Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Osong Public Health Res Perspect > Volume 11(2); 2020 > Article
-
Original Article
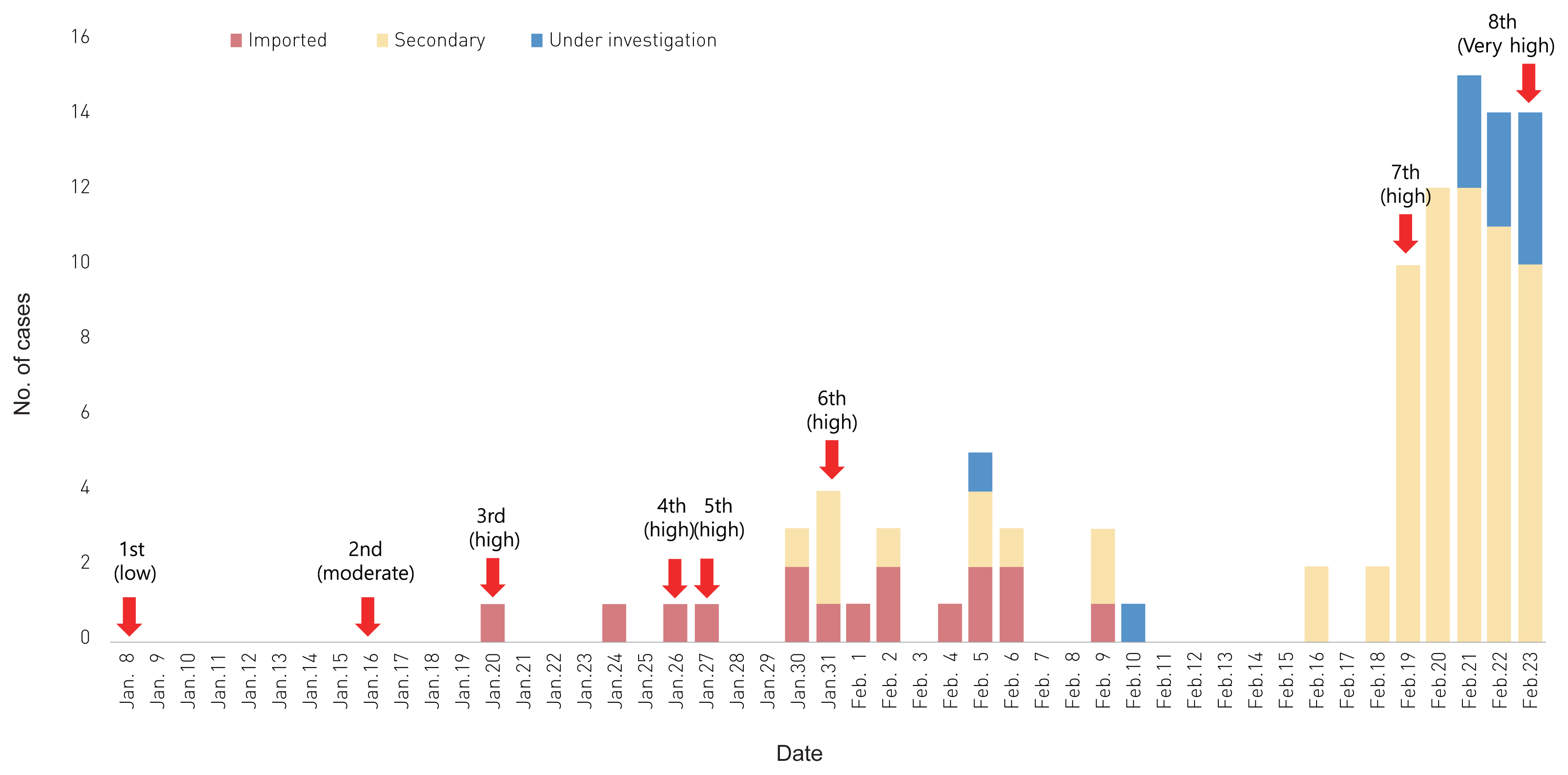
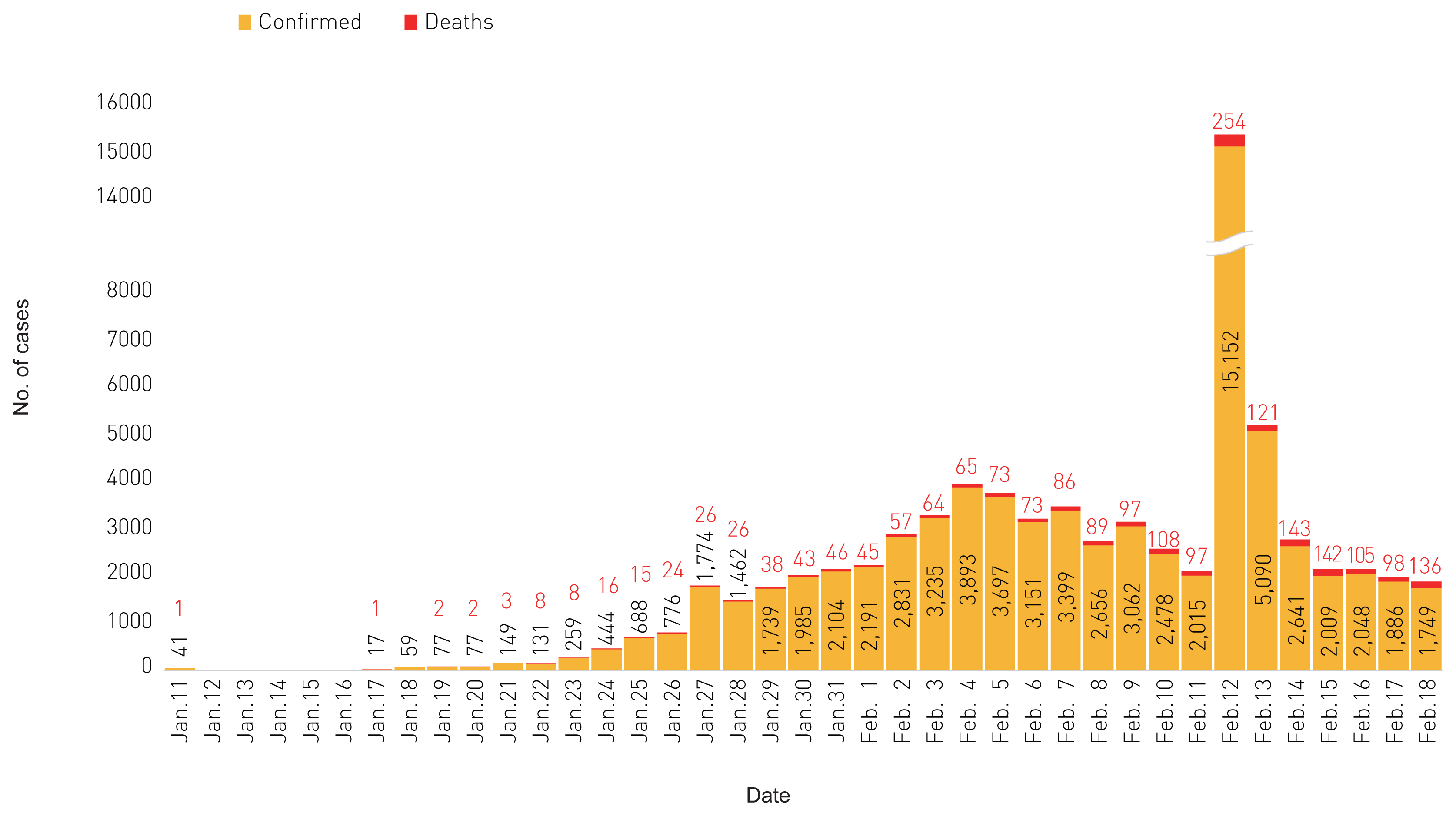
KCDC Risk Assessments on the Initial Phase of the COVID-19 Outbreak in Korea - Inho Kim, Jia Lee, Jihee Lee, Eensuk Shin, Chaeshin Chu, Seon Kui Lee
-
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives 2020;11(2):67-73.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2020.11.2.02
Published online: April 30, 2020
Division of Risk Assessment and International Cooperation, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Cheongju, Korea
- *Corresponding author: Seon Kui Lee, Division of Risk Assessment and International Cooperation, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Cheongju, Korea, E-mail: byuly74@korea.kr
• Received: March 23, 2020 • Revised: March 24, 2020 • Accepted: March 25, 2020
Copyright ©2020, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
Figure & Data
References
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- COVID-19 Pandemic Risk Assessment: Systematic Review
Amanda Chu, Patrick Kwok, Jacky Chan, Mike So
Risk Management and Healthcare Policy.2024; Volume 17: 903. CrossRef - COVID-19 Cases and Deaths among Healthcare Personnel with the Progression of the Pandemic in Korea from March 2020 to February 2022
Yeonju Kim, Sung-Chan Yang, Jinhwa Jang, Shin Young Park, Seong Sun Kim, Chansoo Kim, Donghyok Kwon, Sang-Won Lee
Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease.2023; 8(6): 308. CrossRef - A resposta da Coreia do Sul à pandemia de COVID-19: lições aprendidas e recomendações a gestores
Thais Regis Aranha Rossi, Catharina Leite Matos Soares, Gerluce Alves Silva, Jairnilson Silva Paim, Lígia Maria Vieira-da-Silva
Cadernos de Saúde Pública.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Nursing Experience of New Nurses Caring for COVID-19 Patients in Military Hospitals: A Qualitative Study
Young-Hoon Kwon, Hye-Ju Han, Eunyoung Park
Healthcare.2022; 10(4): 744. CrossRef - South Korea’s fast response to coronavirus disease: implications on public policy and public management theory
Pan Suk Kim
Public Management Review.2021; 23(12): 1736. CrossRef - Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in Fecal Samples From Patients With Asymptomatic and Mild COVID-19 in Korea
Soo-kyung Park, Chil-Woo Lee, Dong-Il Park, Hee-Yeon Woo, Hae Suk Cheong, Ho Cheol Shin, Kwangsung Ahn, Min-Jung Kwon, Eun-Jeong Joo
Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2021; 19(7): 1387. CrossRef - Systematic assessment of South Korea’s capabilities to control COVID-19
Katelyn J. Yoo, Soonman Kwon, Yoonjung Choi, David M. Bishai
Health Policy.2021; 125(5): 568. CrossRef - Environmental risk assessment and comprehensive index model of disaster loss for COVID-19 transmission
Sulin Pang, Xiaofeng Hu, Zhiming Wen
Environmental Technology & Innovation.2021; 23: 101597. CrossRef - Transmission dynamics and control of two epidemic waves of SARS-CoV-2 in South Korea
Sukhyun Ryu, Sheikh Taslim Ali, Eunbi Noh, Dasom Kim, Eric H. Y. Lau, Benjamin J. Cowling
BMC Infectious Diseases.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Identifying and Prioritizing Ways to Improve Oman’s Tourism Sector in the Corona Period
Zakiya Salim Al-Hasni
Journal of Intercultural Management.2021; 13(1): 144. CrossRef - Decreased Use of Broad-Spectrum Antibiotics During the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Epidemic in South Korea
Sukhyun Ryu, Youngsik Hwang, Sheikh Taslim Ali, Dong-Sook Kim, Eili Y Klein, Eric H Y Lau, Benjamin J Cowling
The Journal of Infectious Diseases.2021; 224(6): 949. CrossRef - COVID-19 and Cancer Therapy: Interrelationships and Management of Cancer Cases in the Era of COVID-19
Simon N. Mbugua, Lydia W. Njenga, Ruth A. Odhiambo, Shem O. Wandiga, Martin O. Onani, Nenad Ignjatovic
Journal of Chemistry.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Challenges to manage pandemic of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in Iran with a special situation: a qualitative multi-method study
Hamidreza Khankeh, Mehrdad Farrokhi, Juliet Roudini, Negar Pourvakhshoori, Shokoufeh Ahmadi, Masoumeh Abbasabadi-Arab, Nader Majidi Bajerge, Babak Farzinnia, Pirhossain Kolivand, Vahid Delshad, Mohammad Saeed Khanjani, Sadegh Ahmadi-Mazhin, Ali Sadeghi-Mo
BMC Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Nonpharmaceutical Interventions on Transmission of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2, South Korea, 2020
Sukhyun Ryu, Seikh Taslim Ali, Cheolsun Jang, Baekjin Kim, Benjamin J. Cowling
Emerging Infectious Diseases.2020; 26(10): 2406. CrossRef - Early Trend of Imported COVID-19 Cases in South Korea
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2020; 11(3): 140. CrossRef - Effect of Underlying Comorbidities on the Infection and Severity of COVID-19 in Korea: a Nationwide Case-Control Study
Wonjun Ji, Kyungmin Huh, Minsun Kang, Jinwook Hong, Gi Hwan Bae, Rugyeom Lee, Yewon Na, Hyoseon Choi, Seon Yeong Gong, Yoon-Hyeong Choi, Kwang-Pil Ko, Jeong-Soo Im, Jaehun Jung
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Innovative countermeasures can maintain cancer care continuity during the coronavirus disease-2019 pandemic in Korea
Soohyeon Lee, Ah-reum Lim, Min Ja Kim, Yoon Ji Choi, Ju Won Kim, Kyong Hwa Park, Sang Won Shin, Yeul Hong Kim
European Journal of Cancer.2020; 136: 69. CrossRef




 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite