Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Osong Public Health Res Perspect > Volume 6(3); 2015 > Article
-
Original Article
Modification of AxSYM Human Immunodeficiency Virus Assay to Identify Recent Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infections in Korean Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Positive Individuals - Jin-Sook Wanga,b, Mee-Kyung Keea, Byeong-Sun Choia, Sung Soon Kima
-
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives 2015;6(3):184-191.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2015.06.002
Published online: June 9, 2015
aDivision of AIDS, Korea National Institute of Health, Cheongju, Korea
bDivision of Biobank for Health Sciences, Korea National Institute of Health, Cheongju, Korea
- ∗Corresponding author. sungskim63@gmail.comsungskim@korea.kr
- 1These authors contributed equally to the study.
© 2015 Published by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the CC-BY-NC License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0).
Abstract
-
Objectives
- To estimate human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) incidence using HIV avidity assays in Korea, we established a serological testing method to differentiate recent HIV infections from long-standing ones.
-
Methods
- We adopted two incidence assays, the BED HIV-1 incidence test (Calypte Biomedical) and an HIV avidity assay (using Abbott AxSYM HIV Antigen/Antibody Combo), and performed them on Korean HIV samples obtained from 81 HIV seroconverters (n = 193), 135 HIV-positive samples, and three HIV commercial incidence panels (PRB965, PRB933, and PRB601 from SeaCare). To determine the most optimal concentration of the chaotropic agent (Guanidine) and the cutoff value for the avidity assay, we evaluated the sensitivity and specificity of the assay at different concentration levels.
-
Results
- We determined that the concentration of Guanidine to be used in the avidity assay was 1.5M. The cutoff value of the avidity index (AI) was 0.8, and the sensitivity and specificity were 90.2% and 83.8%, respectively, under this condition. The gray zone for the avidity assay was 0.75–0.85 AI. The mean of coefficient of variation was low, at 5.43%.
-
Conclusion
- An optimized avidity assay for the diagnosis of recent HIV infections using Korean samples was established. This assay will be applied to investigate the level of recent infection and will provide basic data to the HIV prevention policy in Korea.
- Recently, the focus of epidemiological studies on human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) has shifted from the surveillance of prevalence to the measurement of incidence [1]. As a barometer to monitor the current level and changes in infection, HIV incidence can provide a scientific rationale for new policy development as well as for immediate and direct evaluation of preventive programs.
- In the case of HIV, antibody levels peak within 6 months after infection because of a rapid immunological response. As a result, it is difficult to distinguish recent infections using standard commercial screening and confirmatory tests [2]. Previous studies and clinical practice often relied on the analysis of the antigen–antibody response after infection for diagnosis, and assessed the progression of infection by measuring changes in antibody levels [3,4]. Furthermore, considerable effort has been made to develop assays that can discriminate between recent and long-term HIV infections from a single sampling [5].
- The avidity assay is a type of modified enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), in which a sample is treated with a chaotropic agent (e.g., Guanidine or urea) that disrupts hydrogen bonds to inhibit antigen–antibody binding.
- The avidity index (AI) is based on the understanding that antibodies show a low avidity in the early phase of infection, however, with time antibody avidity increases progressively [6]. The AI has been used in prior studies of infectious diseases including toxoplasma, rubella, and cytomegalovirus to diagnose recent primary infections [7–9]. It is now being applied to other infectious agents such as hepatitis viruses and herpes viruses [10–12]. Over the past decade, research studies using the AI to diagnose early HIV infections have been published [13,14].
- Even though several incidence assays have been developed or are under development [2,15], the Sedia HIV-1 LAG Avidity EIA (Sedia Biosciences Corp., Portland, OR, USA) and the BED assay are commercially available kits [15,16]. Nevertheless, the World Health Organization Working Group on HIV Incidence Assays recommends using the BED assay in combination with another assay measuring different biological endpoints, such as avidity assay, to compensate for the limitations of the BED assay, the most important of which is the generation of false positive results [17].
- In setting up the avidity assay, each laboratory has to resolve various matters such as determining the chaotropic agent and the cutoff value under the optimal condition using reasonable samples such as representative samples for their regions. In this study, we developed and optimized an avidity assay using samples from Korean HIV seroconverters and HIV-positive individuals.
Introduction
- 2.1 Specimens
- We used samples from Korean HIV seroconverters, HIV-positive Koreans, and two commercial HIV seroconversion panels, an HIV-1 incidence performance panel.
- A total of 81 Korean HIV seroconverters were collected from a pool of HIV seroconverters detected from 2005 to 2012 at the Korea Centers for Diseases Control and Prevention (KCDC). A total of 193 specimens collected from these 81 individuals were used in this study. At least two observations including one indeterminate specimen with results by several seroimmunological patterns were carried out prior to the diagnosis of HIV infection. According to the Fiebig classification, the infection stage of each person was grouped into six laboratory stages of primary HIV infection based on the antigen–antibody response pattern (HIV RNA, ELISA antigen, ELISA antibody, and Western blot) found in the first sample [18,19]. We estimated the HIV infection period for all 193 longitudinal samples using the Fiebig classification.
- We selected 135 Korean HIV-positive samples, and classified two groups. The first group consisted of 30 HIV-positive samples shown positive with HIV nucleic acid amplification, antigen/antibody ELISA, and Western blot. The samples were taken from blood donors to obtain enough volumes for repeated tests, and these individuals had not received antiretroviral therapy. These samples were used to select the optimal concentration of the chaotropic agent, and the precision of the avidity assay. The second group consisted of 105 samples obtained from long-term infected persons who passed away more than 2 years after the initial diagnosis of HIV at the KCDC. The samples were used to set up the optimal cutoff value in the avidity assay.
- The two sets of HIV seroconversion standard panels (PRB933, PRB965: BBI; SeraCare, Milford, MA, USA) used in this study consisted of samples that converted from negative, to indeterminate, and to positive for HIV testing; which are the early stage of incidence samples under 30 days since seroconversion. The standard panel for HIV-1 incidence performance (PRB601: SeraCare) contained a total of 15 samples; seven are recent infection and eight are established infection.
- 2.2 Laboratory testing: BED assay
- The BED assay (Calypte Biomedical Corporation, Portland, OR, USA) was conducted according to the manufacturer's instructions. Samples were diluted to a ratio of 1:100, transferred to a plate coated with goat-antihuman-IgG, and incubated for 1 hour at 37°C. After washing, a BED-biotin peptide (gp41) was added after being diluted at 1:1000. Then, after an additional 1-hour incubation at 37°C and a second round of washing, a conjugate, which was diluted 1:1000, was added. This was followed by a 90-minute incubation at 37°C, a third round of washing, and the addition of 3,3′,5,5′-Tetramethylbenzidine. The samples were then incubated for 15 minutes at 25°C and processed using a stop solution. Finally, using a spectrophotometer, absorbance was measured at a wavelength of 450 nm.
- 2.3 Laboratory testing: avidity assay
- In the present study, we chose to perform the AxSYM HIV antigen–antibody Combo assay (Abbott Laboratories, Wiesbaden, Germany), which is a fourth-generation assay, to calculate the AI. The chaotropic agent used in this study was guanidine hydrochloride (Guanidine: Sigma # G 7294-100ML; Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA). Guanidine concentrations used were 1.0M, 1.5M, and 2.0M and for the control, a phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) solution (PBL06-500ML; Caisson Labs, North Logan, UT, USA) was used. Each sample was divided into 20-μl aliquots, which were diluted 1:10 with 1.0M, 1.5M, and 2.0M Guanidine or PBS, left at room temperature for 15 minutes, and then subjected to the automated AxSYM assay. Based on the signal/cutoff (S/CO) ratios of the Guanidine and PBS aliquots, the AI of HIV antibodies was calculated using the following formula: AI = (S/CO of the Guanidine aliquot)/(S/CO of the PBS aliquot).
- 2.4 Statistical analysis
- For this study, sensitivity was defined as the proportion to be identified as recent results among the incident samples in the panels, whereas specificity was defined as the proportion of samples identified as established infection among the established samples in the panels. We also defined that false-reactive was the misclassified results as established infection among the recent infection samples, whereas the nonreactive was the misclassified results as recent infection among the established infection samples.
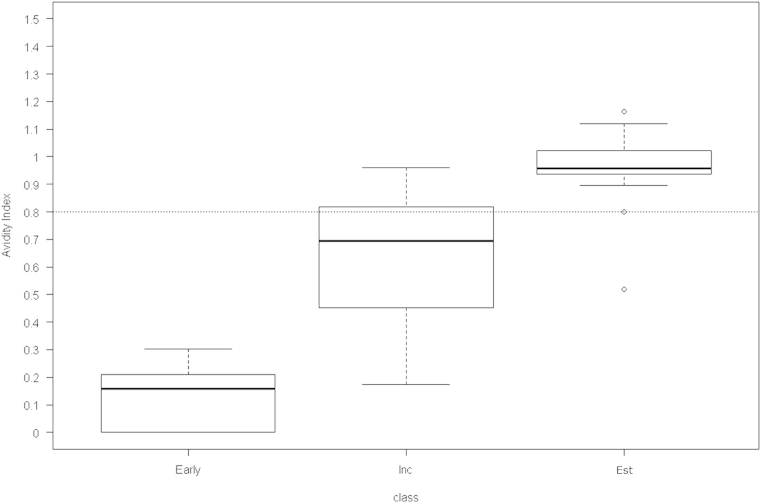
- To construct a gray zone, we applied the formula—{cutoff value ± [coefficient of variation (CV) × cutoff value]}—of Suligoi et al [20]. The precision of the repeat test results was expressed as the CV. The AI distributions of three sample groups—early stage of incidence, incidence, and established—were compared using a nonparametric method (Figure 1).
- 2.5 Ethics statement
- Our research protocol was reviewed and approved by the KCDC Institutional Review Board Ethics Committee (Approval Number: 2011-03CON-01-R and 2012-05CON-11-P). All HIV-positive and seroconverter specimens used in this study are taken from stored diagnostic materials from HIV diagnoses at the KCDC. Because all specimens are identified by their serial number, they do not contain any personally identifiable information. Therefore, this study was exempted from the requirement of informed consent, which was affirmed by the KCDC Institutional Review Board.
Materials and methods
- 3.1 Determination of the concentration of chaotropic agent for the avidity assay using HIV-positive samples
- The results of the BED assay for the commercial HIV panels (PRB933, PRB965, and PRB601) were all in good agreement with the reference results. For each of the 30 Korean HIV-positive samples, two repeat tests of the BED assay were performed. The results demonstrated that 14 were recent infections and the other 16 were long-term infections. The repeat tests gave the same results (data not shown).
- To select an appropriate concentration for the chaotropic agent, five repeat tests were performed with Guanidine concentrations of 1.0M, 1.5M, and 2.0M each. Based on the BED assay results, the samples were classified as recent or established infections. We then calculated the sensitivity and specificity of each Guanidine concentration used in the avidity assay. For Guanidine concentrations of 1.0M, 1.5M, and 2.0M, sensitivity and specificity were calculated for the cutoff value of 0.05 increments from 0.70 to 1.00. Using 1.0M Guanidine, sensitivity ranged from 28.6% to 87.1%, which was lower than what was observed using 1.5M or 2.0M Guanidine. However, specificity was highest with 1.0M Guanidine, ranging from 56.3% to 93.8%. By contrast, sensitivity was highest with 2.0M Guanidine (60.0–100%), whereas specificity was lowest with 2.0M Guanidine (15.0–91.3%). We decided that 1.5M Guanidine was the most suitable concentration to use in consideration of the sensitivity and specificity levels obtained at most of the cutoff values (Table 1).
- 3.2 Determination of cutoff value for the avidity assay using HIV seroconverter samples
- To determine the cutoff value for the avidity assay, we used samples collected from 81 Korean seroconverters whose date of HIV infection could be reliably estimated. The characteristics of these seroconverters and their longitudinal samples are shown in Table 2. Regarding the infection period, 40.7% and 46.9% of the participants fell into Fiebig Stages II and IV, respectively. The results of the Fiebig classification in 193 longitudinal samples showed that 90% of the seroconverter samples were within 200 days of seroconversion and were thus classified to be in the early stage of HIV infection.
- An analysis of the BED assay results performed on these Korean HIV seroconversion samples showed that at the cutoff value of 0.8 stated in the kit insert for the BED assay, the most useful recency period was 200 days (data not shown).
- The most optimal cutoff value for the avidity assay was 0.80 in the Korean seroconverter samples and long-term infection samples, and the sensitivity and specificity were 90.2% and 83.8%, respectively, at the cutoff value (Table 3). As shown in Table 4, 87.9% (153/174) of recent infection samples were identified as recent, whereas 12.3% (13/105) of established infection samples were all misclassified based on the dual testing results. The agreement results of the two incidence assays were 90.2% (157/174) and 85.7% (90/105) in the recent infection and established infection samples, respectively. The BED assay had more false recent results on the established samples.
- 3.3 Precision of AI for detecting recent HIV infections
- To ensure the validity of the procedure, we conducted repeat tests and analyzed the assay's reproducibility. Table 5 presents the precision of the AI for five repeat tests performed on 30 HIV-positive samples treated with 1.5M Guanidine. The mean CV obtained from the five repeat tests for each of the 30 samples was 5.43%. In addition, the mean correlation coefficient between the optical density/CO ratio of AxSYM HIV Antigen/Antibody and AI was 0.706 (p < 0.001), suggesting a positive correlation.
- Moreover, we established a gray zone to reduce the error in the identification of recent infections among samples that showed values close to the cutoff value. After applying the CV obtained from five repeat tests on 30 HIV-positive samples, we obtained a gray zone of 0.75–0.85 (data not shown).
- 3.4 Distributions of AI by progression stages of HIV infection
- We divided the samples in PRB933, PRB965, and PRB601 and 30 Korean HIV-positive samples into three groups—samples in the early stage of incidence (n = 9; 3 from PRB933 and 6 from PRB965), incident samples (n = 21; 7 from PRB601 and 14 from Korean Positive), and established samples (n = 24; 8 from PRB601 and 16 from Korean Positive). Each group of samples was subjected to a Guanidine-based avidity assay with a concentration of 1.5M Guanidine to study the distribution of AI compared with elapsed time since seroconversion (Figure 1). The median values showed significant variations between the groups: 0.159, 0.694, and 0.958 in the early-stage, incident, and established samples, respectively (p < 0.001).
- 3.5 Avidity results on three HIV commercial incidence panels
- The results of the avidity assay on the two sets of HIV seroconversion panels (PRB933, PRB965) were all in good agreement with the reference results. In the performance panel (PRB601), the results showed that six were recent infections and nine were established infections. One misclassified sample resulted in false-reactive with 0.83 AI, which belongs to the gray zone range (data not shown).
Results
- This study showed that for the identification of recently acquired infections, we could measure HIV incidence by establishing a laboratory-based serological test method based on the changes in antigen–antibody response pattern relative to time since HIV infection. Even though earlier studies suggested the use of Guanidine or urea as the preferred chaotropic agent for the avidity assay [21], we found that, from an examination of panels that contained both incident and established samples, sensitivity and specificity were highest when Guanidine was used (data not shown).
- The most optimal concentration of Guanidine was 1.5M, and the most useful cutoff for the avidity assay to detect recent HIV infection was 0.80.
- The mean CV obtained from the precision test was 5.43%, which indicated that the entire procedure was highly precise. In general, precision is defined as the variability in the results from replicated performance of the homogeneous sample under the normal assay condition. For enzyme assays, precision is usually <10% [22].
- In this study, at the cutoff value of 0.8 for the BED assay, samples from HIV seroconverters showed a recency period of 200 days, which is longer than the period (155 days) suggested by the kit insert for the BED assay. However, recent studies have also reported similar findings. According to Braunstein et al [23], prospective seroconverters among Rwandan sex workers showed a mean recency period of 330 days. In addition, a study conducted by Parekh et al [24] on longitudinal specimens collected from various groups showed a recency period of 197 days. As a result, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention were planning to adjust the recency period stated in the BED kit insert in consideration of the findings cited above.
- Generally, when trying to establish an avidity assay, various obstacles must be overcome. First, each laboratory has to validate the methods used for the entire procedure including selection of an appropriate chaotropic agent for the AI and determination of the cutoff value. Second, it is difficult to secure panels that reflect a diverse period of infection stages and for which the date of seroconversion can be estimated. Third, there may be limitations to interpreting HIV incidence test results because they are determined solely by the AI. Not only are there individual differences in the immune response to HIV, window periods also vary by HIV subtype or race [24]. In this study, 9.8% of recent infection samples and 16.2% of established infection samples were misclassified in the avidity assay (Table 3). Furthermore, 2.3% (4/174) of recent infection samples were all misclassified as established infection from the two incidence assays (Table 4). These discordant results of studies have been reported by Braunstein et al [23] and Moyo et al [25]. Therefore, incidence assay results should be analyzed in combination with other information such as HIV test results and patient's history [26].
- Despite these limitations, this study is important because it enabled the establishment of an avidity assay using Korean samples from HIV-positive and seroconverters. It will enhance the reliability of the estimation of HIV incidence by combining data from both the avidity assay and the BED assay and comparing the results. In addition, a gray zone was included so that samples with values close to the cutoff point, and thus difficult to determine, would be subjected to further testing. In this case, we interpreted the results comprehensively—considering laboratory examination data such as antigen test results, nucleic acid analysis, CD4+ T cell count, and patient information such as treatment history. This led to a more accurate discrimination between recent and established infections and reduced the risk of misclassification. It seems, however, that further research will need to be conducted using samples that showed conflicting results in the BED and avidity assays from an immunological and serological perspective. We expect that a comprehensive algorithm to analyze incidence assay results will emerge from such future research.
- The incidence assay established in this study is very significant because it enables the detection of recent infections among newly reported cases of HIV using a serological test method. Furthermore, the results provide basic data to assess HIV incidence, the progression of the disease after infection, and the survival rate. This is the first study on recent HIV infection assays, and it will help in epidemiologic studies of HIV/AIDS and can be applied to the national HIV/AIDS prevention policy in Korea.
Discussion
- The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Conflicts of interests
-
Acknowledgements
- This study was supported by Intramural Research Grant from the Korea National Institute of Health (Funding No.4800-4845-300-210-13, Project No. 2011-N51001-00). We thank HyoJung Sim for technical support.
Acknowledgments
-
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Article information
- 1. Hall H.I., Song R., Rhodes P.. HIV Incidence Surveillance Group. Estimation of HIV incidence in the United States. JAMA 300(5). 2008 Aug;520−529. PMID: 18677024.ArticlePubMed
- 2. Murphy G., Parry J.V.. Assays for the detection of recent infections with human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Euro Surveill 13(36). 2008 Sep;pii: 18966.Article
- 3. Janssen R.S., Satten G.A., Stramer S.L.. New testing strategy to detect early HIV-1 infection for use in incidence estimates and for clinical and prevention purposes. JAMA 280(1). 1998 Jul;42−48. PMID: 9660362.ArticlePubMed
- 4. Parekh B.S., Pau C.P., Kennedy M.S.. Assessment of antibody assays for identifying and distinguishing recent from long-term HIV type 1 infection. AIDS Res Hum Retrovir 17(2). 2001 Jan;137−146. PMID: 11177393.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Martro E., Suligoi B., Gonzalez V.. Comparison of the avidity index method and the serologic testing algorithm for recent human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) seroconversion, two methods using a single serum sample for identification of recent HIV infections. J Clin Microbiol 43(12). 2005 Dec;6197−6199. PMID: 16333129.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Eisen H.N., Siskind G.W.. Variations in affinities of antibodies during the immune response. Biochemistry 3(7). 1964 Jul;996−1008. PMID: 14214095.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Eggers M., Baeder U., Enders G.. Combination of microneutralization and avidity assays: improved diagnosis of recent primary human cytomegalovirus infection in single serum sample of second trimester pregnancy. J Med Virol 60(3). 2000 Mar;324−330. PMID: 10630965.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Jenum P.A., Stray-Pedersen B., Gundersen A.G.. Improved diagnosis of primary Toxoplasma gondii infection in early pregnancy by determination of antitoxoplasma immunoglobulin G avidity. J Clin Microbiol. 35(8). 1997 Aug;1972−1977. PMID: 9230365.ArticlePubMed
- 9. Matter L., Kogelschatz K., Germann D.. Serum levels of rubella virus antibodies indicating immunity: response to vaccination of subjects with low or undetectable antibody concentration. J Infect Dis 175(4). 1997 Apr;749−755. PMID: 9086126.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Thomas H.I.. Relative functional affinity of specific anti-core IgG in different categories of hepatitis B virus infection. J Med Virol 51(3). 1997 Mar;189−197. PMID: 9139082.ArticlePubMed
- 11. Ward K.N., Turner D.J., Parada X.G.. Use of immunoglobulin G antibody avidity for differentiation of primary human herpesvirus 6 and 7 infections. J Clin Microbiol 39(3). 2001 Mar;959−963. PMID: 11230411.ArticlePubMed
- 12. Ward K.N., Dhaliwal W., Ashworth K.L.. Measurement of antibody avidity for hepatitis C virus distinguishes primary antibody responses from passively acquired antibody. J Med Virol 43(4). 1994 Aug;367−372. PMID: 7525865.ArticlePubMed
- 13. Parekh B.S., Kennedy M.S., Dobbs T.. Quantitative detection of increasing HIV type 1 antibodies after seroconversion: a simple assay for detecting recent HIV infection and estimating incidence. AIDS Res Hum Retrovir 18(4). 2002 Mar;295−307. PMID: 11860677.ArticlePubMed
- 14. Suligoi B., Galli C., Massi M.. Precision and accuracy of a procedure for detecting recent human immunodeficiency virus infections by calculating the antibody avidity index by an automated immunoassay-based method. J Clin Microbiol 40(11). 2002 Nov;4015−4020. PMID: 12409368.ArticlePubMed
- 15. Duong Y.T., Qiu M., De A.K.. Detection of recent HIV-1 infection using a new limiting-antigen avidity assay: potential for HIV-1 incidence estimates and avidity maturation studies. PLoS One 7(3). 2012 Mar;e33328PMID: 22479384.ArticlePubMed
- 16. UNAIDS . WHO/UNAIDS Technical Update on HIV incidence assays for surveillance and epidemic monitoring. 2013 May. UNAIDS; Geneva.
- 17. WHO . Meeting Report: WHO Working Group on HIV Incidence Assays Annual Meeting 18–24 August 2011. 2011. WHO; Atlanta, GA, USA.
- 18. Levy J.A.. HIV and the pathogenesis of AIDS. Acute HIV infection. 3rd ed.2007. ASM Press; Washington, DC: pp 79−87.
- 19. McMichael A.J., Borrow P., Tomaras G.D.. The immune response during acute HIV-1 infection: clues for vaccine development. Nat Rev Immunol 10(1). 2010 Jan;11−23. PMID: 20010788.ArticlePubMed
- 20. Suligoi B., Rodella A., Raimondo M.. Avidity index for anti-HIV antibodies: comparison between third- and fourth-generation automated immunoassays. J Clin Microbiol 49(7). 2011 Jul;2610−2613. PMID: 21543577.ArticlePubMed
- 21. Chawla A., Murphy G., Donnelly C.. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) antibody avidity testing to identify recent infection in newly diagnosed HIV type 1 (HIV-1)-seropositive persons infected with diverse HIV-1 subtypes. J Clin Microbiol 45(2). 2007 Feb;415−420. PMID: 17151211.ArticlePubMed
- 22. Law B.. Immunoassay, a practical guide. Taylor & Francis e-library. Chapter 10, Quality of immunoasssays and quality control procedures. 2005. pp 193−212. ISBN 0-203-79173-7 (Adobe eReader Format).
- 23. Braunstein S.L., Nash D., Kim A.A.. Dual testing algorithm of BED assay and AxSYM avidity index assays performs best in identifying recent HIV infection in a sample of Rwandan sex workers. PLoS ONE 6(4). 2011 Apr;e18402PMID: 21532753.ArticlePubMed
- 24. Parekh B.S., Hanson D.L., Hargrove J.. Determination of mean recency period for estimation of HIV type 1 incidence with the BED-capture EIA in persons infected with diverse subtypes. AIDS Res Hum Retrovir 27(3). 2011 Mar;265−273. PMID: 20954834.ArticlePubMed
- 25. Moyo S., LeCuyer T., Wang R.. Evaluation of the false recent classification rates of multiassay algorithms in estimating HIV type 1 subtype C incidence. AIDS Res Hum Retrovir 30(1). 2014 Jan;29−36. PMID: 23937344.ArticlePubMed
- 26. Selleri M., Orchi N., Zaniratti M.S.. Effective highly active antiretroviral therapy in patients with primary HIV-1 infection prevents the evolution of the avidity of HIV-1-specific antibodies. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 46(2). 2007 Oct;145−150. PMID: 17589369.ArticlePubMed
References
Based on the BED assay results, 30 Korean HIV-positive samples were classified: 14 were recent infections and the other 16 were established infections. These HIV-infected Koreans tested positive in three HIV tests—nucleic acid amplification, HIV antigen/antibody ELISA, and Western blot—and had not received antiretroviral therapy.
For the avidity assay, 1.0M, 1.5M, and 2.0M Guanidine concentrations were used, and the 30 HIV positive samples were tested repeatedly using the assay five times (n = 150).
E = established infection; ELISA = enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; HIV = human immunodeficiency virus; R = recent infection.
| Categories | Number (%) | Cumulative no. (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Fiebig stagesa (81 individuals) | ||
| Eclipse phase | — | — |
| I | 2 (2.5) | 2 (2.5) |
| II | 33 (40.7) | 35 (43.2) |
| III | 6 (7.4) | 41 (50.6) |
| IV | 38 (46.9) | 79 (97.5) |
| V | 2 (2.5) | 81 (100.0) |
| VI | — | 81 (100.0) |
| Estimated days (d) following HIV transmissionb (193 samples) | ||
| 1–30 | 20 (10.4) | 20 (10.4) |
| 31–60 | 55 (28.5) | 75 (38.9) |
| 61–90 | 33 (17.1) | 108 (56.0) |
| 91–120 | 29 (15.0) | 137 (72.0) |
| 121–150 | 22 (11.4) | 159 (82.4) |
| 151–180 | 10 (5.2) | 169 (87.6) |
| 181–200 | 5 (2.6) | 174 (90.2) |
| >200 | 19 (9.8) | 193 (100.0) |
a Fiebig stage of each person was classified into six laboratory stages of primary HIV infection based on the antigen–antibody response patterns (HIV RNA, ELISA antigen, ELISA antibody, Western blots) found in the sample [16,17]. Days following HIV transmission of each stage were as follows: Eclipse phase (10 days), I (17 days), II (22 days), III (25 days), IV (31 days), V (101 days), and VI (open ended).
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Characteristics of recent HIV infection among individuals newly diagnosed as HIV-positive in South Korea (2008–2015)
Myeongsu Yoo, Jin-Sook Wang, Su-Jin Park, Jeong-ok Cha, Yoonhee Jung, Yoon-Seok Chung, Myung Guk Han, Byeong-Sun Choi, Sung-Soon Kim, Mee-Kyung Kee
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef


 PubReader
PubReader Cite
Cite
