Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Epidemiological analysis and prevention strategies in response to a shigellosis cluster outbreak: a retrospective case series in an alternative school in the Republic of Korea, 2023
- Yeongseo Ahn, Sunmi Jin, Gemma Park, Hye Young Lee, Hyungyong Lee, Eunkyung Shin, Junyoung Kim, Jaeil Yoo, Yuna Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2024;15(1):68-76. Published online February 7, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0298
- 964 View
- 51 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 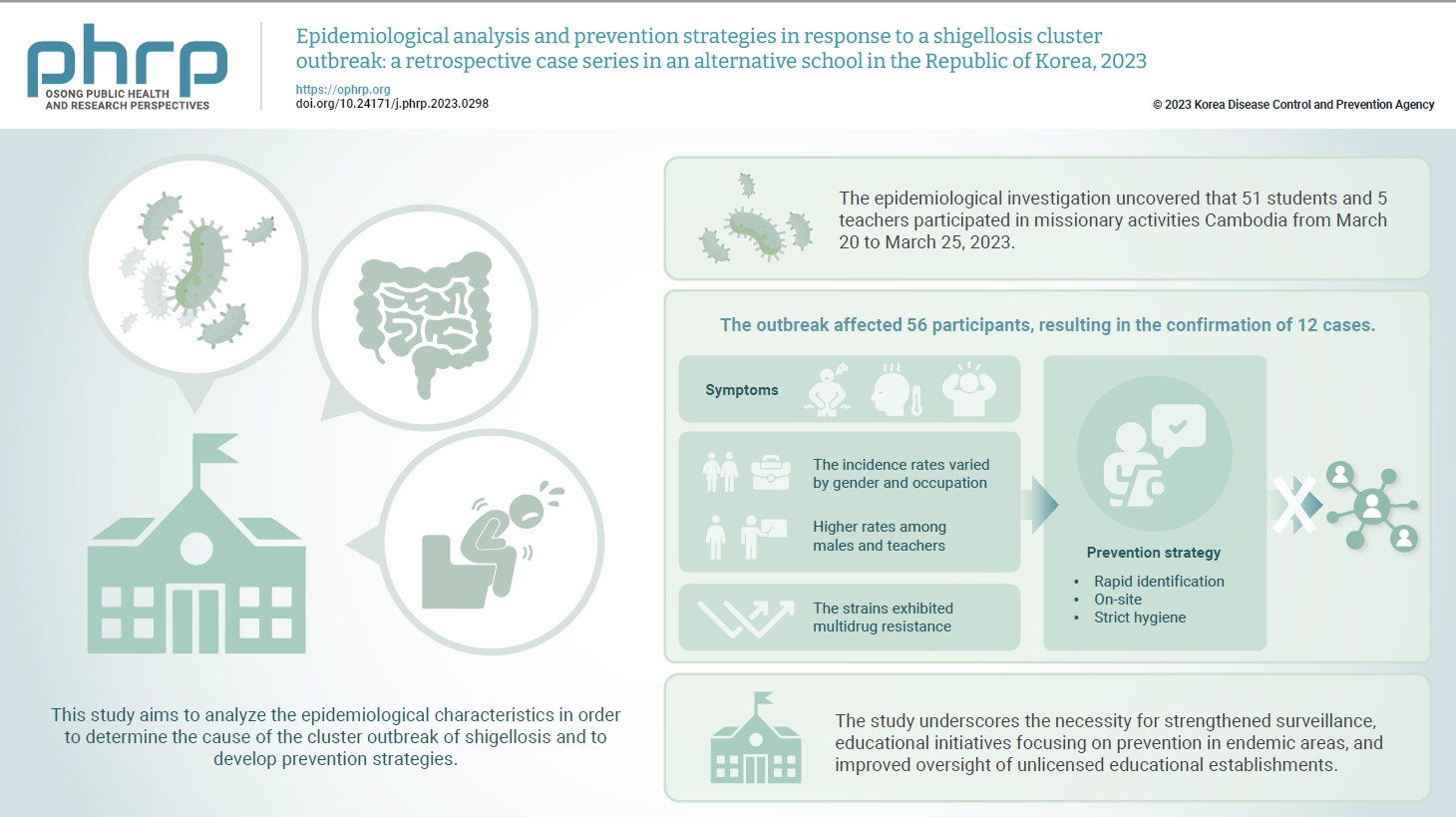
- Objectives
In March 2023, an alternative school in the Republic of Korea reported 12 cases of shigellosis. This study aims to analyze the epidemiological characteristics in order to determine the cause of the cluster outbreak of shigellosis and to develop prevention strategies. Methods: This study focused on 12 patients with confirmed Shigella infection and investigated their demographics, clinical features, epidemiology, diagnostics, and antimicrobial susceptibility. Following the identification of Shigella, we conducted follow-up rectal smear cultures to manage patients, implementing isolation and control measures. Results: This study investigated the emergence of multidrug-resistant Shigella following missionary activities in Cambodia, documenting a cluster infection within an alternative school in Daejeon, the Republic of Korea. The outbreak affected 56 participants, resulting in the confirmation of 12 cases. The incidence rates varied by gender and occupation, with higher rates among males and teachers. All 12 cases demonstrated multidrug resistance. Challenges included delayed pathogen confirmation and suboptimal adherence to isolation criteria. The incident prompted revisions in the criteria for isolation release, focusing on symptom resolution. The study underscores the necessity for strengthened surveillance, educational initiatives focusing on prevention in endemic areas, and improved oversight of unlicensed educational establishments. Conclusion: Successful response strategies included swift situation assessment, collaborative efforts, effective infection control measures, and modified criteria for isolation release. Continued surveillance of multidrug-resistant strains is recommended, especially in regions with a high prevalence.
- The effect of an application-based educational intervention with a social cognitive theory model on pregnant women in Denpasar, Bali, Indonesia: a randomized controlled trial
- Ni Wayan Ariyani, I Made Ady Wirawan, Gede Ngurah Indraguna Pinatih, Anak Agung Ngurah Jaya Kusuma
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(2):153-161. Published online April 14, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.0209
- 3,863 View
- 105 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The aim of this study was to elucidate the effect of application-based antenatal education based on social cognitive theory (SCT) on Health Promoting Lifestyle Profile II (HPLP II) scores, compliance with iron tablet consumption, and readiness for childbirth and complications among pregnant women in Denpasar, Bali, Indonesia. Methods: This randomized controlled trial included 71 pregnant women in the treatment group and 74 pregnant women in the control group. The treatment group application-based antenatal education based on SCT, while the control group attended a conventional pregnancy class. Iron tablet consumption was verified by counting the remaining iron tablets. Information on participants’ lifestyles was collected using the HPLP II questionnaire with the help of an assistant. The collected data were statistically analyzed using IBM SPSS ver. 24.0. Results: The antenatal education intervention effectively increased the HPLP II score by 0.32 points (2.62±0.331 before the intervention and 2.94±0.273 after). Meanwhile, the control group had a 0.13-point increase (p=0.001), from 2.67±0.336 to 2.80±0.275. There was no significant difference in iron tablet consumption (p=0.333) or readiness for delivery and complications (p=0.557) between the treatment and control groups. Conclusion: Application-based antenatal education with SCT effectively increased the HPLP II scores of pregnant women in Denpasar, Bali. Although there was no significant difference in iron tablet consumption or readiness for delivery and complications, the values increased to a greater extent in the treatment group than in the control group. This education model is more suited to urban pregnant women who employed and have good internet access. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effects of mHealth interventions on improving institutional delivery and uptake of postnatal care services in low-and lower-middle-income countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Reta Tsegaye Gayesa, Fei Wan Ngai, Yao Jie Xie
BMC Health Services Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Dietitian-led cluster randomised controlled trial on the effectiveness of mHealth education on health outcomes among pregnant women: a protocol paper
Ying Ting Er, Yoke Mun Chan, Zalilah Mohd Shariff, Habibah Abdul Hamid, Zulfitri 'Azuan Mat Daud, Heng Yaw Yong
BMJ Open.2023; 13(11): e075937. CrossRef
- The effects of mHealth interventions on improving institutional delivery and uptake of postnatal care services in low-and lower-middle-income countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Designing and Evaluating Educational Intervention to Improve Preventive Behavior Against Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in Endemic Areas in Iran
- Musalreza Ghodsi, Mina Maheri, Hamid Joveini, Mohammad Hassan Rakhshani, Ali Mehri
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2019;10(4):253-262. Published online August 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2019.10.4.09
- 8,811 View
- 109 Download
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives Health education programs are one of the most important strategies for controlling cutaneous leishmaniasis (CL) in endemic areas such as Neshabur city. This study aimed to develop and evaluate a comprehensive health education program to improve preventive behaviors for CL.
Methods This was an interventional study conducted on 136 high school students in Neishabur city. Data collection instruments included a demographic questionnaire and a researcher-made questionnaire based on the “Health Belief Model” and “Beliefs, Attitudes, Subjective Norms and Enabling Factors Model” constructs. The control and intervention groups completed the questionnaires before and 2 months after the intervention. The intervention was conducted in 6, 1-hour educational sessions for the intervention group students and 2, 1-hour sessions for school administrators, teachers, and students’ parents.
Results There was no significant difference between the 2 groups in the pre-intervention phase. However, in the post-intervention phase, there were significant differences between the 2 groups for mean scores of knowledge, perceived susceptibility, perceived severity, perceived benefits, cues to action, self-efficacy, attitude, subjective norms, behavioral intention, enabling factors, and behavior associated with CL.
Conclusion Health education program based on the “Health Belief Model” and the “Beliefs, Attitudes, Subjective Norms and Enabling Factors Model” model constructs may be a comprehensive and effective educational program to improve preventive behaviors against CL in students.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Antiparasitic activity of the iron-containing milk protein lactoferrin and its potential derivatives against human intestinal and blood parasites
Namrata Anand
Frontiers in Parasitology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Cutaneous leishmaniasis situation analysis in the Islamic Republic of Iran in preparation for an elimination plan
Iraj Sharifi, Ahmad Khosravi, Mohammad Reza Aflatoonian, Ehsan Salarkia, Mehdi Bamorovat, Ali Karamoozian, Mahmoud Nekoei Moghadam, Fatemeh Sharifi, Abbas Aghaei Afshar, Setareh Agha Kuchak Afshari, Faranak Gharachorloo, Mohammad Reza Shirzadi, Behzad Ami
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Mutual Role of Patients and the Healthcare System in the Control of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis
Mehdi Bamorovat, Iraj Sharifi, Setareh Agha Kuchak Afshari, Pooya Ghasemi Nejad Almani, Fedor Korennoy
Transboundary and Emerging Diseases.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Knowledge, perceptions and practices of health students and professionals regarding leishmaniasis in Portugal: a cross-sectional study
Rafael Rocha, Cláudia Conceição, Luzia Gonçalves, Carla Maia
Parasites & Vectors.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Investigating Iranians’ Attitude, Practice, and Perceived Self-Efficacy towards COVID-19 Preventive Behaviors
Hamid Joveini, Zahra Zare, Masoumeh Hashemian, Ali Mehri, Reza Shahrabadi, Neda Mahdavifar, Hamideh Ebrahimi Aval
The Open Public Health Journal.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Şark çıbanı vakalarında bilgi ve farkındalık düzeyini artırmaya yönelik müdahale çalışması: Şanlıurfa örneği
Burcu BEYAZGÜL, İbrahim KORUK, Rüstem KUZAN, Şule ALLAHVERDİ
Mersin Üniversitesi Sağlık Bilimleri Dergisi.2022; 15(2): 188. CrossRef - Congregational Worshiping and Implementation of the COVID-19 Preventive Behavioral Measures During the Re-opening Phase of Worship Places Among Indonesian Muslims
Mochamad Iqbal Nurmansyah, Sarah Handayani, Deni Wahyudi Kurniawan, Emma Rachmawati, Hidayati, Ahmad Muttaqin Alim
Journal of Religion and Health.2022; 61(5): 4169. CrossRef - Development and psychometric assessment of cutaneous leishmaniasis prevention behaviors questionnaire in adolescent female students: Application of integration of cultural model and extended parallel process model
Masoumeh Alidosti, Hossein Shahnazi, Zahra Heidari, Fereshteh Zamani-Alavijeh, Mona Dür
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(8): e0273400. CrossRef - Community-Based Interventions for the Prevention and Control of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis: A Systematic Review
Kay Polidano, Brianne Wenning, Alejandra Ruiz-Cadavid, Baheya Dawaishan, Jay Panchal, Sonali Gunasekara, Haftom Abebe, Marciglei Morais, Helen Price, Lisa Dikomitis
Social Sciences.2022; 11(10): 490. CrossRef - Design and evaluation of two educational media in the form of animation and games to promote the cutaneous leishmaniasis prevention behaviors in adolescent female
Masoumeh Alidosti, Hossein Shahnazi, Zahra Heidari, Fereshteh Zamani-Alavijeh
BMC Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Knowledge, attitude, and practice toward Zika virus among staff of comprehensive health services centers affiliated with Tehran University of Medical Sciences in 2020
Hamidreza Farrokh‐Eslamlou, Mina Maheri
Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research.2021; 47(6): 2204. CrossRef - Behaviors and Perceptions Related to Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in Endemic Areas of the World: A Review
Masoumeh Alidosti, Zahra Heidari, Hossein Shahnazi, Fereshteh Zamani-Alavijeh
Acta Tropica.2021; 223: 106090. CrossRef - Application of BASNEF model in students training regarding cutaneous leishmaniasis prevention behaviors: a school-based quasi experimental study
Gholamreza Alizadeh, Hossein Shahnazi, Akbar Hassanzadeh
BMC Infectious Diseases.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Predicting the Preventive Behaviors of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in families with Children Under 10 Years, Applied the Precede Model
Hosein Jajarmi, Mahdi Gholian-Aval, Asma pourtaheri, Habibollah Esmaily, Hamid Hosseini, Rezvan Rajabzadeh, Hadi Tehrani
ranian Journal of Health Education and Health Prom.2021; 9(4): 360. CrossRef - Effects of an Educational Intervention on Male Students’ Intention to Quit Water Pipe Smoking: an Application of the Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB) and Health Action Process Approach (HAPA)
Hamid Joveini, Tahereh Dehdari, Masoumeh Hashemian, Mina Maheri, Reza Shahrabadi, Alireza Rohban, Ali Mehri, Hasan Eftekhar Ardebili
Journal of Education and Community Health.2020; 7(2): 73. CrossRef
- Antiparasitic activity of the iron-containing milk protein lactoferrin and its potential derivatives against human intestinal and blood parasites
- Development of a Food Safety and Nutrition Education Program for Adolescents by Applying Social Cognitive Theory
- Jounghee Lee, Soyeon Jeong, Gyeongah Ko, Hyunshin Park, Youngsook Ko
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2016;7(4):248-260. Published online August 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2016.05.005
- 3,202 View
- 20 Download
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The purpose of this study was to develop an educational model regarding food safety and nutrition. In particular, we aimed to develop educational materials, such as middle- and high-school textbooks, a teacher’s guidebook, and school posters, by applying social cognitive theory.
Methods
To develop a food safety and nutrition education program, we took into account diverse factors influencing an individual’s behavior, such as personal, behavioral, and environmental factors, based on social cognitive theory. We also conducted a pilot study of the educational materials targeting middle-school students (n = 26), high-school students (n = 24), and dietitians (n = 13) regarding comprehension level, content, design, and quality by employing the 5-point Likert scale in May 2016.
Results
The food safety and nutrition education program covered six themes: (1) caffeine; (2) food additives; (3) foodborne illness; (4) nutrition and meal planning; (5) obesity and eating disorders; and (6) nutrition labeling. Each class activity was created to improve self-efficacy by setting one’s own goal and to increase self-control by monitoring one’s dietary intake. We also considered environmental factors by creating school posters and leaflets to educate teachers and parents. The overall evaluation score for the textbook was 4.0 points among middle- and high-school students, and 4.5 points among dietitians.
Conclusion
This study provides a useful program model that could serve as a guide to develop educational materials for nutrition-related subjects in the curriculum. This program model was created to increase awareness of nutrition problems and self-efficacy. This program also helped to improve nutrition management skills and to promote a healthy eating environment in middle- and high-school students. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Chinese families' knowledge, attitudes, and practices regarding seizure management for children with epilepsy: a mixed-methods study
Cui Cui, Shuangzi Li, Wenjin Chen, Hengyu Zhou, Xianlan Zheng
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of a Health-Related Education Program on Food-Related Behaviors of Vulnerable Women in Zanjan: A Pilot Randomized Clinical Trial
Jalal Hejazi, Sahar Nazari Darab Khani, Mohammad Masoud Vakili, Majid Aminzare
Journal of Human Environment and Health Promotion.2023; 9(3): 146. CrossRef - Analyzing consumer behaviour towards food and nutrition labeling: A comprehensive review
K.M. Priya, Sivakumar Alur
Heliyon.2023; 9(9): e19401. CrossRef - The effect of a nutrition program based on the Health Behavior Interaction Model on primary school students’ nutritional attitudes and behaviors
Ayşe Burcu Başçı, Oya Nuran Emiroğlu, Bilge Kalanlar
Journal of Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluating the Consistency Between Conceptual Frameworks and Factors Influencing the Safe Behavior of Iranian Workers in the Petrochemical Industry: Mixed Methods Study
Azita Zahiri Harsini, Philip Bohle, Lynda R Matthews, Fazlollah Ghofranipour, Hormoz Sanaeinasab, Farkhondeh Amin Shokravi, Krishan Prasad
JMIR Public Health and Surveillance.2021; 7(5): e22851. CrossRef - Critical Consciousness of Food Systems as a Potential Lifestyle Intervention on Health Issues
Sothy Eng, Carli Donoghue, Tricia Khun, Whitney Szmodis
American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine.2020; 14(3): 258. CrossRef - Development, Implementation, and Process Evaluation of a Theory-Based Nutrition Education Programme for Adults Living With HIV in Abeokuta, Nigeria
Temitope K. Bello, Gerda J. Gericke, Una E. MacIntyre
Frontiers in Public Health.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - What matters for higher education success of private educational institutions? Senior students’ perceptions in Malaysia
Jayaraman Krishnaswamy, Zarif Hossain, Mohan Kumar Kavigtha, Annamalai Nagaletchimee
Journal of Applied Research in Higher Education.2019; 11(3): 616. CrossRef - Augmented reality of traditional food for nutrition education
Cica Yulia, H Hasbullah, E.E. Nikmawati, S.R. Mubaroq, Cep Ubad Abdullah, Isma Widiaty, Ade Gafar Abdullah, Asep Bayu Dani Nandiyanto
MATEC Web of Conferences.2018; 197: 16001. CrossRef - Decreasing the use of edible oils in China using WeChat and theories of behavior change: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Rui Zhu, Xianglong Xu, Yong Zhao, Manoj Sharma, Zumin Shi
Trials.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Chemicals as additives in food processing -a review
KUMARESAN D, NITHYA SERMUGAPANDIAN, HEMASHREE S, RUBINI K R
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Science.2017;[Epub] CrossRef
- Chinese families' knowledge, attitudes, and practices regarding seizure management for children with epilepsy: a mixed-methods study
- Knowledge of Diabetes Mellitus: Does Gender Make a Difference?
- Patrício Fernando Lemes dos Santos, Poliana Rodrigues dos Santos, Graziele Souza Lira Ferrari, Gisele Almeida Amaral Fonseca, Carlos Kusano Bucalen Ferrari
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2014;5(4):199-203. Published online August 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2014.06.004
- 3,207 View
- 21 Download
- 16 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objective
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a chronic disease considered an important public health problem. In recent years, its prevalence has been exponentially rising in many developing countries. Chronic complications of DM are important causes of morbidity and mortality among patients, which impair their health and quality of life. Knowledge on disease prevention, etiology, and management is essential to deal with parents, patients, and caregivers. The aim of this study was to evaluate the knowledge regarding DM in an adult population from a Middle-western Brazilian city.
Methods
This was a cross-sectional study covering 178 adults, aged 18–64 years, who answered a diabetes knowledge questionnaire. In order to identify the difference between groups, analysis of variance was used.
Results
Higher knowledge scores were found regarding the role of sugars on DM causality, diabetic foot care, and the effects of DM on patients (blindness, impaired wound healing, and male sexual dysfunction). However, lower scores were found amongst types of DM, hyperglycemic symptoms, and normal blood glucose levels. Females tended to achieve better knowledge scores than males.
Conclusion
Women had better knowledge regarding types of DM, normal blood glucose values, and consequences of hyperglycemia revealed that diabetes education should be improved. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Relationship Between Diabetes Knowledge Level, Physical Activity, and Quality of Life in Older Adults
Burçin AKÇAY, Tuğba KURU ÇOLAK, Sultan İĞREK, Bahar ÖZGÜL, Adnan APTI
Bandırma Onyedi Eylül Üniversitesi Sağlık Bilimler.2023; 5(2): 162. CrossRef - Assessment of prediabetes knowledge among adults in Al-Madinah, Saudi Arabia
Ameerah Almaski, Manal Almughamisi
Nutrition and Health.2023; : 026010602311557. CrossRef - Knowledge, Attitude, and Practices Related to Foot Care Among Diabetic Patients in Tabuk City, Saudi Arabia
Tariq M Shaqran, Saud N Alqahtani, Abdullah F Alhalafi , Norah M Alsabeelah, Rafaa A Algethmi, Ammar S Azhari, Abdulrahman Y Alhashmi, Abdullah N Almaghrabi, Hibah A Alshammari, Mohammed Saeed Alshahrani
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychometric properties of the revised Diabetes Knowledge Test using Rasch analysis
Eun-Hyun Lee, Young Whee Lee, Hyun-Jung Kang
Patient Education and Counseling.2022; 105(4): 851. CrossRef - Recognition of diabetes and sociodemographic predictors: results of a cross-sectional nationwide population-based survey in Singapore
Kumarasan Roystonn, Jue Hua Lau, PV AshaRani, Fiona Devi Siva Kumar, Peizhi Wang, Chee Fang Sum, Eng Sing Lee, Siow Ann Chong, Mythily Subramaniam
BMJ Open.2022; 12(3): e050425. CrossRef - Public knowledge and awareness of diabetes mellitus, its risk factors, complications, and prevention methods among adults in Poland—A 2022 nationwide cross-sectional survey
Kuba Sękowski, Justyna Grudziąż-Sękowska, Jarosław Pinkas, Mateusz Jankowski
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Physical Comorbidity According to Diagnoses and Sex among Psychiatric Inpatients in South Korea
Suin Park, Go-Un Kim, Hyunlye Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2021; 18(8): 4187. CrossRef - Diabetes knowledge, risk perception, and quality of life among South Asian caregivers in young adulthood
Angela Koipuram, Sandra Carroll, Zubin Punthakee, Diana Sherifali
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2020; 8(2): e001268. CrossRef - Small molecule IVQ, as a prodrug of gluconeogenesis inhibitor QVO, efficiently ameliorates glucose homeostasis in type 2 diabetic mice
Ting-ting Zhou, Tong Zhao, Fei Ma, Yi-nan Zhang, Jing Jiang, Yuan Ruan, Qiu-ying Yan, Gai-hong Wang, Jin Ren, Xiao-wei Guan, Jun Guo, Yong-hua Zhao, Ji-ming Ye, Li-hong Hu, Jing Chen, Xu Shen
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica.2019; 40(9): 1193. CrossRef - Problematic drinking in the old and its association with muscle mass and muscle function in type II diabetes
Nikolaus Buchmann, Dominik Spira, Maximilian König, Kristina Norman, Ilja Demuth, Elisabeth Steinhagen-Thiessen
Scientific Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - A survey to validate the traditional Siddha perception of diabetes mellitus
Amulya Vijay, Priyadharshan Ranganathan, Balachandar Vellingiri
Journal of Public Health.2019; 27(5): 581. CrossRef - Knowledge and self-care management of the uncontrolled diabetes patients
Somsak Thojampa
International Journal of Africa Nursing Sciences.2019; 10: 1. CrossRef - Acculturation and Dietary Intakes by Gender Among Mongolians in South Korea: Nutrition Education Implication for Multicultural Families
Hae Ryun Park, Zuunnast Tserendejid, Joung Hee Lee, Young Suk Lim
Asia Pacific Journal of Public Health.2017; 29(7): 608. CrossRef - Knowledge of type 2 diabetic patients about their condition in Kimpese Hospital diabetic clinic, Democratic Republic of the Congo
Patrick N. Ntontolo, Philippe N. Lukanu, Gboyega A. Ogunbanjo, Jean-Pierre L. Fina, Léon N.M. Kintaudi
African Journal of Primary Health Care & Family Me.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of Knowledge of Diabetes Mellitus in the Urban Areas of Klang District, Malaysia
Sasikala Chinnappan, Palanisamy Sivanandy, Rajenthina Sagaran, Nagashekhara Molugulu
Pharmacy.2017; 5(4): 11. CrossRef - Affective Bond, Loneliness and Socioeconomic Aspects of an Elderly Population in Midwest, Brazil
CKB Ferrari, GSL Ferrari, LD Nery, DF dos Santos, NS Pereira
Archives of Nursing Practice and Care.2016; 2(1): 024. CrossRef
- The Relationship Between Diabetes Knowledge Level, Physical Activity, and Quality of Life in Older Adults
- Peer-to-Peer JXTA Architecture for Continuing Mobile Medical Education Incorporated in Rural Public Health Centers
- Rajkumar Rajasekaran, Nallani Chackravatula Sriman Narayana Iyengar
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2013;4(2):99-106. Published online April 30, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2013.03.004
- 3,247 View
- 13 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Mobile technology helps to improve continuing medical education; this includes all aspects of public health care as well as keeping one’s knowledge up-to-date. The program of continuing medical and health education is intertwined with mobile health technology, which forms an imperative component of national strategies in health. Continuing mobile medical education (CMME) programs are designed to ensure that all medical and health-care professionals stay up-to-date with the knowledge required through mobile JXTA to appraise modernized strategies so as to achieve national goals of health-care information distribution.
Methods
In this study, a 20-item questionnaire was distributed to 280 health professionals practicing traditional training learning methodologies (180 nurses, 60 doctors, and 40 health inspectors) in 25 rural hospitals. Among the 83% respondents, 56% are eager to take new learning methodologies as part of their evaluation, which is considered for promotion to higher grades, increments, or as part of their work-related activities.
Results
The proposed model was executed in five public health centers in which nurses and health inspectors registered in the JXTA network were referred to the record peer group by administrators. A mobile training program on immunization was conducted through the ADVT, with the lectures delivered on their mobiles. Credits are given after taking the course and completing an evaluation test. The system is faster compared with traditional learning.
Conclusion
Medical knowledge management and mobile-streaming application support the CMME system through JXTA. The mobile system includes online lectures and practice quizzes, as well as assignments and interactions with health professionals. Evaluation and assessments are done online and credits certificates are provided based on the score the student obtains. The acceptance of mobile JXTA peer-to-peer learning has created a drastic change in learning methods among rural health professionals. The professionals undergo training and should pass an exam in order to obtain the credits. The system is controlled and monitored by the administrator peer group, which makes it more flexible and structured. Compared with traditional learning system, enhanced study improves cloud-based mobile medical education technology. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effects of mobile applications in cardiopulmonary assessment education
In-Young Yoo, Young-Mi Lee
Nurse Education Today.2015; 35(2): e19. CrossRef
- The effects of mobile applications in cardiopulmonary assessment education



 First
First Prev
Prev


