Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Osong Public Health Res Perspect > Volume 4(3); 2013 > Article
-
Brief Report
Epidemiological Characteristics of Imported Shigellosis in Korea, 2010–2011 - Hee-Jung Kim, Seung-Ki Youn, Sangwon Lee, Yeon Hwa Choi
-
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives 2013;4(3):159-165.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2013.02.002
Published online: March 21, 2013
Division of Epidemic Intelligence Service, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Osong, Korea
- ∗Corresponding author. yunki7777@naver.com
© 2013 Published by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Demographic Characteristics of Imported Cases of Shigellosis
- Disease Characteristics Over Time
- Geographic Distribution of Patients Residing in Korea
- Clinical Symptoms (Multiple Responses)
- Diarrhea Aspects
- Regional Infection Status by Visiting Country
- Discussion
- Acknowledgments
- Article information
- References
Abstract
- Shigellosis is a global disease as food poisoning by infection of Shigella spp (S. dysenteriae, S. flexneri, S. boydii and S. sonnei). In Korea, approximately 500 cases of shigellosis have reported every year since 2004, and imported shigellosis is increasing gradually from 2006 in particular. According to increase of numbers of overseas travelers, the numbers of patients diseased with imported shigellosis is also increasing. We need continuous surveillance studies network (SSN) for control of imported shigellosis. We studied epidemiological characteristic of imported shigellosis by using database of Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (KCDC) from 2010 to 2011. The imported shigellosis is analyzed on correlation with variable factors such as sex, age, symptom, visited country as well as Shigella spp in the database. Total 399 patients diseased with shigellosis have been reported between 2010 and 2011, The 212 patients (53.1%) among them were disease with imported shigellosis and the 205 patients (96.7%) were diagnosed as definite shigellosis. Shigella sonnei (65.6%) and Shigella flexneri (20.3%) were isolated in order. Clinical symptoms of the shigellosis were diarrhea (96.5%), abdominal pain (54.7%), fever (52.8%), chill (31.6%), and weakness (21.7% etc) in order. Duration of diarrhea was 1 to 5 days, the number of diarrhea was mostly more than 10 times, and type of stool was almost yellow stool. Almost shigellosis was occurred in the travelers visited to Asia (98.1%). Particularly, the occurrence rate of shigellosis was highest in traveler visited to Southeast Asia which is India (21.7%), Cambodia (19.8%), Philippines (17.9%), and Vietnam (9.0%) in order. According to increase of traveler to Southeast Asia, imported Shigellosis also increased. We need to strengthen the public health and hygiene, which is infection prevention rules, eating properly-cook food, washing hands, drinking boiled water, for traveler to Asia. The quarantine and surveillance system to control imported shigellosis is need continually in Korea.
- Shigellosis is an acute infectious colitis caused by Shigella spp. that is transmitted by the direct and indirect fecal–oral route as well as by contact with contaminated water, food, hand, stool, and flies [1–5]. When compared with other pathogens, a very small amount (10–100) of Shigella spp. is enough to cause infection. Although infected healthy people recover from diarrhea within 5 days, infected young children, the elderly, and people with chronic illness are usually diseased with various other complications or severe dehydration that may become life threatening within a few days [6]. Approximately 1.4 million people have been infected by Shigella spp., with reports suggesting 600,000 deaths due to the infection. The majority of those who died because of this infection were children from developing countries under the age of 5 years old with bad hygiene practices, such as poor hand hygiene [7].
- According to the report released by the Korea National Tourism Organization, the number of foreign tourists to the country has been on the rise since 2005, when 10.08 million people were reportedly visiting Korea every year [8], but the number temporarily decreased to 0.9494 million people in 2009 when swine flu was declared pandemic. However, the numbers increased again to 12.487 million people in 2010, and then to 12.694 millions in 2011. In particular, the number of tourists visiting Southeast Asia was increasing due to cheap travel costs for various cultural and sports activities available. It has been reported that the infection rates of tourists are high after visiting countries in the Southeast Asian region.
- Shigellosis is the most common among a group of infectious diseases caused by various pathogens in Korea, including infections by six species of bacteria. A total of 927, 767, and 1117 cases were diagnosed with shigellosis in 2001, 2002, and 2003, respectively. Because of poor water quality and poor hygiene practices, less than 500 people have been reported to be infected annually since 2004 [9]. However, 104 of the 228 cases (45.6%) reported in 2010 and 108 of the 171 cases (63.2%) in 2011 were reported to be infected during their stay abroad. The number of cases of imported shigellosis is greatly increasing every year, noticeably since 2007, with a 43.8% percent increase in 2010 and a 7.9% increase in 2011, respectively, when compared with the previous years. This increase in rate could be attributed to the increasing number of overseas tourists. Therefore, continued analysis, observation, and research on the imported cases of shigellosis are needed.
- In this study, we investigated a Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (KCDC) statistical web report released in 2010–2011, which reported that 202 people were infected during their stay abroad among a total of 399 people studied. Based on the web reporting statistics of infectious diseases and an epidemiology survey, the general characteristics, occurrence, clinical symptoms, and country of infection of the imported shigellosis were studied.
Introduction
- The KCDC confirmed infection in 205 cases (96.7%) and suspected infection in seven cases (3.3%) among a total of 212 imported cases reported. Compared with men (77 cases, 36.3%), women were more infected (135 cases, 63.7%). In addition, patients in the age group of 20–29 years (47.2%) were the most commonly infected. An analysis based on occupation showed that 86 students (40.6%), including kindergarten, elementary, middle, high school, and college students, accounted for the most distributions (Table 1). Table 2 presents information on imported infection caused by various Shigella spp.
Demographic Characteristics of Imported Cases of Shigellosis
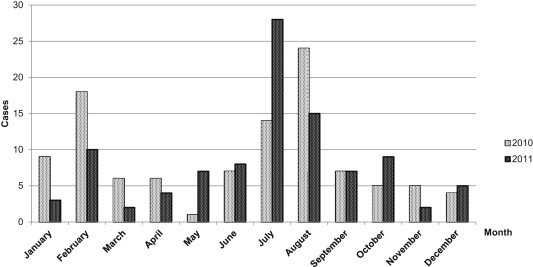
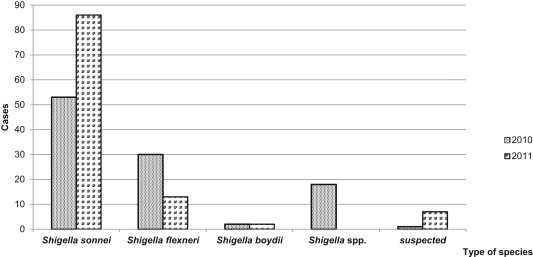
- Shigella infection most commonly occurred during the period from July to August, in which 81 cases (38.2%) of shigellosis were reported, followed by 30 cases (14.2%) from January to February, 15 cases (7.1%) in June, 10 cases (4.7%) in March. Less than 10 cases were reported during the other month. Imported shigellosis outbreaks were highest during vacation season when the number of overseas travelers increased (Figure 1). Shigella sonnei was the most frequently isolated bacterium [found in 139 cases (65.6%)], followed by Shigella flexneri [found in 43 cases (20.3%)] (Figure 2).
Disease Characteristics Over Time
- The highest number of patients resided in Seoul (60 cases, 28.3%) and Kyunggi (49 cases, 23.1%), followed by Busan (18 cases, 8.5%), Gyeongnam (17 cases, 8.0%), Incheon (15 cases, 7.1%), Daegu (12 cases, 5.7%), Chungnam (10 cases, 4.7%), Ulsan (8 cases, 3.8%), Jeonnam (7 cases, 3.3%), Gwangju (6 cases, 2.8%), Chungbuk and Gyeongbuk (3 cases each, 1.4%), Jeju (2 cases, 0.9%), and Daejeon and Jeonbuk (1 case each, 0.5%) (Table 3).
Geographic Distribution of Patients Residing in Korea
- Diarrhea was the most commonly reported (198 cases, 93.4%) clinical symptom, followed by abdominal pain (54.7%), fever (52.8%), chills (31.6%), weakness (21.7%), and vomiting (20.8%). In addition to nausea, feelings such as tenesmus and headache (reported in the order of maximum rates) were also reported (Table 4).
Clinical Symptoms (Multiple Responses)
- The main clinical symptom of shigellosis was diarrhea (93.4%) with abdominal pain. The period of diarrhea varied between 1 day and 5 days in 139 cases (65.6%) and between 6 days and 10 days in 45 cases (21.2%), with most symptoms subsiding within 10 days. However, in four cases, diarrhea continued for more than 26 days (1.9%).
- Diarrhea was typically characterized by yellow watery stools in 143 cases (67.5%) and bloody stools in 16 cases (7.5%). The frequency of diarrhea was more than 10 times in 101 cases (47.6%), three to four times in 21 cases (9.9%), five to seven times in 19 cases (9.0%), eight to nine times in 13 cases (6.1%), and less than three times in 10 cases (4.7%) (Table 5).
- Bloody stools caused by S. flexneri and S. sonnei infections were detected in 20.9% and 4.3% cases, respectively (Table 6). In order to compare the clinical severity of the symptoms between the two strains, we analyzed the fraction of bloody diarrhea using the Chi-square test, the results of which showed p = 0.0017, and the fraction of bloody diarrhea was significantly high in patients infected with S. flexneri (Table 7).
Diarrhea Aspects
- A total of 208 cases (98.1%) of imported shigellosis were reported to be infected during their travel to Asian countries. In particular, the occurrence rate of shigellosis was highest when they traveled to the Southeast Asian countries. The highest number of cases was reported in those who visited India (46 cases, 21.7%), followed by Cambodia (42 cases, 19.8%), Philippines (38 cases, 17.9%), Vietnam (19 cases, 9.0%), and Indonesia (18 cases, 8.5%). In addition, infections were also reported in those who visited China (17 cases, 8.0%), Mongolia (11 cases, 5.2%), Laos (7 cases, 3.3%), Taiwan (4 cases, 1.9%), Myanmar and Thailand (2 cases each, 0.9%), Japan and Nepal (1 case each, 0.5%). By contrast, only one case each was reported in those who traveled to Egypt, Sudan, United States, and Brazil (Table 8).
Regional Infection Status by Visiting Country
- Shigellosis is a global disease caused by Shigella spp. food poisoning (S. dysenteriae, S. flexneri, S. boydii, and S. sonnei). In Korea, approximately 500 cases of shigellosis have been reported every year since 2004, and the number of imported cases of shigellosis has been gradually increasing since 2007. Because of the increase in the numbers of overseas travelers, the numbers of patients infected with imported shigellosis are also increasing. Therefore, there is a need for continuous surveillance studies in order to control imported shigellosis infection. In this study, we investigated the epidemiological characteristics of imported shigellosis infection using the KCDC statistics from 2010 to 2011. The imported shigellosis infection is analyzed based on correlation with variable factors such as gender, age, symptom, visited country, as well as Shigella spp. mentioned in the statistics database. A total of 399 patients were diagnosed with shigellosis between 2010 and 2011, of which 212 (53.1%) were with imported shigellosis, 205 (96.7%) of which were diagnosed as definite shigellosis. The infection was mostly caused by S. sonnei (65.6%), followed by S. flexneri (20.3%). Shigellosis infections were most common in the age group of 20–29 years (47.2%), and gender-wise it was more common in females (63.7%). Clinical symptoms of the shigellosis infection were (in the order of highest) diarrhea (96.5%), abdominal pain (54.7%), fever (52.8%), chill (31.6%), and weakness (21.7%). The duration of diarrhea was 1–5 days, and the frequency of diarrhea was mostly more than 10 times. The type of stool was almost yellow. Shigellosis occurred in travelers who mainly visited Asia (98.1%). In particular, the occurrence rate of shigellosis was highest in travelers who visited Southeast Asia countries, with the highest rate reported in the following order: India (21.7%), Cambodia (19.8%), Philippines (17.9%), and Vietnam (9.0%). With increases in the number of travelers to Southeast Asia, the rates of imported shigellosis also increased. Therefore, there is a need to strengthen public health and hygiene practices, including implementing infection prevention rules, as well as creating awareness on the following for travelers to Asian countries: eating properly cook food, washing hands, drinking boiled water. A quarantine and surveillance system to control imported shigellosis is continually needed in Korea.
Discussion
-
Acknowledgements
- This study is supported by an intramural grant of Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (No. 4848-300-210-13).
Acknowledgments
-
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Article information
- 1. He F., Han K., Liu L.. Shigellosis outbreak associated with contaminated well water in a rural elementary school: Sichuan Province. China. June 7–16. 2009. PLoS One 7(10). 2012;e47239.Article
- 2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Notes from the field: Outbreak of infections caused by Shigella sonnei with decreased susceptiblitiy to azithromycin–Los Angeles, California, 2012. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 62(9). 2013 Mar 8;171PMID: 23466436.
- 3. Bhattacharya S.K., Sur D., Mahalanabis D.. Public health significance of shigellosis. Indian Pediatr 49(4). 2012 Apr;269−270. PMID: 22565071.PubMed
- 4. Nygren B.L., Schilling K.A., Blanton E.M., Silk B.J., Cole D.J., Mintz E.D.. Foodborne outbreaks of shigellosis in the USA, 1998–2008. Epidemiolo Infect 24:2012 Feb;1−9.Article
- 5. Nandy S., Dutta S., Ghosh S.. Foodborne-associated Shigellal sonnei, India, 2009 and 2010. Emerg Infect dis 17(11). 2011 Nov;2072−2074. PMID: 22099103.PubMed
- 6. Marchou B.. Traveller's diarrhea: epidemiology, clinical practice guideline for the prevention and treatment. Press Med 42(1). 2013 Jan;76−81.Article
- 7. Shiferaw B., Solghan S., Palmer A.. Antimicrobial susceptibility patters of Shgella isolates in foodborne diseases acitive surveillance network (foodnet) sites, 2000–2010. Clin Infect Dis 54(Suppl. 5). 2012 Jun;S458−S463. PMID: 22572670.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Korea Tourism Organization. Korea tourism statistics [Internet]. Available from. http://kto.visitkorea.or.kr.
- 9. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Annual epidemiological studies of infectious diseases. Osong: Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 2010.
References
| S. flexneri | S. sonnei | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Melena (+) | 9 | 6 | 0.0017 |
| Melena (−) | 34 | 133 |
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- An in vivo acute toxicity and anti-shigellosis effect of designed formulation on rat
Devendra Singh, Vishnu Agarwal
Journal of Ayurveda and Integrative Medicine.2023; 14(1): 100536. CrossRef - Shigellosis in Southeast Asia: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Basilua Andre Muzembo, Kei Kitahara, Debmalya Mitra, Ayumu Ohno, Januka Khatiwada, Shanta Dutta, Shin-Ichi Miyoshi
Travel Medicine and Infectious Disease.2023; 52: 102554. CrossRef - Epidemic Trends of Imported Shigellosis Cases in Korea and Japan, 2016–2020
Won-Chang Lee, Myeon-Jin Lee, Kyu Sung Kim, Young Hwan Kwon
The Korean Journal of Aerospace and Environmental .2023; 33(3): 71. CrossRef - History and Epidemiology of Bacillary Dysentery in Korea: from Korean War to 2017
Hyunjoo Pai
Infection & Chemotherapy.2020; 52(1): 123. CrossRef - Principal Component Analysis for Clustering Probiotic-Fortified Beverage Matrices Efficient in Elimination of Shigella sp.
Srijita Sireswar, Didier Montet, Gargi Dey
Fermentation.2018; 4(2): 34. CrossRef - Importation of travel-related infectious diseases is increasing in South Korea: An analysis of salmonellosis, shigellosis, malaria, and dengue surveillance data
Young-June Choe, Seung-Ah Choe, Sung-Il Cho
Travel Medicine and Infectious Disease.2017; 19: 22. CrossRef - Current state on the development of nanoparticles for use against bacterial gastrointestinal pathogens. Focus on chitosan nanoparticles loaded with phenolic compounds
Ana Raquel Madureira, Adriana Pereira, Manuela Pintado
Carbohydrate Polymers.2015; 130: 429. CrossRef


 PubReader
PubReader Cite
Cite
