Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Evaluation of COVID-19 vaccine effectiveness in different high-risk facility types during a period of Delta variant dominance in the Republic of Korea: a cross-sectional study
- Min Jei Lee, Myung-Jae Hwang, Dong Seob Kim, Seon Kyeong Park, Jihyun Choi, Ji Joo Lee, Jong Mu Kim, Young-Man Kim, Young-Joon Park, Jin Gwack, Sang-Eun Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(5):418-426. Published online October 19, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0188
- 1,335 View
- 45 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 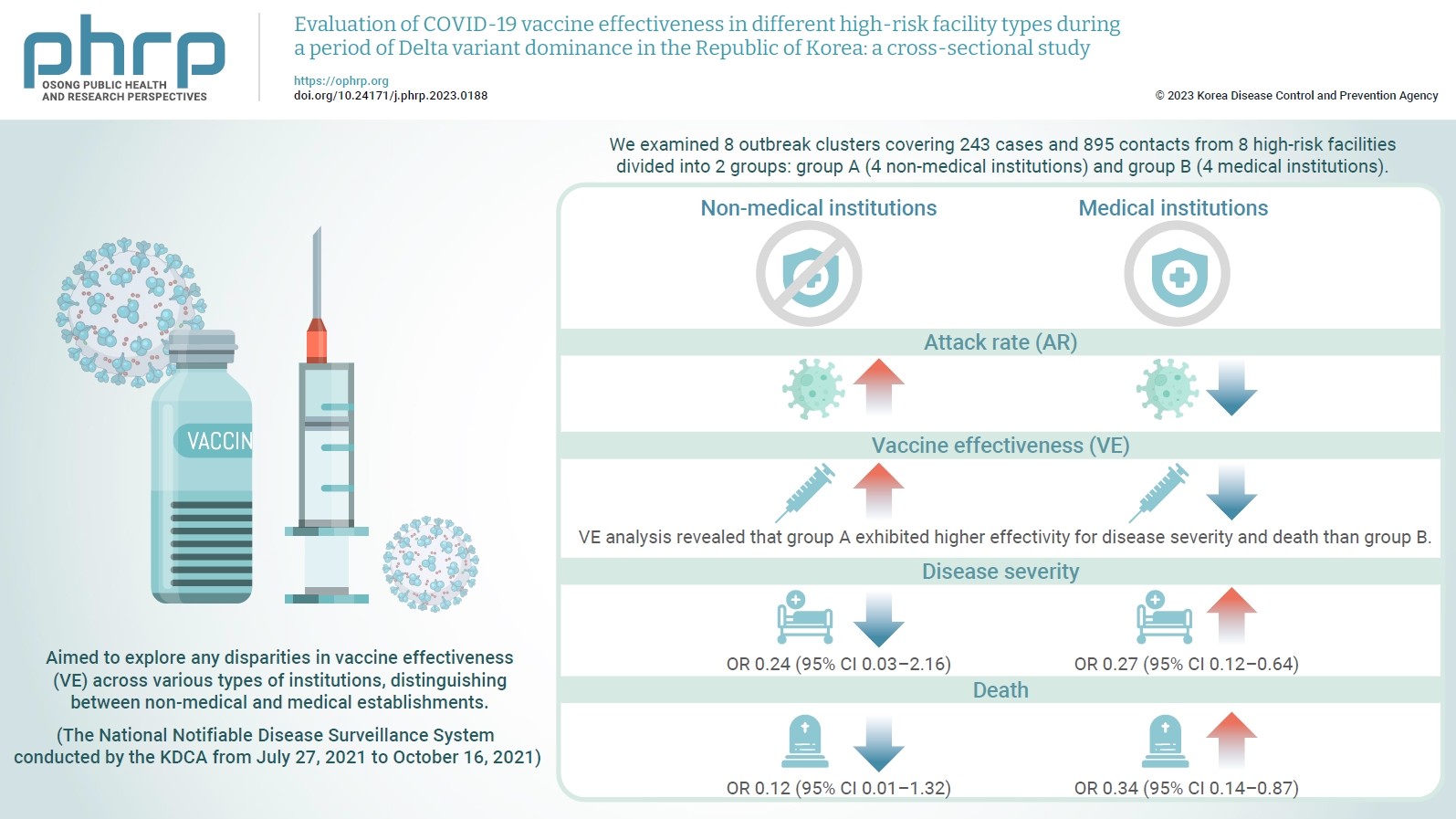
- Objectives
We evaluated the effectiveness of coronavirus disease 2019 vaccination in high-risk facilities in the Republic of Korea during the period when the highly transmissible Delta variant was prevalent. Additionally, we aimed to explore any disparities in vaccine effectiveness (VE) across various types of institutions, specifically distinguishing between non-medical and medical establishments. Methods: We examined 8 outbreak clusters covering 243 cases and 895 contacts from 8 high-risk facilities divided into 2 groups: group A (4 non-medical institutions) and group B (4 medical institutions). These clusters were observed from July 27, 2021 to October 16, 2021 for the attack rate (AR) and VE with respect to disease severity. A generalized linear model with a binomial distribution was used to determine the odds ratio (OR) for disease severity and death. Results: AR was notably lower in group B (medical institutions). Furthermore, VE analysis revealed that group A exhibited higher effectivity for disease severity and death than group B. The OR for disease severity was 0.24 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.03–2.16) for group A and 0.27 (95% CI, 0.12–0.64) for group B, with the OR for death at 0.12 (95% CI, 0.01–1.32) in group A and 0.34 (95% CI, 0.14–0.87) in group B. Conclusion: Although VE may vary across institutions, our findings underscore the importance of implementing vaccinations in high-risk facilities. Customized vaccination programs, tailored response plans, and competent management personnel are essential for effectively addressing and mitigating public health challenges.
- Vaccine effectiveness and the epidemiological characteristics of a COVID-19 outbreak in a tertiary hospital in Republic of Korea
- Seonhee Ahn, Tae Jong Son, Yoonsuk Jang, Jihyun Choi, Young Joon Park, Jiseon Seong, Hyun Hee Kwon, Muk Ju Kim, Donghyok Kwon
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(3):188-196. Published online June 8, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0066
- 1,521 View
- 74 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 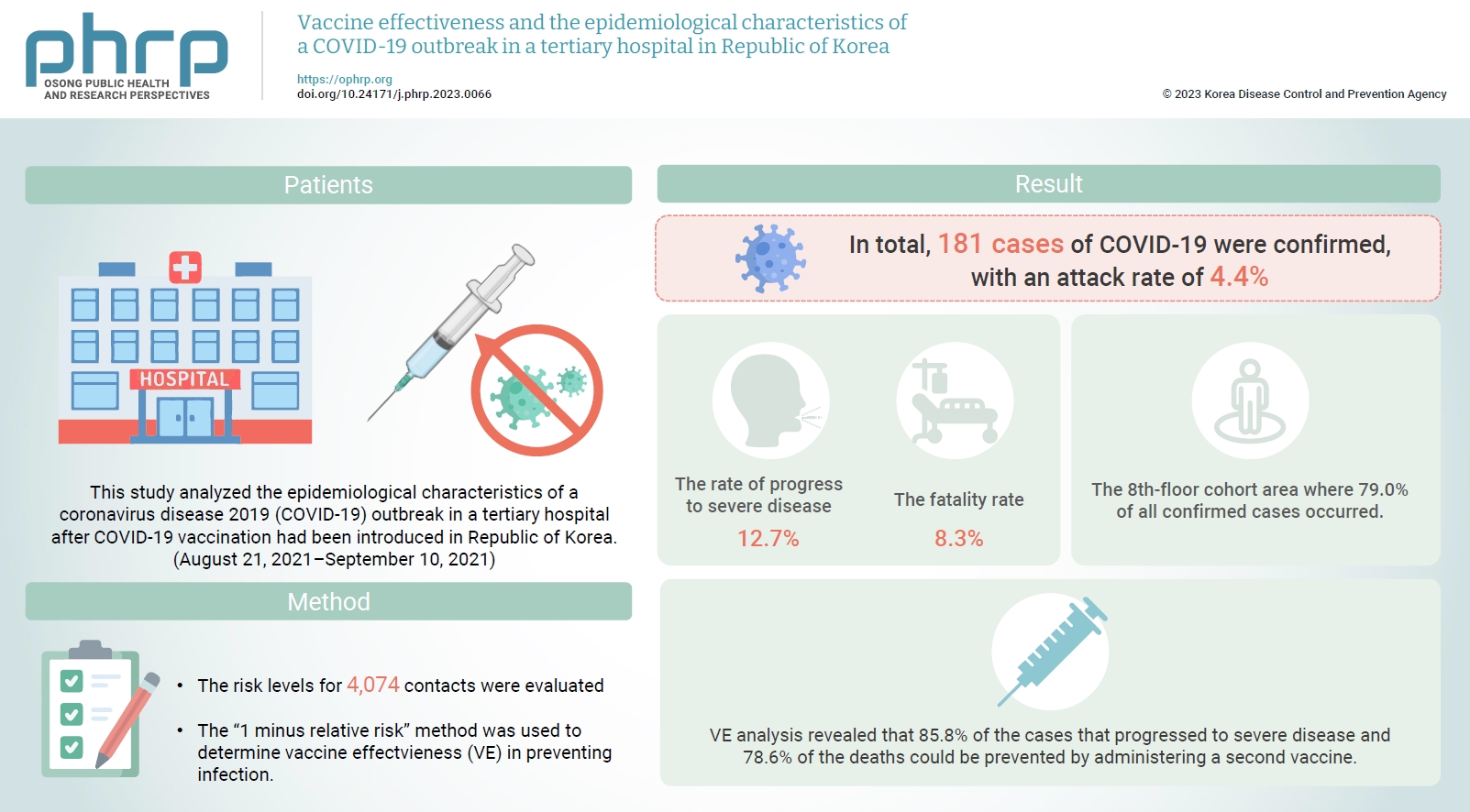
- Objectives
Healthcare facilities are high-risk sites for infection. This study analyzed the epidemiological characteristics of a coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in a tertiary hospital after COVID-19 vaccination had been introduced in Republic of Korea. Vaccine effectiveness (VE) and shared anti-infection strategies are also assessed.
Methods
The risk levels for 4,074 contacts were evaluated. The epidemiological characteristics of confirmed cases were evaluated using the chi-square test. The “1 minus relative risk” method was used to determine VE in preventing infection, progression to severe disease, and death. In the largest affected area (the 8th floor), a separate relative risk analysis was conducted. A multivariate logistic regression analysis (with 95% confidence interval [CIs]) was used to identify transmission risk factors with a significance level <10% via the backward elimination method.
Results
In total, 181 cases of COVID-19 were confirmed, with an attack rate of 4.4%. Of those cases, 12.7% progressed to severe disease, and 8.3% died. In the cohort isolation area on the 8th floor, where 79.0% of the confirmed cases occurred, the adjusted odds ratio was 6.55 (95% CI, 2.99–14.33) and 2.19 (95% CI, 1.24–3.88) for caregivers and the unvaccinated group, respectively. VE analysis revealed that 85.8% of the cases that progressed to severe disease and 78.6% of the deaths could be prevented by administering a second vaccine.
Conclusion
Caregiver training for infection prevention and control is necessary to reduce infection risk. Vaccination is an important intervention to reduce the risk of progression to severe disease and death.
- Effectiveness of the COVID-19 vaccine in the Honam region of the Republic of Korea
- In-Sook Shin, Yong-Pyo Lee, Seung-Hoon Lee, Jae-Young Lee, Jong-Ha Park, Yoon-Seok Chung
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(3):197-206. Published online June 8, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0308
- 2,051 View
- 65 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 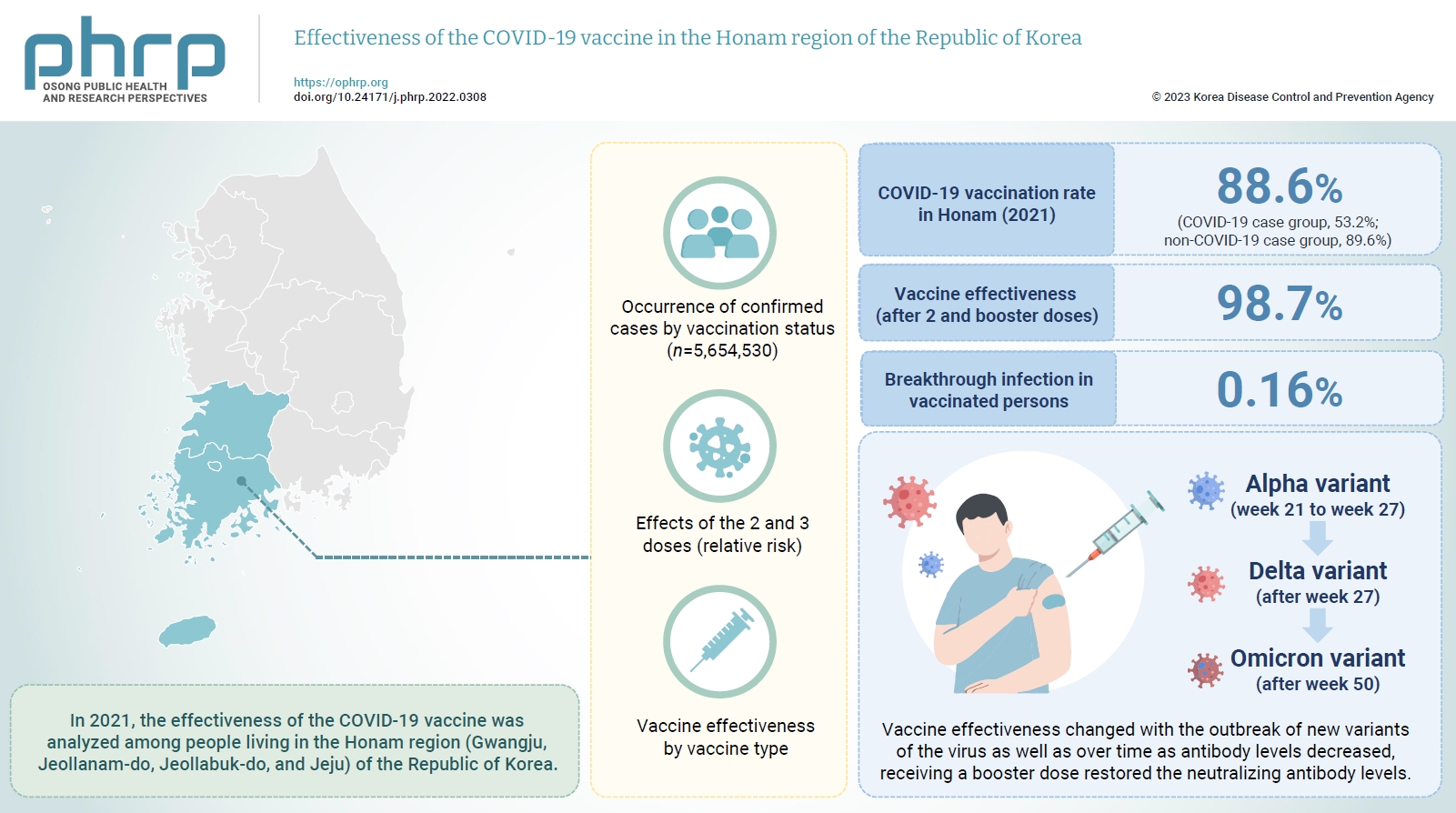
- Objectives
In 2021, the effectiveness of the COVID-19 vaccine was analyzed among people living in the Honam region (Gwangju, Jeollanam-do, Jeollabuk-do, and Jeju) of the Republic of Korea. And we investigated changes in the dominant virus strain.
Methods
This study used the data provided by the Korean Ministry of the Interior and Safety for individuals ≥12 years old in the Honam region, and the Integrated Disease and Health Management System of the Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for COVID-19-vaccinated individuals as of December 31, 2021. Statistical analyzes were performed using IBM SPSS ver. 23.0. The occurrence of confirmed cases by vaccination status, the relative risk, and vaccine effectiveness by vaccine type were calculated.
Results
In 2021, the COVID-19 vaccination rate in Honam was 88.6%. The overall vaccine effectiveness (after 2 and 3 doses) was 98.7% (p<0.001). and the breakthrough infection rate was 0.16%. From week 21 to week 27 of 2021 (June 27 to July 3), the genome sequencing results were mostly alpha variants. The Delta variant emerged as the dominant variant after 27 weeks and the Omicron variant was found at 50 weeks (December 5–11).
Conclusion
Vaccine effectiveness changed with the outbreak of new variants of the virus as well as over time as antibody levels decreased. that the prevention effectiveness of vaccination in Honam was >98%, and the effect among persons who received 2 doses was >90% regardless of the vaccine type. Although vaccine effectiveness decreased because of reduced antibody levels over time (as observed in breakthrough infections), receiving a booster dose restored the neutralizing antibody levels.
- Points to consider when developing drugs for dry eye syndrome
- Suyoung Bae, Hosun Seung, Ho Jung Oh
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(2):70-75. Published online April 26, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0031
- 1,631 View
- 116 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 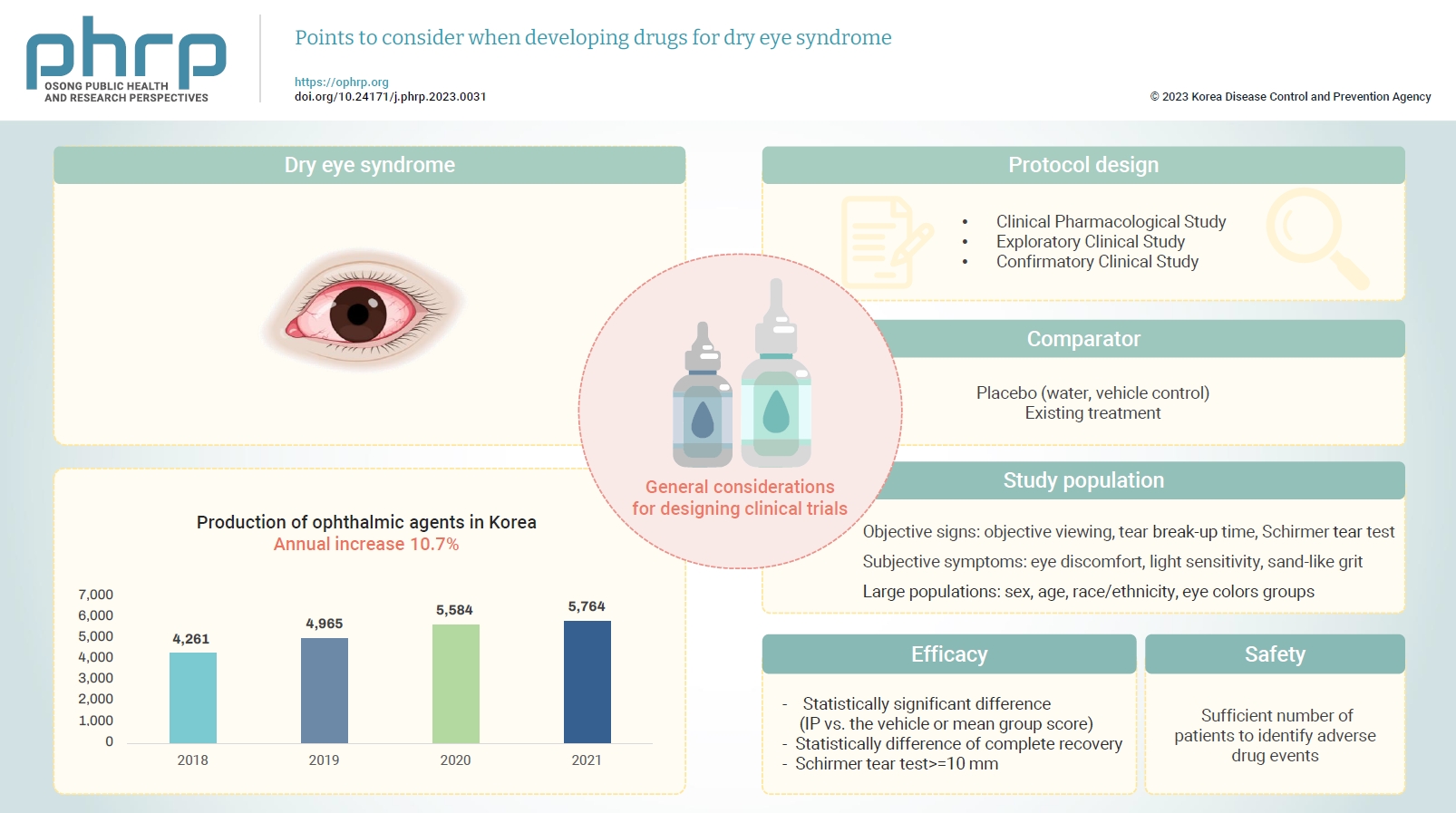
- Changes in both the social environment (e.g., the increased use of electronic media) and the atmospheric environment (e.g., air pollution and dust) have contributed to an increasing incidence of eye disease and an increased need for eye care. Notably, the signs and symptoms of dry eye syndrome can impact the daily quality of life for various age groups, including the elderly, and usually requires active treatment. The symptoms of dry eye syndrome include tear film instability, hyperosmolarity, ocular surface inflammation and damage, and neurosensory abnormalities. As treatments for dry eye are being developed, a standardized guideline is needed to increase the efficiency of drug development and improve the quality of clinical trial data. In this paper, we present general considerations for the pharmaceutical industry and clinical trial investigators designing clinical trials focused on the development of drugs to treat dry eye syndrome.
- mRNA vaccine effectiveness against SARS-CoV-2 B.1.617.2 (Delta) and B.1.1.529 (Omicron) variant transmission from home care cases to household contacts in South Korea
- Hanul Park, Young Joon Park, Sang Eun Lee, Min Jei Lee, Hyungtae Ahn
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(6):435-442. Published online November 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0243
- 4,856 View
- 173 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 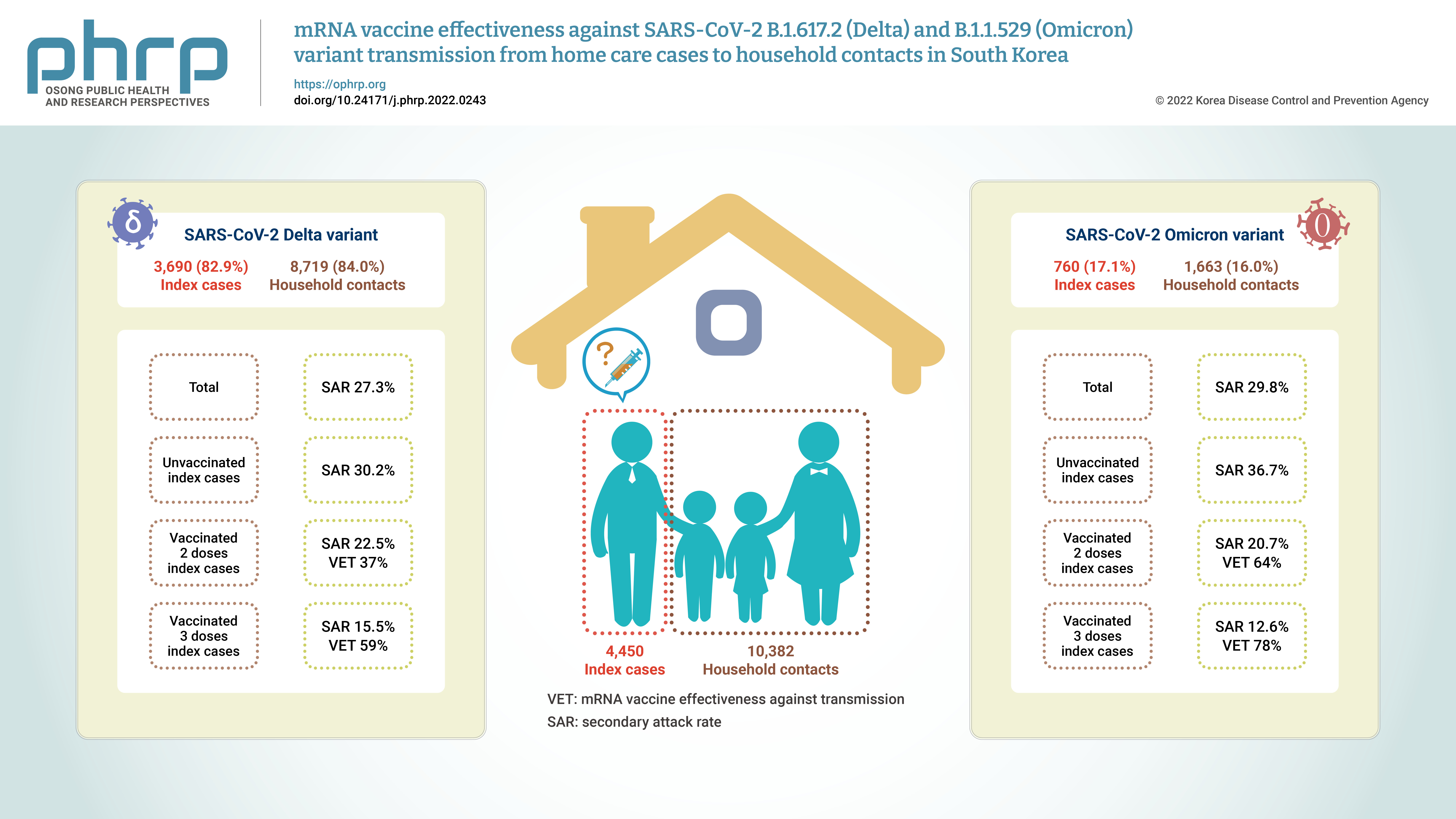
- Objectives
Household contacts of confirmed cases of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) areexposed to a high risk of viral transmission, and secondary incidence is an important indicatorof community transmission. This study analyzed the secondary attack rate and mRNA vaccineeffectiveness against transmission (VET) for index cases (patients treated at home) confirmedto be infected with the Delta and Omicron variants.Methods: The subjects of the study were 4,450 index cases and 10,382 household contacts.Logistic regression analysis was performed to compare the secondary attack rate byvaccination status, and adjusted relative risk and 95% confidence intervals were identified.Results: The secondary attack rate of the Delta variant was 27.3%, while the secondary attackrate of the Omicron variant was 29.8%. For the Delta variant, groups with less than 90 daysand more than 90 days after 2 doses of mRNA vaccination both showed a VET of 37%. For theOmicron variant, a 64% VET was found among those with less than 90 days after 2 doses ofmRNA vaccination.Conclusion: This study provides useful data on the secondary attack rate and VET of mRNAvaccines for household contacts of COVID-19 cases in South Korea. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Household secondary attack rates and risk factors during periods of SARS-CoV-2 Delta and Omicron variant predominance in the Republic of Korea
Jin Lee, Mijeong Ko, Seontae Kim, Dosang Lim, Gemma Park, Sang-Eun Lee
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2023; 14(4): 263. CrossRef
- Household secondary attack rates and risk factors during periods of SARS-CoV-2 Delta and Omicron variant predominance in the Republic of Korea
- Study of the Relationship Between Self-Efficacy, General Health and Burnout Among Iranian Health Workers
- Mohammad Amiri, Hassan Vahedi, Seyed Reza Mirhoseini, Ahmad Reza Eghtesadi, Ahmad Khosravi
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2019;10(6):359-367. Published online December 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2019.10.6.06
- 6,264 View
- 172 Download
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives To evaluate the relationship between self-efficacy, general health and burnout of the staff at Shahroud University of Medical Sciences.
Methods In 2015, 249 staff at Shahroud University of Medical Sciences (from a total reference population of 520 staff members) were selected through stratified random sampling. To collect the data, Sherer self-efficacy Scale, General Health Questionnaire and Maslach Burnout Inventory were used. The collected data were analyzed through ANOVA, Pearson correlation and Chi-square tests using SPSS 16. The relationship between self-efficacy, general health and burnout (latent factors) were studied using structural equation modeling with Stata 14.
Results The mean age of participants was 36.97 ± 7.60 years, and the mean number of years work experience was 12.29 ± 7.57. The mean scores of general health, self-efficacy and burnout were 28.24 ± 11.14, 62.30 ± 9.21 and 81.67 ± 22.18, respectively. The results of the study showed a statistically significant relationship between self-efficacy and general health which equals −0.32. A statistically significant relationship also existed between burnout scores and general health scores (beta = 0.78).
Conclusion The results showed that high self-efficacy improves the general health of employees at the Shahroud University of Medical Sciences and reduces burnout. Special attention should be paid to self-efficacy in the prevention of burnout.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Healthcare Workers’ General Health and Its Relation with Anxiety, Anger, and Posttraumatic Stress Disorder during COVID-19 Outbreak in Southeast Iran
Alireza Malakoutikhah, Leila Ahmadi Lari, Pooya Baharloo, Rasmieh Al-Amer, Mohamed Alnaiem, Hossein Khaluei, Mahlagha Dehghan, Lut Tamam
Mental Illness.2024; 2024: 1. CrossRef - Health-promoting lifestyle and its determining factors among students of public and private universities in Iran
Mohammad Amiri, Mehdi Raei, Elham Sadeghi, Leila Keikavoosi-Arani, Ahmad Khosravi
Journal of Education and Health Promotion.2023; 12(1): 239. CrossRef - The relations between mental well-being and burnout in medical staff during the COVID-19 pandemic: A network analysis
Chen Chen, Fengzhan Li, Chang Liu, Kuiliang Li, Qun Yang, Lei Ren
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The role of organizational and supervisor support in young adult workers’ resilience, efficacy and burnout during the COVID-19 pandemic
Heewon Kim, L. D. Mattson, Dacheng Zhang, Hee Jung Cho
Journal of Applied Communication Research.2022; 50(6): 691. CrossRef - A psychological health support scheme for medical teams in COVID-19 outbreak and its effectiveness
Wenhong Cheng, Fang Zhang, Zhen Liu, Hao Zhang, Yifan Lyu, Hao Xu, Yingqi Hua, Jiarong Gu, Zhi Yang, Jun Liu
General Psychiatry.2020; 33(5): e100288. CrossRef - Impact of the Family Environment on the Emotional State of Medical Staff During the COVID-19 Outbreak: The Mediating Effect of Self-Efficacy
Na Hu, Ying Li, Su-Shuang He, Lei-Lei Wang, Yan-Yan Wei, Lu Yin, Jing-Xu Chen
Frontiers in Psychology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Investigation of Health-Promoting Lifestyle and its Determinants Among Students of Medical Sciences in Iran
Mohammad Amiri, Ahmad Khosravi, Niloofar Aboozarzadeh, Leila Khojasteh, Zakieh Sadeghi, Mehdi Raei
The Open Public Health Journal.2020; 13(1): 627. CrossRef
- Healthcare Workers’ General Health and Its Relation with Anxiety, Anger, and Posttraumatic Stress Disorder during COVID-19 Outbreak in Southeast Iran
- Community-Based Risk Communication Survey: Risk Prevention Behaviors in Communities during the H1N1 crisis, 2010
- Soo Jeong Kim, Jin A. Han, Tae-Yong Lee, Tae-Yoon Hwang, Keun-Sang Kwon, Ki Soo Park, Kyung Jong Lee, Moon Shik Kim, Soon Young Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2014;5(1):9-19. Published online February 28, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2013.12.001
- 3,777 View
- 19 Download
- 22 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The present study aimed to investigate the prevalence of and factors associated with H1N1 preventive behaviors in a community-based population.
Methods
A cross-sectional study was conducted in three urban and two rural communities in Korea. Interviews were conducted with 3462 individuals (1608 men and 1854 women) aged ≥ 19 years during February–March 2010. Influenza-related information including anxiety, preventive behaviors and their perceived effectiveness, vaccination status, past influenza-like illness symptoms, and sources of and trust in information was obtained.
Results
Among 3462 participants, 173 reported experiencing influenza-like illness symptoms within the past 12 months. The mean H1N1 preventive behavior score was 25.5 ± 5.5 (out of a possible 40). The percent of participants reporting high perceived effectiveness and high anxiety was 46.2% and 21.4%, respectively. After controlling for potential confounders, H1N1 preventive behavior scores were predicted by a high (β = 3.577, p < 0.001) or moderate (β = 2.529, p < 0.001) perception of their effectiveness. Similarly, moderate (β = 1.516, p < 0.001) and high (β = 4.103, p < 0.001) anxiety scores predicted high preventive behavior scores.
Conclusion
Effective methods of promoting population behavior change may be nationwide campaigns through mass media, as well as education and promotion by health care providers and broadcasters. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Assessment of anxiety and depression among professional healthcare workers during the COVID-19 pandemic – observational cross-sectional study
Mohammed Mahmood Mohammed, Hayder Adnan Fawzi
Pharmacia.2024; 71: 1. CrossRef - Exploring the changes of individuals’ travel behavior in response to COVID-19 and their influencing factors based on mobile phone data
Shuli Zhou, Suhong Zhou, Fengrui Jing, Luhui Qi, Jianjun Li
Journal of Transport & Health.2024; 36: 101788. CrossRef - The Role of Social Media in Communication and Learning at the Time of COVID-19 Lockdown—An Online Survey
Mohammed Nahidh, Noor F. K. Al-Khawaja, Hala Mohammed Jasim, Gabriele Cervino, Marco Cicciù, Giuseppe Minervini
Dentistry Journal.2023; 11(2): 48. CrossRef - Depressive Symptomatology in Adults during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Álvaro Alexander Ocampo González, Javier Ferney Castillo García, Laura Carolina Pabón Sandoval, José Rafael Tovar Cuevas, Sirsa Aleyda Hidalgo Ibarra, Diego Alejandro Calle Sandoval, Edwin Cortés González, Kevin Steven Garcia Chica, Jonnathan Steven Pabón
Journal of Investigative Medicine.2022; 70(2): 436. CrossRef - Assessing Governments’ Emergency Responses to the COVID-19 Outbreak Using a Social Network Analysis (SNA)
Wignyo Adiyoso
SAGE Open.2022; 12(2): 215824402110711. CrossRef - Reducing Anxiety with Nature and Gardening (RANG): Evaluating the Impacts of Gardening and Outdoor Activities on Anxiety among U.S. Adults during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Megan E. Gerdes, Lucy A. Aistis, Naomi A. Sachs, Marcus Williams, Jennifer D. Roberts, Rachel E. Rosenberg Goldstein
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2022; 19(9): 5121. CrossRef - Difference between Impacts of COVID-19 on Women and Men’s Psychological, Social, Vulnerable Work Situations, and Economic Well-Being
Enrique Iglesias Martínez, Jorge Roces García, Estibaliz Jiménez Arberas, José Antonio Llosa
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2022; 19(14): 8849. CrossRef - Anxiety in Mexican adults throughout the COVID-19 pandemic: A cross sectional study
Erasmo Saucedo-Uribe, Jessica Treviño-Lozano, Pedro Jehú González-Mallozzi, Moisés Karika Enríquez-Navarro, Carlos de la Cruz-de la Cruz, Ada Nayeli Rangel-Gómez, Farid Carranza-Navarro, Dania Dalel Pardiñaz-García, Juan Manuel Fuentes-Garza
Archives of Psychiatric Nursing.2022; 41: 201. CrossRef - Influence of social responsibility and pandemic awareness of nursing students on COVID-19 preventive behaviours: a cross-sectional online survey in South Korea
Minji Kim, Hyeonkyeong Lee
BMJ Open.2022; 12(12): e061767. CrossRef - Psychological Impact on the Orthodontic Postgraduate Residents and Their Anxiety Level during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Hareem Sultan, Sameeruddin Shaikh, Sadaf Shaheen, Hana Pervez, Syed Adnan Ali, Saman Baseer, Marco Farronato
International Journal of Dentistry.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Prevalence of Health Misinformation on Social Media: Systematic Review
Victor Suarez-Lledo, Javier Alvarez-Galvez
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2021; 23(1): e17187. CrossRef - Lockdowned: Everyday mobility changes in response to COVID-19
Przemysław Borkowski, Magdalena Jażdżewska-Gutta, Agnieszka Szmelter-Jarosz
Journal of Transport Geography.2021; 90: 102906. CrossRef - Anxiety levels of university hospital nurses during the Covid‐19 pandemic
Şeyma Yurtseven, Sevban Arslan
Perspectives in Psychiatric Care.2021; 57(4): 1558. CrossRef - Assessing Mental Health of Women Living in Karachi During the Covid-19 Pandemic
Shabnam Shamim Asim, Samrah Ghani, Maheen Ahmed, Anushae Asim, Afzal Fatima Karim Qureshi
Frontiers in Global Women's Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of the Impact of a Daily Rehabilitation Program on Anxiety and Depression Symptoms and the Quality of Life of People with Mental Disorders during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Joanna Smolarczyk-Kosowska, Anna Szczegielniak, Mateusz Legutko, Adam Zaczek, Łukasz Kunert, Magdalena Piegza, Robert Pudlo
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2021; 18(4): 1434. CrossRef - Determinants of Infodemics During Disease Outbreaks: A Systematic Review
Javier Alvarez-Galvez, Victor Suarez-Lledo, Antonio Rojas-Garcia
Frontiers in Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of Decision Making of Energy Enterprises on Adaptive Behavior Amid COVID-19
Xiurui Yang, Jizu Li
Frontiers in Energy Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Women Suffered More Emotional and Life Distress than Men during the COVID-19 Pandemic: The Role of Pathogen Disgust Sensitivity
Yi Ding, Jie Yang, Tingting Ji, Yongyu Guo
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2021; 18(16): 8539. CrossRef - Towards a data-driven characterization of behavioral changes induced by the seasonal flu
Nicolò Gozzi, Daniela Perrotta, Daniela Paolotti, Nicola Perra, Benjamin Althouse
PLOS Computational Biology.2020; 16(5): e1007879. CrossRef - Social Distancing and Transmission-reducing Practices during the 2019 Coronavirus Disease and 2015 Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Outbreaks in Korea
Won Mo Jang, Deok Hyun Jang, Jin Yong Lee
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Trends in Infectious Disease Mortality, South Korea, 1983–2015
Young June Choe, Seung-Ah Choe, Sung-Il Cho
Emerging Infectious Diseases.2018; 24(2): 320. CrossRef - Preventive behaviors by the level of recognized sensitivity to infection during the MERS outbreak in 2015
Soon Young Lee, Hee Jung Yang, Gawon Kim, Hae-Kwan Cheong, Bo Youl Choi
Epidemiology and Health.2016; : e2016051. CrossRef
- Assessment of anxiety and depression among professional healthcare workers during the COVID-19 pandemic – observational cross-sectional study



 First
First Prev
Prev


