the visceral cavity during pregnancy decreases when breastmilk containing high-calorie fat is generated [43]. Thus, a longer duration of breastfeeding is associated with a greater decrease in general and abdominal obesity rates [36,44].
- According to a meta-analysis, depressive symptoms are associated with general obesity in women [45,46]. Another study reported that depressive symptoms were associated among middle-aged women, though not among middle-aged men, with an increased likelihood of developing general and central obesity [21]. Furthermore, depressive symptoms have been associated with general obesity in adults who have abdominal obesity [47]. However, a previous study on middle-aged and older Chinese participants reported that obesity was not associated with depressive symptoms in women [48]. Since obesity and depressive symptoms are interrelated, they cause emotional problems (e.g., depression), resulting in an increase in emotion-driven eating (eating in response to negative emotions rather than a physical need). An increase in energy intake promotes obesity with decreased energy expenditure via low physical activity levels, due to reduced self-efficacy [49]. In particular, since middle-aged women seem vulnerable to depressive symptoms [49], they may experience increased weight and WC.
- A sedentary lifestyle is associated with general and abdominal obesity in middle-aged women [50]. According to a national study, watching television and videos for 2 hours or more per day is associated with a 1.66-fold increase in general and abdominal obesity among women [22]. In addition, sitting for 8 hours or more per day has been associated with a 1.38-fold increase in the prevalence of obesity and a 1.05-fold increase in the prevalence of abdominal obesity in a population-based study [51]. Sedentary behavior is defined as participation in minimal activities requiring a resting level of energy expenditure (1.0–1.5 times the basal metabolic rate), such as watching television [52]. Thus, prolonged sedentary behavior might be associated with an overall decrease in energy expenditure, which may result in a positive energy balance, even when energy intake does not increase by eating. Therefore, interventions should be developed to decrease sedentary behavior in middle-aged and older women.
- Educational level and socioeconomic status are crucial factors associated with obesity [53]. According to KNHANES data gathered from 1998 to 2018, among women, a high educational level and socioeconomic class were inversely associated with increased general and abdominal obesity rates [54]. Educational level is positively associated with access to resources to assist in a healthy lifestyle. Thus, individuals with higher educational levels have greater access to health-related resources that provide information and assistance for following healthy lifestyles [15]. A previous study reported that women with low educational levels did not follow recommendations for obesity prevention [15]. In addition, individuals currently spend more money to maintain a healthy lifestyle, including the consumption of foods without junk calories (e.g., fresh fruits and vegetables), which is beneficial for preventing excessive weight gain [55]. Thus, it may be easier for individuals with a high socioeconomic status to maintain a healthy lifestyle, which costs more. In particular, Korean women who experience social pressure to be slender (culturally ideal body weight) may try to maintain a normal weight and slender body shape with a healthy lifestyle [54]. Thus, women with a high socioeconomic status can actively maintain a healthy lifestyle, which contributes to the prevention of general and abdominal obesity, while those with low socioeconomic status and educational levels may need public support to maintain healthy lifestyles and prevent general and abdominal obesity.
- In a secondary analysis of Korean national data, this study identified factors associated with the combination of general and abdominal obesity in middle-aged and older Korean women. In particular, although Lu et al. [13] reported a few factors associated with the combination of general and abdominal obesity, such as age, smoking, and alcohol consumption, the current study identified multiple factors (biomedical, psychosocial, and biosocial) associated with the combination of general and abdominal obesity based on the biopsychosocial model. The results showed that comprehensive intervention strategies should be developed to prevent and manage the combination of general and abdominal obesity in middle-aged and older Korean women. In addition, cohort studies could be proposed to identify the cumulative effects of aging with associated factors on developing the combination of general and abdominal obesity.
- However, this study had some limitations. First, a cross-sectional study design was applied, which limited the verification of causal relationships among the potential factors associated with the combination of general and abdominal obesity. Further cohort studies are needed to identify causal associations. Second, the factors associated with the combination of general and abdominal obesity may differ according to sex and ethnicity. Thus, sex-based and ethnic differences need to be identified in factors associated with general and abdominal obesity. Finally, this study focused on identifying factors associated with general and abdominal obesity. Since other obesity patterns (e.g., abdominal obesity without general obesity) are also associated with obesity-related complications, further studies are needed to identify and compare the factors associated with obesity patterns.
Discussion
- According to the results of this study, women older than 65 years, with postmenopausal status, without breastfeeding experience, with a low educational level, and/or with a low socioeconomic household status may be at risk for the combination of general and abdominal obesity. Prevention and early management of depressive symptoms and decreased sedentary behavior may be important to prevent general and abdominal obesity in middle-aged and older women. Thus, healthcare providers in communities and public health clinics should screen for risk factors for the combination of general and abdominal obesity with non-modifiable biomedical (e.g., age) and biosocial factors (e.g., educational level). In addition, prevention strategies for obesity (the combination of general and abdominal obesity) should be developed with a focus on modifiable psychosocial factors (e.g., sedentary behavior).
Conclusion
- • Age >65 years, postmenopausal status, and without breastfeeding experience were positively correlated with the combination of general and abdominal obesity.
- • Depressive symptoms and prolonged sedentary behavior were positively correlated with the combination of general and abdominal obesity.
- • Lower educational level and lower income were positively correlated with the combination of general and abdominal obesity.
HIGHLIGHTS
-
Ethics Approval
This study was approved by the institutional review board of Chungnam National University and was exempted from review because it was a secondary analysis (202210-SB-147-01). It was performed in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki.
-
Conflicts of Interest
The author has no conflicts of interest to declare.
-
Funding
This study was supported by a National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT (2021R1A2C100682811).
-
Availability of Data
The datasets are not publicly available but are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Article information
| Variable | Measurements |
|---|---|
| Biomedical factors | |
| Age (y) | Categorized into 45 to 64 years and ≥65 years |
| Post-menopause | Assessed by a single question asking whether the respondent had stopped regularly menstruating Answers were classified as post-menopause (yes) or pre-menopause (no). |
| Breastfeeding experience | Assessed by a single question asking whether the respondent had prior breastfeeding experience for more than 1 month. Answers were categorized as yes or no. |
| Psychosocial factors | |
| Depression symptoms | Assessed by a single question asking whether the respondent had experienced depressed moods lasting more than 2 weeks in total over the preceding year. Answers were classified as yes or no. |
| Skipping breakfast (1 wk) | Frequency of skipping breakfast was assessed by a single question asking about the respondent’s frequency of having breakfast over the preceding week. Answers were categorized as ≤2 days in 1 week, 3 to 6 days in 1 week, and every day (all 7 days). |
| Eating out | Assessed by a single question asking about the respondent’s average frequency of eating at restaurants over the preceding year. Answers were classified as ≤3 times/mo, 1 to 6 times/wk, and ≥1 time/d. |
| Sedentary behaviors | Assessed by a single question asking about the respondent’s number of hours spent sitting or lying down per day. Answers were categorized as appropriate (<8 h/d) or prolonged (≥8 h/d) [29]. |
| Physical activity (walking, 1 wk) | Assessed by a single question asking about the number of days the respondent walked for at least 10 minutes over the preceding week (7 days). Answers were categorized as none, 1 to 2 days, 3 to 4 days, and 5 to 7 days [30]. |
| Smoking | Assessed by a single question asking the respondent about current or past smoking habits over the preceding year. Answers were classified as yes or no. |
| Alcohol consumption | Assessed by a single question asking the respondent about their average frequency of alcohol consumption over the preceding year. Answers were classified into <1 time/mo, 1 to 4 times/mo, 2 to 3 times/wk, and ≥4 times/wk. |
| Biosocial factors | |
| Education level | Assessed by a single question asking about the highest level of education attained by the respondent. Answers were categorized into ≤completion of middle school, graduation from high school, and ≥graduation from college. |
| Employment | Assessed by a single question asking about whether the respondent had worked for income over the preceding week. Answers were classified as yes or no. |
| Socioeconomic household status | Assessed using equalized monthly household income. Income levels were divided into 4 quartiles (first quartile, second quartile, third quartile, and fourth quartile). |
| Variable | Category | na) (%)b) |
|---|---|---|
| Obesity patterns | ||
| Combination of general obesity and abdominal obesity | 1,416 (33.1) | |
| General obesity without abdominal obesity | 1,002 (24.9) | |
| Abdominal obesity without general obesity | 180 (4.3) | |
| Neither general nor abdominal obesity | 1,478 (37.7) | |
| Biomedical factors | ||
| Age (y) | 45–64 | 2,714 (71.7) |
| ≥65 | 1,362 (28.3) | |
| Post-menopause | Yes | 3,106 (76.7) |
| No | 970 (23.3) | |
| Breastfeeding experience | Yes | 3,489 (83.5) |
| No | 587 (16.5) | |
| Psychosocial factors | ||
| Depressive symptoms | Yes | 615 (14.7) |
| No | 3,461 (85.3) | |
| Skipping breakfast (a week) | ≤2 days | 3,170 (75.2) |
| 3 to 6 days | 572 (15.7) | |
| 7 days (daily) | 334 (9.1) | |
| Eating out | ≤3 times/mo | 1,672 (37.9) |
| 1 to 6 times/wk | 1,989 (51.2) | |
| ≥1 time/d | 415 (10.9) | |
| Sedentary behaviors | Appropriate (<8 h/d) | 2,097 (50.2) |
| Prolonged (≥8 h/d) | 1,979 (49.8) | |
| Physical activity (days of walking per week) | Never | 765 (17.6) |
| 1–2 days | 630 (14.9) | |
| 3–4 days | 870 (22.1) | |
| 5–7 days | 1,811 (45.4) | |
| Smoking consumption | Never | 3,718 (90.9) |
| Past | 148 (4.2) | |
| Current | 210 (4.9) | |
| Alcohol consumption | <1 time/mo | 2,418 (57.5) |
| 1–4 times/mo | 1,267 (32.5) | |
| 2–3 times/wk | 288 (7.6) | |
| ≥4 times/wk | 103 (2.4) | |
| Biosocial factors | ||
| Educational level | ≤Middle school | 1,918 (41.6) |
| High school | 1,320 (35.8) | |
| ≥College | 838 (22.6) | |
| Employment | Employed | 2,053 (51.5) |
| Unemployed | 2,023 (48.5) | |
| Socioeconomic household status | 1st quantile (lowest) | 928 (22.3) |
| 2nd quantile | 1,028 (24.8) | |
| 3rd quantile | 1,069 (26.3) | |
| 4th quantile (highest) | 1,051 (26.6) |
- 1. Sun J, Qu Q, Yuan Y, et al. Normal-weight abdominal obesity: a risk factor for hypertension and cardiometabolic dysregulation. Cardiol Discov 2022;2:13−21.Article
- 2. Yang YS, Han BD, Han K, et al. Obesity fact sheet in Korea, 2021: trends in obesity prevalence and obesity-related comorbidity incidence stratified by age from 2009 to 2019. J Obes Metab Syndr 2022;31:169−77.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 3. Lee JH, Cho AR, Kwon YJ. Association between dairy protein and body composition in middle-aged and older women: a community-based, 12-year, prospective cohort study. Clin Nutr 2022;41:460−7.ArticlePubMed
- 4. Jung HH, Chung YJ, No NR, et al. Effects of physical activity and other factors on abdominal obesity in Korean middle-aged women: the 7th Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2016-2017. Korean J Fam Pract 2020;10:461−8. Korean.Article
- 5. Gravena AA, Brischiliari SC, Lopes TC, et al. Excess weight and abdominal obesity in postmenopausal Brazilian women: a population-based study. BMC Womens Health 2013;13:46. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 6. Lee HA, Park H. Comorbidity network analysis related to obesity in middle-aged and older adults: findings from Korean population-based survey data. Epidemiol Health 2021;43:e2021018.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 7. Parra-Soto S, Petermann-Rocha F, Boonpor J, et al. Combined association of general and central obesity with incidence and mortality of cancers in 22 sites. Am J Clin Nutr 2021;113:401−9.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 8. Coutinho T, Goel K, Correa de Sa D, et al. Central obesity and survival in subjects with coronary artery disease: a systematic review of the literature and collaborative analysis with individual subject data. J Am Coll Cardiol 2011;57:1877−86.PubMed
- 9. Coutinho T, Goel K, Correa de Sa D, et al. Combining body mass index with measures of central obesity in the assessment of mortality in subjects with coronary disease: role of “normal weight central obesity”. J Am Coll Cardiol 2013;61:553−60.PubMed
- 10. Kim HY, Kim JK, Shin GG, et al. Association between abdominal obesity and cardiovascular risk factors in adults with normal body mass index: based on the sixth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. J Obes Metab Syndr 2019;28:262−70.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 11. Cong X, Liu S, Wang W, et al. Combined consideration of body mass index and waist circumference identifies obesity patterns associated with risk of stroke in a Chinese prospective cohort study. BMC Public Health 2022;22:347. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 12. Choi D, Choi S, Son JS, et al. Impact of discrepancies in general and abdominal obesity on major adverse cardiac events. J Am Heart Assoc 2019;8:e013471.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 13. Lu Y, Yang H, Xu Z, et al. Association between different obesity patterns and the risk of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus among adults in eastern China: a cross-sectional study. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes 2021;14:2631−9.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 14. Ra JS. Sex differences in factors associated with prediabetes in Korean adults. Osong Public Health Res Perspect 2022;13:142−52.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 15. Chung GK, Lai FTT, Yeoh EK, et al. Gender-specific trends of educational inequality in diagnosed diabetes from 1999 to 2014 in Hong Kong: a serial cross-sectional study of 97,481 community-dwelling Chinese adults. Popul Health Metr 2021;19:37. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 16. Straub RO. Health psychology: a biopsychosocial approach. 4th ed. Worth Publisher; 2014.
- 17. Hoffman MA, Driscoll JM. Health promotion and disease prevention: a concentric biopsychosocial model of health status. In: Brown SD, Lent RW, editors. Handbook of counseling psychology. 3rd ed. John Wiley & Sons Inc; 2000. p. 532–67.
- 18. Engel GL. The need for a new medical model: a challenge for biomedicine. Science 1977;196:129−36.ArticlePubMed
- 19. Kholmatova K, Krettek A, Leon DA, et al. Obesity prevalence and associated socio-demographic characteristics and health behaviors in Russia and Norway. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2022;19:9428. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 20. Chen JL, Guo J, Mao P, et al. Are the factors associated with overweight/general obesity and abdominal obesity different depending on menopausal status? PLoS One 2021;16:e0245150.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 21. Mulugeta A, Zhou A, Power C, et al. Obesity and depressive symptoms in mid-life: a population-based cohort study. BMC Psychiatry 2018;18:297. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 22. Kim D, Hou W, Wang F, et al. Factors affecting obesity and waist circumference among US adults. Prev Chronic Dis 2019;16:E02. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 23. Bunc V, Skalska M. Walking as a prevention of overweight and obesity in women of middle age. MOJ Womens Health 2016;3:00062. Article
- 24. Wedell-Neergaard AS, Eriksen L, Gronbaek M, et al. Low fitness is associated with abdominal adiposity and low-grade inflammation independent of BMI. PLoS One 2018;13:e0190645.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 25. Kwak JW, Jeon CH, Kwak MH, et al. Relationship between obesity and lifestyle factors in young Korean women: the seventh Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2016. Korean J Health Promot 2019;19:9−15. Korean.ArticlePDF
- 26. Cattafesta M, Petarli GB, Zandonade E, et al. Prevalence and determinants of obesity and abdominal obesity among rural workers in Southeastern Brazil. PLoS One 2022;17:e0270233.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 27. Kim MK, Lee WY, Kang JH, et al. 2014 clinical practice guidelines for overweight and obesity in Korea. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul) 2014;29:405−9.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 28. Lee S, Park HS, Kim SM, et al. Cut-off points of waist circumference for defining abdominal obesity in the Korean population. Korean J Obes 2006;15:1−9. Korean.
- 29. Son N, Sung H, Kim Y. The association between the levels of sedentary time, physical activity, and obesity in Korean older adults. Korean J Sports Med 2021;39:60−7. Korean.Article
- 30. Ju SY, Park YK. Low fruit and vegetable intake is associated with depression among Korean adults in data from the 2014 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. J Health Popul Nutr 2019;38:39. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 31. Jura M, Kozak LP. Obesity and related consequences to ageing. Age (Dordr) 2016;38:23. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 32. Kozakowski J, Gietka-Czernel M, Leszczynska D, et al. Obesity in menopause: our negligence or an unfortunate inevitability? Prz Menopauzalny 2017;16:61−5.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 33. Barzilai N, Huffman DM, Muzumdar RH, et al. The critical role of metabolic pathways in aging. Diabetes 2012;61:1315−22.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 34. Slawik M, Vidal-Puig AJ. Lipotoxicity, overnutrition and energy metabolism in aging. Ageing Res Rev 2006;5:144−64.ArticlePubMed
- 35. Rosique-Esteban N, Babio N, Diaz-Lopez A, et al. Leisure-time physical activity at moderate and high intensity is associated with parameters of body composition, muscle strength and sarcopenia in aged adults with obesity and metabolic syndrome from the PREDIMED-Plus study. Clin Nutr 2019;38:1324−31.ArticlePubMed
- 36. Ciesla E, Stochmal E, Gluszek S, et al. Breastfeeding history and the risk of overweight and obesity in middle-aged women. BMC Womens Health 2021;21:196. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 37. Suliga E, Ciesla E, Gluszek-Osuch M, et al. Breastfeeding and prevalence of metabolic syndrome among perimenopausal women. Nutrients 2020;12:2691. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 38. Ra JS, Kim SO. Beneficial effects of breastfeeding on the prevention of metabolic syndrome among postmenopausal women. Asian Nurs Res (Korean Soc Nurs Sci) 2020;14:173−7.ArticlePubMed
- 39. Bobrow KL, Quigley MA, Green J, et al. Persistent effects of women’s parity and breastfeeding patterns on their body mass index: results from the Million Women Study. Int J Obes (Lond) 2013;37:712−7.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 40. Sharma AJ, Dee DL, Harden SM. Adherence to breastfeeding guidelines and maternal weight 6 years after delivery. Pediatrics 2014;134 Suppl 1(01). S42−9.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 41. Armenta RF, Kritz-Silverstein D, Wingard D, et al. Association of breastfeeding with postmenopausal visceral adiposity among three racial/ethnic groups. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2015;23:475−80.ArticlePubMed
- 42. Williams CM. Lipid metabolism in women. Proc Nutr Soc 2004;63:153−60.ArticlePubMed
- 43. Butte NF, Hopkinson JM, Nicolson MA. Leptin in human reproduction: serum leptin levels in pregnant and lactating women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1997;82:585−9.ArticlePubMed
- 44. Choi SR, Kim YM, Cho MS, et al. Association between duration of breast feeding and metabolic syndrome: the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys. J Womens Health (Larchmt) 2017;26:361−7.ArticlePubMed
- 45. de Wit L, Luppino F, van Straten A, et al. Depression and obesity: a meta-analysis of community-based studies. Psychiatry Res 2010;178:230−5.ArticlePubMed
- 46. Hawkins MA, Goldstein CM, Dolansky MA, et al. Depressive symptoms are associated with obesity in adults with heart failure: an analysis of gender differences. Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs 2015;14:516−24.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 47. Zhao G, Ford ES, Li C, et al. Waist circumference, abdominal obesity, and depression among overweight and obese U.S. adults: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2005-2006. BMC Psychiatry 2011;11:130. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 48. Luo H, Li J, Zhang Q, et al. Obesity and the onset of depressive symptoms among middle-aged and older adults in China: evidence from the CHARLS. BMC Public Health 2018;18:909. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 49. Clum GA, Rice JC, Broussard M, et al. Associations between depressive symptoms, self-efficacy, eating styles, exercise and body mass index in women. J Behav Med 2014;37:577−86.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 50. Blumel JE, Fica J, Chedraui P, et al. Sedentary lifestyle in middle-aged women is associated with severe menopausal symptoms and obesity. Menopause 2016;23:488−93.ArticlePubMed
- 51. Paz-Krumdiek M, Rodriguez-Velez SG, Mayta-Tristan P, et al. Association between sitting time and obesity: a population-based study in Peru. Nutr Diet 2020;77:189−95.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 52. Kikuchi H, Inoue S, Odagiri Y, et al. Occupational sitting time and risk of all-cause mortality among Japanese workers. Scand J Work Environ Health 2015;41:519−28.ArticlePubMed
- 53. Cohen AK, Rai M, Rehkopf DH, et al. Educational attainment and obesity: a systematic review. Obes Rev 2013;14:989−1005.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 54. Jang HJ, Oh H. Trends and inequalities in overall and abdominal obesity by sociodemographic factors in Korean adults, 1998-2018. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2021;18:4162. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 55. Kim TH, Park Y, Myung J, et al. Food price trends in South Korea through time series analysis. Public Health 2018;165:67−73.ArticlePubMed
References
Figure & Data
References
Citations




 Cite
Cite