Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- Epidemiological analysis and prevention strategies in response to a shigellosis cluster outbreak: a retrospective case series in an alternative school in the Republic of Korea, 2023
- Yeongseo Ahn, Sunmi Jin, Gemma Park, Hye Young Lee, Hyungyong Lee, Eunkyung Shin, Junyoung Kim, Jaeil Yoo, Yuna Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2024;15(1):68-76. Published online February 7, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0298
- 945 View
- 51 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 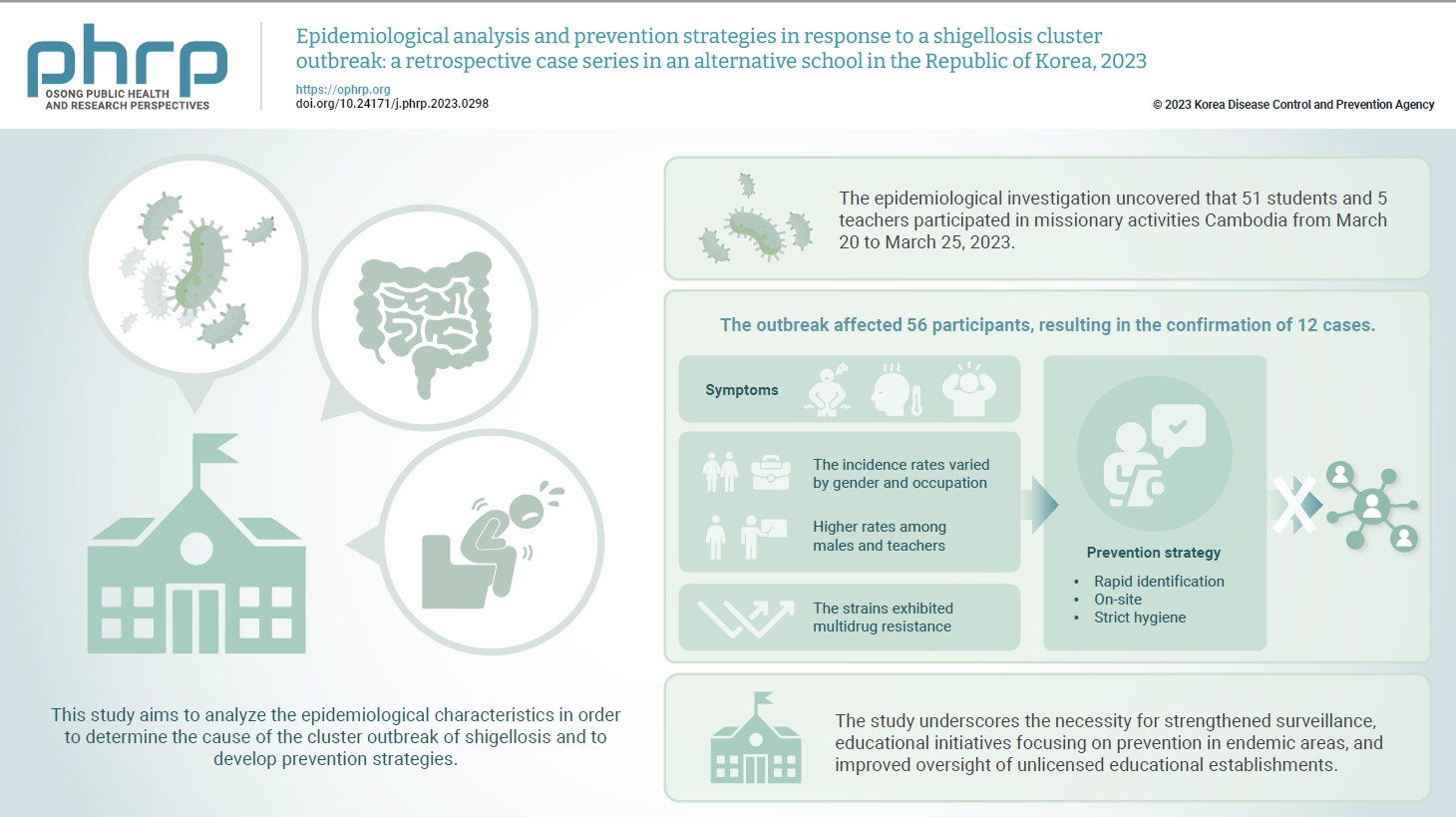
- Objectives
In March 2023, an alternative school in the Republic of Korea reported 12 cases of shigellosis. This study aims to analyze the epidemiological characteristics in order to determine the cause of the cluster outbreak of shigellosis and to develop prevention strategies. Methods: This study focused on 12 patients with confirmed Shigella infection and investigated their demographics, clinical features, epidemiology, diagnostics, and antimicrobial susceptibility. Following the identification of Shigella, we conducted follow-up rectal smear cultures to manage patients, implementing isolation and control measures. Results: This study investigated the emergence of multidrug-resistant Shigella following missionary activities in Cambodia, documenting a cluster infection within an alternative school in Daejeon, the Republic of Korea. The outbreak affected 56 participants, resulting in the confirmation of 12 cases. The incidence rates varied by gender and occupation, with higher rates among males and teachers. All 12 cases demonstrated multidrug resistance. Challenges included delayed pathogen confirmation and suboptimal adherence to isolation criteria. The incident prompted revisions in the criteria for isolation release, focusing on symptom resolution. The study underscores the necessity for strengthened surveillance, educational initiatives focusing on prevention in endemic areas, and improved oversight of unlicensed educational establishments. Conclusion: Successful response strategies included swift situation assessment, collaborative efforts, effective infection control measures, and modified criteria for isolation release. Continued surveillance of multidrug-resistant strains is recommended, especially in regions with a high prevalence.
Short Communication
- Characteristics of a large outbreak arising from a school field trip after COVID-19 restrictions were eased in 2022
- Sueng-Jin Kim, Eun-Young Kim, Jeonghee Yu
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2024;15(1):83-89. Published online February 5, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0264
- 853 View
- 21 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 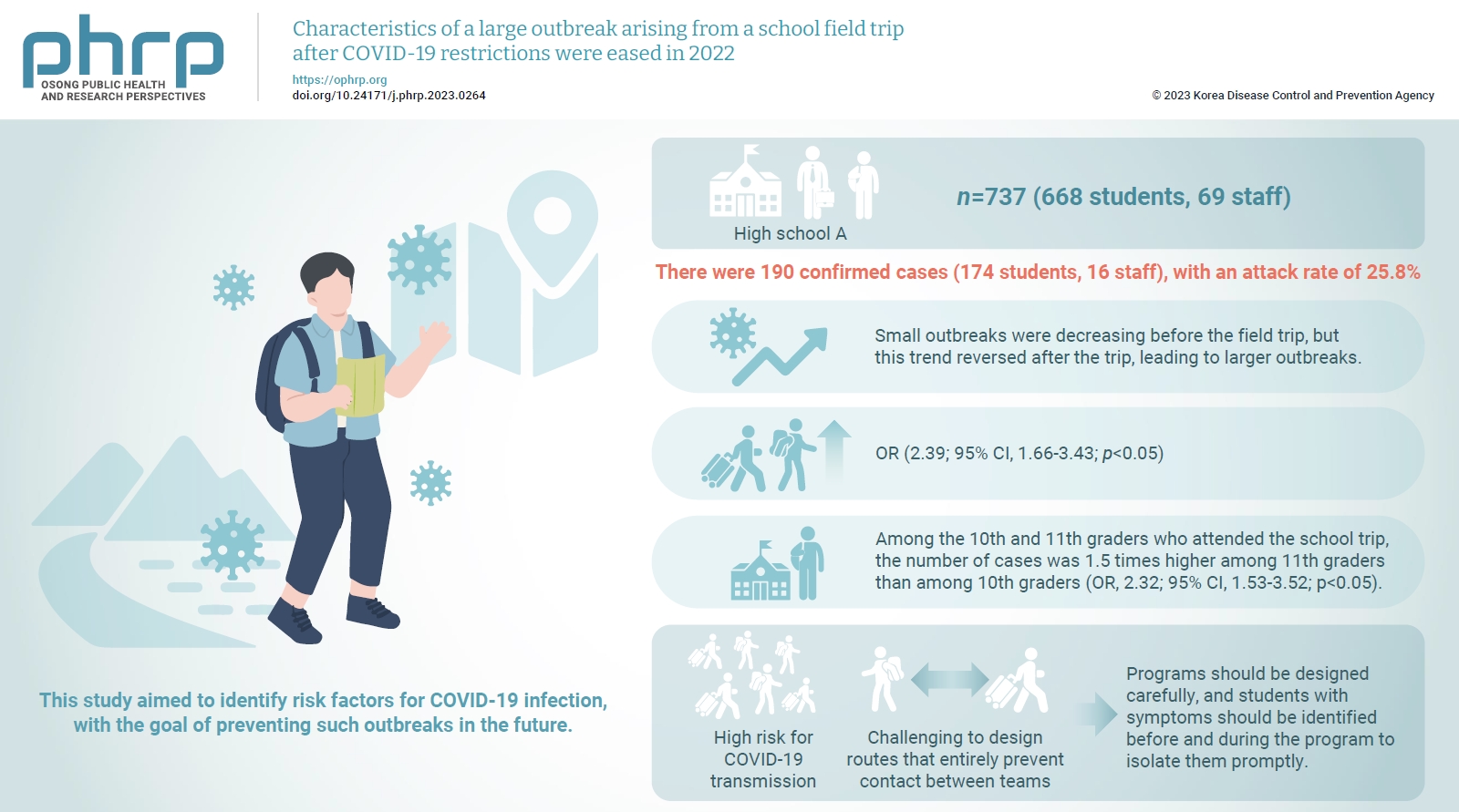
- Objectives
This study analyzed a large outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) that occurred during a high school field trip in the Jeonbuk region and aimed to identify risk factors for COVID-19 infection, with the goal of preventing such outbreaks in the future. Methods: A retrospective cohort study of 737 participants, including 668 students and 69 staff at High School A, was designed to describe the epidemiological characteristics of this large COVID-19 outbreak. Logistic regression analysis was performed to calculate relative risks (odds ratios [ORs]) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Results: There were 190 confirmed cases (174 students, 16 staff), with an attack rate of 25.8%. Small outbreaks were decreasing before the field trip, but this trend reversed after the trip, leading to larger outbreaks. Logistic regression showed an OR of 2.39 (95% CI, 1.66–3.43; p<0.05) for COVID-19 infection among field trip participants. Among them, 11th graders had an OR of 2.32 (95% CI, 1.53–3.52; p<0.05) compared to 10th graders, while no significant risk difference was found within same-grade teams. Conclusion: There was a high risk for COVID-19 transmission during extracurricular activities with a large number of participants, such as field trips, even after the nationwide Omicron variant epidemic subsided. Even when students are separated into teams and follow different routes, it is challenging to design routes that entirely prevent contact between teams. Thus, programs should be designed carefully, and students with symptoms should be identified before and during the program to isolate them promptly.
Original Articles
- Risk factors for SARS-CoV-2 transmission during a movie theater outbreak in Incheon in the Republic of Korea, November 2021: a retrospective study
- Hye Young Lee, Young-Joon Park, Sang-Eun Lee, Han-Na Yoo, Il-Hwan Kim, Jin Sun No, Eun-Jin Kim, Jungyeon Yu, Sanghwan Bae, Mi Yu
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2024;15(1):45-55. Published online January 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0269
- 10,547 View
- 324 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 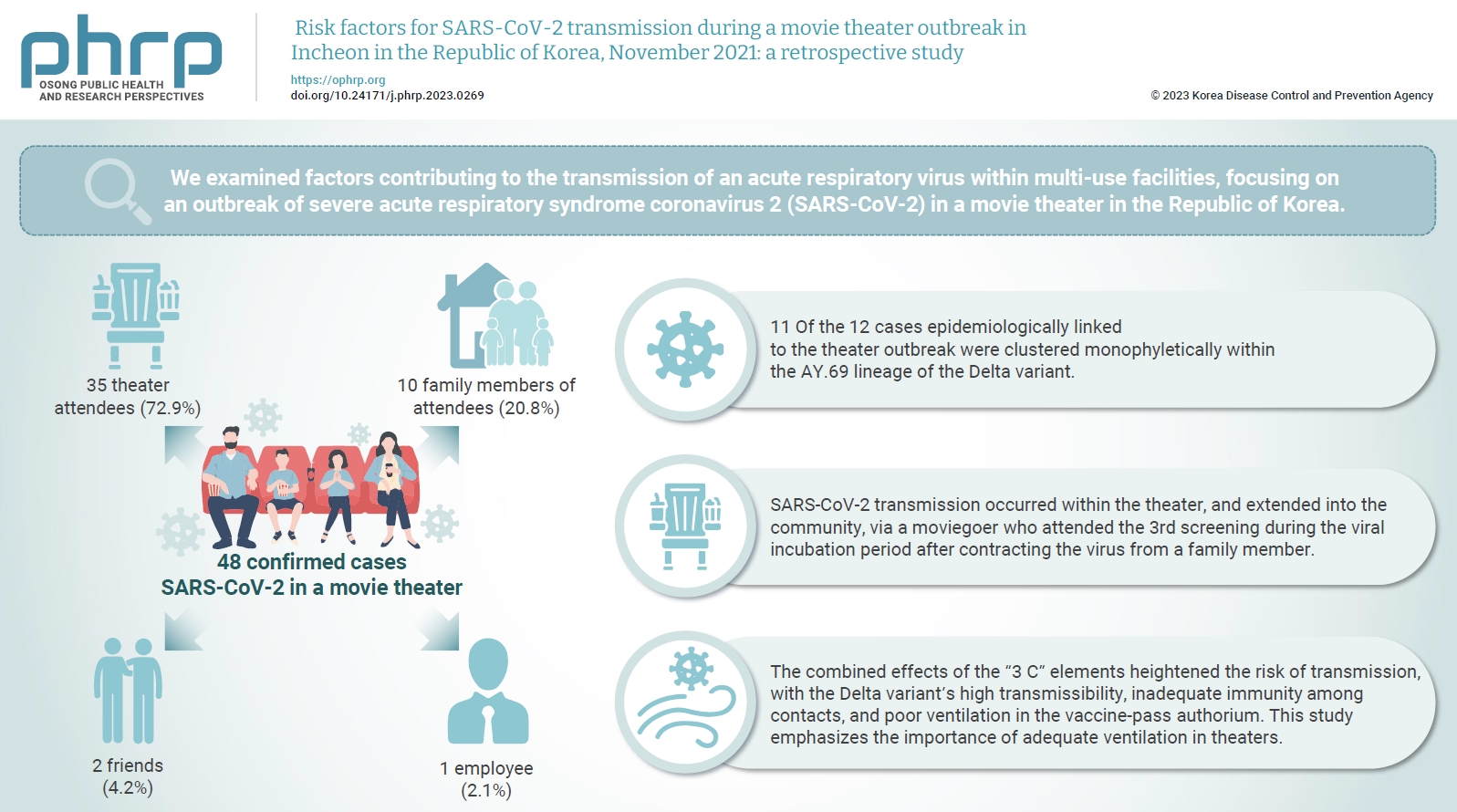
- Objectives
We examined factors contributing to the transmission of an acute respiratory virus within multi-use facilities, focusing on an outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in a movie theater in the Republic of Korea. Methods: This retrospective cohort study involved a descriptive analysis of 48 confirmed cases. Logistic regression was applied to a cohort of 80 theater attendees to identify risk factors for infection. The infection source and transmission route were determined through gene sequencing data analysis. Results: Of the 48 confirmed cases, 35 were theater attendees (72.9%), 10 were family members of attendees (20.8%), 2 were friends (4.2%), and 1 was an employee (2.1%). Among the 80 individuals who attended the 3rd to 5th screenings of the day, 35 became infected, representing a 43.8% attack rate. Specifically, 28 of the 33 third-screening attendees developed confirmed SARSCoV-2, constituting an 84.8% attack rate. Furthermore, 11 of the 12 cases epidemiologically linked to the theater outbreak were clustered monophyletically within the AY.69 lineage. At the time of the screening, 35 individuals (72.9%) had received 2 vaccine doses. However, vaccination status did not significantly influence infection risk. Multivariate analysis revealed that close contacts had a 15.9-fold higher risk of infection (95% confidence interval, 4.37–78.39) than casual contacts. Conclusion: SARS-CoV-2 transmission occurred within the theater, and extended into the community, via a moviegoer who attended the 3rd screening during the viral incubation period after contracting the virus from a family member. This study emphasizes the importance of adequate ventilation in theaters.
- Characteristics and related factors of waterborne and foodborne infectious disease outbreaks before and after the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic (2017–2021) in the Republic of Korea: a descriptive study
- Eunkyoung Kim, Bryan Inho Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(6):483-493. Published online December 14, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0221
- 789 View
- 43 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 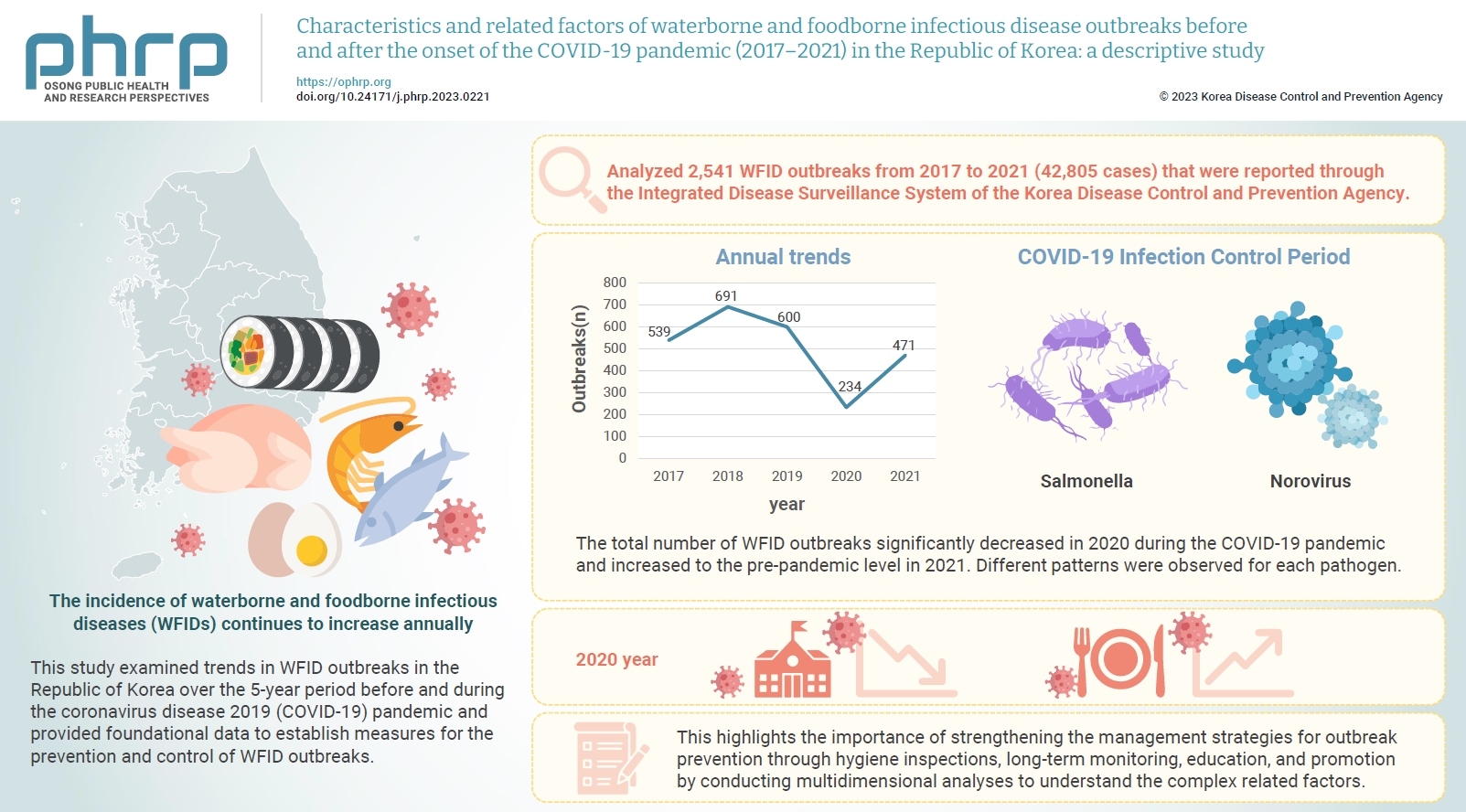
- Objectives
The incidence of waterborne and foodborne infectious diseases (WFIDs) continues to increase annually, attracting significant global attention. This study examined trends in WFID outbreaks in the Republic of Korea over the 5-year period before and during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic and provided foundational data to establish measures for the prevention and control of WFID outbreaks. Methods: We analyzed 2,541 WFID outbreaks from 2017 to 2021 (42,805 cases) that were reported through the Integrated Disease Surveillance System of the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency. Outbreaks were defined as the occurrence of gastrointestinal symptoms in ≥2 individuals within a group with temporal and regional epidemiological associations. The related factors associated with WFID outbreaks during the observation period were statistically analyzed. Results: The total number of WFID outbreaks significantly decreased in 2020 during the COVID-19 pandemic and increased to the pre-pandemic level in 2021. Different patterns were observed for each pathogen. The incidence of Salmonella outbreaks more than doubled, while norovirus outbreaks decreased significantly. Conclusion: WFID outbreaks in the Republic of Korea showed different patterns before and during the COVID-19 pandemic, influenced by infection control measures and changes in dietary consumption patterns. Outbreaks of some diseases increased, but the infection control measures applied during the pandemic resulted in a significant decrease in the overall number of WFID outbreaks. This highlights the importance of strengthening the management strategies for outbreak prevention through hygiene inspections, long-term monitoring, education, and promotion by conducting multidimensional analyses to understand the complex related factors.
Short Communication
- Epidemiological characteristics of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae outbreaks in the Republic of Korea between 2017 and 2022
- Hyoseon Jeong, Junghee Hyun, Yeon-Kyeng Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(4):312-320. Published online August 21, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0069
- 1,083 View
- 144 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Objectives
We aimed to describe the epidemiological characteristics of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae (CPE) outbreaks in healthcare settings in the Republic of Korea between 2017 and 2022.
Methods
Under the national notifiable disease surveillance system, we obtained annual descriptive statistics regarding the isolated species, carbapenemase genotype, healthcare facility type, outbreak location and duration, and number of patients affected and recommended interventions. We used epidemiological investigation reports on CPE outbreaks reported to Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency from June 2017 to September 2022.
Results
Among the 168 reports analyzed, Klebsiella pneumoniae (85.1%) was the most frequently reported species, while K. pneumoniae carbapenemase (KPC, 82.7%) was the most common carbapenemase genotype. Both categories increased from 2017 to 2022 (p<0.01). General hospitals had the highest proportion (54.8%), while tertiary general hospitals demonstrated a decreasing trend (p<0.01). The largest proportion of outbreaks occurred exclusively in intensive care units (ICUs, 44.0%), and the frequency of concurrent outbreaks in ICUs and general wards increased over time (p<0.01). The median outbreak duration rose from 43.5 days before the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic (2017–2019) to 79.5 days during the pandemic (2020–2022) (p=0.01), and the median number of patients associated with each outbreak increased from 5.0 to 6.0 (p=0.03). Frequently recommended interventions included employee education (38.1%), and 3 or more measures were proposed for 45.2% of outbreaks.
Conclusion
In the Republic of Korea, CPE outbreaks have been consistently dominated by K. pneumoniae and KPC. The size of these outbreaks increased during the COVID-19 pandemic. Our findings highlight the need for continuing efforts to control CPE outbreaks using a multimodal approach, while considering their epidemiology. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of clinical outcomes of patients with serial negative surveillance cultures according to a subsequent polymerase chain reaction test for carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales
H. Seo, S. Kim, Y.W. Lee, H.S. Oh, H-S. Kim, Y.K. Kim
Journal of Hospital Infection.2024; 146: 93. CrossRef - Identifying Contact Time Required for Secondary Transmission of Clostridioides difficile Infections by Using Real-Time Locating System
Min Hyung Kim, Jaewoong Kim, Heejin Ra, Sooyeon Jeong, Yoon Soo Park, Dongju Won, Hyukmin Lee, Heejung Kim
Emerging Infectious Diseases.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Comparison of clinical outcomes of patients with serial negative surveillance cultures according to a subsequent polymerase chain reaction test for carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales
Original Articles
- Vaccine effectiveness and the epidemiological characteristics of a COVID-19 outbreak in a tertiary hospital in Republic of Korea
- Seonhee Ahn, Tae Jong Son, Yoonsuk Jang, Jihyun Choi, Young Joon Park, Jiseon Seong, Hyun Hee Kwon, Muk Ju Kim, Donghyok Kwon
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(3):188-196. Published online June 8, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0066
- 1,456 View
- 72 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 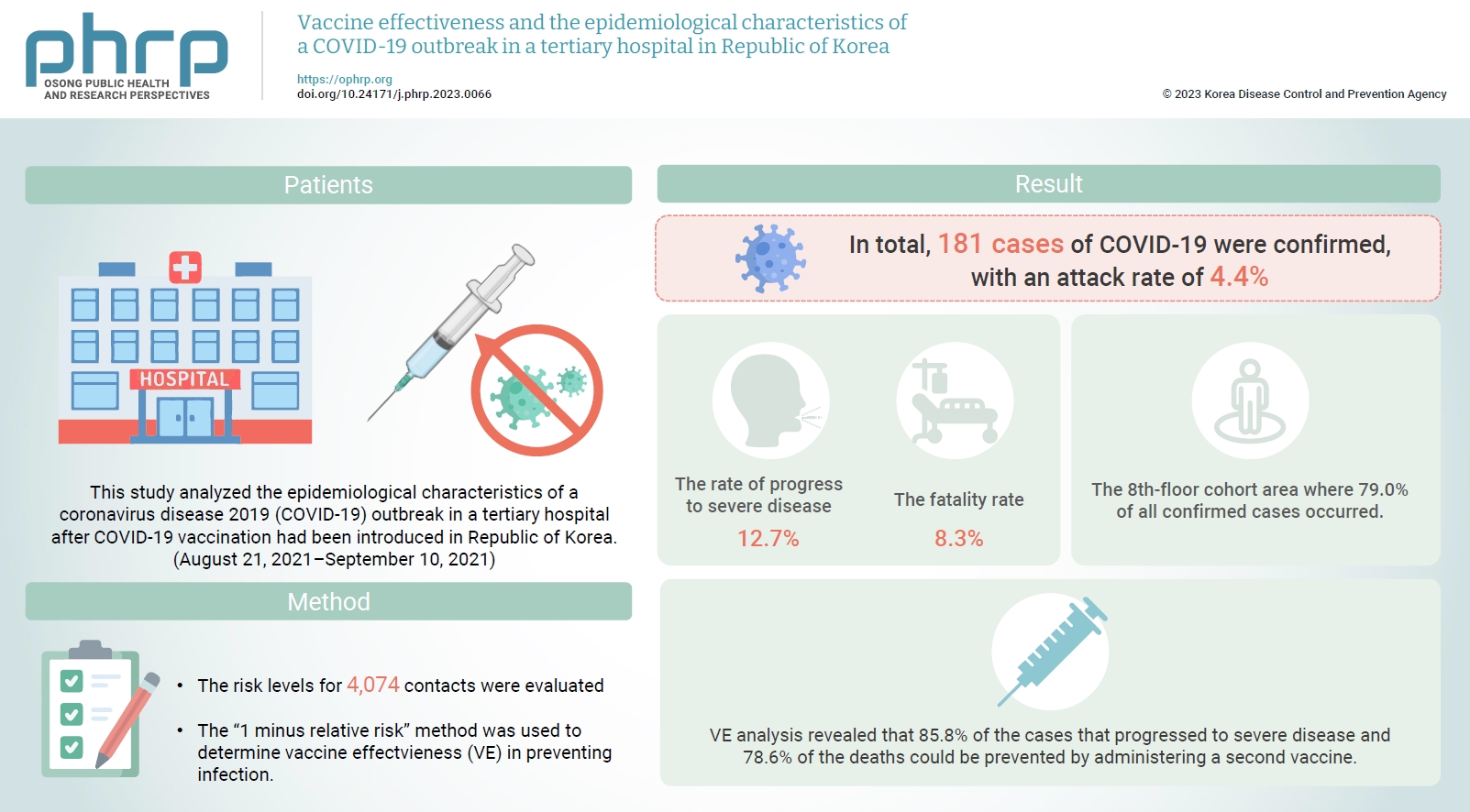
- Objectives
Healthcare facilities are high-risk sites for infection. This study analyzed the epidemiological characteristics of a coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in a tertiary hospital after COVID-19 vaccination had been introduced in Republic of Korea. Vaccine effectiveness (VE) and shared anti-infection strategies are also assessed.
Methods
The risk levels for 4,074 contacts were evaluated. The epidemiological characteristics of confirmed cases were evaluated using the chi-square test. The “1 minus relative risk” method was used to determine VE in preventing infection, progression to severe disease, and death. In the largest affected area (the 8th floor), a separate relative risk analysis was conducted. A multivariate logistic regression analysis (with 95% confidence interval [CIs]) was used to identify transmission risk factors with a significance level <10% via the backward elimination method.
Results
In total, 181 cases of COVID-19 were confirmed, with an attack rate of 4.4%. Of those cases, 12.7% progressed to severe disease, and 8.3% died. In the cohort isolation area on the 8th floor, where 79.0% of the confirmed cases occurred, the adjusted odds ratio was 6.55 (95% CI, 2.99–14.33) and 2.19 (95% CI, 1.24–3.88) for caregivers and the unvaccinated group, respectively. VE analysis revealed that 85.8% of the cases that progressed to severe disease and 78.6% of the deaths could be prevented by administering a second vaccine.
Conclusion
Caregiver training for infection prevention and control is necessary to reduce infection risk. Vaccination is an important intervention to reduce the risk of progression to severe disease and death.
- Risk factors for COVID-19 outbreaks in livestock slaughtering and processing facilities in Republic of Korea
- Seongju Choi, Tae Jong Son, Yeon-Kyung Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(3):207-218. Published online June 8, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0035
- 1,203 View
- 48 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 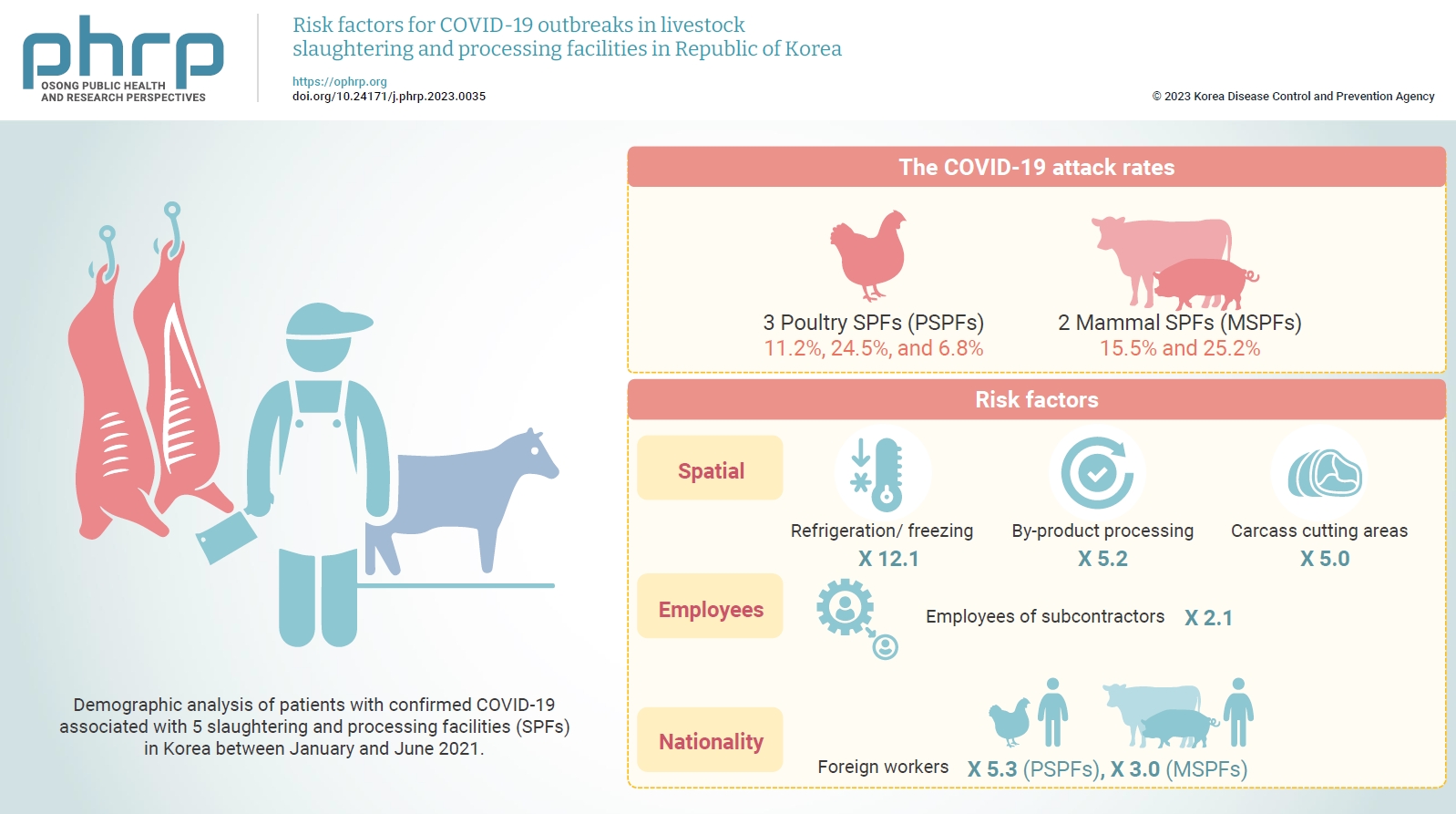
- Objectives
The goal of this study was to help prevent and control the spread of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) by identifying transmission routes and risk factors in livestock slaughtering and processing facilities (SPFs) and establishing an optimal intervention strategy for outbreaks.
Methods
This case series study was a demographic analysis of patients with confirmed COVID-19 associated with 5 SPFs in Korea between January and June 2021. Additionally, in a retrospective cohort study, the association between COVID-19 infection and risk factors was analyzed for SPFs at which outbreaks occurred.
Results
The COVID-19 attack rates were 11.2%, 24.5%, and 6.8% at 3 poultry SPFs (PSPFs) and 15.5% and 25.2% at 2 mammal SPFs (MSPFs). Regarding spatial risk factors, the COVID-19 risk levels were 12.1-, 5.2-, and 5.0-fold higher in the refrigeration/ freezing, by-product processing, and carcass cutting areas, respectively, than in the office area. The risk of COVID-19 infection was 2.1 times higher among employees of subcontractors than among employees of contractors. The COVID-19 risk levels were 5.3- and 3.0-fold higher in foreign workers than in native Korean workers in the PSPFs and MSPFs, respectively.
Conclusion
As the COVID-19 pandemic continues, a detailed policy for infectious disease prevention and control intervention is needed, without interrupting economic activities. Thus, we propose an ideal intervention plan to prevent COVID-19 through disinfection and preemptive testing and to block its transmission through effective contact management during outbreaks at SPFs.
- COVID-19 outbreak in a religious village community in Republic of Korea and risk factors for transmission
- Jiae Shim, Eunju Lee, Eunyoung Kim, Yeonhwa Choi, Giseok Kang, Bryan Inho Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(2):110-118. Published online April 5, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0002
- 1,493 View
- 72 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 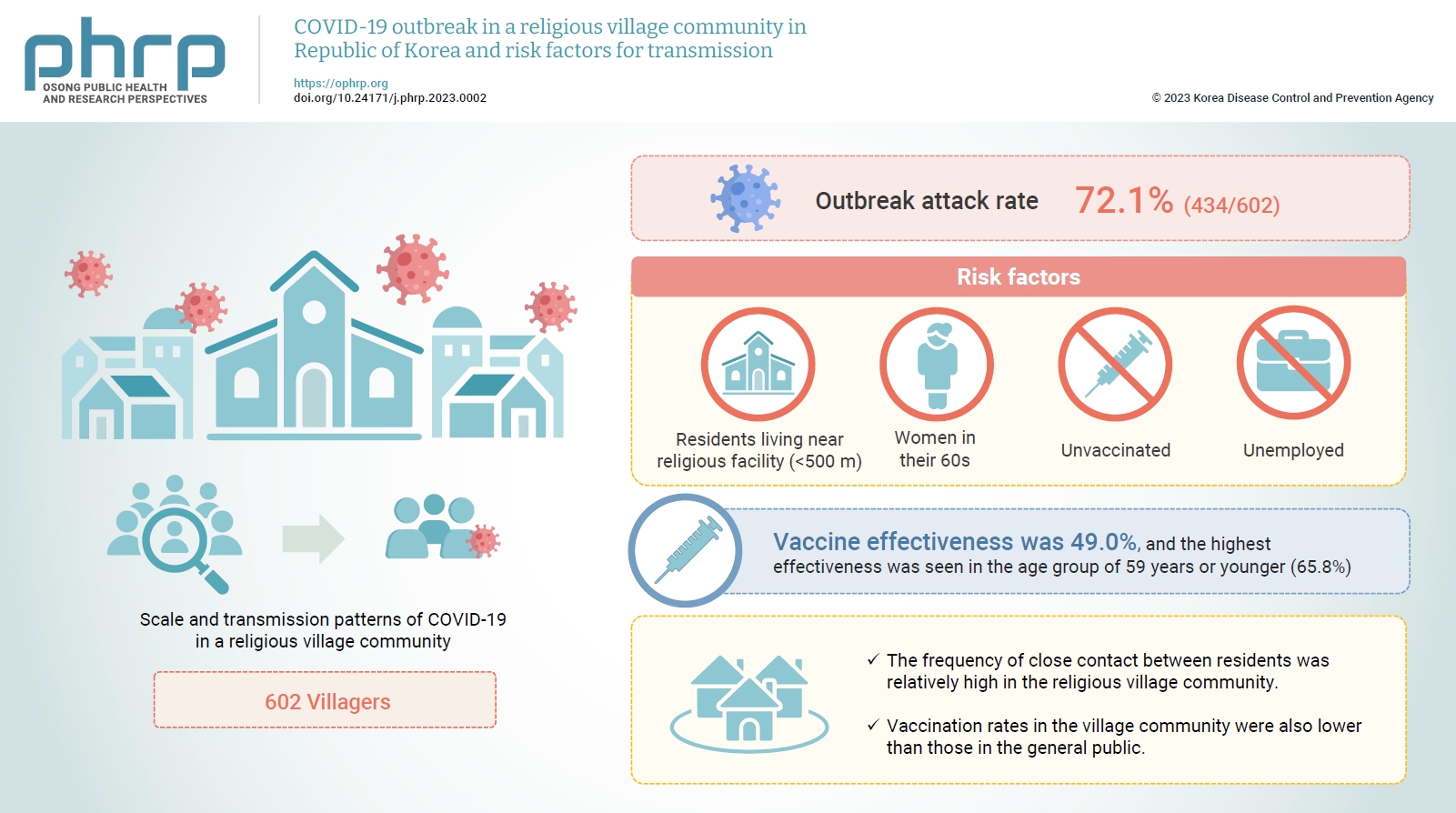
- Objectives
This study aimed to assess the scale and transmission patterns of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in a religious village community in South Korea, to determine the risk factors of transmission, and to evaluate vaccine effectiveness.
Methods
An epidemiological survey was conducted, and data were collected and analyzed from 602 villagers in the religious village community. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was used to identify the risk factors for COVID-19 transmission and to evaluate vaccine effectiveness.
Results
The outbreak attack rate was 72.1% (434/602). The attack rate was high among women in their 60s, the unemployed, residents living near religious facility (<500 m), and the unvaccinated. Age, the distance between religious facility and residences, and the absence of vaccination were identified as risk factors for transmission. Vaccine effectiveness was 49.0%, and the highest effectiveness was seen in the age group of 59 years or younger (65.8%).
Conclusion
This village community was isolated, with little communication with the outside world. However, the frequency of close contact between residents was relatively high, contributing to the spread of COVID-19 in the village even with relatively short exposure. Vaccination rates in the village community were also lower than those in the general public. Public health authorities should consider the potential impact of cultural factors, including religion, that could lead to the exponential spread of COVID-19 in closed village communities.
- The first reported hepatitis E outbreak in a food manufacturing factory: Korea, 2022
- Hansol Yeom, Soonryu Seo, Youngsil Yoon, Jaeeun Lee, Myung-Guk Han, Deog-Yong Lee, Sun-Whan Park, Song A Park, Sook-Hyang Jeong, Jin Gwack
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(1):15-22. Published online February 22, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0305
- 1,643 View
- 137 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 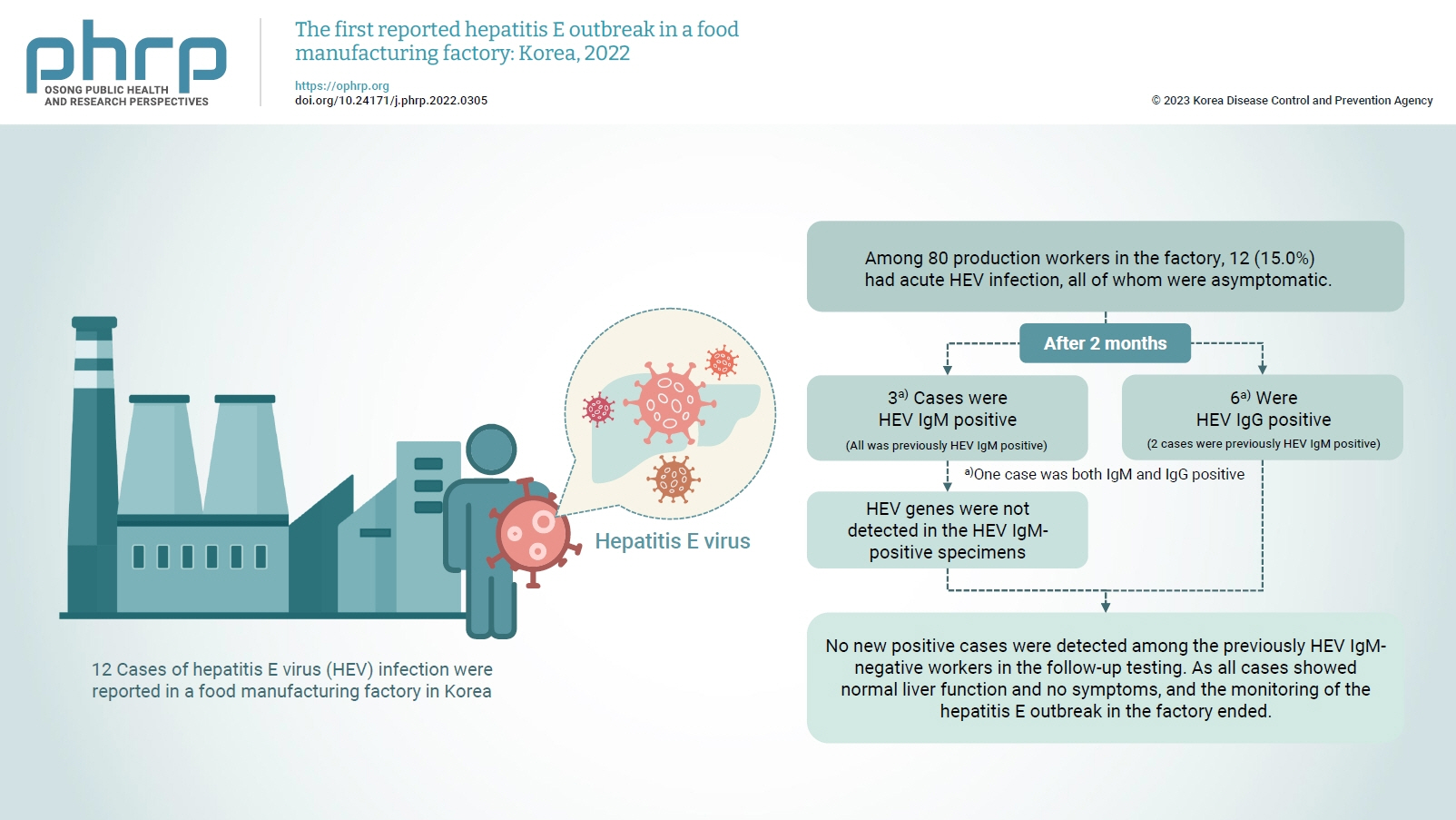
- Objectives
On February 16, 2022, 12 cases of hepatitis E virus (HEV) infection were reported in a food manufacturing factory in Korea. The aim of this study was to identify additional cases and to determine the source of this HEV outbreak. Methods: This study was an in-depth investigation of 12 HEV immunoglobulin M (IgM)-positive cases and their demographic, clinical, and epidemiological characteristics. On-site specimens were collected from the environment and from humans, and a follow-up investigation was conducted 2 to 3 months after the outbreak. Results: Among 80 production workers in the factory, 12 (15.0%) had acute HEV infection, all of whom were asymptomatic. The follow-up investigation showed that 3 cases were HEV IgMpositive, while 6 were HEV IgG-positive. HEV genes were not detected in the HEV IgM-positive specimens. HEV genes were not detected in the food products or environmental specimens collected on-site. HEV was presumed to be the causative pathogen. However, it could not be confirmed that the source of infection was common consumption inside the factory. Conclusion: This was the first domestic case of an HEV infection outbreak in a food manufacturing factory in Korea. Our results provide information for the future control of outbreaks and for the preparation of measures to prevent domestic outbreaks of HEV infection.
Review Article
- SARS-CoV-2 in brief: from virus to prevention
- Hassan Karami, Zeinab Karimi, Negin Karami
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(6):394-406. Published online November 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0155
- 2,815 View
- 94 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The recent outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), ahighly transmissible virus with a likely animal origin, has posed major and unprecedentedchallenges to millions of lives across the affected nations of the world. This outbreak firstoccurred in China, and despite massive regional and global attempts shortly thereafter, itspread to other countries and caused millions of deaths worldwide. This review presents keyinformation about the characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and its associated disease (namely,coronavirus disease 2019) and briefly discusses the origin of the virus. Herein, we also brieflysummarize the strategies used against viral spread and transmission.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Polysaccharides and Lectins: A Natural Complementary Approach against the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic
Radu Lefter, Prairna Balyan, Ioana-Miruna Balmus, Abdellah Ech-Chahad, Ahmad Ali, Alin Ciobica, Antoneta Dacia Petroaie, Gabriela Halitchi, Bogdan Novac, Catalina Ionescu, Fatima Zahra Kamal
Microbiology Research.2024; 15(2): 525. CrossRef - Surveillance of endemic coronaviruses during the COVID‐19 pandemic in Iran, 2021–2022
Hassan Karami, Kaveh Sadeghi, Sevrin Zadheidar, Fatemeh Saadatmand, Negar Mirsalehi, Nima Hoveidi Ardestani, Shirin Kalantari, Mohammad Farahmand, Jila Yavarian, Talat Mokhtari‐Azad
Influenza and Other Respiratory Viruses.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Polysaccharides and Lectins: A Natural Complementary Approach against the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic
Original Articles
- A case-control study of acute hepatitis A in South Korea, 2019
- Jung Hee Hyun, Ju Young Yoon, Sang Hyuk Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(5):352-359. Published online October 12, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0141
- 2,903 View
- 117 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Objectives
We aimed to reconfirm the source of hepatitis A virus (HAV) infection through epidemiological and genotype investigations of individual cases in a 2019 outbreak in South Korea. Methods: We investigated food intake histories, associations with hepatitis A, and genotypes of HAV in 31 patients with hepatitis aged 20 to 49 years registered in the integrated disease and health management system during December 1–7, 2019 (case group) and in 35 sex- and agematched people without a history of HAV vaccination or infection among patients’ families and colleagues (control group). Results: The consumption of salted clams was a significant factor (odds ratio, 4.33; 95% confidence interval, 1.32–14.18) in the risk factor analysis of food intake history. HAV genotypes were analyzed in 24 of 31 patients. Type IA and type IIIA were found in 23 and 1 cases, respectively. Conclusion: Salted clams are considered to have been the source of HAV infection at 49 weeks of the HAV outbreak in 2019; this result was consistent with that of a previous epidemiological investigation conducted by the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency in September 2019. Therefore, monitoring of the production and distribution of salted clams needs to be continued. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Monitoring viruses and beta-lactam resistance genes through wastewater surveillance during a COVID-19 surge in Suwon, South Korea
Rajendra Singh, Jaewon Ryu, Sung Soo Park, Sungpyo Kim, Keugtae Kim
Science of The Total Environment.2024; 922: 171223. CrossRef - Prevalence of foodborne viruses and influenza A virus from poultry processing plants to retailed chickens
Daseul Yeo, Mengxiao Song, Md. Iqbal Hossain, Soontag Jung, Zhaoqi Wang, Dong Joo Seo, Min Suk Rhee, Changsun Choi
Frontiers in Sustainable Food Systems.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A Study on the Detection Rate of Hepatitis A from Gastroenteritis Patients and the Genotype Analysis of Hepatitis A Virus in Busan
Sun Hee Park, Chanhee Kim, Summi Lee, Jihye Jeong, Junghye Choi, Seung Ju Lee
Journal of Bacteriology and Virology.2023; 53(2): 74. CrossRef - A Study on the Detection Rate of Hepatitis A from Gastroenteritis Patients and the Genotype Analysis of Hepatitis A Virus in Busan
Sun Hee Park, Chanhee Kim, Summi Lee, Jihye Jeong, Junghye Choi, Seung Ju Lee
Journal of Bacteriology and Virology.2023; 53(2): 74. CrossRef
- Monitoring viruses and beta-lactam resistance genes through wastewater surveillance during a COVID-19 surge in Suwon, South Korea
- Epidemiological characteristics of varicella outbreaks in the Republic of Korea, 2016–2020
- Eun-Young Kim, Chungmin Park, Gyehee Lee, Suyeon Jeong, Jeongsuk Song, Dong-Han Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(2):133-141. Published online April 26, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0087
- 3,435 View
- 89 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
We described the trends and epidemiological characteristics of varicella outbreaks from 2016 to 2020 in the Republic of Korea. Methods: We investigated variables such as the outbreak setting, age of patients, vaccination status, and lesion count. The collected data were analyzed with the Cochrane-Armitage trend test and Kruskal-Wallis test. These statistical tests were performed using R ver. 4.0.3. Results: The number of varicella outbreaks increased from 2016 to 2018; however, after a slight decrease in the number of outbreaks in 2019, the number fell sharply in 2020. The median size of outbreaks decreased from 8 to 9 cases during 2016−2019 to 6 cases in 2020. The median duration of outbreaks was 18 days during 2016−2017, 28 days in 2018, 29 days in 2019, and 15 days in 2020. Varicella outbreaks occurred most frequently in elementary schools, and vaccination coverage of patients increased from 89.4% in 2016 to 97.2% in 2019. The median age of patients with outbreak-related varicella decreased from 8 years in 2016 to 6 years in 2020. Conclusion: Significant changes were observed in the age of patients with outbreak-related varicella. Ongoing monitoring of varicella outbreaks should be conducted. Further research will be needed to measure the disease burden of varicella and enable evidence-based policy decisions. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Protective Effectiveness of 2-Dose Varicella Vaccination in Children in Korea: A Case-control Study
Young Hwa Lee, Young June Choe, Kwan Hong, Yoonsun Yoon, Yun-Kyung Kim
Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal.2023; 42(8): 719. CrossRef - Epidemiological Characteristics of Varicella Outbreaks — China, 2006–2022
Miaomiao Wang, Xudong Li, Meiying You, Yuanyuan Wang, Xinyu Liu, Zihan Li, Wenjia Zhao, Zhuojun Jiang, Yuehua Hu, Dapeng Yin
China CDC Weekly.2023; 5(52): 1161. CrossRef
- The Protective Effectiveness of 2-Dose Varicella Vaccination in Children in Korea: A Case-control Study
- COVID-19 outbreak response at a nursing hospital in South Korea in the post-vaccination era, including an estimation of the effectiveness of the first shot of the Oxford-AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine (ChAdOx1-S)
- Chanhee Kim, Geon Kang, Sun Gu Kang, Heeyoung Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(2):114-122. Published online April 26, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.0262
- 4,171 View
- 92 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
We descriptively reviewed a coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak at a nursing hospital in Gyeonggi Province (South Korea) and assessed the effectiveness of the first dose of the Oxford-AstraZeneca vaccine in a real-world population. Methods: The general process of the epidemiological investigation included a public health intervention. The relative risk (RR) of vaccinated and unvaccinated groups was calculated and compared to confirm the risk of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARSCoV-2) infection, and vaccine effectiveness was evaluated based on the calculated RR. Results: The population at risk was confined to ward E among 8 wards of Hospital X, where the outbreak occurred. This population comprised 55 people, including 39 patients, 12 nurses, and 4 caregivers, and 19 cases were identified. The RR between the vaccinated and unvaccinated groups was 0.04, resulting in a vaccine effectiveness of 95.3%. The vaccination rate of the nonpatients in ward E was the lowest in the entire hospital, whereas the overall vaccination rate of the combined patient and non-patient groups in ward E was the third lowest. Conclusion: The first dose of the Oxford-AstraZeneca vaccine (ChAdOx1-S) was effective in preventing SARS-CoV-2 infection. To prevent COVID-19 outbreaks in medical facilities, it is important to prioritize the vaccination of healthcare providers. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- COVID-19 Vaccination in Korea: Past, Present, and the Way Forward
Eliel Nham, Joon Young Song, Ji Yun Noh, Hee Jin Cheong, Woo Joo Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- COVID-19 Vaccination in Korea: Past, Present, and the Way Forward
Short Communication
- COVID-19 outbreak and risk factors for infection in a taekwondo gym in the Republic of Korea
- Seung Hwan Shin, Eonjoo Park, Sookhyun Kim, Minji Jang, Subin Park, Dong-Hwi Kim, Tae Jong Son, Ji-Hyuk Park
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(2):162-170. Published online March 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.0295
- 4,298 View
- 115 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Relatively few studies have assessed risk factors for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in public facilities used by children and adolescents. This study presents an analysis of a COVID-19 outbreak that occurred in a taekwondo gym in Korea, predominantly among children and adolescents, with the aim of providing insights on managing COVID-19 outbreaks in similar facilities. Methods: All 108 taekwondo gym students and staff received COVID-19 tests. A survey and closed-circuit television analyses were used to identify risk factors. A univariate analysis was conducted, followed by multivariate logistic regression analysis with backward elimination for variables with a significance level <0.10 in the univariate analysis. Results: COVID-19 was confirmed in 30 of 108 subjects at the taekwondo gym (attack rate, 27.8%). The outbreak started in an adult class student. This student transmitted the virus to the staff, who consequently transmitted the virus to adolescent students. In the univariate analysis, the relative risk for younger age (≤9 years) was 2.14 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.01–4.54; p=0.054), and that for food consumption inside the gym was 2.12 (95% CI, 1.04–4.30; p=0.048). In the multivariate logistic regression analysis, the odds ratio for younger age was 2.96 (95% CI, 1.07–8.20; p=0.036), and that for food consumption inside the gym was 3.00 (95% CI, 1.10–8.17; p=0.032). Conclusion: Food consumption inside the facility and young age were significant risk factors for COVID-19 transmission in this taekwondo gym. Food consumption should be prohibited in sports facilities, and infection prevention education for young students is also required. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The First Outbreak of Novel Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) at an Outdoor Camping Site in South Korea, 2020
Na-Young Kim, Seonhee Ahn, GwangJin Kim, Donghyok Kwon, Young-Joon Park, Sang-Eun Lee
Journal of Epidemiology.2024; 34(4): 203. CrossRef - Risk evaluation of venue types and human behaviors of COVID-19 outbreaks in public indoor environments: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Weiwei Huang, Caroline X. Gao, Danting Luo, Yong Wang, Xiaohong Zheng, Cong Liu, Ying Wang, Yuguo Li, Hua Qian
Environmental Pollution.2024; 341: 122970. CrossRef - SARS-CoV-2 transmission modes: Why and how contamination occurs around shared meals and drinks?
Aure Saulnier, Jean-Michel Wendling, Benoit Hermant, Didier Lepelletier
Food Microbiology.2023; 114: 104297. CrossRef - Risk factors for COVID-19 outbreaks in livestock slaughtering and processing facilities in Republic of Korea
Seongju Choi, Tae Jong Son, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2023; 14(3): 207. CrossRef - Protective facemask-induced facial thermal stress and breathing burden during exercise in gyms
Qilong Zhong, Jiyun Song, Dachuan Shi, Chung-Hin Dung
Building and Environment.2023; 244: 110840. CrossRef
- The First Outbreak of Novel Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) at an Outdoor Camping Site in South Korea, 2020
Original Article
- Delays in the diagnosis and treatment of tuberculosis during the COVID-19 outbreak in the Republic of Korea in 2020
- Jiyeon Yang, Yunhyung Kwon, Jaetae Kim, Yoojin Jang, Jiyeon Han, Daae Kim, Hyeran Jeong, Hyekyung Park, Eunhye Shim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2021;12(5):293-303. Published online September 23, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.0063
- 7,358 View
- 188 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Objectives
We investigated the impact of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic on tuberculosis (TB) management in the Republic of Korea (ROK).
Methods
This retrospective cross-sectional study used nationwide ROK TB notification data (98,346 cases) from 2017 to 2020. The median time from the onset of TB symptoms to treatment initiation and the compliance rates with the required timing for notification and individual case investigations were measured and compared across periods and regions affected by the COVID-19 epidemic.
Results
TB diagnosis during the COVID-19 pandemic was delayed. The median time to TB treatment initiation (25 days) in 2020 increased by 3 days compared to that of the previous 3 years (22 days) (p<0.0001). In the outbreak in Seoul, Incheon, and Gyeonggi province during August, the time to TB diagnosis was 4 days longer than in the previous 3 years (p=0.0303). In the outbreak in Daegu and Gyeongbuk province from February to March 2020, the compliance rate with the required timing for individual case investigations was 2.2%p points lower than in other areas in 2020 (p=0.0148). For public health centers, the rate was 13%p lower than in other areas (80.3% vs. 93.3%, p=0.0003).
Conclusion
TB diagnoses during the COVID-19 pandemic in the ROK were delayed nationwide, especially for patients notified by public-private mix TB control hospitals. TB individual case investigations were delayed in regional COVID-19 outbreak areas (Daegu and Gyeongbuk province), especially in public health centers. Developing strategies to address this issue will be helpful for sustainable TB management during future outbreaks. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Review of the Impact of Patent Medicine Vendors in Driving Community Tuberculosis Case Finding in the COVID-19 Pandemic in Nigeria
Arinze Emmanuel Ajogwu, Onwubiko Iheanyichukwu Samuel, Nnanyelugo Longinus Ochike, Uzoma Chidinma Ajegbo, Chinedu Paschal Maduka
Matrix Science Medica.2024; 8(2): 33. CrossRef - Tuberculosis: Republic of Korea, 2021
Jinsoo Min, Hyung Woo Kim, Ju Sang Kim
Tuberculosis and Respiratory Diseases.2023; 86(1): 67. CrossRef - Prevalence and associated factors of diabetes mellitus among patients with tuberculosis in South Korea from 2011 to 2018: a nationwide cohort study
Dawoon Jeong, Jeongha Mok, Doosoo Jeon, Hee-Yeon Kang, Hee Jin Kim, Hee-Sun Kim, Jeong Mi Seo, Hongjo Choi, Young Ae Kang
BMJ Open.2023; 13(3): e069642. CrossRef - Increased Healthcare Delays in Tuberculosis Patients During the First Wave of COVID-19 Pandemic in Korea: A Nationwide Cross-Sectional Study
Jinsoo Min, Yousang Ko, Hyung Woo Kim, Hyeon-Kyoung Koo, Jee Youn Oh, Yun-Jeong Jeong, Hyeon Hui Kang, Kwang Joo Park, Yong Il Hwang, Jin Woo Kim, Joong Hyun Ahn, Yangjin Jegal, Ji Young Kang, Sung-Soon Lee, Jae Seuk Park, Ju Sang Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Time trend prediction and spatial–temporal analysis of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in Guizhou Province, China, during 2014–2020
Wang Yun, Chen Huijuan, Liao Long, Lu Xiaolong, Zhang Aihua
BMC Infectious Diseases.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Real-world association of adherence with outcomes and economic burden in patients with tuberculosis from South Korea claims data
Sun-Hong Kwon, Jin Hyun Nam, Hye-Lin Kim, Hae-Young Park, Jin-Won Kwon
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Tuberculosis Case Notification and Treatment Outcomes in Eswatini
Hloniphile Victory Masina, I-Feng Lin, Li-Yin Chien
International Journal of Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Trends in incidences of newly notified tuberculosis in Jeju Province, Korea, 2017-2021
Jinhee Kim, Nam-Hun Kang, Jong-Myon Bae
Journal of Medicine and Life Science.2022; 19(3): 103. CrossRef
- A Review of the Impact of Patent Medicine Vendors in Driving Community Tuberculosis Case Finding in the COVID-19 Pandemic in Nigeria



 First
First Prev
Prev


