Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Effects of an arteriovenous fistula stenosis prevention program in patients receiving hemodialysis
- Haegyeong Lee, Gyuli Baek, Eunju Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(4):279-290. Published online August 9, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0101
- 1,292 View
- 144 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 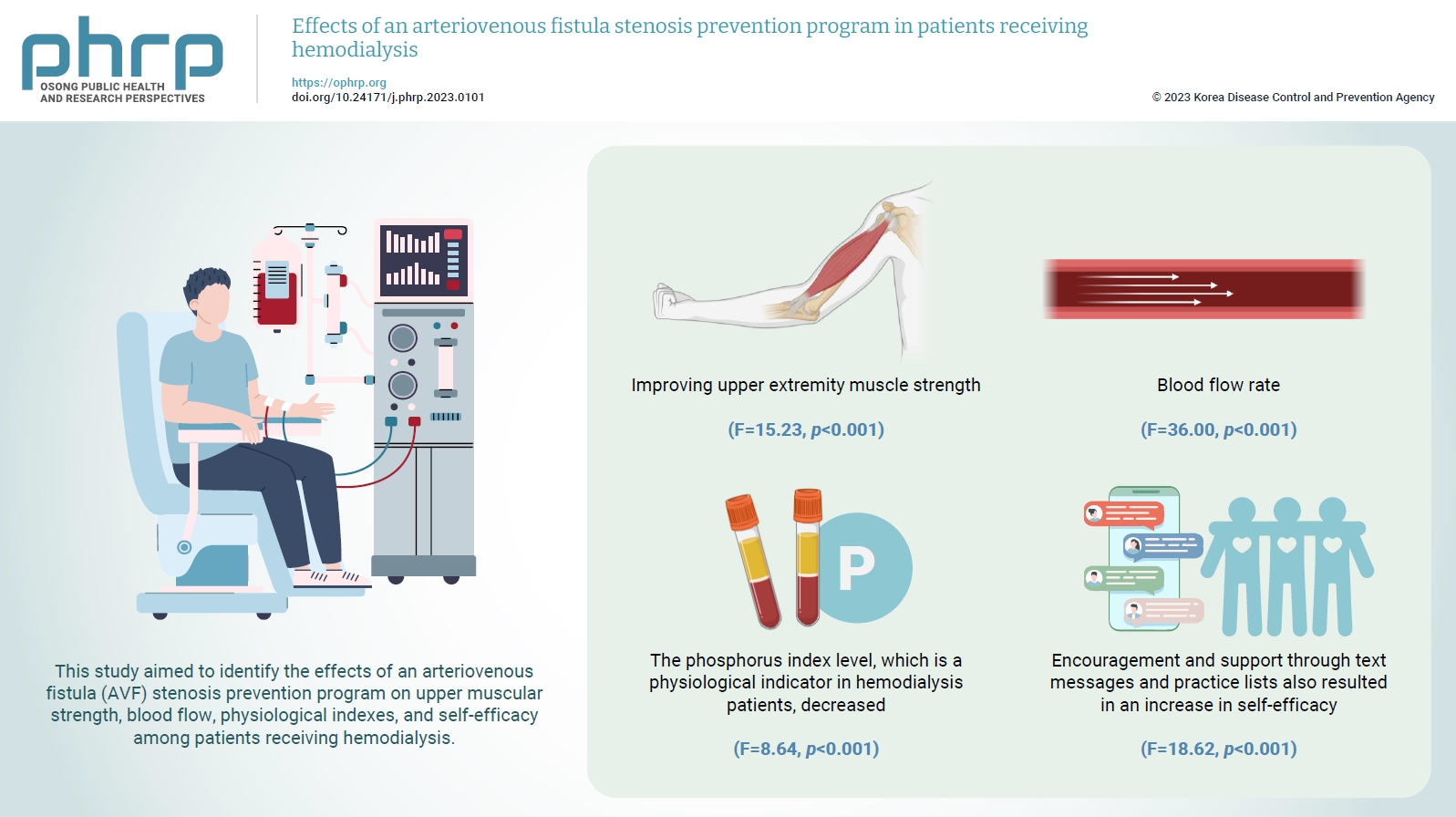
- Objectives
To increase the efficiency of hemodialysis, an appropriate vascular pathway must be created, and its function must be maintained. This study aimed to identify the effects of an arteriovenous fistula (AVF) stenosis prevention program on upper muscular strength, blood flow, physiological indexes, and self-efficacy among patients receiving hemodialysis.
Methods
The participants were patients receiving hemodialysis at Keimyung University Dongsan Medical Center in Daegu, Republic of Korea. They were divided into experimental and control groups based on the day of the week they received hemodialysis at the outpatient department and included 25 participants each. The study was conducted for 8 weeks.
Results
The AVF stenosis prevention program was effective in improving upper extremity muscle strength (F=15.23, p<0.001) and blood flow rate (F=36.00, p<0.001). As a result of the program, the phosphorus index level, which is a physiological indicator in hemodialysis patients, decreased (F=8.64, p<0.001). Encouragement and support through text messages and practice lists also resulted in an increase in self-efficacy (F=18.62, p<0.001).
Conclusion
The AVF stenosis prevention program in this study resulted in an increase in upper extremity muscle strength through grip strength exercises and was effective in preventing AVF stenosis by increasing the blood flow rate.
- The COVID-19 pandemic and healthcare utilization in Iran: evidence from an interrupted time series analysis
- Monireh Mahmoodpour-Azari, Satar Rezaei, Nasim Badiee, Mohammad Hajizadeh, Ali Mohammadi, Ali Kazemi-Karyani, Shahin Soltani, Mehdi Khezeli
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(3):180-187. Published online June 22, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0041
- 1,427 View
- 67 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 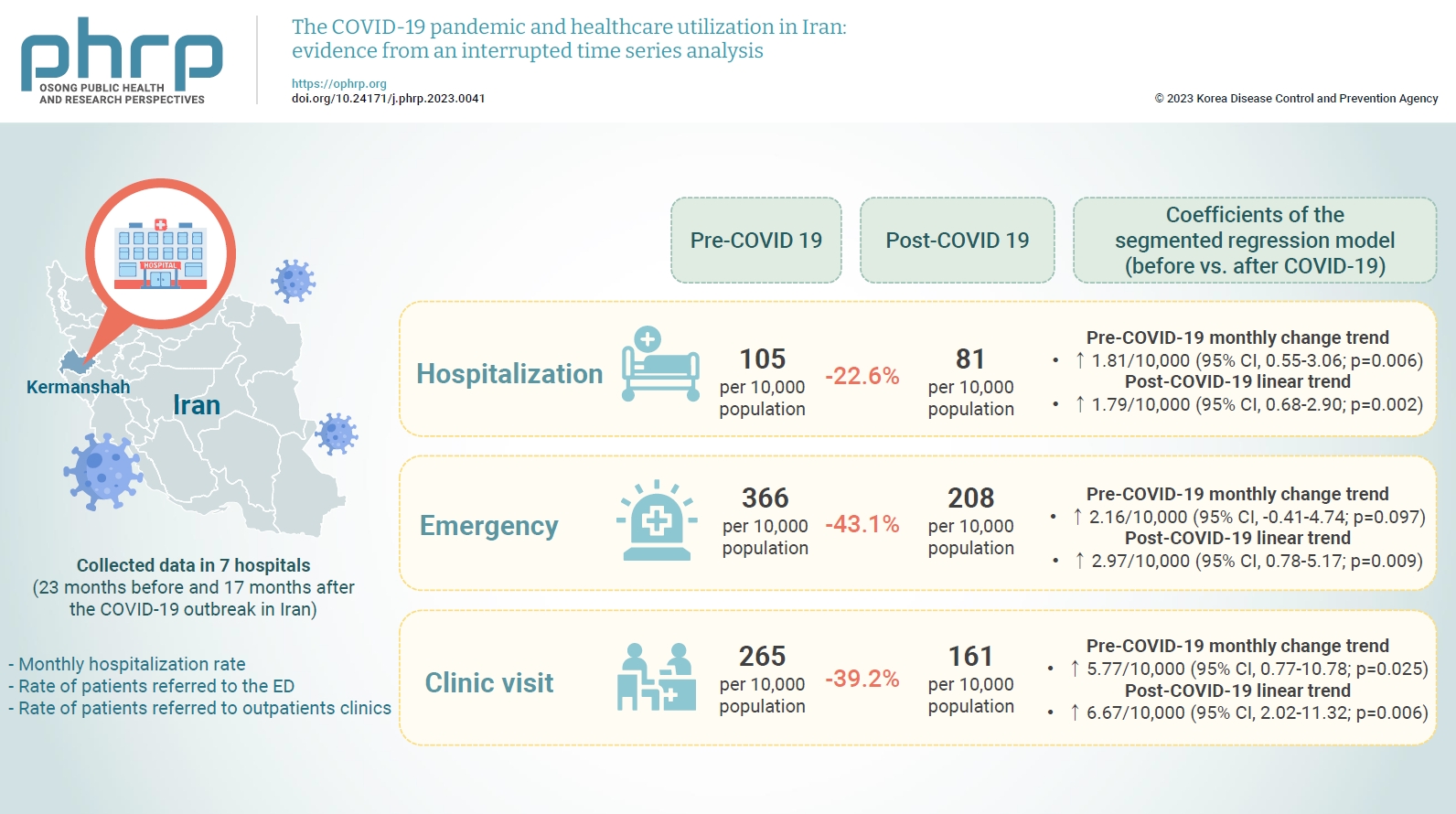
- Objectives
This study aimed to examine the effect of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak on the hospitalization rate, emergency department (ED) visits, and outpatient clinic visits in western Iran.
Methods
We collected data on the monthly hospitalization rate, rate of patients referred to the ED, and rate of patients referred to outpatient clinics for a period of 40 months (23 months before and 17 months after the COVID-19 outbreak in Iran) from all 7 public hospitals in the city of Kermanshah. An interrupted time series analysis was conducted to examine the impact of COVID-19 on the outcome variables in this study.
Results
A statistically significant decrease of 38.11 hospitalizations per 10,000 population (95% confidence interval [CI], 24.93–51.29) was observed in the first month of the COVID-19 outbreak. The corresponding reductions in ED visits and outpatient visits per 10,000 population were 191.65 (95% CI, 166.63–216.66) and 168.57 (95% CI, 126.41–210.73), respectively. After the initial reduction, significant monthly increases in the hospitalization rate (an increase of 1.81 per 10,000 population), ED visits (an increase of 2.16 per 10,000 population), and outpatient clinic visits (an increase of 5.77 per 10,000 population) were observed during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Conclusion
Our study showed that the utilization of outpatient and inpatient services in hospitals and clinics significantly declined after the COVID-19 outbreak, and use of these services did not return to pre-outbreak levels as of June 2021.


 First
First Prev
Prev


