Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- Epidemiological analysis and prevention strategies in response to a shigellosis cluster outbreak: a retrospective case series in an alternative school in the Republic of Korea, 2023
- Yeongseo Ahn, Sunmi Jin, Gemma Park, Hye Young Lee, Hyungyong Lee, Eunkyung Shin, Junyoung Kim, Jaeil Yoo, Yuna Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2024;15(1):68-76. Published online February 7, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0298
- 1,087 View
- 56 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 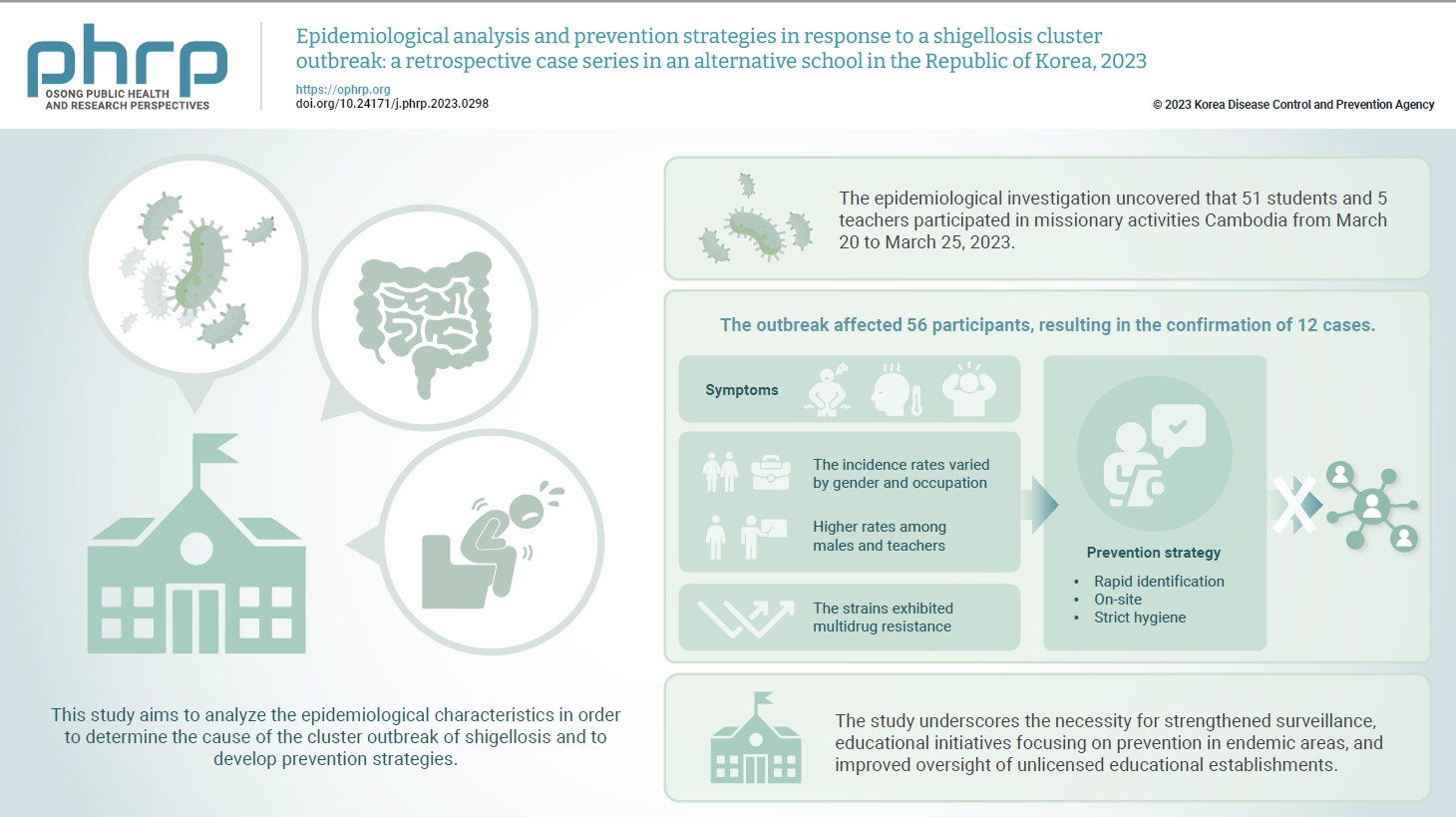
- Objectives
In March 2023, an alternative school in the Republic of Korea reported 12 cases of shigellosis. This study aims to analyze the epidemiological characteristics in order to determine the cause of the cluster outbreak of shigellosis and to develop prevention strategies. Methods: This study focused on 12 patients with confirmed Shigella infection and investigated their demographics, clinical features, epidemiology, diagnostics, and antimicrobial susceptibility. Following the identification of Shigella, we conducted follow-up rectal smear cultures to manage patients, implementing isolation and control measures. Results: This study investigated the emergence of multidrug-resistant Shigella following missionary activities in Cambodia, documenting a cluster infection within an alternative school in Daejeon, the Republic of Korea. The outbreak affected 56 participants, resulting in the confirmation of 12 cases. The incidence rates varied by gender and occupation, with higher rates among males and teachers. All 12 cases demonstrated multidrug resistance. Challenges included delayed pathogen confirmation and suboptimal adherence to isolation criteria. The incident prompted revisions in the criteria for isolation release, focusing on symptom resolution. The study underscores the necessity for strengthened surveillance, educational initiatives focusing on prevention in endemic areas, and improved oversight of unlicensed educational establishments. Conclusion: Successful response strategies included swift situation assessment, collaborative efforts, effective infection control measures, and modified criteria for isolation release. Continued surveillance of multidrug-resistant strains is recommended, especially in regions with a high prevalence.
Review Article
- Strategies to combat Gram-negative bacterial resistance to conventional antibacterial drugs: a review
- Priyanka Bhowmik, Barkha Modi, Parijat Roy, Antarika Chowdhury
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(5):333-346. Published online October 18, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0323
- 2,286 View
- 179 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 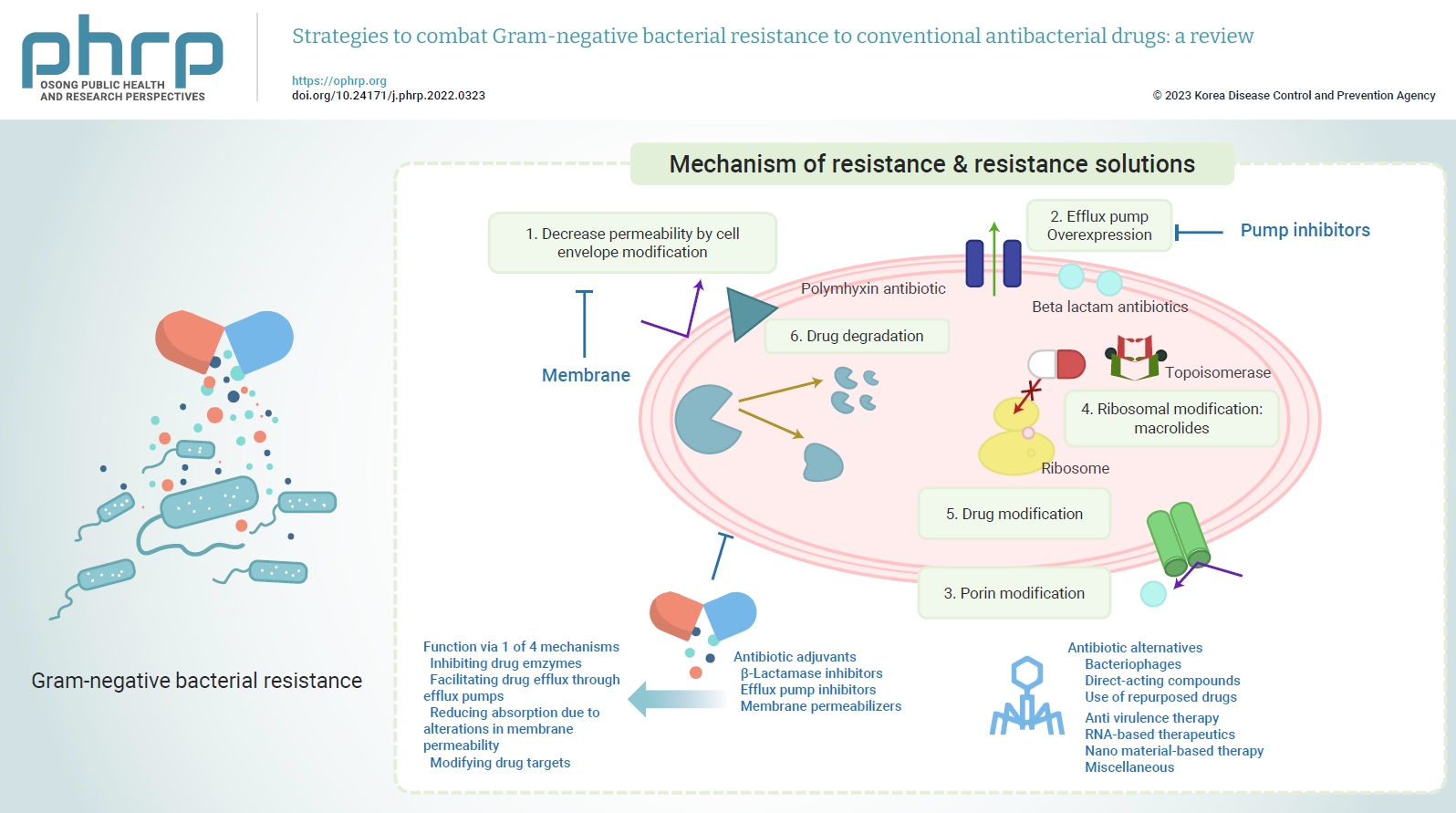
- The emergence of antimicrobial resistance raises the fear of untreatable diseases. Antimicrobial resistance is a multifaceted and dynamic phenomenon that is the cumulative result of different factors. While Gram-positive pathogens, such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Clostridium difficile, were previously the most concerning issues in the field of public health, Gram-negative pathogens are now of prime importance. The World Health Organization’s priority list of pathogens mostly includes multidrug-resistant Gram-negative organisms particularly carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales, carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and extensively drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. The spread of Gram-negative bacterial resistance is a global issue, involving a variety of mechanisms. Several strategies have been proposed to control resistant Gram-negative bacteria, such as the development of antimicrobial auxiliary agents and research into chemical compounds with new modes of action. Another emerging trend is the development of naturally derived antibacterial compounds that aim for targets novel areas, including engineered bacteriophages, probiotics, metal-based antibacterial agents, odilorhabdins, quorum sensing inhibitors, and microbiome-modifying agents. This review focuses on the current status of alternative treatment regimens against multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria, aiming to provide a snapshot of the situation and some information on the broader context.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficacy of new generation biosorbents for the sustainable treatment of antibiotic residues and antibiotic resistance genes from polluted waste effluent
Barkha Madhogaria, Sangeeta Banerjee, Atreyee Kundu, Prasanta Dhak
Infectious Medicine.2024; 3(1): 100092. CrossRef - Evaluation of Plant-Based Silver Nanoparticles for Antioxidant Activity and Promising Wound-Healing Applications
Maria Qubtia, Shazia Akram Ghumman, Sobia Noreen, Huma Hameed, Shazia Noureen, Rizwana Kausar, Ali Irfan, Pervaiz Akhtar Shah, Hafsa Afzal, Misbah Hameed, Mohammad Raish, Maria Rana, Ajaz Ahmad, Katarzyna Kotwica-Mojzych, Yousef A. Bin Jardan
ACS Omega.2024; 9(10): 12146. CrossRef
- Efficacy of new generation biosorbents for the sustainable treatment of antibiotic residues and antibiotic resistance genes from polluted waste effluent



 First
First Prev
Prev


