Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Predictors of health-related quality of life in Koreans with cardiovascular disease
- Jung-Hye Lim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(1):62-70. Published online February 22, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.0286
- 3,945 View
- 86 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 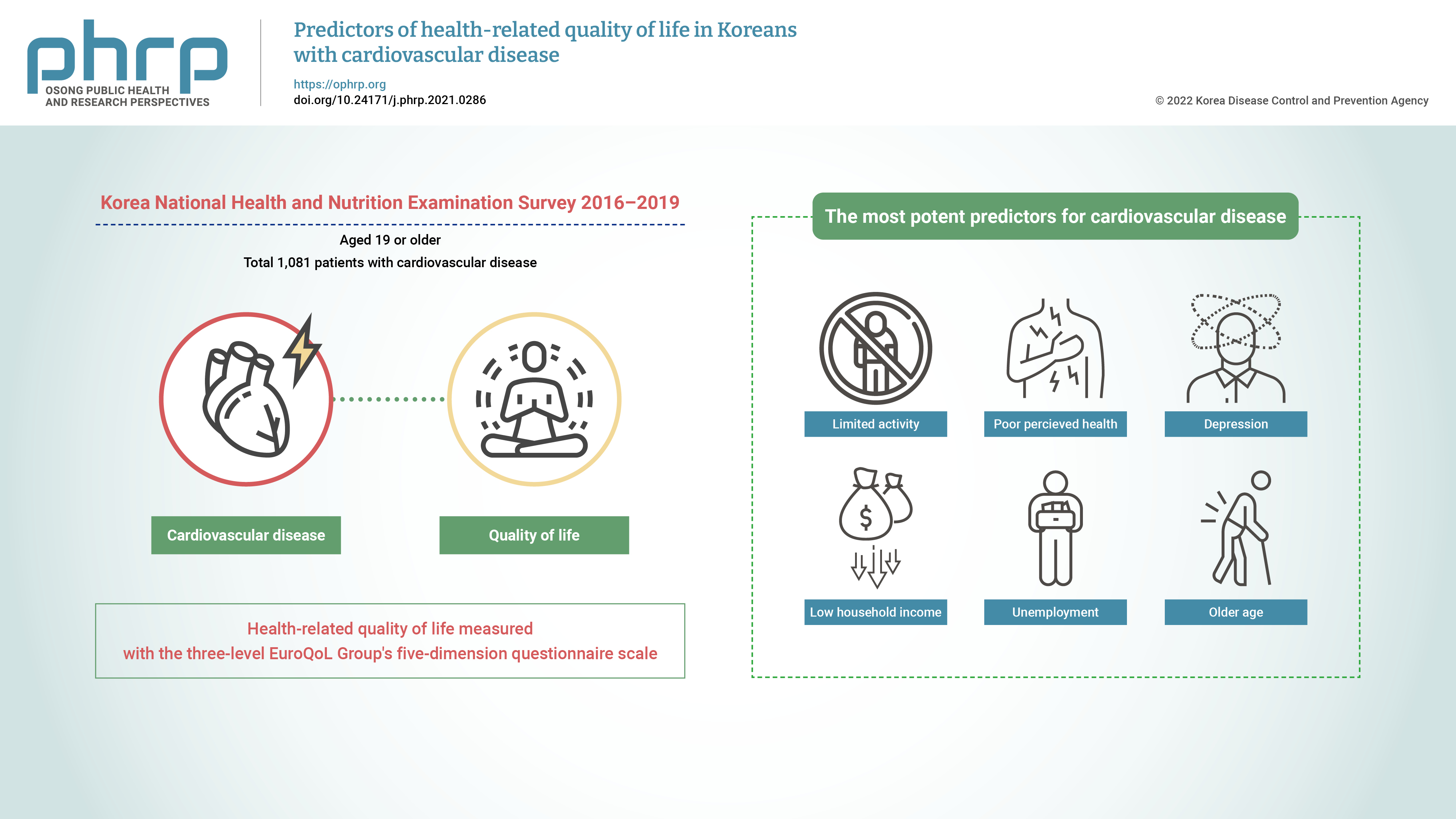
- Objectives
This study aimed to identify the predictors of health-related quality of life (HRQoL) in Korean adults with cardiovascular disease (CVD). Methods: This was a cross-sectional study with a stratified multistage probability sampling design. Data from the 2016 to 2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (n=32,379) were used. Among the participants aged 19 years or older (n=25,995), 1,081 patients with CVD were extracted after excluding those with missing data and those who had cancer. The participants’ HRQoL was measured using the three-level EuroQoL Group’s five-dimension questionnaire (EQ-5D) scale. Data were analyzed using the t-test, one-way analysis of variance, and general linear regression for complex samples. Results: The most potent predictors of HRQoL in Korean adults with CVD were limited activity (β =−0.103, p <0.001), poor perceived health (β =−0.089, p <0.001), depression (β =−0.065, p<0.01), low household income (β=−0.033, p<0.05), unemployment (β=−0.023, p<0.05), and older age (β=−0.002, p<0.01), which explained 37.2% of the variance. Conclusion: Comprehensive interventions that address both physical and mental factors and social systems that provide financial help need to be implemented to improve the HRQoL of Korean adults with CVD. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors associated with health-related quality of life in patients with coronary heart disease
Febio Gutama, Melisa Intan Barliana, Irma Melyani Puspitasari
Pharmacia.2022; 69(3): 771. CrossRef
- Factors associated with health-related quality of life in patients with coronary heart disease
- Sex differences in the relationship between depression and cardiovascular disease risk: a nationwide study in Korea
- Seol-bin Kim, Ihn Sook Jeong
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2021;12(2):105-114. Published online April 29, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.12.2.08
- 6,350 View
- 88 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Objectives
This study aimed to identify sex differences in the association between depression and the risk of developing cardiovascular disease (CVD).
Methods
A secondary analysis was conducted of data from the fifth to seventh waves (2010−2018) of the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. The participants were adults aged 30−74 years who had no diagnosis of CVD. The CVD risk was calculated using the Framingham Risk Score algorithm. Multiple linear regression analysis was conducted to identify the association between depression and CVD risk using a complex sample design.
Results
The mean CVD risk was higher in males and females with current depression (14.72% vs. 6.35%, respectively) than in males without current depression (11.67% and 4.42%, respectively). Current depression showed a significant association with CVD risk after controlling for only health-related characteristics, but the significance disappeared in both males and females when demographic characteristics were additionally controlled.
Conclusion
The presence of depression was not associated with CVD risk regardless of sex after controlling for confounding factors. Further studies are recommended to investigate the relationship between depression and CVD risk in a larger sample of both males and females with depression. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sex Differences in the Association Between Depression and Incident Cardiovascular Disease
Keitaro Senoo, Hidehiro Kaneko, Kensuke Ueno, Yuta Suzuki, Akira Okada, Katsuhito Fujiu, Taisuke Jo, Norifumi Takeda, Hiroyuki Morita, Kentaro Kamiya, Junya Ako, Koichi Node, Hideo Yasunaga, Issei Komuro
JACC: Asia.2024; 4(4): 279. CrossRef
- Sex Differences in the Association Between Depression and Incident Cardiovascular Disease
- Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors and Obesity Levels in Korean Adults: Results from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2007–2015
- Kwanjun Park, Sunmi Lim, Yoonhyung Park, Woong Ju, Yoonhee Shin, Hansol Yeom
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2018;9(4):150-159. Published online August 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2018.9.4.03
- 5,190 View
- 34 Download
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives The increase in the obesity rate in adult males in Korea is higher than countries in the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development and other Asian countries. We examined the trends and prevalence of major risk factors for cardiovascular disease by evaluating the weight status amongst adults from 2007 to 2015.
Methods The study included 37,402 adults, who participated in the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. The prevalence trends of cardiovascular disease risk factors were estimated for each body mass index group.
Results From 2007 to 2015, significant increases in the prevalence of hypertension, diabetes, and hypercholesterolemia were observed in normal weight adults (0.03 percentage point (%p), 0.06%p, and 0.13%p, respectively). Amongst the overweight and obese adults, a significant increase in the prevalence of hypercholesterolemia was observed, During this period, the prevalence of smoking decreased amongst obese adults and no significant changes in drinking habits and physical activity were noted across all body mass index groups.
Conclusion The prevalence of obesity in Korean adults is increasing, and it is necessary to implement interventions to prevent further weight gain and obesity-associated cardiovascular disease.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors in middle-aged Lithuanian women in different body mass index and waist circumference groups
Egidija Rinkūnienė, Emilija Petrulionytė, Vilma Dženkevičiūtė, Žaneta Petrulionienė, Augustė Senulytė, Roma Puronaitė, Aleksandras Laucevičius
Primary Care Diabetes.2023; 17(1): 27. CrossRef - The effect of a nutrition program based on the Health Behavior Interaction Model on primary school students’ nutritional attitudes and behaviors
Ayşe Burcu Başçı, Oya Nuran Emiroğlu, Bilge Kalanlar
Journal of Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Thirty-six Year Trends in Mortality from Diseases of Circulatory System in Korea
Jongmin Baek, Hokyou Lee, Hyeok-Hee Lee, Ji Eun Heo, So Mi Jemma Cho, Hyeon Chang Kim
Korean Circulation Journal.2021; 51(4): 320. CrossRef - The identification of established modifiable mid-life risk factors for cardiovascular disease which contribute to cognitive decline: Korean Longitudinal Study of Aging (KLoSA)
Yebeen Ysabelle Boo, Otto-Emil Jutila, Meghan A. Cupp, Logan Manikam, Sung-Il Cho
Aging Clinical and Experimental Research.2021; 33(9): 2573. CrossRef - A Healthy Diet Rich in Calcium and Vitamin C Is Inversely Associated with Metabolic Syndrome Risk in Korean Adults from the KNHANES 2013–2017
Sunmin Park, Kyungjin Kim, Byung-Kook Lee, Jaeouk Ahn
Nutrients.2021; 13(4): 1312. CrossRef - Classification and Prediction on the Effects of Nutritional Intake on Overweight/Obesity, Dyslipidemia, Hypertension and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Using Deep Learning Model: 4–7th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Hyerim Kim, Dong Hoon Lim, Yoona Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2021; 18(11): 5597. CrossRef - Trends in cardiovascular disease risk factors by BMI category among adults in England, 2003‐2018
Shaun Scholes, Linda Ng Fat, Jennifer S. Mindell
Obesity.2021; 29(8): 1347. CrossRef - Precision Medicine and Cardiovascular Health: Insights from Mendelian Randomization Analyses
Wes Spiller, Keum Ji Jung, Ji-Young Lee, Sun Ha Jee
Korean Circulation Journal.2020; 50(2): 91. CrossRef - Association of the Healthy Eating Index with Estimated Cardiovascular Age in Adults from the KNHANES 2013–2017
Sunmin Park, Kyungjin Kim, Byung-Kook Lee, Jaeouk Ahn
Nutrients.2020; 12(10): 2912. CrossRef
- Prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors in middle-aged Lithuanian women in different body mass index and waist circumference groups
- Accuracy of Self-reported Hypertension, Diabetes, and Hypercholesterolemia: Analysis of a Representative Sample of Korean Older Adults
- Heeran Chun, Il-Ho Kim, Kyung-Duk Min
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2016;7(2):108-115. Published online April 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2015.12.002
- 3,362 View
- 24 Download
- 46 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study will assess the accuracy of self-reported hypertension, diabetes, and hypercholesterolemia among Korean older adults.
Methods
Using data from the fourth Korean National Health Examination and Nutrition Survey (KNHANES IV, 2007–2009), we selected 7,270 individuals aged 50 years and older who participated in both a health examination and a health interview survey. Self-reported prevalence of hypertension (HTN), diabetes mellitus (DM), and hypercholesterolemia was compared with measured data (arterial systolic/diastolic blood pressure, fasting glucose, and total cholesterol).
Results
An agreement between self-reported and measured data was only moderate for hypercholesterolemia (κ, 0.48), even though it was high for HTN (κ, 0.72) and DM (κ, 0. 82). Sensitivity was low in hypercholesterolemia (46.7%), but high in HTN and DM (73% and 79.3%, respectively). Multiple analysis shows that predictors for sensitivity differed by disease. People with less education were more likely to exhibit lower sensitivity to HTN and hypercholesterolemia, and people living in rural areas were less sensitive to DM and hypercholesterolemia.
Conclusion
Caution is needed in interpreting the results of community studies using self-reported data on chronic diseases, especially hypercholesterolemia, among adults aged 50 years and older. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Validation of the self-reported diagnosis of diabetes mellitus, hypercholesterolemia, and hypertension in Iran; STEPS 2016
Mohsen Merati, Farnam Mohebi, Ehsan Alipour, Masoud Masinaei, Atefe Pooyan, Parinaz Mehdipour, Bahram Mohajer, Hamidreza Komaki, Maryam Mobarakabadi, Farshad Farzadfar
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Social engagement and allostatic load mediate between adverse childhood experiences and multimorbidity in mid to late adulthood: the Canadian Longitudinal Study on Aging
Leslie Atkinson, Divya Joshi, Parminder Raina, Lauren E. Griffith, Harriet MacMillan, Andrea Gonzalez
Psychological Medicine.2023; 53(4): 1437. CrossRef - Validity of self‐reported hypertension and related factors in the adult population: Preliminary results from the cohort in the west of Iran
Negar Piri, Yousef Moradi, Reza Ghanei Gheshlagh, Mahsa Abdullahi, Eghbal Fattahi, Farhad Moradpour
The Journal of Clinical Hypertension.2023; 25(2): 146. CrossRef - Concordance of self-reporting of diabetes compared with medical records: A comparative study using polyclinic data in Singapore
Khai Wei Tan, Jeremy Kaiwei Lew, Poay Sian Sabrina Lee, Sin Kee Ong, Hui Li Koh, Doris Yee Ling Young, Eng Sing Lee
Annals of the Academy of Medicine, Singapore.2023; 52(2): 62. CrossRef - Using random-forest multiple imputation to address bias of self-reported anthropometric measures, hypertension and hypercholesterolemia in the Belgian health interview survey
Ingrid Pelgrims, Brecht Devleesschauwer, Stefanie Vandevijvere, Eva M. De Clercq, Stijn Vansteelandt, Vanessa Gorasso, Johan Van der Heyden
BMC Medical Research Methodology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparing Risk Assessment Between Payers and Providers: Inconsistent Agreement in Medical Comorbidity Records for Patients Undergoing Total Joint Arthroplasty
John R. Hobbs, Justin A. Magnuson, Erik Woelber, Kalpak Sarangdhar, P. Maxwell Courtney, Chad A. Krueger
The Journal of Arthroplasty.2023; 38(10): 2105. CrossRef - Validade do autorrelato de hipertensão arterial em trabalhadores
Rafael Cavalcante Mota, Janaína Santos de Siqueira, Rita de Cássia Pereira Fernandes
Cadernos Saúde Coletiva.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Validity of self-reported hypertension and associated factors among Vietnamese adults: a cross-sectional study
Hoang Thi Hai Van, Dang Thi Huong, Tran Ngoc Anh
Blood Pressure.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Vascular risk factors and stroke risk across the life span: A population-representative study of half a million people
Raed A Joundi, Scott B Patten, Jeanne VA Williams, Eric E Smith
International Journal of Stroke.2022; 17(9): 1021. CrossRef - Comparing self-reported and measured hypertension and hypercholesterolaemia at standard and more stringent diagnostic thresholds: the cross-sectional 2010–2015 Busselton Healthy Ageing study
Angela J Burvill, Kevin Murray, Matthew W Knuiman, Joseph Hung
Clinical Hypertension.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Socio-demographic correlates of diabetes self-reporting validity: a study on the adult Kurdish population
Farhad Moradpour, Negar Piri, Hojat Dehghanbanadaki, Ghobad Moradi, Mahdiyeh Fotouk-Kiai, Yousef Moradi
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Socioeconomic Inequalities in the Prevalence of Diabetes in Argentina: A Repeated Cross-Sectional Study in Urban Women and Men
Carlos Rojas-Roque, Akram Hernández-Vásquez, Diego Azañedo, Guido Bendezu-Quispe
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2022; 19(15): 8888. CrossRef - The Associations between Depression, Acculturation, and Cardiovascular Health among African Immigrants in the United States
Nwakaego A. Nmezi, Ruth-Alma Turkson-Ocran, Carolyn M. Tucker, Yvonne Commodore-Mensah
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2022; 19(11): 6658. CrossRef - Validity of self‐reported hypertension in India: Evidence from nationally representative survey of adult population over 45 years
Mrigesh Bhatia, Priyanka Dixit, Manish Kumar, Laxmi Kant Dwivedi
The Journal of Clinical Hypertension.2022; 24(11): 1506. CrossRef - Determinants of self-reported hypertension among women in South Africa: evidence from the population-based survey
Peter Austin Morton Ntenda, Walaa Mamdouh Reyad El-Meidany, Fentanesh Nibret Tiruneh, Mfundi President Sebenele Motsa, Joyce Nyirongo, Gowokani Chijere Chirwa, Arnold Kapachika, Owen Nkoka
Clinical Hypertension.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The difference between hypertension determined by self-report versus examination in the adult population of the USA: Continuous NHANES 1999–2016
Leanna Delhey, Catherine Shoults, Kemmian Johnson, Mohammed Orloff, Mohammed F Faramawi, Robert Delongchamp
Journal of Public Health.2021; 43(2): 316. CrossRef - Bi-directional association between allergic rhinitis and diabetes mellitus from the national representative data of South Korea
Tae Kyung Lee, Ye Jin Jeon, Sun Jae Jung
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Cut-off points of anthropometric markers associated with hypertension and diabetes in Peru: Demographic and Health Survey 2018
Akram Hernández-Vásquez, Diego Azañedo, Rodrigo Vargas-Fernández, Juan Pablo Aparco, Raul Martín Chaparro, Marilina Santero
Public Health Nutrition.2021; 24(4): 611. CrossRef - Examining elevated blood pressure and the effects of diabetes self-management education on blood pressure among a sample of Marshallese with type 2 diabetes in Arkansas
Pearl A. McElfish, Christopher R. Long, Zoran Bursac, Aaron J. Scott, Harish E. Chatrathi, Ka‘imi A. Sinclair, Nirav Nagarsheth, Mikaila Calcagni, Jay Patolia, Marie-Rachelle Narcisse, Solveig A. Cunningham
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(4): e0250489. CrossRef - Self-Reported Modifiable Risk Factors of Cardiovascular Disease among Older Adults in Malaysia: A Cross-Sectional Study of Prevalence and Clustering
Ying Ying Chan, Norhafizah Sahril, Muhammad Solihin Rezali, Lim Kuang Kuay, Azli Baharudin, Mohamad Aznuddin Abd Razak, Mohd Shaiful Azlan Kassim, Muhammad Fadhli Mohd Yusoff, Mohd Azahadi Omar, Noor Ani Ahmad
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2021; 18(15): 7941. CrossRef - Usefulness of Relative Handgrip Strength as a Simple Indicator of Cardiovascular Risk in Middle-Aged Koreans
Won Bin Kim, Jun-Bean Park, Yong-Jin Kim
The American Journal of the Medical Sciences.2021; 362(5): 486. CrossRef - Agreement Between Self-Reported Information and Administrative Data on Comorbidities, Imaging and Treatment in Denmark – A Validation Study of 38,745 Patients with Knee or Hip Osteoarthritis
Halit Selçuk, Ewa M Roos, Dorte T Grønne, Martin T Ernst, Søren T Skou
Clinical Epidemiology.2021; Volume 13: 779. CrossRef - Validity of self-reported diabetes varies with sociodemographic charecteristics: Example from Iran
Mehdi Moradinazar, Yahya Pasdar, Farid Najafi, Ebrahim Shakiba, Behrooz Hamzeh, Mehnoosh Samadi, Maryam Mirzaei, Annette J. Dobson
Clinical Epidemiology and Global Health.2020; 8(1): 70. CrossRef - Dietary patterns and cardiovascular disease in Greek adults: The Hellenic National Nutrition and Health Survey (HNNHS)
Dimitra Karageorgou, Emmanouella Magriplis, Ioanna Bakogianni, Anastasia V. Mitsopoulou, Ioannis Dimakopoulos, Renata Micha, George Michas, Triantafyllia Ntouroupi, Sophia M. Tsaniklidou, Konstantina Argyri, Michail Chourdakis, Demosthenes B. Panagiotakos
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2020; 30(2): 201. CrossRef - Accuracy of self‐reported hypertension: Effect of age, gender, and history of alcohol dependence
Jeannette L. Wellman, Brian Holmes, Shirley Y. Hill
The Journal of Clinical Hypertension.2020; 22(5): 842. CrossRef - Spatial Epidemiology of Diabetes and Tuberculosis in India
Daniel J Corsi
JAMA Network Open.2020; 3(5): e203892. CrossRef - Credibility of self-reported health parameters in elderly population
Roi Amster, Iris Reychav, Roger McHaney, Lin Zhu, Joseph Azuri
Primary Health Care Research & Development.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - What are the illnesses associated with frailty in community-dwelling older adults: the Korean Frailty and Aging Cohort Study
Sunyoung Kim, Hee-Won Jung, Chang Won Won
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2020; 35(4): 1004. CrossRef - The Demographic Representativeness and Health Outcomes of Digital Health Station Users: Longitudinal Study
Leah Flitcroft, Won Sun Chen, Denny Meyer
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2020; 22(6): e14977. CrossRef - Self‐reported diabetes, hypertension and hypercholesterolemia among older persons in Malaysia
Nur Liana Ab Majid, Wan Shakira Rodzlan Hasani, Halizah Mat Rifin, Tania Gayle Robert Lourdes, Miaw Yn Jane Ling, Thamil Arasu Saminanthan, Hasimah Ismail, Ahzairin Ahmad, Muhammad Fadhli Mohd Yusoff
Geriatrics & Gerontology International.2020; 20(S2): 79. CrossRef - Association between number of medications used and nutritional markers among elderly persons with chronic diseases: National Health Survey (2013)
Isabel Cristina Bento, Mary Anne Nascimento Souza, Sérgio Viana Peixoto
Revista Brasileira de Geriatria e Gerontologia.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence, determinants and association of unawareness of diabetes, hypertension and hypercholesterolemia with poor disease control in a multi-ethnic Asian population without cardiovascular disease
Ryan E. K. Man, Alvin Hong Wei Gan, Eva K. Fenwick, Alfred Tau Liang Gan, Preeti Gupta, Charumathi Sabanayagam, Nicholas Tan, Kah Hie Wong, Tien Yin Wong, Ching-Yu Cheng, Ecosse L. Lamoureux
Population Health Metrics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Differential self-report error by socioeconomic status in hypertension and hypercholesterolemia: INSEF 2015 study
Irina Kislaya, Hanna Tolonen, Ana Paula Rodrigues, Marta Barreto, Ana Paula Gil, Vânia Gaio, Sónia Namorado, Ana João Santos, Carlos Matias Dias, Baltazar Nunes
European Journal of Public Health.2019; 29(2): 273. CrossRef - Validity of Self-reported Hypertension and Factors Related to Discordance Between Self-reported and Objectively Measured Hypertension: Evidence From a Cohort Study in Iran
Farid Najafi, Yahya Pasdar, Ebrahim Shakiba, Behrooz Hamzeh, Mitra Darbandi, Mehdi Moradinazar, Jafar Navabi, Bita Anvari, Mohammad Reza Saidi, Shahrzad Bazargan-Hejazi
Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health.2019; 52(2): 131. CrossRef - Public health monitoring of hypertension, diabetes and elevated cholesterol: comparison of different data sources
Laura Paalanen, Päivikki Koponen, Tiina Laatikainen, Hanna Tolonen
European Journal of Public Health.2018; 28(4): 754. CrossRef - Low potassium and high sodium intakes: a double health threat to Cape Verdeans
Daniela Alves, Zélia Santos, Miguel Amado, Isabel Craveiro, António Pedro Delgado, Artur Correia, Luzia Gonçalves
BMC Public Health.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Diet-Related Risk Factors for Incident Hypertension During an 11-Year Follow-Up: The Korean Genome Epidemiology Study
Hye Lee, Hyesook Park
Nutrients.2018; 10(8): 1077. CrossRef - Evaluation of the association between the number of natural teeth and anemia among Korean adults using nationally representative data
Kyungdo Han, Jun‐Beom Park
Journal of Periodontology.2018; 89(10): 1184. CrossRef - Diabetes Fact Sheet in Korea, 2016: An Appraisal of Current Status
Jong Chul Won, Jae Hyuk Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim, Eun Seok Kang, Kyu Chang Won, Dae Jung Kim, Moon-Kyu Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(5): 415. CrossRef - Accuracy of self-reported hypertension
Vivian S.S. Gonçalves, Keitty R.C. Andrade, Kenia M.B. Carvalho, Marcus T. Silva, Mauricio G. Pereira, Tais F. Galvao
Journal of Hypertension.2018; 36(5): 970. CrossRef - Trends in Determinants of Hypercholesterolemia among Chinese Adults between 2002 and 2012: Results from the National Nutrition Survey
Peng-kun Song, Hong Li, Qing-qing Man, Shan-shan Jia, Li-xiang Li, Jian Zhang
Nutrients.2017; 9(3): 279. CrossRef - High Level Physical Activity and Prevalence of Cardiovascular Disease Using the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data, 2007-2013
Kyounghoon Park, Byung-Joo Park
Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health.2017; 50(5): 320. CrossRef - Association between underweight and tooth loss among Korean adults
In-Seok Song, Kyungdo Han, Jae-Jun Ryu, Jun-Beom Park
Scientific Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Potential use of telephone-based survey for non-communicable disease surveillance in Sri Lanka
H. M. M. Herath, N. P. Weerasinghe, T. P. Weerarathna, A. Hemantha, A. Amarathunga
BMC Public Health.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Level of Agreement and Factors Associated With Discrepancies Between Nationwide Medical History Questionnaires and Hospital Claims Data
Yeon-Yong Kim, Jong Heon Park, Hee-Jin Kang, Eun Joo Lee, Seongjun Ha, Soon-Ae Shin
Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health.2017; 50(5): 294. CrossRef - Evaluation of Self-assessment in Cardiovascular Diseases Among Korean Older Population
Hae-Wol Cho, Chaeshin Chu
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2016; 7(2): 75. CrossRef
- Validation of the self-reported diagnosis of diabetes mellitus, hypercholesterolemia, and hypertension in Iran; STEPS 2016
- Increased Prevalence of low High-density Lipoprotein Cholesterol (HDL-C) Levels in Korean Adults: Analysis of the Three Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (KNHANES 1998–2005)
- Sun-Ja Choi, Sung-Hee Park, Hyun-Young Park
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2011;2(2):94-103. Published online June 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2011.07.006
- 3,152 View
- 13 Download
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
High-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) is an independent risk factor for cardiovascular diseases that has shown a remarkable increase, but little is known about the prevalence of low HDL-C in Korea. This study aimed to evaluate changing trends of low HDL-C prevalence, and indicate other risk factors associated with low HDL-C.
Methods
We selected subjects aged ≥20 years from the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) 1998, 2001, and 2005 (n = 7962, 6436, and 6412). The mean level of HDL-C and the prevalence of low HDL-C was calculated, and cardiovascular risk factors associated with low HDL-C, as well as demographic, anthropometric, lifestyle, and nutrition factors, were assessed using the KNHANES 2005 data.
Results
Mean HDL-C levels in men and women between KNHANES 1998 and 2005 decreased significantly, from 48.1 to 42.3 and from 51.6 to 47.1 mg/dL, respectively (both p < 0.001). The decrease was slightly less for women compared with men for the same period, and women had higher HDL-C levels at all periods. Covariate-adjusted OR revealed that body mass index, waist circumference, and non-alcohol drinker in both men and women were associated with low HDL-C levels by KNHANES 2005, as were employed and light physical activity in men and low fat intake in women.
Conclusion
The prevalence of low HDL-C increased significantly from KNHANES 1998 to 2001 and 2005 (p < 0.001) in both men and women. body mass index, waist circumference, and non-alcohol drinker were identified as associated with low HDL-C in Korean adults. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Beneficial Effect of Cuban Policosanol on Blood Pressure and Serum Lipoproteins Accompanied with Lowered Glycated Hemoglobin and Enhanced High-Density Lipoprotein Functionalities in a Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, and Double-Blinded Trial with Healthy J
Kyung-Hyun Cho, Hyo-Seon Nam, Seung-Hee Baek, Dae-Jin Kang, Hyejee Na, Tomohiro Komatsu, Yoshinari Uehara
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(6): 5185. CrossRef - Interactive effects of the low‐carbohydrate diet score and genetic risk score on Hypo‐HDL‐cholesterolemia among Korean adults: A cross‐sectional analysis from the Ansan and Ansung Study of the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study
SoHyun Park, Min‐Jae Jang, Min Young Park, Jun‐Mo Kim, Sangah Shin
Food Science & Nutrition.2022; 10(9): 3106. CrossRef - Decrease in HDL-C is Associated with Age and Household Income in Adults from the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2017: Correlation Analysis of Low HDL-C and Poverty
Kyung-Hyun Cho, Hye-Jeong Park, Suk-Jeong Kim, Jae-Ryong Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2019; 16(18): 3329. CrossRef - The association between lipid profiles and the neurologic outcome in patients with out-of-hospital cardiac arrest
Hyoung Youn Lee, Dong Hun Lee, Byung Kook Lee, Kyung Woon Jeung, Yong Hun Jung, Jung Soo Park, Jin Hong Min, Yong Il Min
Resuscitation.2019; 145: 26. CrossRef - Differential association of dietary carbohydrate intake with metabolic syndrome in the US and Korean adults: data from the 2007–2012 NHANES and KNHANES
Kyungho Ha, Kijoon Kim, Ock K. Chun, Hyojee Joung, YoonJu Song
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition.2018; 72(6): 848. CrossRef - The High Prevalence of Low HDL-Cholesterol Levels and Dyslipidemia in Rural Populations in Northwestern China
Pengfei Ge, Caixia Dong, Xiaolan Ren, Elisabete Weiderpass, Chouji Zhang, Haoqiang Fan, Jing Zhang, Yongrui Zhang, Jinen Xi, Shahrad Taheri
PLOS ONE.2015; 10(12): e0144104. CrossRef - Treino de natação para pessoas sedentárias com lesão medular e concentração de colesterol-HDL
Fabio Barreto Rodrigues, Carmen Silvia Grubert Campbell
Revista Neurociências.2015; 23(2): 233. CrossRef - Composition of Metabolic Syndrome Among Korean Adults in a Lifestyle Modification Intervention
Nan-He Yoon, Seunghyun Yoo, Hyekyeong Kim
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2014; 5(6): 370. CrossRef
- Beneficial Effect of Cuban Policosanol on Blood Pressure and Serum Lipoproteins Accompanied with Lowered Glycated Hemoglobin and Enhanced High-Density Lipoprotein Functionalities in a Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, and Double-Blinded Trial with Healthy J



 First
First Prev
Prev


