Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Estimation of the onset time of diabetic complications in type 2 diabetes patients in Thailand: a survival analysis
- Natthanicha Sauenram, Jutatip Sillabutra, Chukiat Viwatwongkasem, Pratana Satitvipawee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(6):508-519. Published online November 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0084
- 1,029 View
- 58 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 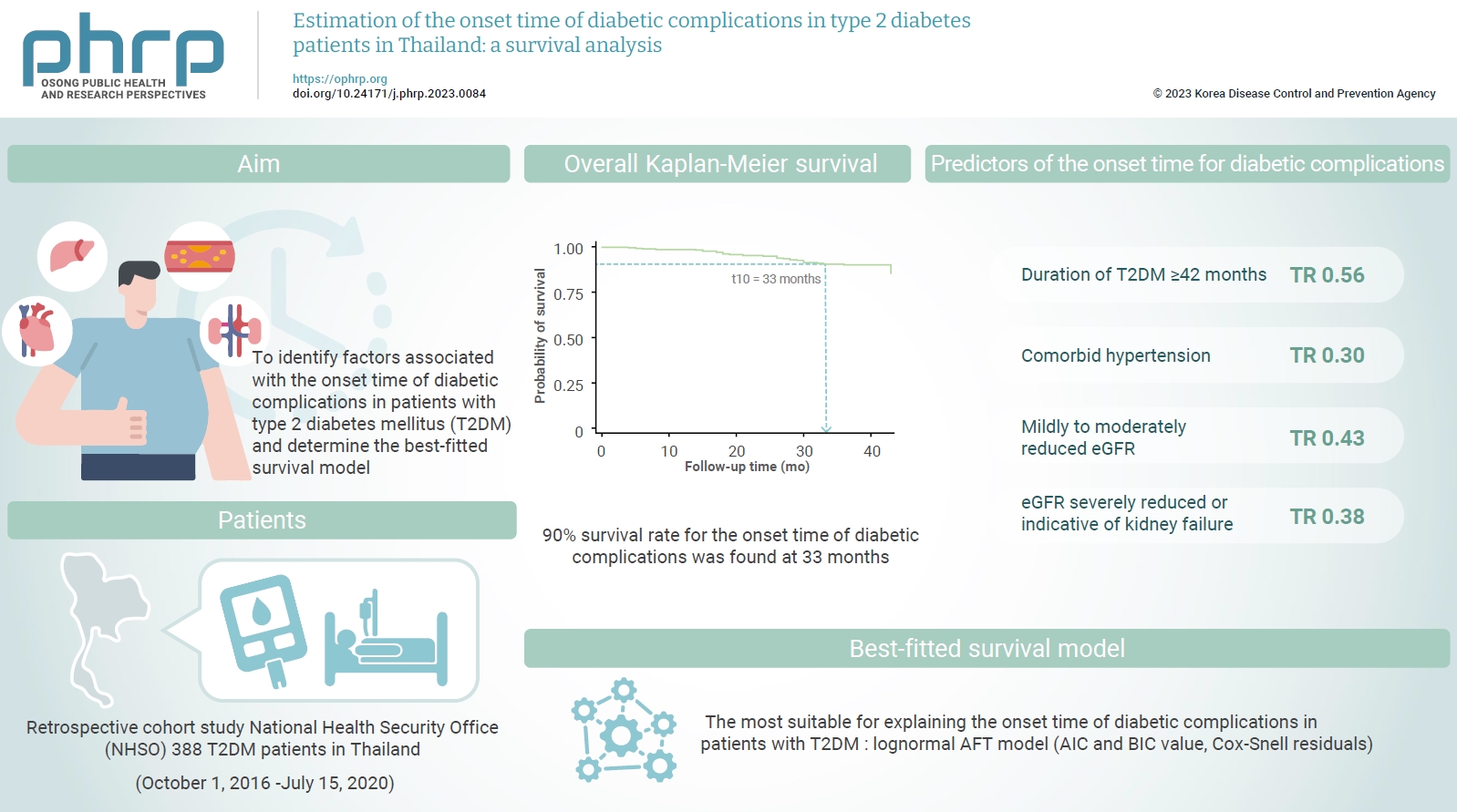
- Objectives
This study aimed to identify factors associated with the onset time of diabetic complications in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and determine the best-fitted survival model. Methods: A retrospective cohort study was conducted among T2DM patients enrolled from October 1, 2016 to July 15, 2020 at the National Health Security Office (NHSO). In total, 388 T2DM patients were included. Cox proportional-hazard and parametric models were used to identify factors related to the onset time of diabetic complications. The Akaike information criterion, Bayesian information criterion, and Cox-Snell residual were compared to determine the best-fitted survival model. Results: Thirty diabetic complication events were detected among the 388 patients (7.7%). A 90% survival rate for the onset time of diabetic complications was found at 33 months after the first T2DM diagnosis. According to multivariate analysis, a duration of T2DM ≥42 months (time ratio [TR], 0.56; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.33–0.96; p=0.034), comorbid hypertension (TR, 0.30; 95% CI, 0.15–0.60; p=0.001), mildly to moderately reduced levels of the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) (TR, 0.43; 95% CI, 0.24–0.75; p=0.003) and an eGFR that was severely reduced or indicative of kidney failure (TR, 0.38; 95% CI, 0.16–0.88; p=0.025) were significantly associated with the onset time of diabetic complications (p<0.05). Conclusion: Patients with T2DM durations of more than 42 months, comorbid hypertension, and decreased eGFR were at risk of developing diabetic complications. The NHSO should be aware of these factors to establish a policy to prevent diabetic complications after the diagnosis of T2DM.
- Evaluation of COVID-19 vaccine effectiveness in different high-risk facility types during a period of Delta variant dominance in the Republic of Korea: a cross-sectional study
- Min Jei Lee, Myung-Jae Hwang, Dong Seob Kim, Seon Kyeong Park, Jihyun Choi, Ji Joo Lee, Jong Mu Kim, Young-Man Kim, Young-Joon Park, Jin Gwack, Sang-Eun Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(5):418-426. Published online October 19, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0188
- 1,250 View
- 43 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 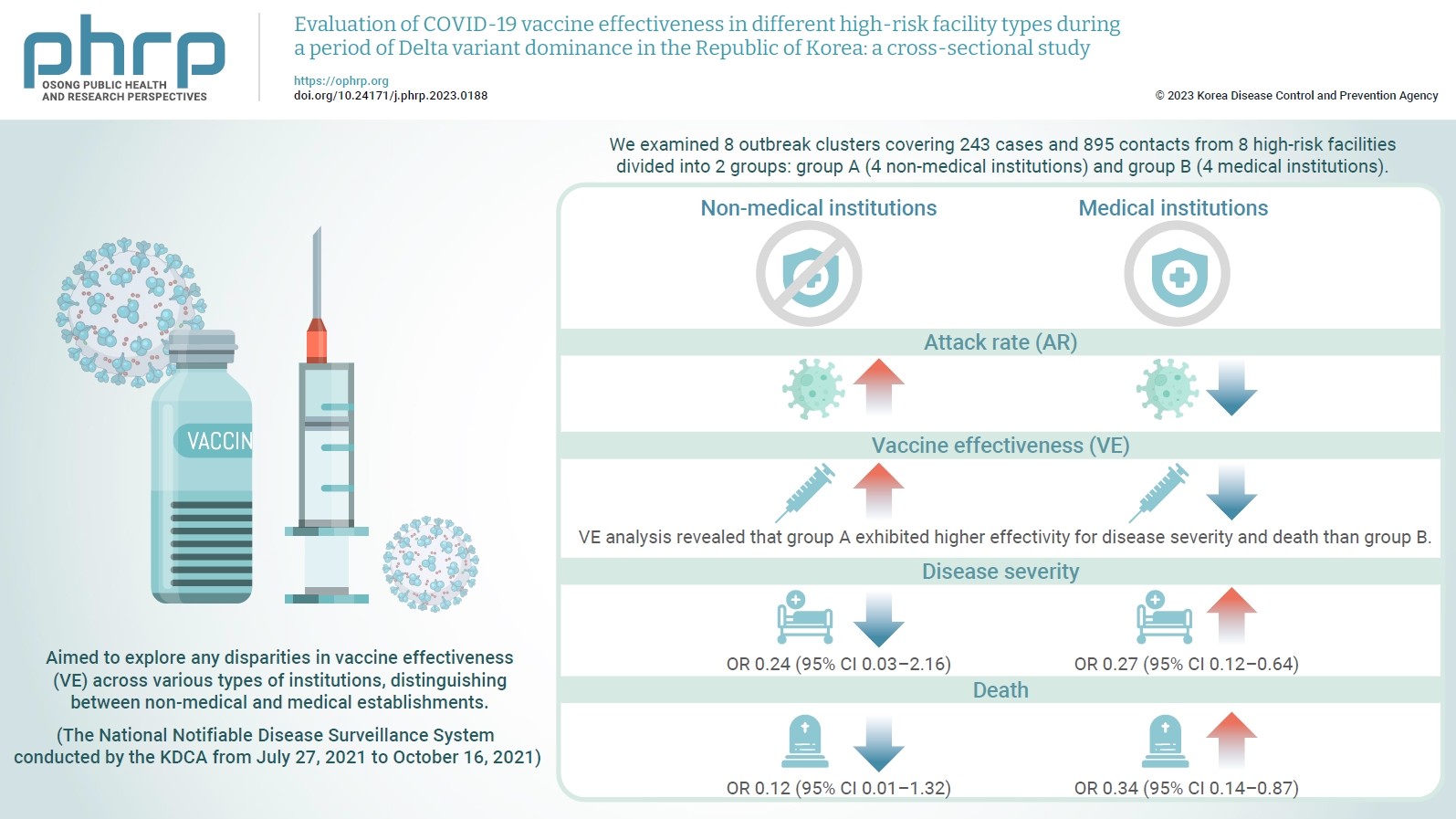
- Objectives
We evaluated the effectiveness of coronavirus disease 2019 vaccination in high-risk facilities in the Republic of Korea during the period when the highly transmissible Delta variant was prevalent. Additionally, we aimed to explore any disparities in vaccine effectiveness (VE) across various types of institutions, specifically distinguishing between non-medical and medical establishments. Methods: We examined 8 outbreak clusters covering 243 cases and 895 contacts from 8 high-risk facilities divided into 2 groups: group A (4 non-medical institutions) and group B (4 medical institutions). These clusters were observed from July 27, 2021 to October 16, 2021 for the attack rate (AR) and VE with respect to disease severity. A generalized linear model with a binomial distribution was used to determine the odds ratio (OR) for disease severity and death. Results: AR was notably lower in group B (medical institutions). Furthermore, VE analysis revealed that group A exhibited higher effectivity for disease severity and death than group B. The OR for disease severity was 0.24 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.03–2.16) for group A and 0.27 (95% CI, 0.12–0.64) for group B, with the OR for death at 0.12 (95% CI, 0.01–1.32) in group A and 0.34 (95% CI, 0.14–0.87) in group B. Conclusion: Although VE may vary across institutions, our findings underscore the importance of implementing vaccinations in high-risk facilities. Customized vaccination programs, tailored response plans, and competent management personnel are essential for effectively addressing and mitigating public health challenges.
- The risk associated with psychiatric disturbances in patients with diabetes in Indonesia (2018): a cross-sectional observational study
- Siti Isfandari, Betty Roosihermiatie, Sulistyowati Tuminah, Laurentia Konadi Mihardja
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(5):368-378. Published online October 18, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0144
- Correction in: Osong Public Health Res Perspect 2023;14(6):530
- 1,400 View
- 68 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 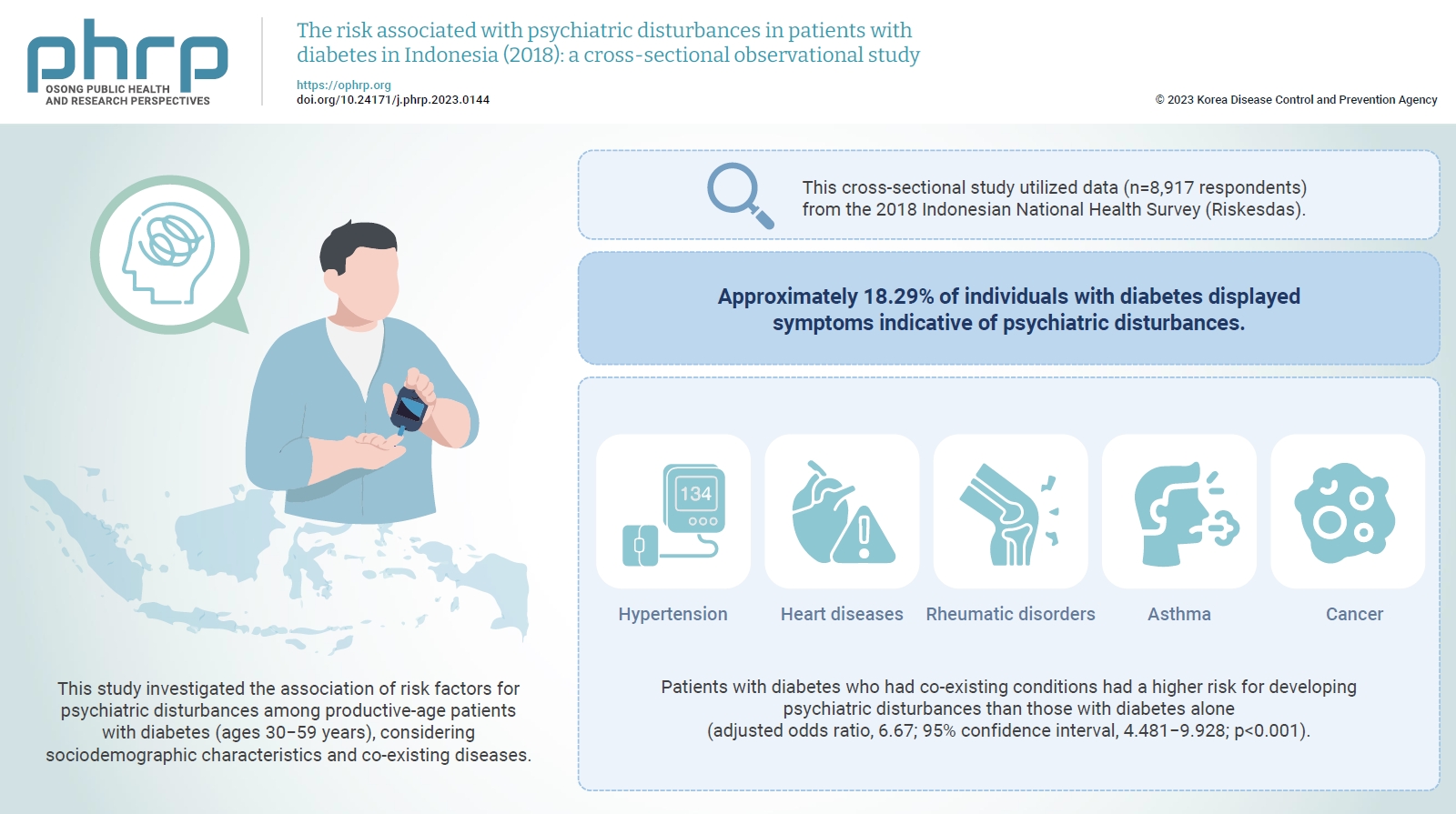
- Objectives
The global prevalence of psychiatric disturbances is rising, detrimentally affecting the quality of care and treatment outcomes for individuals, particularly those with diabetes.This study investigated the association of risk factors for psychiatric disturbances among productive-age patients with diabetes (ages 30−59 years), considering sociodemographic characteristics and co-existing diseases. The risk factors considered included sociodemographic factors (e.g., residence, age, sex, marital status, education, and occupation) and co-existing diseases (e.g., hypertension, heart disease, stroke, renal failure, rheumatism, asthma, and cancer). Methods: This cross-sectional study utilized data from the 2018 Indonesian National Health Survey (Riskesdas). The study population comprised respondents aged between 30 and 59 years who had diabetes and had completed the 20-question self-reporting questionnaire (SRQ-20). After the exclusion of incomplete SRQ-20 data, the sample included 8,917 respondents. Data were analyzed using logistic regression. Results: Approximately 18.29% of individuals with diabetes displayed symptoms indicative of psychiatric disturbances. After adjusting for sociodemographic factors such as age, sex, education level, occupation, marital status, and place of residence, patients with diabetes who had co-existing conditions such as hypertension, heart diseases, rheumatic disorders, asthma, or cancer had a higher risk for developing psychiatric disturbances than those with diabetes alone (adjusted odds ratio, 6.67; 95% confidence interval, 4.481−9.928; p<0.001). Conclusion: The elevated risk of psychiatric disturbances among patients with diabetes who had comorbidities underscores the importance of addressing mental health issues in the management of diabetes, especially in patients with concurrent disease conditions. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Correction to “The risk associated with psychiatric disturbances in patients with diabetes in Indonesia (2018): a cross-sectional observational study” [Osong Public Health Res Perspect 2023;14(5):368–78]
Siti Isfandari, Betty Roosihermiatie, Sulistyowati Tuminah, Laurentia Konadi Mihardja
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2023; 14(6): 530. CrossRef
- Correction to “The risk associated with psychiatric disturbances in patients with diabetes in Indonesia (2018): a cross-sectional observational study” [Osong Public Health Res Perspect 2023;14(5):368–78]
Short Communication
- Perceptions of older adults and generativity among older citizens in Japan: a descriptive cross-sectional study
- Yuho Shimizu, Tomoya Takahashi, Kenichiro Sato, Susumu Ogawa, Daisuke Cho, Yoshifumi Takahashi, Daichi Yamashiro, Yan Li, Keigo Hinakura, Ai Iizuka, Tomoki Furuya, Hiroyuki Suzuki
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(5):427-432. Published online October 10, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0063
- 1,209 View
- 55 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 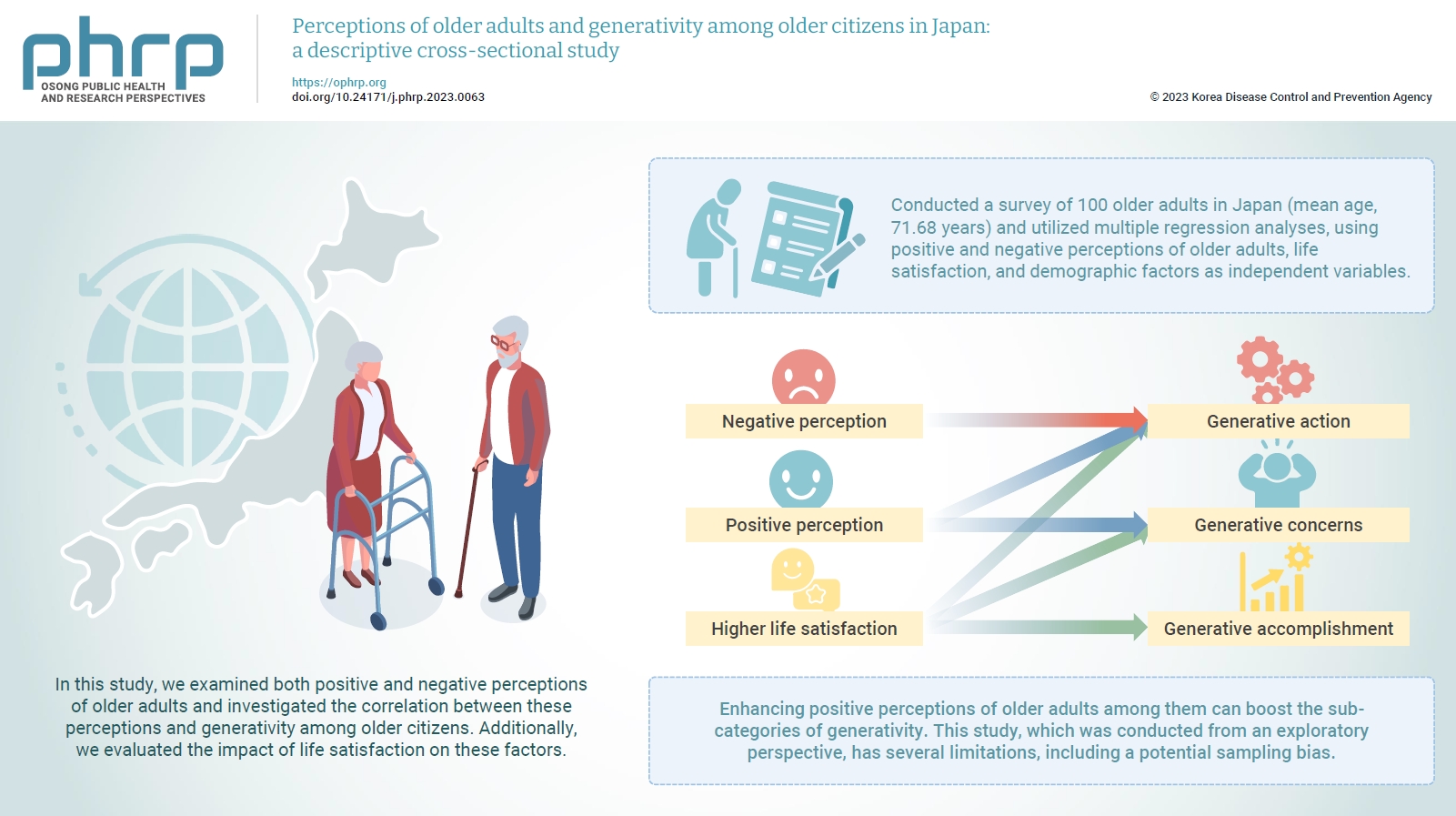
- Objectives
As the population ages worldwide, including in Japan, there is a growing expectation for older adults to remain active participants in society. The act of sharing one’s experiences and knowledge with younger generations through social engagement not only enriches the lives of older individuals, but also holds significant value for our society. In this study, we examined both positive and negative perceptions of older adults and investigated the correlation between these perceptions and generativity among older citizens. Additionally, we evaluated the impact of life satisfaction on these factors. Methods: We conducted a survey of 100 older adults in Japan (mean age, 71.68 years) and utilized multiple regression analyses, using positive and negative perceptions of older adults, life satisfaction, and demographic factors as independent variables. The sub-categories of generativity—namely, generative action, concern, and accomplishment—were used as dependent variables. Results: Participants who held a more positive perception of older adults demonstrated a higher level of generative actions and concerns. Additionally, participants who reported higher levels of life satisfaction also exhibited more generative actions, concerns, and accomplishments. Conversely, those who held a more negative perception of older adults were found to have higher levels of generative actions. Conclusion: Enhancing positive perceptions of older adults among them can boost the sub-categories of generativity. This study, which was conducted from an exploratory perspective, has several limitations, including a potential sampling bias. A more comprehensive examination of the relationship between perceptions of older adults and generativity is anticipated in future research.
Review Article
- Public health agencies’ use of social media for communication during pandemics: a scoping review of the literature
- Babatunde Abiodun Balogun, Anne Hogden, Nenagh Kemp, Lin Yang, Maria Agaliotis
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(4):235-251. Published online August 9, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0095
- 1,674 View
- 146 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Public health agencies (PHAs) have increasingly incorporated social media into their communication mix during successive pandemics in the 21st century. However, the quality, timing, and accuracy of their health messages have varied significantly, resulting in mixed outcomes for communication, audience engagement, and pandemic management. This study aimed to identify factors influencing the effectiveness of pandemic-related health messages shared by PHAs on social media and to report their impact on public engagement as documented in the literature. A scoping literature review was conducted following a predefined protocol. An electronic search of 7 relevant databases and 5 grey literature repositories yielded 9,714 papers published between January 2003 and November 2022. Seventy-three papers were deemed eligible and selected for review. The results underscored the insufficiency of social media guidance policies for PHAs. Six themes were identified: message source, message topic, message style, message timing, content credibility and reliability, and message recipient profile. These themes encompassed 20 variables that could inform PHAs’ social media public health communication during pandemics. Additionally, the findings revealed potential interconnectedness among the variables, and this study concluded by proposing a conceptual model that expands upon existing theoretical foundations for developing and evaluating pandemic-related health messaging.
Original Articles
- Vaccine effectiveness and the epidemiological characteristics of a COVID-19 outbreak in a tertiary hospital in Republic of Korea
- Seonhee Ahn, Tae Jong Son, Yoonsuk Jang, Jihyun Choi, Young Joon Park, Jiseon Seong, Hyun Hee Kwon, Muk Ju Kim, Donghyok Kwon
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(3):188-196. Published online June 8, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0066
- 1,437 View
- 71 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 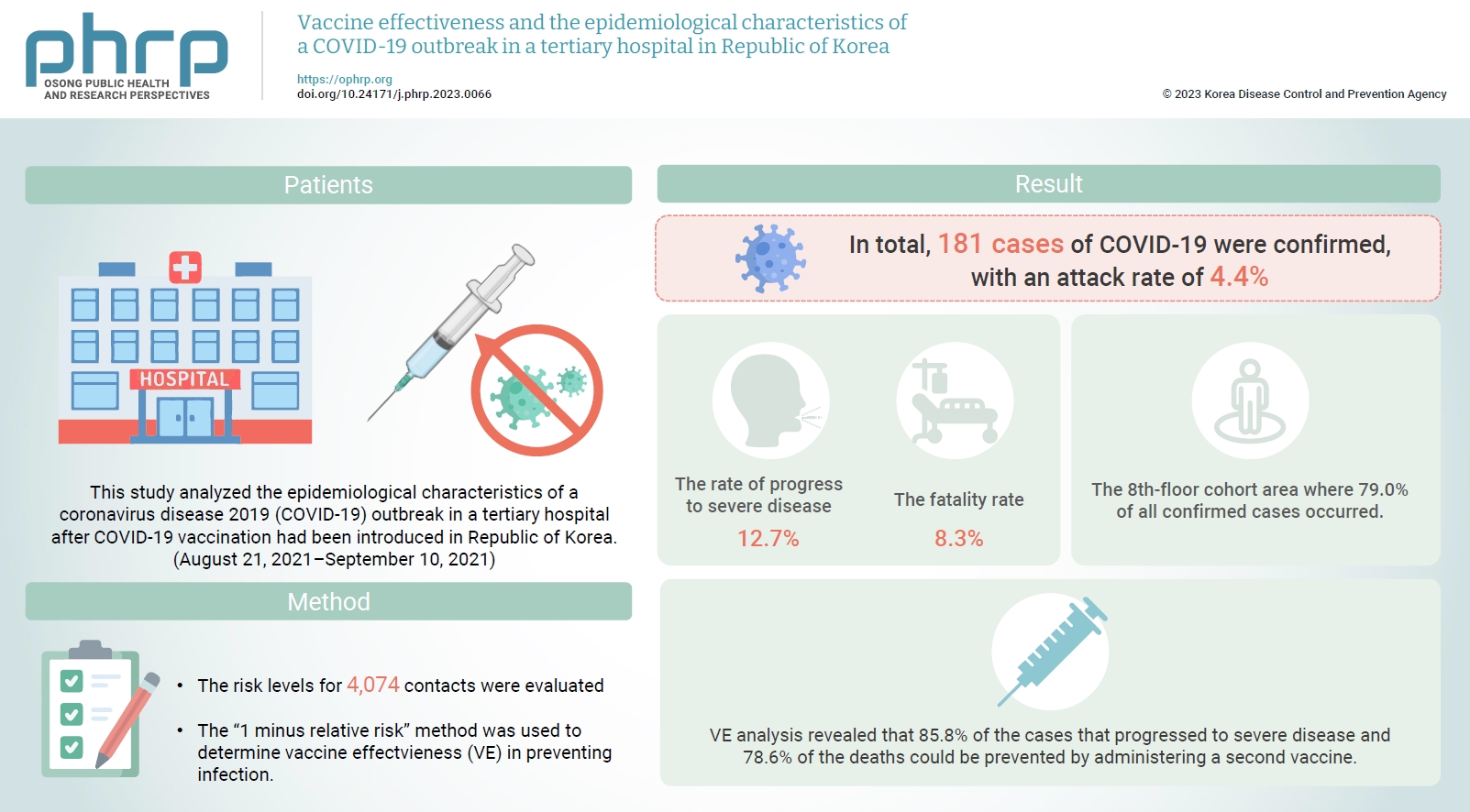
- Objectives
Healthcare facilities are high-risk sites for infection. This study analyzed the epidemiological characteristics of a coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in a tertiary hospital after COVID-19 vaccination had been introduced in Republic of Korea. Vaccine effectiveness (VE) and shared anti-infection strategies are also assessed.
Methods
The risk levels for 4,074 contacts were evaluated. The epidemiological characteristics of confirmed cases were evaluated using the chi-square test. The “1 minus relative risk” method was used to determine VE in preventing infection, progression to severe disease, and death. In the largest affected area (the 8th floor), a separate relative risk analysis was conducted. A multivariate logistic regression analysis (with 95% confidence interval [CIs]) was used to identify transmission risk factors with a significance level <10% via the backward elimination method.
Results
In total, 181 cases of COVID-19 were confirmed, with an attack rate of 4.4%. Of those cases, 12.7% progressed to severe disease, and 8.3% died. In the cohort isolation area on the 8th floor, where 79.0% of the confirmed cases occurred, the adjusted odds ratio was 6.55 (95% CI, 2.99–14.33) and 2.19 (95% CI, 1.24–3.88) for caregivers and the unvaccinated group, respectively. VE analysis revealed that 85.8% of the cases that progressed to severe disease and 78.6% of the deaths could be prevented by administering a second vaccine.
Conclusion
Caregiver training for infection prevention and control is necessary to reduce infection risk. Vaccination is an important intervention to reduce the risk of progression to severe disease and death.
- Risk factors associated with death due to severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in hospitalized Korean patients (2018–2022)
- Jia Kim, Hyo-jeong Hong, Ji-hye Hwang, Na-Ri Shin, Kyungwon Hwang
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(3):151-163. Published online June 8, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0048
- 1,644 View
- 173 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 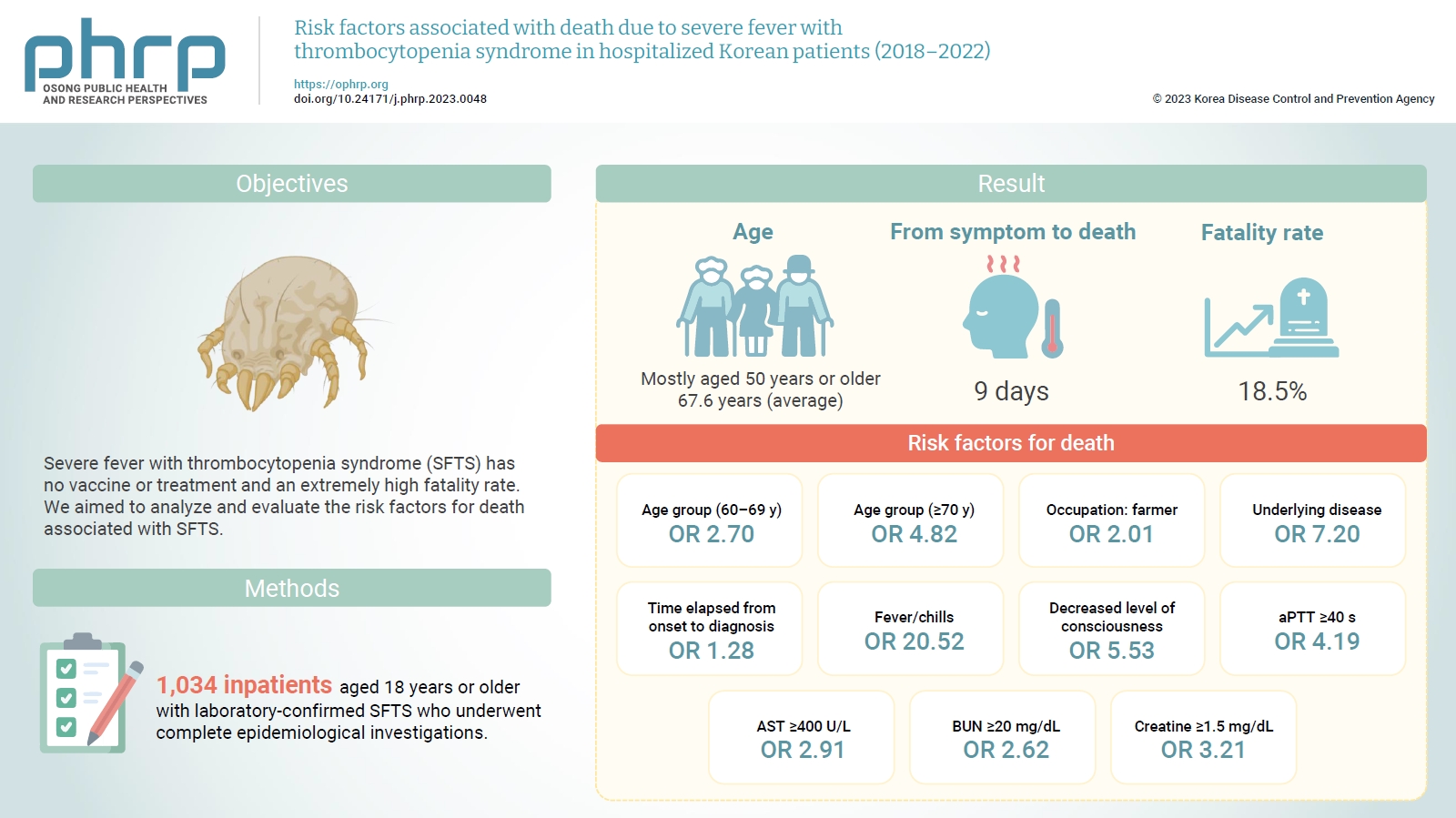
- Objectives
Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS) has no vaccine or treatment and an extremely high fatality rate. We aimed to analyze and evaluate the risk factors for death associated with SFTS.
Methods
Among reports from 2018 to 2022, we compared and analyzed 1,034 inpatients aged 18 years or older with laboratory-confirmed SFTS who underwent complete epidemiological investigations.
Results
Most of the inpatients with SFTS were aged 50 years or older (average age, 67.6 years). The median time from symptom onset to death was 9 days, and the average case fatality rate was 18.5%. Risk factors for death included age of 70 years or older (odds ratio [OR], 4.82); agriculture-related occupation (OR, 2.01); underlying disease (OR, 7.20); delayed diagnosis (OR, 1.28 per day); decreased level of consciousness (OR, 5.53); fever/chills (OR, 20.52); prolonged activated partial thromboplastin time (OR, 4.19); and elevated levels of aspartate aminotransferase (OR, 2.91), blood urea nitrogen (OR, 2.62), and creatine (OR, 3.21).
Conclusion
The risk factors for death in patients with SFTS were old age; agriculture-related occupation; underlying disease; delayed clinical suspicion; fever/chills; decreased level of consciousness; and elevated activated partial thromboplastin time, aspartate aminotransferase, blood urea nitrogen, and creatine levels.
- Effectiveness of the COVID-19 vaccine in the Honam region of the Republic of Korea
- In-Sook Shin, Yong-Pyo Lee, Seung-Hoon Lee, Jae-Young Lee, Jong-Ha Park, Yoon-Seok Chung
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(3):197-206. Published online June 8, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0308
- 1,826 View
- 62 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 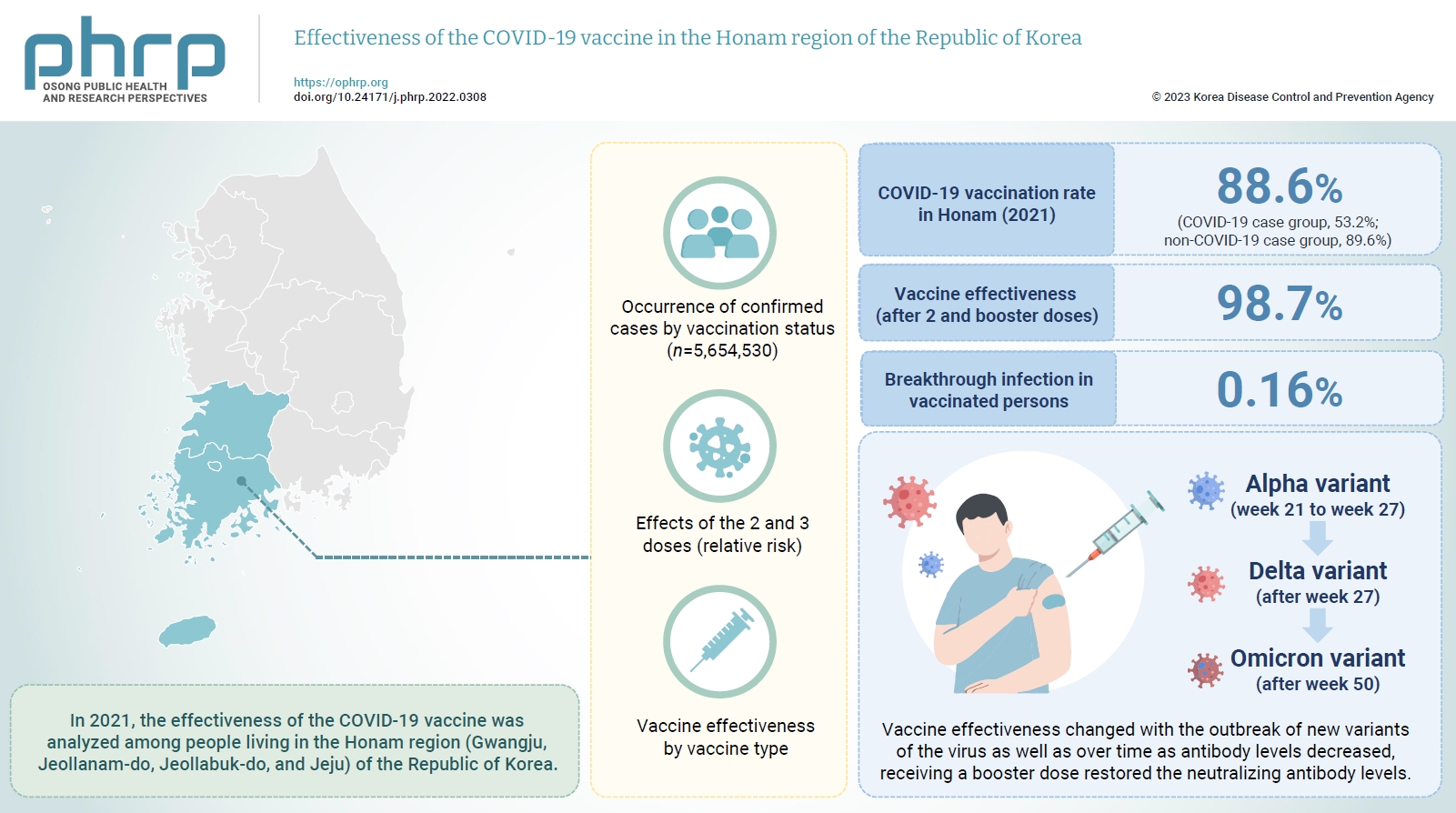
- Objectives
In 2021, the effectiveness of the COVID-19 vaccine was analyzed among people living in the Honam region (Gwangju, Jeollanam-do, Jeollabuk-do, and Jeju) of the Republic of Korea. And we investigated changes in the dominant virus strain.
Methods
This study used the data provided by the Korean Ministry of the Interior and Safety for individuals ≥12 years old in the Honam region, and the Integrated Disease and Health Management System of the Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for COVID-19-vaccinated individuals as of December 31, 2021. Statistical analyzes were performed using IBM SPSS ver. 23.0. The occurrence of confirmed cases by vaccination status, the relative risk, and vaccine effectiveness by vaccine type were calculated.
Results
In 2021, the COVID-19 vaccination rate in Honam was 88.6%. The overall vaccine effectiveness (after 2 and 3 doses) was 98.7% (p<0.001). and the breakthrough infection rate was 0.16%. From week 21 to week 27 of 2021 (June 27 to July 3), the genome sequencing results were mostly alpha variants. The Delta variant emerged as the dominant variant after 27 weeks and the Omicron variant was found at 50 weeks (December 5–11).
Conclusion
Vaccine effectiveness changed with the outbreak of new variants of the virus as well as over time as antibody levels decreased. that the prevention effectiveness of vaccination in Honam was >98%, and the effect among persons who received 2 doses was >90% regardless of the vaccine type. Although vaccine effectiveness decreased because of reduced antibody levels over time (as observed in breakthrough infections), receiving a booster dose restored the neutralizing antibody levels.
Review Article
- Points to consider when developing drugs for dry eye syndrome
- Suyoung Bae, Hosun Seung, Ho Jung Oh
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(2):70-75. Published online April 26, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0031
- 1,525 View
- 112 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 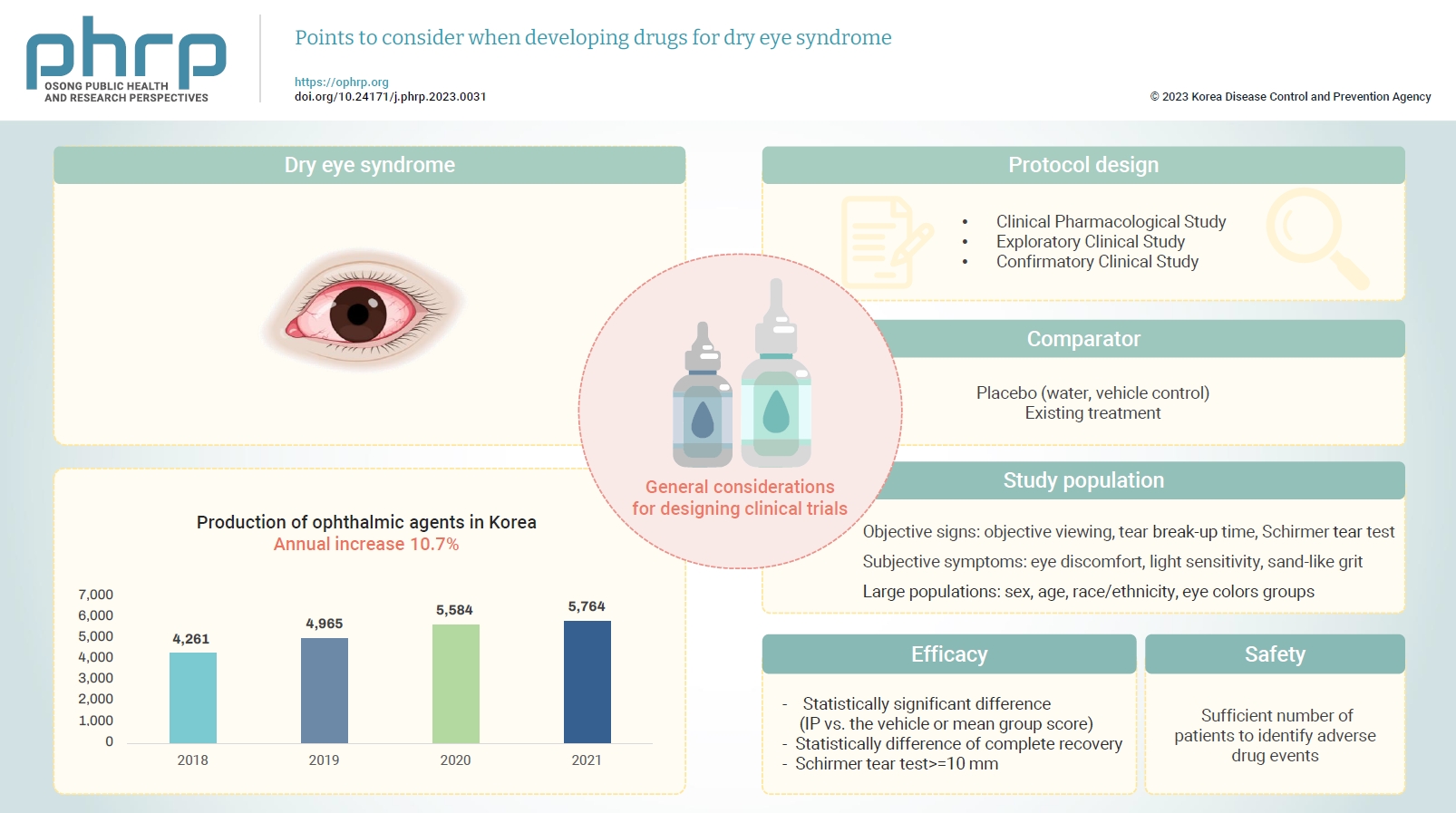
- Changes in both the social environment (e.g., the increased use of electronic media) and the atmospheric environment (e.g., air pollution and dust) have contributed to an increasing incidence of eye disease and an increased need for eye care. Notably, the signs and symptoms of dry eye syndrome can impact the daily quality of life for various age groups, including the elderly, and usually requires active treatment. The symptoms of dry eye syndrome include tear film instability, hyperosmolarity, ocular surface inflammation and damage, and neurosensory abnormalities. As treatments for dry eye are being developed, a standardized guideline is needed to increase the efficiency of drug development and improve the quality of clinical trial data. In this paper, we present general considerations for the pharmaceutical industry and clinical trial investigators designing clinical trials focused on the development of drugs to treat dry eye syndrome.
Original Articles
- The incidence and clinical characteristics of myocarditis and pericarditis following mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccination in Republic of Korea adolescents from July 2021 to September 2022
- Ju-Young Sim, Seung-Yun Kim, Eun-Kyoung Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(2):76-88. Published online April 18, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0032
- 3,867 View
- 230 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 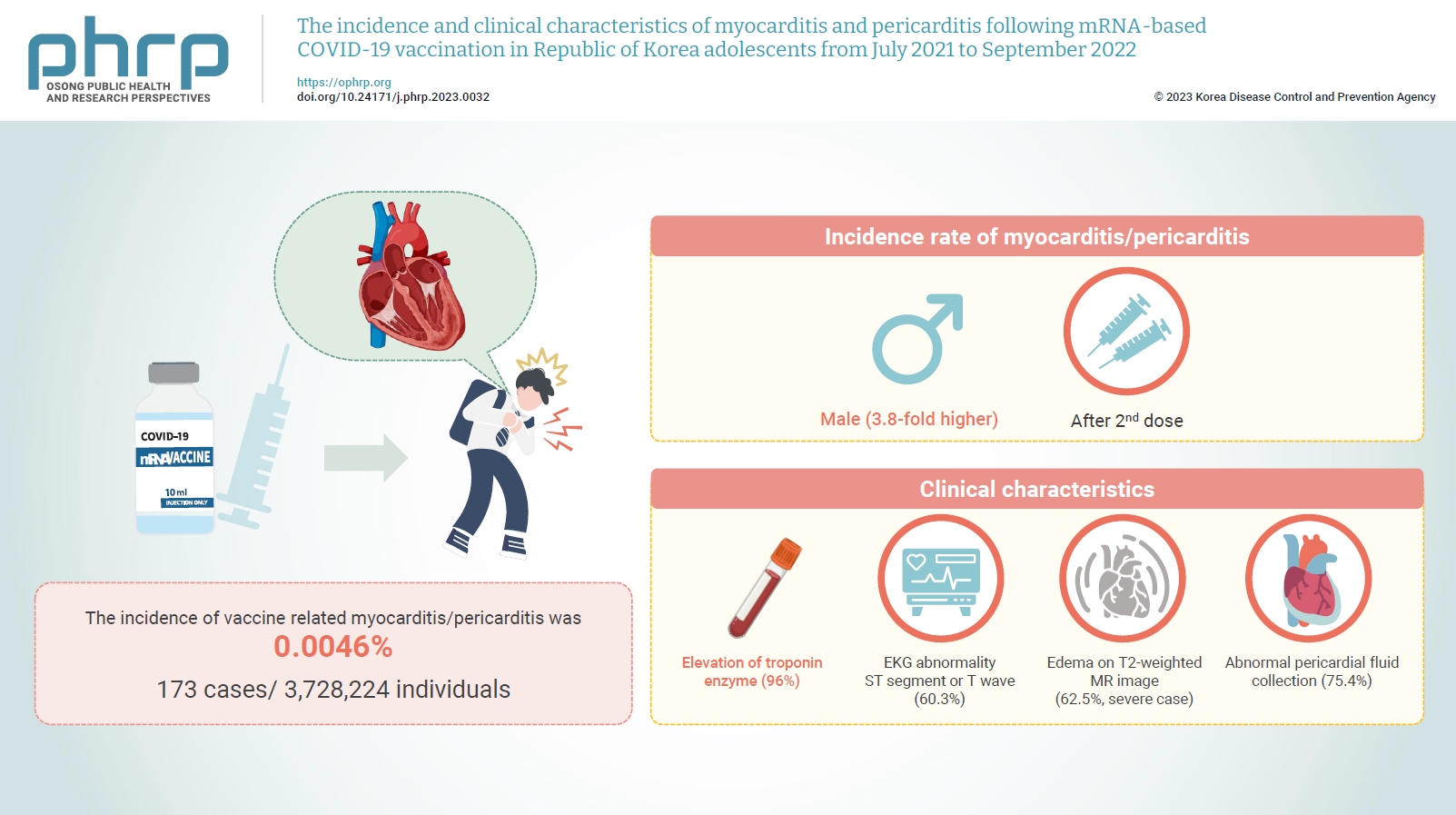
- Objectives
Age-specific information regarding myocarditis/pericarditis in adolescents following mRNA-based coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccination in Asia remains insufficient. This study investigated the incidence and clinical characteristics of myocarditis/pericarditis in Republic of Korea adolescents after mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccination.
Methods
This retrospective descriptive study utilized patient data from the Korea Immunization Management System. Incidence rates were calculated according to age and sex. Clinical characteristics (symptoms/signs, laboratory values, and imaging results) were compared between mild and severe cases.
Results
Between July 19, 2021 and September 30, 2022, 3,728,224 individuals aged 12 to 19 years received 6,484,165 mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines, and 173 cases met the case definition for myocarditis/pericarditis: 151 mild (87.3%) and 22 severe (12.7%). The incidence was 3.8-fold higher in males than in females. Troponin I/ troponin T was elevated in 96% of myocarditis cases, demonstrating higher sensitivity than creatine kinase-myocardial band (67.6%) or C-reactive protein (75.2%). ST-segment or Twave on electrography abnormalities were found in 60.3% (85/141). Paroxysmal/sustained atrial/ventricular arrhythmias were more common in severe than in mild cases (45.5% vs. 16.8%, p=0.008). Edema on T2-weighted magnetic imaging occurred in 21.6% (8/37) and 62.5% (5/8) of mild and severe cases, respectively (p=0.03). Abnormal pericardial fluid collection or pericardial inflammation was found in 75.4% of pericarditis cases (49/65).
Conclusion
Myocarditis/pericarditis occurred in rare cases following mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccination. Most cases were mild, but the incidence was higher in adolescent males and after the second dose. As bivalent severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 mRNA vaccination started in Republic of Korea in October 2022, the post-vaccination incidence of myocarditis/pericarditis should be closely monitored, considering clinical characteristics. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Responses to Common Misconceptions Relating to COVID-19 Variant-Adapted mRNA Vaccines
George Kassianos, Pauline MacDonald, Ivan Aloysius, Shanti Pather
Vaccines.2024; 12(1): 57. CrossRef - To become a more stronger and safer country
Jong-Koo Lee
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2023; 14(2): 67. CrossRef
- Responses to Common Misconceptions Relating to COVID-19 Variant-Adapted mRNA Vaccines
- Association between the empirical dietary inflammatory index and musculoskeletal pain in community-dwelling older adults: a cross-sectional study
- Mahshid Rezaei, Zahra Tajary, Zahra Esmaeily, Atefeh Eyvazkhani, Shahrzad Daei, Marjan Mansouri Dara, Mohaddeseh Rezaei, Abolghassem Djazayeri, Ahmadreza Dorosty Motlagh
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(1):51-58. Published online February 20, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0194
- 1,994 View
- 69 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 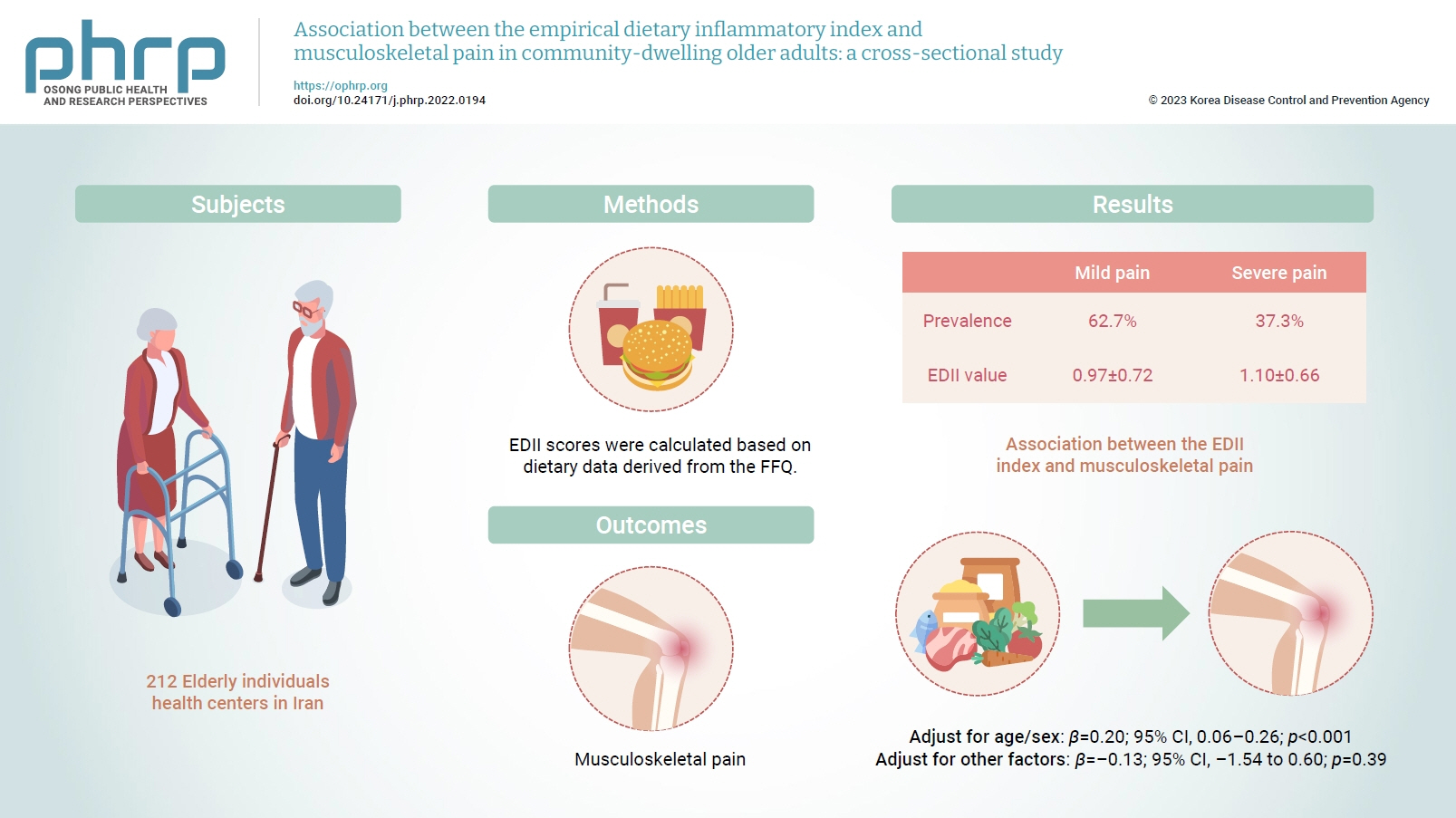
- Objectives
Inflammation has been proposed to be one of the main causes of musculoskeletal pain. Diet is a lifestyle factor that plays an important role in managing inflammation; thus, we assessed the inflammatory potential of diets using the empirical dietary inflammatory index (EDII) to investigate the relationship between diet and musculoskeletal pain.
Methods
This cross-sectional study included 212 elderly individuals who were selected from health centers in Tehran, Iran. Dietary intake was evaluated using a valid and reliable 147-item food frequency questionnaire. To measure the intensity of pain, a visual analogue scale was used. Multiple linear regression was applied to assess the association between the EDII and musculoskeletal pain.
Results
In total, 62.7% and 37.3% of participants had mild and severe pain, respectively. The EDII values were 0.97±0.72 and 1.10±0.66, respectively, in those with mild and severe pain. A higher EDII score was associated with more intense musculoskeletal pain after adjusting for age and sex (β=0.20; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.06–0.26; p<0.001), but not after adjustment for other confounders (β=–0.13; 95% CI, –1.54 to 0.60; p=0.39).
Conclusion
Our findings indicated that higher dietary inflammation might not be associated with musculoskeletal pain in older adults. However, further investigations are required to confirm these findings. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between dietary inflammatory index and musculoskeletal disorders in adults
Firoozeh Khamoushi, Davood Soleimani, Farid Najafi, Neshat Ahmadi, Neda Heidarzadeh-Esfahani, Bita Anvari, Ebrahim Shakiba, Yahya Pasdar
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Association between dietary inflammatory index and musculoskeletal disorders in adults
- mRNA vaccine effectiveness against SARS-CoV-2 B.1.617.2 (Delta) and B.1.1.529 (Omicron) variant transmission from home care cases to household contacts in South Korea
- Hanul Park, Young Joon Park, Sang Eun Lee, Min Jei Lee, Hyungtae Ahn
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(6):435-442. Published online November 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0243
- 4,702 View
- 170 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 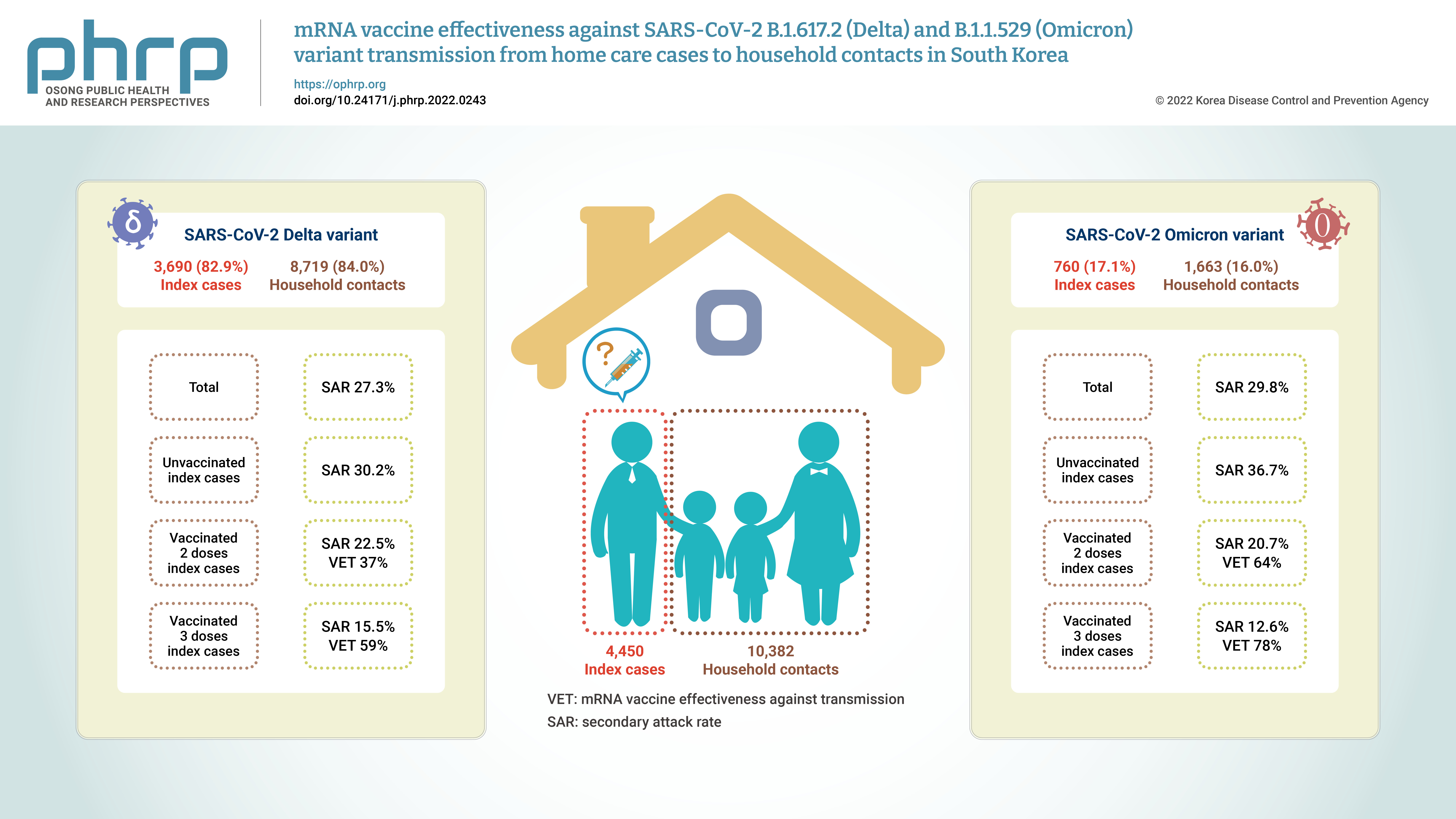
- Objectives
Household contacts of confirmed cases of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) areexposed to a high risk of viral transmission, and secondary incidence is an important indicatorof community transmission. This study analyzed the secondary attack rate and mRNA vaccineeffectiveness against transmission (VET) for index cases (patients treated at home) confirmedto be infected with the Delta and Omicron variants.Methods: The subjects of the study were 4,450 index cases and 10,382 household contacts.Logistic regression analysis was performed to compare the secondary attack rate byvaccination status, and adjusted relative risk and 95% confidence intervals were identified.Results: The secondary attack rate of the Delta variant was 27.3%, while the secondary attackrate of the Omicron variant was 29.8%. For the Delta variant, groups with less than 90 daysand more than 90 days after 2 doses of mRNA vaccination both showed a VET of 37%. For theOmicron variant, a 64% VET was found among those with less than 90 days after 2 doses ofmRNA vaccination.Conclusion: This study provides useful data on the secondary attack rate and VET of mRNAvaccines for household contacts of COVID-19 cases in South Korea. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Household secondary attack rates and risk factors during periods of SARS-CoV-2 Delta and Omicron variant predominance in the Republic of Korea
Jin Lee, Mijeong Ko, Seontae Kim, Dosang Lim, Gemma Park, Sang-Eun Lee
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2023; 14(4): 263. CrossRef
- Household secondary attack rates and risk factors during periods of SARS-CoV-2 Delta and Omicron variant predominance in the Republic of Korea
- Clinical outcomes of remdesivir-treated COVID-19 patients in South Korea
- Mi Yu, Bryan Inho Kim, Jungyeon Kim, Jin Gwack
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(5):370-376. Published online October 18, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0138
- 2,030 View
- 70 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study analyzed the clinical outcomes of remdesivir treatment in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients in South Korea.
Methods
This retrospective cohort study involved the secondary analysis of epidemiological data. Among patients diagnosed with COVID-19 from July 2, 2020 to March 23, 2021 (12 AM), 4,868 who received oxygen therapy and were released from isolation after receiving remdesivir treatment were assigned to the treatment group, and 6,068 patients who received oxygen therapy but not remdesivir were assigned to the untreated group. The study subjects included children under the age of 19. The general characteristics and severity were compared between the groups. Differences in the time to death and mortality were also compared.
Results
In the untreated group, the hazard ratio [HR] for mortality was 1.59 among patients aged ≥70 years and 2.32 in patients with severe disease in comparison to the treatment group. In a comparison of survival time among patients with severe disease aged ≥70 years, the HR for mortality before 50 days was 2.09 in the untreated group compared to the treatment group.
Conclusion
Patients with remdesivir treatment showed better clinical outcomes in this study, but these results should be interpreted with caution since this study was not a fully controlled clinical trial. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Role of Multidimensional Prognostic Index to Identify Hospitalized Older Adults with COVID-19 Who Can Benefit from Remdesivir Treatment: An Observational, Prospective, Multicenter Study
Carlo Custodero, Nicola Veronese, Eva Topinkova, Helena Michalkova, Maria Cristina Polidori, Alberto Cella, Alfonso J. Cruz-Jentoft, Christine A. F. von Arnim, Margherita Azzini, Heidi Gruner, Alberto Castagna, Giovanni Cenderello, Romina Custureri, Tania
Drugs & Aging.2023; 40(7): 643. CrossRef - Remdesivir: A Review in COVID-19
Hannah A. Blair
Drugs.2023; 83(13): 1215. CrossRef
- The Role of Multidimensional Prognostic Index to Identify Hospitalized Older Adults with COVID-19 Who Can Benefit from Remdesivir Treatment: An Observational, Prospective, Multicenter Study
Review Article
- Effects of medication adherence interventions for older adults with chronic illnesses: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Hae Ok Jeon, Myung-Ock Chae, Ahrin Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(5):328-340. Published online October 12, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0168
- 3,539 View
- 166 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to understand the characteristics of medication adherence interventions for older adults with chronic illnesses, and to investigate the average effect size by combining the individual effects of these interventions. Data from studies meeting the inclusion criteria were systematically collected in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis guidelines. The results showed that the average effect size (Hedges’ g) of the finally selected medication adherence interventions for older adults with chronic illnesses calculated using a random-effects model was 0.500 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.342−0.659). Of the medication adherence interventions, an implementation intention intervention (using face-to-face meetings and telephone monitoring with personalized behavioral strategies) and a health belief model–based educational program were found to be highly effective. Face-to-face counseling was a significantly effective method of implementing medication adherence interventions for older adults with chronic illnesses (Hedges’ g=0.531, 95% CI, 0.186−0.877), while medication adherence interventions through education and telehealth counseling were not effective. This study verified the effectiveness of personalized behavioral change strategies and cognitive behavioral therapy based on the health belief model, as well as face-to-face meetings, as medication adherence interventions for older adults with chronic illnesses.
Brief Report
- Isolation and identification of monkeypox virus MPXV-ROK-P1-2022 from the first case in the Republic of Korea
- Jin-Won Kim, Minji Lee, Hwachul Shin, Chi-Hwan Choi, Myung-Min Choi, Jee Woong Kim, Hwajung Yi, Cheon-Kwon Yoo, Gi-Eun Rhie
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(4):308-311. Published online August 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0232
- 4,984 View
- 135 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 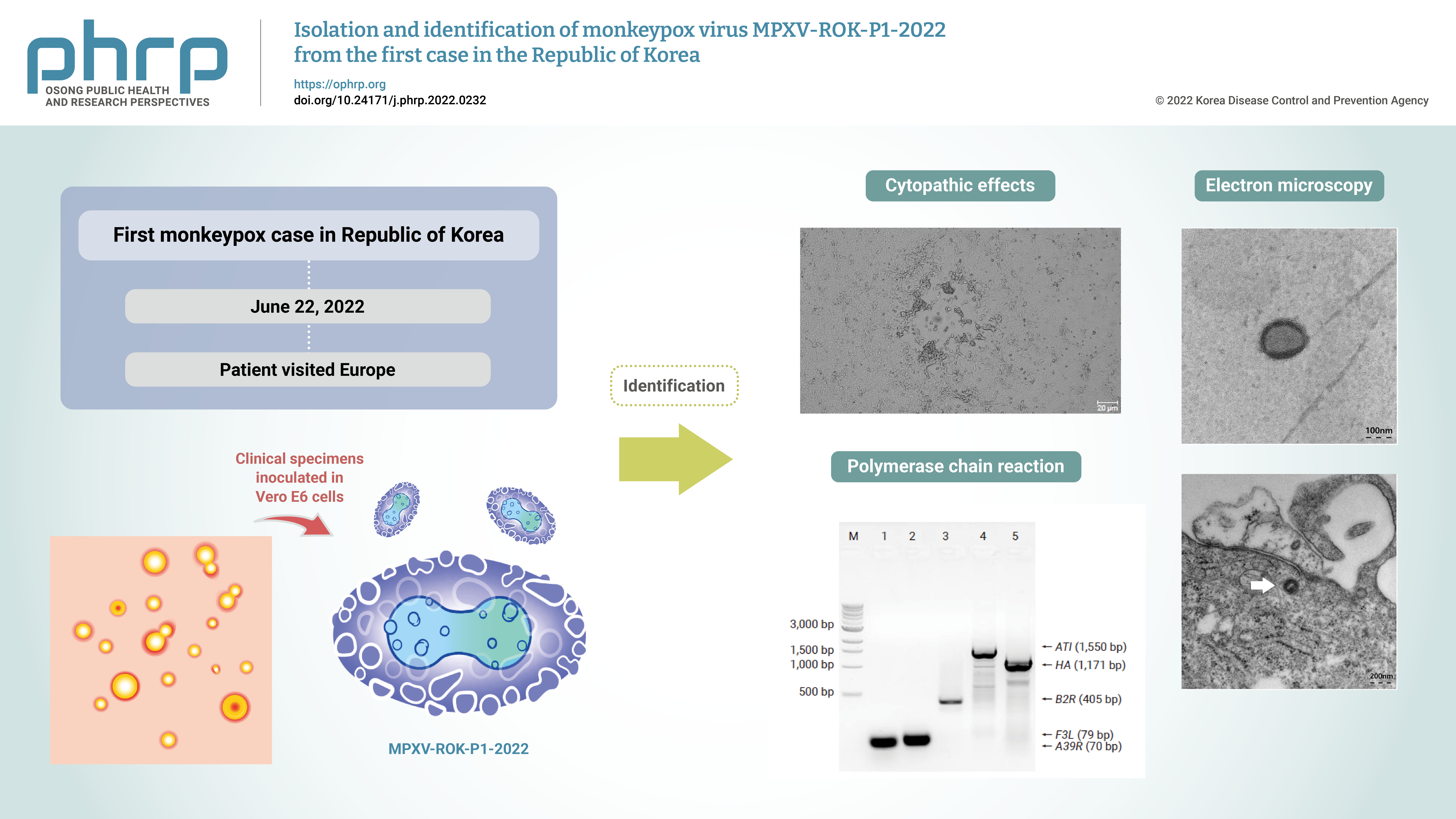
- Objectives
Monkeypox outbreaks in nonendemic countries have been reported since early May 2022. The first case of monkeypox in the Republic of Korea was confirmed in a patient who traveled to Europe in June 2022, and an attempt was made to isolate and identify the monkeypox virus (MPXV) from the patient’s specimens.
Methods
Clinical specimens from the patient were inoculated in Vero E6 cells. The isolated virus was identified as MPXV by the observation of cytopathic effects on Vero E6 cells, transmission electron microscopy, conventional polymerase chain reaction (PCR), and sequencing of PCR products.
Results
Cytopathic effects were observed in Vero E6 cells that were inoculated with skin lesion swab eluates. After multiple passages from the primary culture, orthopoxvirus morphology was observed using transmission electron microscopy. In addition, both MPXV-specific (F3L and ATI) and orthopoxvirus-specific genes (A39R, B2R, and HA) were confirmed by conventional PCR and Sanger sequencing.
Conclusion
These results indicate the successful isolation and identification of MPXV from the first patient in the Republic of Korea. The isolated virus was named MPXV-ROK-P1-2022. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ultrasensitive one-pot detection of monkeypox virus with RPA and CRISPR in a sucrose-aided multiphase aqueous system
Yue Wang, Yixin Tang, Yukang Chen, Guangxi Yu, Xue Zhang, Lihong Yang, Chenjie Zhao, Pei Wang, Song Gao, Frederick S. B. Kibenge, Ruijie Deng, Wei Chen, Shuang Yang
Microbiology Spectrum.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Epidemiological, Clinical, and Virological Investigation of the First Four Cases of Monkeypox in Cartagena during the 2022 Outbreak
Steev Loyola, Mashiel Fernández-Ruiz, Doris Gómez-Camargo
Pathogens.2023; 12(2): 159. CrossRef - 원숭이두창바이러스의 분리 배양과 전장유전체 정보 분석
민지 이, 진원 김, 치환 최, 화철 신, 명민 최, 상은 이, 화중 이, 윤석 정
Public Health Weekly Report.2023; 16(15): 464. CrossRef - Overview of Diagnostic Methods, Disease Prevalence and Transmission of Mpox (Formerly Monkeypox) in Humans and Animal Reservoirs
Ravendra P. Chauhan, Ronen Fogel, Janice Limson
Microorganisms.2023; 11(5): 1186. CrossRef - How to cope with suspected mpox patients in the outpatient clinic
Nam Joong Kim, Sun Huh
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2023; 66(5): 325. CrossRef - An Updated Review on Monkeypox Viral Disease: Emphasis on Genomic Diversity
Ali A. Rabaan, Nada A. Alasiri, Mohammed Aljeldah, Abeer N. Alshukairiis, Zainab AlMusa, Wadha A. Alfouzan, Abdulmonem A. Abuzaid, Aref A. Alamri, Hani M. Al-Afghani, Nadira Al-baghli, Nawal Alqahtani, Nadia Al-baghli, Mashahed Y. Almoutawa, Maha Mahmoud
Biomedicines.2023; 11(7): 1832. CrossRef - Monkeypox (Mpox) virus isolation and ultrastructural characterisation from a Brazilian human sample case
Milene Dias Miranda, Gabriela Cardoso Caldas, Vivian Neuza Ferreira, Ortrud Monika Barth, Aline de Paula Dias da Silva, Mayara Secco Torres Silva, Beatriz Grinsztejn, Valdiléa Gonçalves Veloso, Thiago Moreno Souza, Edson Elias da Silva, Debora Ferreira Ba
Memórias do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Isolation and Characterization of Monkeypox Virus from the First Case of Monkeypox — Chongqing Municipality, China, 2022
Baoying Huang, Hua Zhao, Jingdong Song, Li Zhao, Yao Deng, Wen Wang, Roujian Lu, Wenling Wang, Jiao Ren, Fei Ye, Houwen Tian, Guizhen Wu, Hua Ling, Wenjie Tan
China CDC Weekly.2022; 4(46): 1019. CrossRef
- Ultrasensitive one-pot detection of monkeypox virus with RPA and CRISPR in a sucrose-aided multiphase aqueous system



 First
First Prev
Prev


