Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Osong Public Health Res Perspect > Volume 8(4); 2017 > Article
-
Original Article
Analyzing the Historical Development and Transition of the Korean Health Care System - Sang-Yi Leea, Chul-Woung Kimb, Nam-Kyu Seoc, Seung Eun Leed
-
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives 2017;8(4):247-254.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2017.8.4.03
Published online: August 31, 2017
aDepartment of Health Policy and Management, Jeju National University, School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea
bDepartment of Preventive Medicine and Research Institute for Medical Sciences, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea
cNational Health Insurance Service/Health Insurance Policy Research Institute, Wonju, Korea
dGraduate School of Public Health, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea
- Corresponding author: Chul-Woung Kim, E-mail: woung@cnu.ac.kr
• Received: April 26, 2017 • Revised: June 20, 2017 • Accepted: July 7, 2017
Copyright ©2017, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
Abstract
-
Objectives
- Many economically advanced countries have attempted to minimize public expenditures and pursue privatization based on the principles of neo-liberalism. However, Korea has moved contrary to this global trend. This study examines why and how the Korean health care system was formed, developed, and transformed into an integrated, single-insurer, National Health Insurance (NHI) system.
-
Methods
- We describe the transition in the Korean health care system using an analytical framework that incorporates such critical variables as government economic development strategies and the relationships among social forces, state autonomy, and state power. This study focuses on how the relationships among social forces can change as a nation’s economic development or governing strategy changes in response to changes in international circumstances such as globalization.
-
Results
- The corporatist Social Health Insurance (SHI) system (multiple insurers) introduced in 1977 was transformed into the single-insurer NHI in July 2000. These changes were influenced externally by globalization and internally by political democratization, keeping Korea’s private-dominant health care provision system unchanged over several decades.
-
Conclusion
- Major changes such as integration reform occurred, when high levels of state autonomy were ensured. The state’s power (its policy capability), based on health care infrastructures, acts to limit the direction of any change in the health care system because it is very difficult to build the infrastructure for a health care system in a short timeframe.
- Keywords: healthcare reform; national health programs; Korea; insurance; health
- Many countries facing drastically increasing health care expenditures have worked to make their health care systems more sustainable. Many European countries have attempted to minimize public expenditures and introduce privatization based on the principles of neo-liberalism. These countries have reformed, or are attempting to reform, their health care systems in order to minimize the financial burden on the public, while promoting market competition. In general, changes in health care systems have converged on neo-liberalism.
- The Korean experience has gone against this global trend, however. Korea integrated hundreds of health insurers into a single insurer system and has continued to increase public health care expenditure and benefit coverage in a manner counter to neo-liberalism, which demands a curtailment of public expenditures and a strengthening of competition [1]. However, the share of public beds in 2007 was about 9.5% of the total number of beds in Korea, indicating an extremely weak public health care provision system relative to that of many other nations. These are the main characteristics of Korea’s health care system, arising from historical development processes [2].
- Two major institutional changes took place in the Korean health care system. One was the introduction of compulsory health insurance in 1977, and the other was its transition to universal National Health Insurance (NHI) in 2000. Those major reforms make Korea a good case study of health policy change, given the generalized claims about path dependence within the health sector.
- It is important to examine in detail why and how Korea chose to develop its own health care system in this way. However, only a few studies have attempted to explain the development process of the Korean health care system from social and political perspectives. It is thus necessary to analyze the historical development processes and changes in the Korean health care system. Many developing countries in Asia are either considering, or have recently implemented, public health insurance schemes and want to learn more about Korea’s successful experience. The institutional development process of the Korean health care system should provide a useful example for these developing countries.
INTRODUCTION
- 1. Theoretical discussion
- According to Lee et al. [3], the new typology classifies the world’s national health care systems into national health services (NHS), social health insurance (SHI), NHI, and the liberal model. Table 1 shows the characteristics of each health care system classified by typology.
- According to this typology, Korea has an NHI-type of health care system, distinct from both the German SHI and the British NHS in many ways. This study seeks to determine why the Korean health care system differs from the German SHI and British NHS. This requires an analysis of the historical development process of the Korean health care system using the appropriate theoretical tools and analytical framework.
- Many specialists in welfare politics have tended to explain the formation and development of health care systems from macroscopic standpoints such as the dynamics of political and social forces or changes in political structure [4–10]. Using this perspective, researchers have clearly explained transitions in health care systems. Wong [9] suggested that the transition from SHI to NHI and the universalization of health care in Korea and Taiwan were the results of democratic reforms. However, Wong’s views on the cause of the transition hardly explain why the two countries’ systems transformed into the new type of NHI rather than from corporatist SHI into NHS.
- Meanwhile, health care policy researchers have tended to view health care systems as independent and have focused on their internal mechanisms. The NHS systems established in England and Sweden lasted for 40 to 50 years without major change. This suggests that health care systems undergo little change unless a major event such as a revolution occurs, due to their path-dependent characteristics, particularly their durability and stability [11]. The concept of path dependence, in which preceding steps in a particular direction induce further movement in the same direction, is well-captured by the idea of increasing returns [12]. Using the concept of an increasing return process in path dependence theory allows us to explain much of the historical development of each country’s national health care system. However, this path dependence concept cannot adequately explain major changes in health care financing during the historical development of Korea’s health care system. We thus need an analytical framework that accounts for all of the possible outcomes, including the alteration and persistence of the main institutions and policies.
- Rico and Costa-Font [13] argue that path dependence is not the automatic effect of impersonal institutional inertia but the result of an active, successful struggle by stakeholders to maintain their rights in the face of mounting pressure from stake challengers for changes of institution and policies. Therefore, we need to consider the concepts of power and politics as causes of path dependence in institutional development [13,14].
- Understanding the transition to Korea’s integrated NHI system requires us to consider state intervention in welfare politics. We define the state as the “administrative institutions and the whole institutionalized law systems” as distinct from society, and as “a coercive control and political authority over individuals” occupying a particular territory [7,15]. We employ the concept of state autonomy to describe the relationship between a state and a civil society. In general, state autonomy refers to the state’s capacity to formulate and administer a policy independently in relationship to civil society. State power is formed historically and institutionally over a long period of time and is an institutional capability required to achieve policy goals. Unlike state autonomy, state power is not significantly related to the power relationship between a state and a civil society. Mann [16] categorized state power into despotic power and infrastructural power. In terms of Mann’s state power concept, despotic power is mainly involved in the welfare politics of the health care system because it concerns the relationship between state elites and civil society. On the other hand, infrastructural power is related to health care policy regarding the distribution of health care resources.
- A health care system can be divided into the “provision system” and the “financing system.” A provision system concerns the production and delivery of medical services and is a socially constructed infrastructure. It is difficult to change a provision system if the infrastructural power has not been extensively formed. For the NHS system of United Kingdom, it was comparatively easy to return to an integrated form after the introduction of a quasi-market health care system because the state held extensive public health care resources as the infrastructural power. In countries where privately owned hospitals dominate, however, it is not easy to expand public health care facilities, even with strong political will. Changing a health care financing system also requires a significant amount of social infrastructure, but much less than is necessary to change the provision system.
- A change in relationships among social forces, together with a change in state autonomy, will influence a health care system. This study focuses on how the relationships among social forces can change as a nation’s economic development strategy or governing strategy changes in response to changes in international circumstances such as globalization. We also examine how altered relationships among social forces can influence state intervention in a health care system.
- 2. Analytical framework
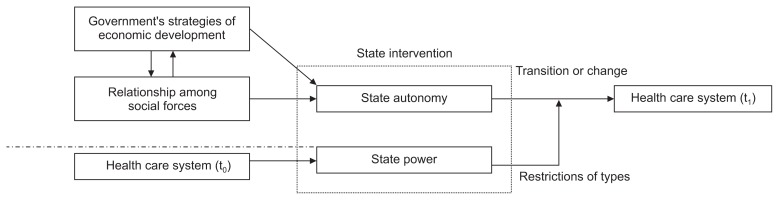
- Figure 1 illustrates the analytical framework used to describe transition and change in Korea’s health care system. The critical variables are the government’s strategies of economic development and change in the relationships among social forces. These two factors influence the transition or change in the health care system by affecting state autonomy. State power steers change in the health care system. It is possible to generate major changes, such as the introduction and transition of a health care system, when government power is despotic. However, even when large forces lead change in the health care system and despotic power is in control, it is not necessarily easy to increase infrastructural power over a short period of time. If a country has extremely weak infrastructural power, transitioning to a progressive type of health care system will be impossible. Historically, such infrastructural power has been formed through the infrastructure of preexisting health care systems.
- Changes in the Korean health care system can be divided into three periods, as presented in Table 2. We analyze how changes were possible in each phase using the analytical frame presented in Figure 1.
- As seen in Table 2, the periods in this study were classified based on changes in the NHI system, the Korean healthcare financing system, as no significant changes have occurred in the supply system, another axis of the Korean healthcare system, and the NHI system has significantly influenced medical supplies, medical fees, and the quality of medical care to such a degree that it has been recognized as Korea’s de facto health care system. In other words, changes in the NHI system account for the most significant portion of changes in the Korean health care system.
- In 1977, Korea introduced the corporatist SHI system. By 1989, this system had been extended to the entire population. Finally, in 1998, the Korean government completed the first integration reform, which transformed the corporatist SHI into the NHI system. Each phase involved different relationships among social forces, economic development strategies, state autonomy, and state powers. We now examine these social changes and discuss their effects on the Korean health care system.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
- 1. Phase 1: Introduction of the corporatist SHI
- In the early 1970s, an authoritarian military government seized power in Korea. This developmental government adopted a strategy of rapid and aggregate economic growth initiated by state elites and focusing on the development of the heavy chemical industry [17,18]. In 1972, the imposition of the highly repressive Yushin Constitution diminished the legitimacy of the Park regime (1961–1979), and a social movement composed of intellectuals and workers challenged the authoritarian developmental state. However, the working class and other social forces were not well organized.
- In 1977, the Park regime implemented a corporatist SHI system for companies with more than 500 employees. Each insurance society operated on the principle of self-supporting accounting systems. To finance each insurance society, employers and employees made equal contributions, and the government bore only administrative costs. The authoritarian Park regime decided to introduce public health insurance, for several reasons. First, the Park regime wanted to gain political legitimacy in the aftermath of the military coup, especially following the Yushin Constitution. Second, the state elites wanted to promote the development of the heavy chemical industry by implementing a decentralized SHI system that was limited to workers in large companies. The authoritarian state overpowered all social forces, including capitalists, laborers, farmers, and doctors. In the 1970s, the Park regime exercised a high degree of state autonomy and supreme state power [19].
- Nevertheless, by 1977, the regime finally implemented severely limited SHI, which covered only 8.6% of the population. Consequently, the reform was not progressive and benefited only those who had relatively little need of social protection, such as workers in economically productive sectors, including conglomerates. This occurred because welfare policy initiatives in Korea were part of the economic growth and industrial development imperatives of the developmental state [20].
- Health care facilities relied heavily on private provision. The Park regime had no intention of using public financing to expand public health care facilities at the expense of investment in economic growth. As a result, the percentage of public hospital beds decreased from 43.3% of total beds in 1970 to 31.5% in 1980. The state thus had only a weak infrastructural power with which to implement health care policies. The historically formed infrastructural power provided institutional legacies that have influenced the forms of state intervention in Korea [21].
- 2. Phase 2: Universalization in the corporatist SHI
- By the late 1970s, Korean economic growth had begun to slow. In 1980, the Chun Doo-Hwan government (1981–1988) pursued different economic development strategies, abandoning Park’s strategy of state-led development of the heavy chemical industry and promoting instead an open economy and economic liberalization. Under Chun’s authoritarian government, large corporations that had grown dramatically under active state support in the 1970s enjoyed more autonomy from the government [22].
- Meanwhile, as industrialization had been increasing the size of the working class since the 1960s, the number of employees joining unions had also steadily increased. The Korean government strongly suppressed the labor movement in the early 1980s, but the working class continually resisted and grew stronger through political struggle [23]. In addition to the labor movement, civic groups, including intellectuals, students, and democratic leaders, mobilized their power resources and led public calls for a constitutional amendment allowing for direct presidential elections; they also favored the dissolution of the military government, which became their slogan in the spring of 1987 [24]. In an unexpected move, Roh Tae-Woo (1988–1993), Chun’s hand-picked successor to lead the ruling Democratic Justice Party, capitulated to several of the opposition’s demands in June of that year. In December 1987, direct presidential elections were held. In 1987, a highly mobilized social movement forced a democratic breakthrough in Korea [25].
- In these political circumstances, Roh decided to expand the number of health insurers to include self-employed workers in rural and urban areas. In January 1988, 138 rural self-employed insurers were created, covering about 6.7 million previously uninsured farmers and fishermen. In 1989, the Roh government created an additional 117 urban self-employed insurers, covering approximately 12.6 million urban residents. These expansions provided health insurance coverage to all Koreans, meaning that universal health coverage had been accomplished in Korea within only 12 years, from 1977 to 1989. The growth of the working class, civil society, and social inequality were only some of the factors that induced the incumbent regime to move to universal coverage in Korea. The main reason for implementing universal coverage was that it formed part of Roh’s political strategy for winning two elections [25].
- Universal coverage in corporatist SHI was attained due not only to the weakened state’s despotic power compared to that of the previous authoritarian regime but also the strengthened social forces. Nevertheless, the state led policy decision-making because of its relatively strong autonomy and power. However, the incumbent regime did not expand public health care facilities. As a result, the share of public beds decreased drastically from 31.5% of the total number of beds in 1980 to 19.7% in 1990. The weak infrastructural power of the state affected the maintenance of the corporatist SHI (multiple insurer), even under the universal coverage system, because the government opposed the NHI (single insurer) type of system, fearing that it would create an excessive financial and political burden [26].
- 3. Phase 3: Transition to the NHI
- The Korean SHI system maintained a large number of decentralized health insurers, numbering 420 by the early 1990s. The high level of out-of-pocket payments made the scheme inherently regressive, which was worsened by the narrow benefit coverage. The structural decentralization undermined the principle of social solidarity and exacerbated the financial disparities between insurers [3].
- Meanwhile, major changes in labor and social movements followed the Korean democracy movement of 1987. As a result, the working class, farmers, and fishermen centered their activism on social movements [27]. Amid this change among social forces, a national-scale social movement attempted to transform the corporatist SHI into an NHI system. In June 1988, the integration reform movement formed a grassroots National Committee for Health Insurance Integration, comprising 48 social movement groups.
- In the 1990s, neoliberal globalization arrived, along with decreased government finance and reduced welfare. The government policy that most clearly reflected this globalization was the financial liberation policy of 1992. This policy enabled Korea’s capitalist forces to become more autonomous from government. Korean economic policy as a whole was also influenced by globalization [28]. Later, in 1997, the effects of globalization struck the Korean economy during the foreign exchange crisis. At this time, the transition to NHI was a major item on the social reform movement’s agenda [29]. One factor in the push for NHI involved changes in the social movement after democratization. The policy process for the transition to NHI between the 1980s and 1990s was distinctive in that social forces, including labor and farmer organizations as well as health care nongovernmental organizations, mobilized their power and demanded health care reform, which the government strongly opposed.
- In 1997, before the presidential election, the ruling and opposition parties passed the National Medical Insurance Act, which integrated all self-employed insurers and society for public officials and private school employees. An act for full integration into a single insurer was passed in 1998, when Kim Dae-Jung (1998–2003) took office. On July 1, 2000, a fully integrated NHI was established in Korea [25].
- To understand the welfare policies of Kim’s government, it is essential to identify two of its major characteristics. First, it was established with the support of progressive social forces that had long espoused social solidarity. Second, Kim had to follow the International Monetary Fund’s reform program resulting from the financial crisis. Kim’s government estimated that the transition to NHI would improve social solidarity, and also enhance the efficiency of administration. In other words, promoting the reform of the health care system both satisfied the aspirations of progressive social forces and improved efficiency by reducing the size of the public sector [19].
- State power was centralized to cope with the external shock of the International Monetary Fund crisis, as a result of which despotic power temporarily increased. This increase overcame policy inertia, such as objections from government officials and capitalist forces, and enabled the transition to NHI, ending 20 years of social debate over health care system reform. The predominantly private health care provision system made it impossible to transform the Korean health care system into an NHS type. In other words, the weakness of infrastructural power in the health care provision system was the major reason the NHS model was not considered.
RESULTS
- The dynamics of state intervention in the health care system have changed according to the relationships between social forces and national economic development strategies, and this has led to various changes in the Korean health care system. In addition, the institutional legacies and characteristics of the historical formation of the Korean health care system have changed along with democratization, as well as with economic growth and crises.
- In the health care financing system, major changes such as the integration reform occurred when high levels of state autonomy were ensured. The state’s policy capability, based on the health care infrastructure, acts to limit the direction of any change in the health care system because it is very difficult to build health care infrastructure within a short time frame.
- In addition, Korea has been influenced by globalization since the late 1980s and also experienced the economic crisis of the late 1990s. During that period, the Korean health care system underwent great changes. Globalization has influenced the changes in social forces and national development strategies, and these changes have subsequently affected state intervention in the health care system.
- The transition to NHI (single insurer) ultimately proved that the German and Japanese type of corporatist SHI (multiple insurer), which had been considered advanced, did not fit Korea’s political, economic, and cultural contexts. The Korean health care system has changed, influenced externally by globalization and internally by democratization. However, Korea introduced neither the liberal type of system such as that in the US nor Britain’s NHS, nor did it maintain Germany’s corporatist SHI (multiple insurer) system. Rather, Korea created an independent model.
- It is not easy to change a health care provision system in a short period of time because policy legacies are path-dependent. In an increasing return process of path dependence, the probability of further steps along the same path increases with each move down that path because the benefits of current activity relative to those of other options increase over time [12]. Owing to this characteristic of path dependence, institutional stability has kept Korea’s private-dominant health care provision system unchanged over several decades. New institutions often entail high startup costs. Therefore, established institutions generate powerful inducements that reinforce their own stability and further development [12]. It is virtually impossible to increase the public share of health care provision dramatically by nationalizing private health care facilities, including private hospitals, because the costs of exit and startup required to escape from path dependence or initiate new institutions are very high.
- No country has established NHI without fierce and bitter political struggle. These conflicts over crucial national health policy, though similar, have not led to the same outcome in all nations [30]. The emergence of NHI conforms to a developmental logic that is as much historical as it is political and institutional [31,32]. We thus need to examine how the historical developments of health care systems compare between advanced nations and Korea. By the early 1970s, the nations of Western Europe had established universal health systems during the development of the Keynesian welfare state. Faced with the global attack of neoliberalism, the West recalibrated their welfare states, but their universal health care systems have remained fundamentally intact. This can be explained by acknowledging the path-dependent characteristics of universal health coverage.
- Only 17 years have passed since 2000, the year of NHI (single insurer) implementation in Korea. Growing private health insurance companies, armed by neoliberalism, are continuously attacking the expansion of benefit coverage in the Korean NHI (single insurer), especially in the current political context of a conservative president and National Assembly. Over the last three decades, Korea has experienced rapid economic growth as well as political and social upheaval. Korea’s health care system has also experienced dramatic upheaval. Korea’s NHI (single insurer) needs enough time to gain the stability and institutional path dependency that have endured in the health care systems of Western nations.
DISCUSSION
-
Acknowledgements
- This work was supported by a research fund from Chungnam National University.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
-
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Article information
- 1. Wong J. Healthy democracies: welfare politics in Taiwan and South Korea. Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press; 2004.
- 2. Lee S. Logic and strategies of dynamic welfare states. Seoul: Mim; 2010. In Korean.
- 3. Lee SY, Chun CB, Lee YG, Seo NK. The national health insurance system as one type of new typology: the case of South Korea and Taiwan. Health Policy 2008;85:105−13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.healthpol.2007.07.006. PMID: 10.1016/j.healthpol.2007.07.006. PMID: 17709152.ArticlePubMed
- 4. Navarro V. Why some countries have national health insurance, others have national health services, and the U.S. has neither. Soc Sci Med 1989;28:887−98. https://doi.org/10.1016/0277-9536(89)90313-4. PMID: 10.1016/0277-9536(89)90313-4. PMID: 2652327.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Navarro V. The politics of health policy: the US reforms, 1980–1994. Cambridge, MA: Blackwell; 1994.
- 6. Esping-Anderson G. The three worlds of welfare capitalism. Cambridge, MA: Polity; 1990.
- 7. Skocpol T. Bringing the state back in: strategies of analysis in current research. Edited by Evans PB, Rueschemeyer D, Skocpol T: Bringing the state back in. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press; 1985. pp 3−37. PMID: 10.1017/CBO9780511628283.002.Article
- 8. Goodman R, Peng I. The east Asian welfare states: peripatetic learning, adaptive change and nation-building. Edited by Esping-Andersen G: Welfare states in transition: National adaptations in global economics. London: Sage Publications; 1996.Article
- 9. Wong J. Democracy and welfare: health policy in Taiwan and South Korea. PhD dissertation. Madison: University of Wisconsin; 2001.
- 10. Kwon H. Democracy and the politics of social welfare: A comparative analysis of welfare systems in East Asia. Edited by Goodman R, White G, Kwon H: The East Asian welfare model: welfare orientalism and the state. London: Routledge; 1998. pp 27−74.
- 11. Cammack P. The new institutionalism: predatory rule, institutional persistence, and macro-social change. Econ Soc 1992;21:397−429. https://doi.org/10.1080/03085149200000018. PMID: 10.1080/03085149200000018.Article
- 12. Pierson P. Increasing returns, path dependence, and the study of politics. Am Polit Sci Rev 2000;94:251−67. https://doi.org/10.2307/2586011. PMID: 10.2307/2586011.Article
- 13. Rico A, Costa-Font J. Power rather than path dependency? The dynamics of institutional change under health care federalism. J Health Polit Policy Law 2005;30:231−52. PMID: 10.1215/03616878-30-1-2-231. PMID: 15943395.ArticlePubMed
- 14. Scharpf FW. Institutions in comparative policy research. Comp Polit Stud 2000;33:762−90. https://doi.org/10.1177/001041400003300604. PMID: 10.1177/001041400003300604.Article
- 15. Skocpol T. Social policy in the United States: future possibilities in historical perspective. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press; 1995.
- 16. Mann M. The sources of social power. Vol. II. the rise of classes and nation-states 1760–1914. New York: Cambridge University Press; 1993.
- 17. Kim E. An inside story about intervention of investments for development of the heavy chemical industry. Shin-Dong-Ah; 1980. 12;pp 252−63. In Korean.
- 18. Chung M. State autonomy, state capacity, and public policy. Korean Public Adm Rev 1993;27:493−516. In Korean..
- 19. Lee S. 19 reasons why a welfare state is good for me. Seoul: Medichi; 2012. In Korean.
- 20. Chang I. Korea, South. Edited by John D, Kim HS: Social welfare in Asia. London: Croom Helm; 1985. pp 176−213.
- 21. Park C. An institutionalist approach to state capacities and the modes of state intervention: a comparative study of economic and medical welfare policies of the Korean state during 1970s. Korean J Sociol 1998;32:787−813.
- 22. Lee B. The developmental process of Korean capitalism after the Korea war. Edited by Kim J:A study on Korea society. Seoul: Han-Wool; 1999. In Korean.
- 23. Kim S. Study on Korean industrialization state. Seoul: Nanam; 1992. In Korean.
- 24. Sung G. Social origin of political democracy in Korea: Social movement theory approach. The Institute for Far Eastern Studies. New current of Korean politics and society. Seoul: The Institute for Far Eastern Studies, Kyungnam University; 1991. In Korean.
- 25. Lee S. Welfare state is life. Seoul: Mim; 2014. In Korean.
- 26. Lee SY, Kim CB, Park HG, et al. Debate on healthcare privatization and the future of Korean healthcare. Seoul: Mim; 2008. In Korean.
- 27. Cho H. History of social movement in modern Korea. Edited by Kim J: A study on Korea society. Seoul: Han-Wool; 1990. In Korean.
- 28. Nam C. The development process of Korean welfare system and its characteristics. Social Science Research Center. The present condition and the issues of Korean social welfare. Seoul: Human and Welfare; 2000. In Korean.
- 29. Kim SY. Policy networks and policy outputs in the process of Korean health care reform. Korean Pub Adm Quart 2005;17:1063−98.
- 30. Hacker JS. The historical logic of national health insurance: structure and sequence in the development of British, Canadian, and U.S. medical policy. Stud Am Polit Dev 1998;12:57−130. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0898588X98001308.Article
- 31. Hacker JS, Skocpol T. The new politics of U.S. health policy. J Health Polit Policy Law 1997;22:315−38. PMID: 10.1215/03616878-22-2-315. PMID: 9159707.ArticlePubMed
- 32. Jacobs LR. The medicare approach: political choice and American institutions. J Health Polit Policy Law 2007;32:159−86. https://doi.org/10.1215/03616878-2006-035. PMID: 10.1215/03616878-2006-035. PMID: 17463404.ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
Table 1New typology of health care system
Table 2Transition of the health care system and state intervention according to the economic and political characteristics of the Korean state
Figure & Data
References
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Estimation of the benefit from pre‐emptive genotyping based on the nationwide cohort data in South Korea
Ki Young Huh, Sejung Hwang, Joo Young Na, Kyung‐Sang Yu, In‐Jin Jang, Jae‐Yong Chung, Seonghae Yoon
Clinical and Translational Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Lessons from health insurance responses in counteracting COVID-19: a qualitative comparative analysis of South Korea and three influential countries
Hey Jin Ko, Eunji Yun, Boryung Ahn, Hyejin Lee, Won Mo Jang, Jin Yong Lee
Archives of Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of Primary Care and Challenges for Public–Private Cooperation during the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic: An Expert Delphi Study in South Korea
Woo-young Shin, Changsoo Kim, Sei Young Lee, Won Lee, Jung-ha Kim
Yonsei Medical Journal.2021; 62(7): 660. CrossRef - The sociopolitical context of the COVID-19 response in South Korea
Hani Kim
BMJ Global Health.2020; 5(5): e002714. CrossRef - Post-COVID healthcare reform in India: What to expect?
SohamD Bhaduri
Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.2020; 9(11): 5427. CrossRef - The Story of Korean Health Insurance System
Hae-Wol Cho, Chaeshin Chu
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2017; 8(4): 235. CrossRef


 PubReader
PubReader Cite
Cite
