Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Factors associated with the combination of general and abdominal obesity in middle-aged and older Korean women: a cross-sectional study
- Jin Suk Ra
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(5):379-387. Published online September 20, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0089
- 1,036 View
- 39 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 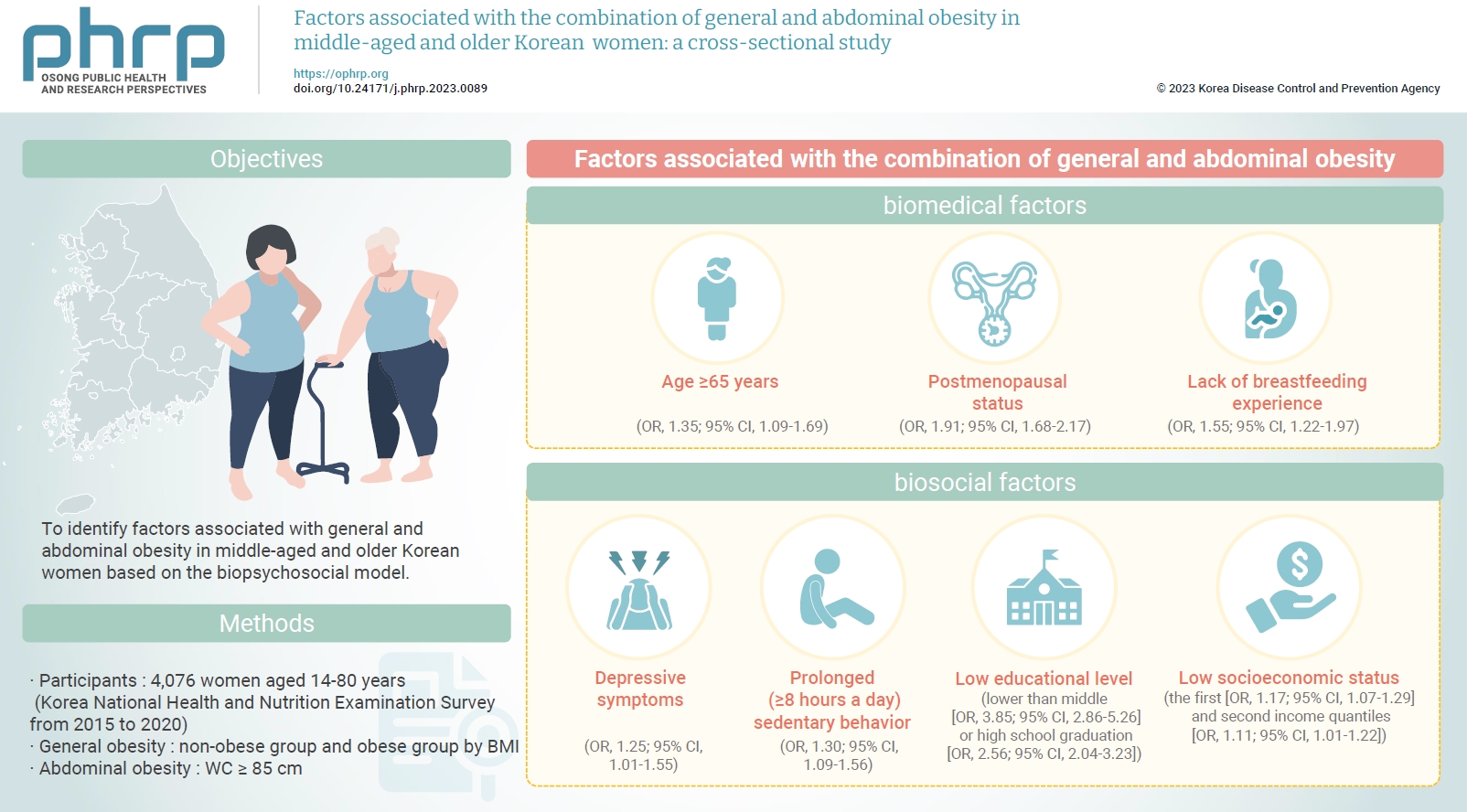
- Objectives
To identify factors associated with general and abdominal obesity in middle-aged and older Korean women based on the biopsychosocial model. Methods: Data from 4,076 women aged ≥45 years who participated in the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey from 2015 to 2020 were analyzed. Complex sampling analysis was performed using IBM SPSS ver. 26.0. Results: The combination of general and abdominal obesity was positively associated with age ≥65 years, postmenopausal status, and without breastfeeding experience among biomedical factors; depressive symptoms and prolonged (≥8 hours a day) sedentary behavior among psychosocial factors; and an educational level lower than middle or high school graduation and the first and second income quantiles among biosocial factors. Conclusion: Healthcare providers in communities and public societies should screen for risk factors for the combination of general and abdominal obesity while considering non-modifiable biomedical (e.g., age) and biosocial factors (e.g., educational level). In addition, intervention strategies should be developed by considering modifiable psychosocial factors such as sedentary behavior.
- Insufficient weight management in pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus
- Kyunghee Han, Dong Wook Kwak, Hyun Mee Ryu, Hyun-Young Park
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(4):242-251. Published online August 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0182
- 2,449 View
- 93 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Objectives
This study investigated whether weight was managed appropriately in pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) and examined the association between insufficient gestational weight gain (GWG) and adverse pregnancy outcomes.
Methods
The study included 235 pregnant women with GDM from the Korean Pregnancy Outcome Study. GWG from the second to the third trimester (kg/wk) and total GWG (kg) were classified as insufficient, appropriate, or excessive according to the 2009 Institute of Medicine guidelines. Adverse pregnancy outcomes included maternal (hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, preterm birth, cesarean delivery, and delivery complications) and infant (low birth weight, high birth weight, neonatal intensive care unit admission, and congenital anomalies) outcomes.
Results
The proportion of pregnant women with GDM who had insufficient GWG from the second to the third trimester was 52.3%, and that of participants with total insufficient GWG was 48.1%. There were no significant associations between insufficient GWG from the second to the third trimester and adverse pregnancy outcomes. Participants with total insufficient GWG had a significantly lower risk of preterm birth (odds ratio [OR], 0.17; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.05–0.60) and high birth weight (OR, 0.23; 95% CI, 0.07–0.80).
Conclusion
Our findings suggest the importance of appropriate weight management and the need for GWG guidelines for pregnant women with GDM.
- Psychological outcomes of the COVID-19 pandemic among pregnant women in Indonesia: a cross-sectional study
- Rahmah Hida Nurrizka, Yuri Nurdiantami, Feda Anisah Makkiyah
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2021;12(2):80-87. Published online April 29, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.12.2.05
- 6,694 View
- 237 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The objective of this study was to analyze the psychological outcomes of pregnant women during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic in several areas that are epicenters for the spread of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in Indonesia.
Methods
This cross-sectional study used data obtained from an online survey administered to 120 women who were pregnant and gave birth during the COVID-19 pandemic in Indonesia. The psychological condition of pregnant women was measured using the Depression, Anxiety, and Stress Scale-21 questionnaire which was modified for conditions experienced during the COVID-19 pandemic. We classified pregnant women into 2 groups according to their psychological condition: pregnant women who experienced anxiety and pregnant women who did not experience anxiety or felt normal. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis was undertaken for the 2 groups. This study also used univariate analysis and bivariate analysis.
Results
The results of the ROC analysis resulted in a cutoff score of 3.56. The proportion of respondents who felt anxious was 53.3% and the proportion of respondents who did not feel anxious or felt normal was 46.7%. Anxiety was most common among pregnant women with high education levels, gestational age <19 weeks, and working pregnant women.
Conclusion
Maternal health services need to be performed with strict health protocols, complemented by pregnancy counseling services. This will provide a feeling of comfort and safety as pregnant women receive health services and give birth. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The prevalence of mental ill-health in women during pregnancy and after childbirth during the Covid-19 pandemic: a systematic review and Meta-analysis
Gayathri Delanerolle, Mary McCauley, Martin Hirsch, Yutian Zeng, Xu Cong, Heitor Cavalini, Sana Sajid, Ashish Shetty, Shanaya Rathod, Jian Qing Shi, Dharani K. Hapangama, Peter Phiri
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of COVID-19 on women’s experiences of pregnancy, birth and postpartum in Indonesia: a rapid online survey
Linda McGowan, Andari Astuti, Firdaus Hafidz, Cesa Pratiwi, Vinami Yulian, Elizabeth Hughes, Arum Pratiwi, Emi Nurjasmi Indomo, Yu Fu
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk factors for depression and anxiety in pregnant women during the COVID-19 pandemic: Evidence from meta-analysis
Yupeng Luo, Kui Zhang, Mengxue Huang, Changjian Qiu, Ali Rostami
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(3): e0265021. CrossRef
- The prevalence of mental ill-health in women during pregnancy and after childbirth during the Covid-19 pandemic: a systematic review and Meta-analysis
- Use of Menstrual Sanitary Products in Women of Reproductive Age: Korea Nurses’ Health Study
- Hansol Choi, Nam-Kyoo Lim, Heeja Jung, Oksoo Kim, Hyun-Young Park
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2021;12(1):20-28. Published online February 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.12.1.04
- 9,566 View
- 257 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material Objectives The use of menstrual hygiene products and its effect on women’s health remains under studied. Patterns of menstrual hygiene product use and the rationale behind choices among Korean women aged 18–45 years were examined.
Methods This cross-sectional study was a part of the Korea Nurses’ Health Study. A total of 20,613 nurses participated, and 8,658 nurses participated in Module 7 which included a menstrual hygiene products-related survey. The data were collected through the mobile survey using a self-reported questionnaire. Participants’ use of menstrual hygiene products and related characteristics were analyzed using frequency (percentage) or mean (SD).
Results The most common types of menstrual hygiene products across all age groups were disposable menstrual pads (89.0%), followed by cloth menstrual pads (4.5%), tampons (4.2%), and only 1.6% used a menstrual cup. Disposable menstrual pads were the most common across all age groups, but in those aged under 30 years this was followed by tampon use (6%). The most important criteria when choosing a menstrual hygiene product was comfort for disposable menstrual pads (31.3%) and tampons (41.5%), natural ingredients or organic products for cloth menstrual pads (51.4%), and custom fit for the menstrual cup (50.7%). However, for all menstrual hygiene products (except cloth menstrual pads), there was a higher proportion of anxiety than perception of safety, and low awareness of toxic shock syndrome.
Conclusion It is important for women to use menstrual hygiene products with confidence. More research is needed to better understand potential health effects of menstrual hygiene products.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- MIMA 2.0 - Compact and portable Multifunctional IoT integrated Menstrual Aid
Kumar J. Jyothish, Shreya Shivangi, Amish Bibhu, Subhankar Mishra, Sulagna Saha
Internet of Things.2024; 25: 101075. CrossRef - Knowledge, attitude, and practice of menstrual hygiene at a medical and health sciences university
Rajani Dube, Huma Zaidi, Shehla Shafi Khan
Journal of Advanced Pharmacy Education and Researc.2024; 14(1): 63. CrossRef - Gynecological and Obstetric Crisis in Gaza Conflict Area: A Call for Action
Ibraheem Alkhawaldeh, Hamza Alsalhi, Mostafa Moawad, Yasmeen Jamal Alabdallat
JAP Academy Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Reusable period products: use and perceptions among young people in Victoria, Australia
Caitlin Ramsay, Julie Hennegan, Caitlin H. Douglass, Sarah Eddy, Alexandra Head, Megan S. C. Lim
BMC Women's Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploratory systematic review and meta-analysis on period poverty
Gayathri Delanerolle, Xiao-Jie Yang, Heitor Cavalini, Om P Kurmi, Camilla Mørk Røstvik, Ashish Shetty, Lucky Saraswat, Julie Taylor, Sana Sajid, Shanaya Rathod, Jian-Qing Shi, Peter Phiri
World Journal of Meta-Analysis.2023; 11(5): 196. CrossRef - Key findings on women’s reproductive health: the Korea Nurses’ Health Study
Chiyoung Cha, Heeja Jung
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2023; 29(2): 81. CrossRef - Nonconventional Menstrual Hygiene Products and its Usage among Reproductive age Group Women in India – A Cross-Sectional Study
Dharmaraj Rock Britto, Neethu George, Abdul Malik Shagirunisha Rizvana, Josephin Shalini Ratchagar, Tamilarasan Muniyapillai, Karthikeyan Kulothungan
Journal of Datta Meghe Institute of Medical Scienc.2023; 18(3): 357. CrossRef - Assessment of knowledge, attitudes, and practices regarding menstruation and menstrual hygiene among early-reproductive aged women in Bangladesh: a cross-sectional survey
Abu Bakkar Siddique, Sudipto Deb Nath, Mahfuza Mubarak, Amena Akter, Sanjida Mehrin, Mst Jemi Hkatun, Antara Parvine Liza, M. Ziaul Amin
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Use and perceptions on reusable and non-reusable menstrual products in Spain: A mixed-methods study
Laura Medina-Perucha, Tomàs López-Jiménez, Anna Sofie Holst, Constanza Jacques-Aviñó, Jordina Munrós-Feliu, Cristina Martínez-Bueno, Carme Valls-Llobet, Diana Pinzón Sanabria, Mª Mercedes Vicente-Hernández, Anna Berenguera, Muhammad Shahzad Aslam
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(3): e0265646. CrossRef - Women’s attitudes toward certification logos, labels, and advertisements for organic disposable sanitary pads: results from a multi-city cross-sectional survey
Hayeon Kim, Jinyoung Jung, Yun-Kyoung Song, Taegwon Chang, Sungmin Park, Jiwon Park, Kyungim Kim
BMC Women's Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Sanitation and hygiene practices of secondary school students from Mtwara town in Tanzania
Obadia Kyetuza Bishoge, Ademola Kabir Aremu, Dickson Dare Ajayi, Sayoki Godfrey Mfinanga
International Journal of Health Promotion and Educ.2022; : 1. CrossRef
- MIMA 2.0 - Compact and portable Multifunctional IoT integrated Menstrual Aid
- Analysis of Women’s Health Online News Articles Using Topic Modeling
- Kyoung Won Cho, Shine Young Kim, Young Woon Woo
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2019;10(3):158-169. Published online June 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2019.10.3.07
- 8,960 View
- 46 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives This research aimed to understand the popularity of topics in the field of women’s health through analysis of online news articles which were chronologically classified and examined to determine how women’s health and diseases had changed over time.
Methods Women’s health and disease news articles were collated from a popular news website between 1993 to 2015 and preprocessed using gynecological medical terminology, Korean words and nouns (excluding general nouns not related to women’s healthcare topics). The resultant articles (N = 7,710) were analyzed using the Latent Dirichlet Allocation algorithm and major topics were extracted. Topic trends were analyzed by year and period for women’s health.
Results It was observed that most of the women’s health articles were focused on “Healthcare”, and 9 other topics were identified that represented a relatively small proportion in 1993–2000. In 2001–2005, most of the articles were focused on “Medical Services” and “Dietary Supplements” with some specific topics that peaked people’s interest, as compared to those focused on “Healthcare” in the 1990s. It was also observed that differences in the proportion of each topic was small after 2011.
Conclusion Changes in topics related to women’s disease were not clearly distinguished in the 1990s but this changed from 2001where articles related to “women disease” appeared as articles on the topics of various diseases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Review on News About Midwifery and Fertility Covered on Newspapers in Turkey
Sümeyye ALTIPARMAK, Emel GÜÇLÜ CİHAN, Hatice Gül ÖZTAŞ, Hülya KAMALAK
Medical Records.2021; 3(2): 118. CrossRef
- Review on News About Midwifery and Fertility Covered on Newspapers in Turkey
- Associated Factors of Ischemic Heart Disease Identified Among Post-Menopausal Women
- Jin Suk Ra, Hye Sun Kim, Yeon-Hee Jeong
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2019;10(2):56-63. Published online April 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2019.10.2.03
- 6,914 View
- 137 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives This study identifies associated factors of ischemic heart disease (IHD) among post-menopausal Korean women at the biomedical (age, family history of hypertension, dyslipidemia, type 2 diabetes mellitus, or cerebro-cardiovascular disease, body mass index, and metabolic syndrome), biosocial (socioeconomic status and educational level), and psychosocial levels (stress, depression, smoking, binge alcohol consumption, and physical activity).
Methods This study used a cross-sectional design with secondary data analysis of the 2013–2016 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Data from 3,636 women were analyzed by logistic regression analysis using a complex sample procedure.
Results Of the biomedical factors, older age [odds ratio (OR): 2.99, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.87–4.80,
p < 0.001], family history (OR: 2.29, 95% CI: 1.44–3.65,p = 0.001), and metabolic syndrome (OR: 1.93, 95% CI: 1.27–2.95,p = 0.002) were associated with IHD in post-menopausal women. Of the psychosocial factors, depression (OR: 2.56, 95% CI: 1.66–3.96,p < 0.001) and smoking (OR: 1.92, CI: 1.04–3.55,p = 0.038) were associated with IHD in post-menopausal women.Conclusion These findings suggest that healthcare providers need to consider the contributing adverse effects of older age, family history, metabolic syndrome, depression and smoking when evaluating risk factors for IHD in post-menopausal women.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Vasomotor symptoms, cardiovascular risk factors, and cardiovascular disease risk among Chinese postmenopausal women in Hong Kong
Sek Ying Chair, Sally Wai Sze Lo, Ho Yu Cheung, Janet Wing Hung Sit, Qun Wang, Huijing Zou
Women & Health.2022; 62(7): 621. CrossRef - Association of rheumatoid arthritis and high sodium intake with major adverse cardiovascular events: a cross-sectional study from the seventh Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Jeong-Hyeon Bae, Min-Young Shin, Eun Ha Kang, Yun Jong Lee, You-Jung Ha
BMJ Open.2021; 11(12): e056255. CrossRef - Comparison of early cardiovascular risk among Brazilian and African university students
Ederson Laurindo Holanda de Sousa, Jânio Emanuel Andrade Cavalcante, Daniel Freire de Sousa, Jamile Magalhães Ferreira, Richard Rarison Cavalcante Meneses, Duaran Lopes Sousa, Allyson Jordan Xavier da Silva, Raimundo Rigoberto Barbosa Xavier Filho, Elias
Clinical Biochemistry.2020; 75: 7. CrossRef - Beneficial Effects of Breastfeeding on the Prevention of Metabolic Syndrome Among Postmenopausal Women
Jin Suk Ra, Soon Ok Kim
Asian Nursing Research.2020; 14(3): 173. CrossRef
- Vasomotor symptoms, cardiovascular risk factors, and cardiovascular disease risk among Chinese postmenopausal women in Hong Kong
- Effect of Obesity on Blood Pressure and Arterial Stiffness in Middle-Aged Korean Women
- Won-Mok Son, Do-Yeon Kim, You-Sin Kim, Min-Seong Ha
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2017;8(6):369-372. Published online December 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2017.8.6.02
- 3,996 View
- 42 Download
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives Our study aims to provide basic scientific data on the importance of obesity management in middle-aged Korean women by analyzing its effects on blood pressure and arterial stiffness. In addition, we examined the correlations of these two parameters.
Methods The study participants were 40 middle-aged female volunteers, who were classified into obesity group (n = 20) and normal weight group (n = 20). Statistical analysis was performed using independent
t -test and the Pearson correlation coefficient was used to correlate blood pressure and arterial stiffness.Results This study evaluated the systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, and pulse wave velocity (PWV). These results were higher in the obesity group than the normal weight group. Furthermore, blood pressure and arterial stiffness (PWV, augmentation pressure) were static correlated.
Conclusion Obesity is closely related to blood pressure and arterial stiffness. Therefore, indices for blood pressure and arterial stiffness may play a vital role in predicting and preventing obesity and its sequelae.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Food readjustment plus exercise training improves cardiovascular autonomic control and baroreflex sensitivity in high‐fat diet‐fed ovariectomized mice
Bruno Nascimento‐Carvalho, Adriano Dos‐Santos, Nicolas Da Costa‐Santos, Sabrina L. Carvalho, Oscar A. de Moraes, Camila P. Santos, Katia De Angelis, Erico C. Caperuto, Maria‐Claudia Irigoyen, Katia B. Scapini, Iris C. Sanches
Physiological Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations between body composition and cardiovascular disease risk in pre- and postmenopausal women
Nirmala Rathnayake, Gayani Alwis, Janaka Lenora, Sarath Lekamwasam
Journal of Health, Population and Nutrition.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Vascular Function, Cardiometabolic Parameters, Hemorheological Function, and Cardiorespiratory Fitness Between Middle-Aged Korean Women With and Without Obesity—A Pilot Study
Hun-Young Park, Won-Sang Jung, Sung-Woo Kim, Kyounghwa Jung, Kiwon Lim
Frontiers in Physiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of femoral and carotid arteries in terms of pulse check in cardiopulmonary resuscitation: A prospective observational study
Gökhan Yılmaz, Oğuzhan Bol
Resuscitation.2021; 162: 56. CrossRef - Effect of yoga on pulse rate and blood pressure among women
G Kaleeswari, CVasantha Kalyani, JS Jayarani, KusumK Rohilla
Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.2021; 10(10): 3670. CrossRef - Association of obesity with arterial stiffness: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA)
Jeongok G. Logan, Hyojung Kang, Soyoun Kim, Daniel Duprez, Younghoon Kwon, David R. Jacobs, Nketi Forbang, Jennifer Mason Lobo, Min-Woong Sohn
Vascular Medicine.2020; 25(4): 309. CrossRef - The Feasibility and Applications of Non-invasive Cardiac Monitoring in Obese Patients Undergoing Day-case Surgery: Results of a Prospective Observational Study
P. Sansone, L.G. Giaccari, U. Colella, F. Coppolino, M.C. Pace, M.B. Passavanti, V. Pota, C. Aurilio
The Open Anesthesia Journal.2020; 14(1): 80. CrossRef - The Impact of Obesity on Nighttime Blood Pressure Dipping
Beata Moczulska, Maciej Zechowicz, Sylwia Leśniewska, Karolina Osowiecka, Leszek Gromadziński
Medicina.2020; 56(12): 700. CrossRef - Greater Adherence to Life’s Simple 7 Is Associated With Less Arterial Stiffness: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study
Abayomi O Oyenuga, Aaron R Folsom, Susan Cheng, Hirofumi Tanaka, Michelle L Meyer
American Journal of Hypertension.2019; 32(8): 769. CrossRef
- Food readjustment plus exercise training improves cardiovascular autonomic control and baroreflex sensitivity in high‐fat diet‐fed ovariectomized mice
- A Case–control Study on the Relationship between
Mycoplasma genitalium Infection in Women with Normal Pregnancy and Spontaneous Abortion using Polymerase Chain Reaction - Rashid Ramazanzadeh, Mazaher Khodabandehloo, Fariba Farhadifar, Samaneh Rouhi, Amjad Ahmadi, Shaho Menbari, Fariba Fallahi, Reza Mirnejad
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2016;7(5):334-338. Published online October 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2016.07.001
- 2,931 View
- 22 Download
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Mycoplasma genitalium infections are suggested as causes of a number of pathological outcomes in pregnant women. The aim of this study was to evaluate the frequency of M. genitalium infections among pregnant women and its association with spontaneous abortion.
Methods
In this case–control study we included 109 women with spontaneous abortion with a gestational age of 10–20 weeks (patients), and 109 women with normal pregnancy with a gestational age of 20–37 weeks (controls) in Sanandaj, Iran. Using specific primers and extracted DNA from endocervical swabs, a polymerase chain reaction was conducted for the detection of M. genitalium infection in both groups.
Results
The frequency of M. genitalium infection in patient and control groups was one (0.91%) and three (2.75%), respectively. In both control and patient groups using Fisher test, no association between mycoplasma infection and spontaneous abortion was seen.
Conclusion
M. genitalium may be positive in the genital tract of some pregnant women but was not associated with spontaneous abortion. Further powerful studies with larger sample sizes are needed for the determination of a possible role of M. genitalium in pregnancy outcomes and spontaneous abortion. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The association between genital mycoplasma infection and spontaneous abortion: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Wei Chen, Shimin Xiong, Xubo Shen, Ting Qiu, Caidie He, Songlin An, Yuanzhong Zhou
Reproductive Toxicology.2023; 116: 108334. CrossRef - Latest Advances in Laboratory Detection of Mycoplasma genitalium
Ken B. Waites, Donna M. Crabb, Amy E. Ratliff, William M. Geisler, T. Prescott Atkinson, Li Xiao, Romney M. Humphries
Journal of Clinical Microbiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Weighing Potential Benefits and Harms of Mycoplasma genitalium Testing and Treatment Approaches
Lisa E. Manhart, William M. Geisler, Catriona S. Bradshaw, Jørgen S. Jensen, David H. Martin
Emerging Infectious Diseases.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Associations of Genital Mycoplasmas with Female Infertility and Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes: a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Caifeng Ma, Jikun Du, Yuhong Dou, Rui Chen, Yuxia Li, Lijun Zhao, Helu Liu, Kebin Zhang
Reproductive Sciences.2021; 28(11): 3013. CrossRef - Mollicutes antibiotic resistance profile and presence of genital abnormalities in couples attending an infertility clinic
Brenda Maldonado-Arriaga, Noé Escobar-Escamilla, Juan Carlos Pérez-Razo, Sofia Lizeth Alcaráz-Estrada, Ignacio Flores-Sánchez, Daniel Moreno-García, Rebeca Pérez-Cabeza de Vaca, Paul Mondragón-Terán, Jonathan Shaw, Cecilia Hernandez-Cortez, Graciela Castr
Journal of International Medical Research.2020; 48(1): 030006051982894. CrossRef - Association of spontaneous abortion and Ureaplasma parvum detected in placental tissue
C. N. T. Oliveira, M. T. S. Oliveira, H. B. M. Oliveira, L. S. C. Silva, R. S. Freire, M. N. Santos Júnior, M. V. Oliveira, J. Timenetsky, G. B. Campos, L. M. Marques
Epidemiology and Infection.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Epidemiology of genital infections caused by Mycoplasma hominis, M. genitalium and Ureaplasma urealyticum in Iran; a systematic review and meta-analysis study (2000–2019)
Khadijeh Moridi, Mohammad Hemmaty, Amir Azimian, Mohammad Hosein Fallah, Hamid Khaneghahi Abyaneh, Kiarash Ghazvini
BMC Public Health.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence and incidence of Mycoplasma genitalium in a cohort of HIV-infected and HIV-uninfected pregnant women in Cape Town, South Africa
Carolyn P Smullin, Hunter Green, Remco Peters, Dorothy Nyemba, Yamkela Qayiya, Landon Myer, Jeffrey Klausner, Dvora Joseph Davey
Sexually Transmitted Infections.2020; 96(7): 501. CrossRef - Frequency of Chlamydia trachomatis, Mycoplasma genitalium, and Ureaplasma urealyticum Isolated From Vaginal Samples of Women in Kerman, Iran
Zahra Zahirnia, Shahla Mansouri, Fereshteh Saffari, Ghazal Mansouri
Archives of Clinical Infectious Diseases.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - High Prevalence of Leptotrichia amnionii, Atopobium vaginae, Sneathia sanguinegens, and Factor 1 Microbes and Association of Spontaneous Abortion among Korean Women
Sang Soo Seo, Selvaraj Arokiyaraj, Mi Kyung Kim, Hea Young Oh, Minji Kwon, Ji Sook Kong, Moon Kyung Shin, Ye Lee Yu, Jae Kwan Lee
BioMed Research International.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef
- The association between genital mycoplasma infection and spontaneous abortion: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Gender-based Violence Among Pregnant Women of Syangja District, Nepal
- Samjhana Gurung, Jeevan Acharya
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2016;7(2):101-107. Published online April 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2015.11.010
- 3,192 View
- 20 Download
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aims to determine prevalence of gender-based violence among pregnant women attending an antenatal care (ANC) clinic.
Methods
Between September 2014 and December 2014, a cross-sectional study was conducted among 202 pregnant women attending the antenatal ward of the Primary Healthcare Centre (PHC) of Syangja district, Nepal. The data were collected using semistructure questionnaires with face-to-face interviews. SPSS software (IBM Corp, Armonk, NY, USA) was used for analysis the data.
Results
The prevalence rate of gender-based violence was found to be 91.1% (184). Most of the respondents (87%) faced economic violence followed by psychological (53.8%), sexual (41.8%), and physical (4.3%) violence. Women experienced: (1) psychological violence with most complaining of angry looks followed by jealousy or anger while talking with other men, insults using abusive language and neglect; (2) economic violence with most complaining of financial hardship, denial of basic needs and an insistence on knowing where respondents were and restricting them to parents' home or friends/relatives' houses (jealousy); (3) physical violence by slapping, pushing, shaking, or throwing something at her, twisting arm or pulling hair, and punching and kicking; and (4) sexual violence by physically forcing her to have sexual intercourse without consent, and hurting or causing injury to private parts. Most (100%) of the perpetrators were found to be husbands and mothers-in-law (10.7%) who violated them rarely.
Conclusion
The prevalence of gender-based violence (GBV) among pregnant women attending the ANC clinic was greater in the Syangja district of Nepal. Women's empowerment, economic autonomy, sensitization, informal or formal training regarding GBV for men and women, and the need for large-scale population-based surveys are the major recommendations of this study. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence of Violence in Iranian Pregnant Women: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Shohreh Shafiei, Maryam Chegeni, Sima Afrashteh, Hamid Reza Shoraka, Azam Bazrafshan, Zohreh Bagherinezhad, Masumeh Ghazanfarpour, Hamid Sharifi
Maternal and Child Health Journal.2022; 26(10): 1983. CrossRef - Gendered consequences of social changes in Nepal: rich possibilities
Radha Adhikari, Jeevan R Sharma
European Bulletin of Himalayan Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Gebelikte aile içi şiddete maruz kalmanın postpartum depresyon ve maternal bağlanmaya etkisi
Ayten TAŞPINAR, Seher SARIKAYA KARABUDAK, Ayden ÇOBAN, Filiz ADANA
Adıyaman Üniversitesi Sağlık Bilimleri Dergisi.2021; : 94. CrossRef - Is there an association between fertility and domestic violence in Nepal?
Sarah Raifman, Mahesh Puri, Jennet Arcara, Nadia Diamond-Smith
AJOG Global Reports.2021; 1(2): 100011. CrossRef - Intimate partner violence among pregnant women attending antenatal care services in the rural Gambia
Joseph W. Jatta, Ararso Baru, Olufunmilayo I. Fawole, Oladosu A. Ojengbede, Yong-hui Dang
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(8): e0255723. CrossRef - Factors associated with contraceptive use in rural Nepal: Gender and decision-making
Preeti K. Mahato, Zoë A. Sheppard, Edwin van Teijlingen, Nisa De Souza
Sexual & Reproductive Healthcare.2020; 24: 100507. CrossRef - Experiences and Perceptions of Abused Turkish Women Regarding Violence Against Women
Emel Bahadir-Yilmaz, Fatma Oz
Community Mental Health Journal.2019; 55(4): 686. CrossRef - Intimate Partner Violence in Relation to Husband Characteristics and Women Empowerment: Evidence from Nepal
Sujan Gautam, Hyoung-Sun Jeong
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2019; 16(5): 709. CrossRef - Criticality as Ideological Becoming: Developing English Teachers for Critical Pedagogy in Nepal
Bal Krishna Sharma, Prem Phyak
Critical Inquiry in Language Studies.2017; 14(2-3): 210. CrossRef - In Bangla There Is No Word for Vagina <br>—Reflections on Language, Sexual Health, and Women’s Access to Healthcare in Resource-Limited Countries
Annekathryn Goodman, Mithila Faruque, Rachel M. Clark
Health.2016; 08(12): 1244. CrossRef
- Prevalence of Violence in Iranian Pregnant Women: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Experience of Late–Middle-Aged Women who Reside in Small and Medium-Sized Cities in Becoming Psychologically Mature Women
- Euna Park, Haeok Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2015;6(3):159-163. Published online June 30, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2015.04.002
- 2,854 View
- 17 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The purpose of this study is to search the inner world of postmenopausal women in late-middle age who are facing senescence and live in small and medium-sized cities.
Methods
The methods of the study were the investigation and classification of answers to questions according to a declarative ethnography analysis. The questions asked to late–middle-aged women living in small and medium-sized cities were “How do you interpret and recognize the changes in the body after menopause?” and “Which methods do you choose and practice to maintain your health in relation to aging during middle age?”.
Results
Four positive topics and two negative topics were drawn from the study. The four positive themes were: ambition; completion of a great mission; life with a sense of affection; and gratitude for maintaining health. The negative themes were: undulating emotion; and filling the emptiness.
Conclusion
The recognition of changes in the body after menopause in late–middle-aged women in small and medium-sized cities can affect their preparation processes towards senescence. It is critical to find the means to manage emergency health cases from early adulthood to middle age, based on the outcomes of the study. The study also emphasizes the importance of the woman's family's alternative strategies and supportive systems, which can fit into the cultural context of the community. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Trend of Women’s Health Research in Korea, 2012–2020: Topic and Text Network Analysis
Ji Eun Park, Saerom Kim, Myoung-Hee Kim, Taemi Kim, Seung-Ah Choe, Hye Sook Min
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The experiences and needs of Asian women experiencing menopausal symptoms: a meta-synthesis
Shefaly Shorey, Esperanza D. Ng
Menopause.2019; 26(5): 557. CrossRef - Effects of Aromatherapy on Menopausal Symptoms, Perceived Stress and Depression in Middle-aged Women: A Systematic Review
Shinmi Kim, Ji-Ah Song, Mi-Eun Kim, Myung-Haeng Hur
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2016; 46(5): 619. CrossRef
- Trend of Women’s Health Research in Korea, 2012–2020: Topic and Text Network Analysis
- Knowledge of Diabetes Mellitus: Does Gender Make a Difference?
- Patrício Fernando Lemes dos Santos, Poliana Rodrigues dos Santos, Graziele Souza Lira Ferrari, Gisele Almeida Amaral Fonseca, Carlos Kusano Bucalen Ferrari
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2014;5(4):199-203. Published online August 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2014.06.004
- 3,197 View
- 21 Download
- 16 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objective
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a chronic disease considered an important public health problem. In recent years, its prevalence has been exponentially rising in many developing countries. Chronic complications of DM are important causes of morbidity and mortality among patients, which impair their health and quality of life. Knowledge on disease prevention, etiology, and management is essential to deal with parents, patients, and caregivers. The aim of this study was to evaluate the knowledge regarding DM in an adult population from a Middle-western Brazilian city.
Methods
This was a cross-sectional study covering 178 adults, aged 18–64 years, who answered a diabetes knowledge questionnaire. In order to identify the difference between groups, analysis of variance was used.
Results
Higher knowledge scores were found regarding the role of sugars on DM causality, diabetic foot care, and the effects of DM on patients (blindness, impaired wound healing, and male sexual dysfunction). However, lower scores were found amongst types of DM, hyperglycemic symptoms, and normal blood glucose levels. Females tended to achieve better knowledge scores than males.
Conclusion
Women had better knowledge regarding types of DM, normal blood glucose values, and consequences of hyperglycemia revealed that diabetes education should be improved. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Relationship Between Diabetes Knowledge Level, Physical Activity, and Quality of Life in Older Adults
Burçin AKÇAY, Tuğba KURU ÇOLAK, Sultan İĞREK, Bahar ÖZGÜL, Adnan APTI
Bandırma Onyedi Eylül Üniversitesi Sağlık Bilimler.2023; 5(2): 162. CrossRef - Assessment of prediabetes knowledge among adults in Al-Madinah, Saudi Arabia
Ameerah Almaski, Manal Almughamisi
Nutrition and Health.2023; : 026010602311557. CrossRef - Knowledge, Attitude, and Practices Related to Foot Care Among Diabetic Patients in Tabuk City, Saudi Arabia
Tariq M Shaqran, Saud N Alqahtani, Abdullah F Alhalafi , Norah M Alsabeelah, Rafaa A Algethmi, Ammar S Azhari, Abdulrahman Y Alhashmi, Abdullah N Almaghrabi, Hibah A Alshammari, Mohammed Saeed Alshahrani
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychometric properties of the revised Diabetes Knowledge Test using Rasch analysis
Eun-Hyun Lee, Young Whee Lee, Hyun-Jung Kang
Patient Education and Counseling.2022; 105(4): 851. CrossRef - Recognition of diabetes and sociodemographic predictors: results of a cross-sectional nationwide population-based survey in Singapore
Kumarasan Roystonn, Jue Hua Lau, PV AshaRani, Fiona Devi Siva Kumar, Peizhi Wang, Chee Fang Sum, Eng Sing Lee, Siow Ann Chong, Mythily Subramaniam
BMJ Open.2022; 12(3): e050425. CrossRef - Public knowledge and awareness of diabetes mellitus, its risk factors, complications, and prevention methods among adults in Poland—A 2022 nationwide cross-sectional survey
Kuba Sękowski, Justyna Grudziąż-Sękowska, Jarosław Pinkas, Mateusz Jankowski
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Physical Comorbidity According to Diagnoses and Sex among Psychiatric Inpatients in South Korea
Suin Park, Go-Un Kim, Hyunlye Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2021; 18(8): 4187. CrossRef - Diabetes knowledge, risk perception, and quality of life among South Asian caregivers in young adulthood
Angela Koipuram, Sandra Carroll, Zubin Punthakee, Diana Sherifali
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2020; 8(2): e001268. CrossRef - Small molecule IVQ, as a prodrug of gluconeogenesis inhibitor QVO, efficiently ameliorates glucose homeostasis in type 2 diabetic mice
Ting-ting Zhou, Tong Zhao, Fei Ma, Yi-nan Zhang, Jing Jiang, Yuan Ruan, Qiu-ying Yan, Gai-hong Wang, Jin Ren, Xiao-wei Guan, Jun Guo, Yong-hua Zhao, Ji-ming Ye, Li-hong Hu, Jing Chen, Xu Shen
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica.2019; 40(9): 1193. CrossRef - Problematic drinking in the old and its association with muscle mass and muscle function in type II diabetes
Nikolaus Buchmann, Dominik Spira, Maximilian König, Kristina Norman, Ilja Demuth, Elisabeth Steinhagen-Thiessen
Scientific Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - A survey to validate the traditional Siddha perception of diabetes mellitus
Amulya Vijay, Priyadharshan Ranganathan, Balachandar Vellingiri
Journal of Public Health.2019; 27(5): 581. CrossRef - Knowledge and self-care management of the uncontrolled diabetes patients
Somsak Thojampa
International Journal of Africa Nursing Sciences.2019; 10: 1. CrossRef - Acculturation and Dietary Intakes by Gender Among Mongolians in South Korea: Nutrition Education Implication for Multicultural Families
Hae Ryun Park, Zuunnast Tserendejid, Joung Hee Lee, Young Suk Lim
Asia Pacific Journal of Public Health.2017; 29(7): 608. CrossRef - Knowledge of type 2 diabetic patients about their condition in Kimpese Hospital diabetic clinic, Democratic Republic of the Congo
Patrick N. Ntontolo, Philippe N. Lukanu, Gboyega A. Ogunbanjo, Jean-Pierre L. Fina, Léon N.M. Kintaudi
African Journal of Primary Health Care & Family Me.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of Knowledge of Diabetes Mellitus in the Urban Areas of Klang District, Malaysia
Sasikala Chinnappan, Palanisamy Sivanandy, Rajenthina Sagaran, Nagashekhara Molugulu
Pharmacy.2017; 5(4): 11. CrossRef - Affective Bond, Loneliness and Socioeconomic Aspects of an Elderly Population in Midwest, Brazil
CKB Ferrari, GSL Ferrari, LD Nery, DF dos Santos, NS Pereira
Archives of Nursing Practice and Care.2016; 2(1): 024. CrossRef
- The Relationship Between Diabetes Knowledge Level, Physical Activity, and Quality of Life in Older Adults



 First
First Prev
Prev


