Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Short Communication
- Perceptions of older adults and generativity among older citizens in Japan: a descriptive cross-sectional study
- Yuho Shimizu, Tomoya Takahashi, Kenichiro Sato, Susumu Ogawa, Daisuke Cho, Yoshifumi Takahashi, Daichi Yamashiro, Yan Li, Keigo Hinakura, Ai Iizuka, Tomoki Furuya, Hiroyuki Suzuki
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(5):427-432. Published online October 10, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0063
- 1,311 View
- 56 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 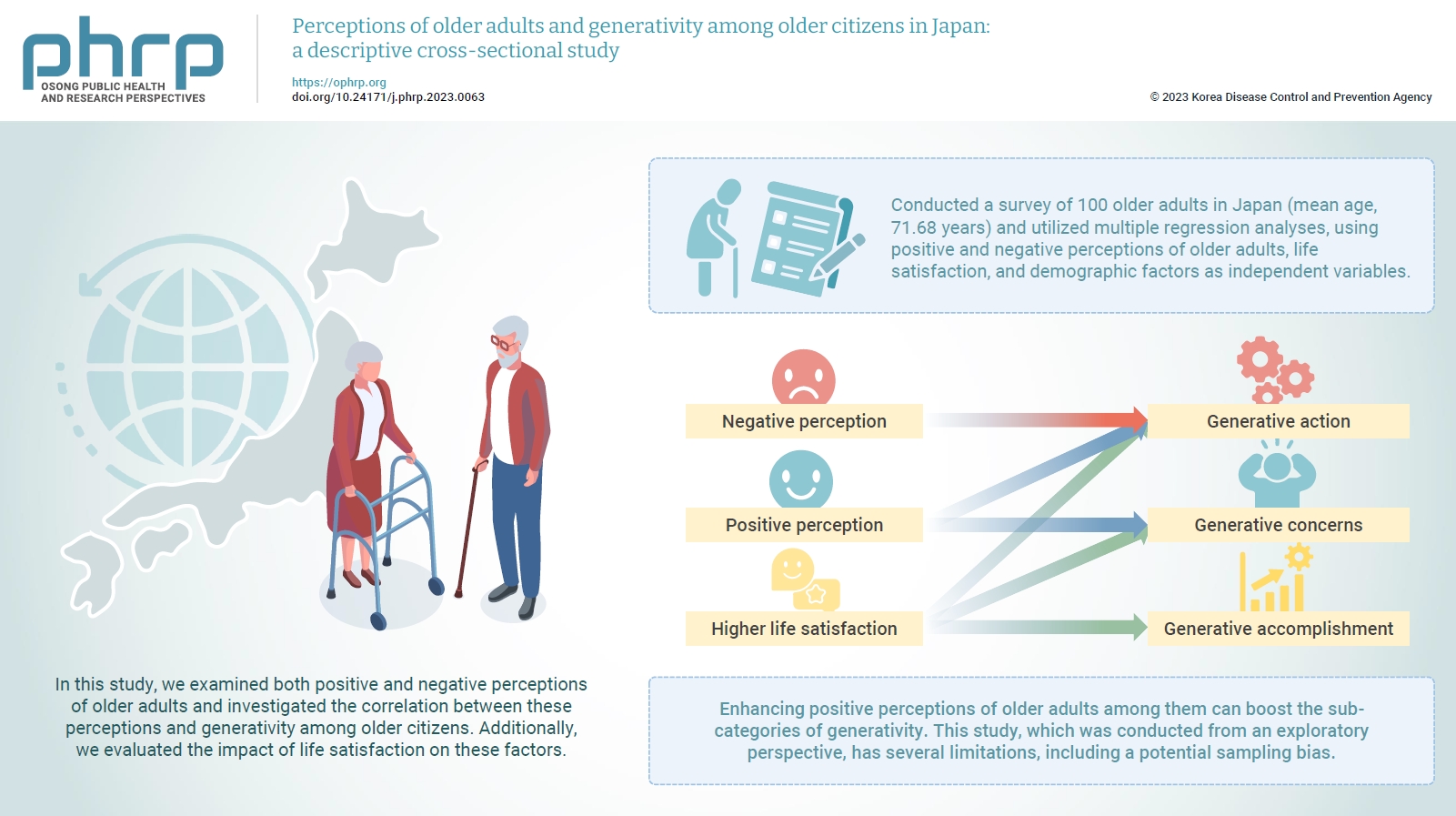
- Objectives
As the population ages worldwide, including in Japan, there is a growing expectation for older adults to remain active participants in society. The act of sharing one’s experiences and knowledge with younger generations through social engagement not only enriches the lives of older individuals, but also holds significant value for our society. In this study, we examined both positive and negative perceptions of older adults and investigated the correlation between these perceptions and generativity among older citizens. Additionally, we evaluated the impact of life satisfaction on these factors. Methods: We conducted a survey of 100 older adults in Japan (mean age, 71.68 years) and utilized multiple regression analyses, using positive and negative perceptions of older adults, life satisfaction, and demographic factors as independent variables. The sub-categories of generativity—namely, generative action, concern, and accomplishment—were used as dependent variables. Results: Participants who held a more positive perception of older adults demonstrated a higher level of generative actions and concerns. Additionally, participants who reported higher levels of life satisfaction also exhibited more generative actions, concerns, and accomplishments. Conversely, those who held a more negative perception of older adults were found to have higher levels of generative actions. Conclusion: Enhancing positive perceptions of older adults among them can boost the sub-categories of generativity. This study, which was conducted from an exploratory perspective, has several limitations, including a potential sampling bias. A more comprehensive examination of the relationship between perceptions of older adults and generativity is anticipated in future research.
Original Article
- A Study of High-Risk Drinking Patterns Among Generations Based on the 2009 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Yeongseon Hong, Sungsoo Chun, Mieun Yun, Lydia Sarponmaa Asante, Chaeshin Chu
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2014;5(1):46-53. Published online February 28, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2014.01.006
- 2,702 View
- 16 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The aim of this study was to identify how the drinking patterns of a generation on the paternal side affect those of the next generations by estimating the number of high-risk drinkers by generation according to the Alcohol Use Disorder Identification Test.
Methods
Data were selected from the 2009 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey conducted by the Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and were analyzed using SPSS 18.0.
Results
Later generations started drinking earlier (62.4%, 71.8% and 91.1%, respectively). The majority of the second generation consumed more than 2–4 drinks a month (83.7%), but only a small proportion experienced difficulty in everyday life (9.6%), felt repentance (9.6%), or experienced memory loss (17.9%) after drinking. Unmarried third-generation adults with high-risk-drinking fathers reported more frequent alcohol consumption [odds ratio (OR) 1.441), greater amounts on one occasion (>7 cups for men, OR 1.661; > 5 cups for women, OR 2.078), temperance failure (OR 2.377), and repentance after drinking (OR 1.577). Unmarried third-generation adults with high-risk-drinking grandfathers consumed greater amounts of alcohol on one occasion (OR 3.642), and unmarried third-generation women more frequently consumed large amounts of alcohol (>5 cups, OR 4.091). Unmarried third-generation adults with high-risk-drinking fathers were more likely to exhibit high-risk drinking patterns (OR 1.608). Second-generation individuals from a high-risk-drinking first generation were more likely to engage in high-risk drinking (OR 3.705).
Conclusion
High-risk drinking by a generation significantly affects the high-risk drinking patterns of subsequent generations. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Age at onset of alcohol consumption and its association with alcohol misuse in adulthood
Soo Y. Kim, Sung H. Jeong, Eun‐Cheol Park
Neuropsychopharmacology Reports.2023; 43(1): 40. CrossRef - Alcohol consumption frequency or alcohol intake per drinking session: Which has a larger impact on the metabolic syndrome and its components?
Sarah Soyeon Oh, Woorim Kim, Kyu-Tae Han, Eun-Cheol Park, Sung-In Jang
Alcohol.2018; 71: 15. CrossRef
- Age at onset of alcohol consumption and its association with alcohol misuse in adulthood



 First
First Prev
Prev


