Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Predictors of outcomes 3 to 12 months after traumatic brain injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Younes Iderdar, Maryem Arraji, Nadia Al Wachami, Morad Guennouni, Karima Boumendil, Yassmine Mourajid, Noureddine Elkhoudri, Elmadani Saad, Mohamed Chahboune
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2024;15(1):3-17. Published online February 5, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0288
- 894 View
- 62 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 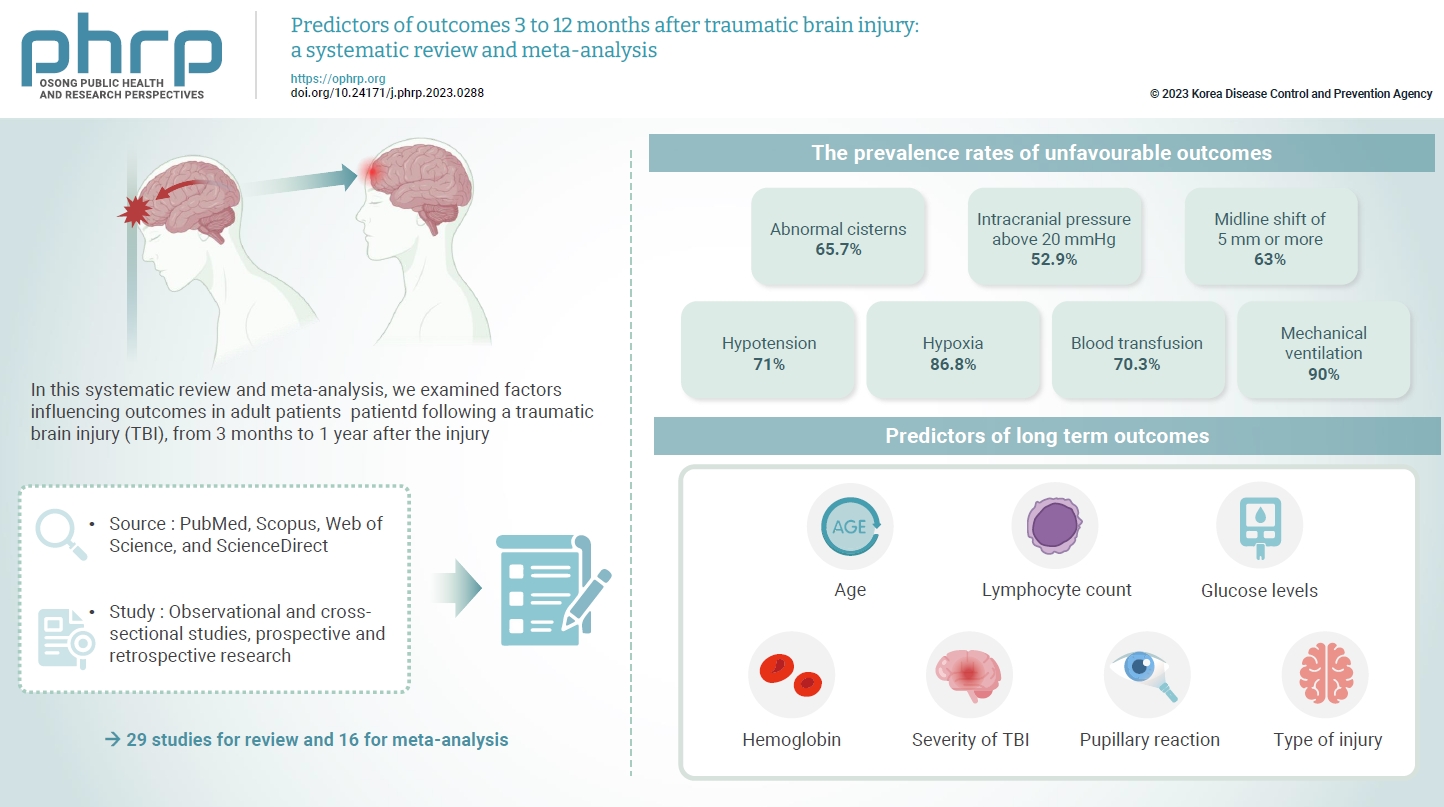
- The exact factors predicting outcomes following traumatic brain injury (TBI) remain elusive. In this systematic review and meta-analysis, we examined factors influencing outcomes in adult patients with TBI, from 3 months to 1 year after injury. A search of four electronic databases—PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and ScienceDirect—yielded 29 studies for review and 16 for meta-analysis, in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis guidelines. In patients with TBI of any severity, mean differences were observed in age (8.72 years; 95% confidence interval [CI], 4.77–12.66 years), lymphocyte count (−0.15 109/L; 95% CI, −0.18 to −0.11), glucose levels (1.20 mmol/L; 95% CI, 0.73–1.68), and haemoglobin levels (−0.91 g/dL; 95% CI, −1.49 to −0.33) between those with favourable and unfavourable outcomes. The prevalence rates of unfavourable outcomes were as follows: abnormal cisterns, 65.7%; intracranial pressure above 20 mmHg, 52.9%; midline shift of 5 mm or more, 63%; hypotension, 71%; hypoxia, 86.8%; blood transfusion, 70.3%; and mechanical ventilation, 90%. Several predictors were strongly associated with outcome. Specifically, age, lymphocyte count, glucose level, haemoglobin level, severity of TBI, pupillary reaction, and type of injury were identified as potential predictors of long-term outcomes.
- Estimation of the onset time of diabetic complications in type 2 diabetes patients in Thailand: a survival analysis
- Natthanicha Sauenram, Jutatip Sillabutra, Chukiat Viwatwongkasem, Pratana Satitvipawee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(6):508-519. Published online November 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0084
- 1,029 View
- 58 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 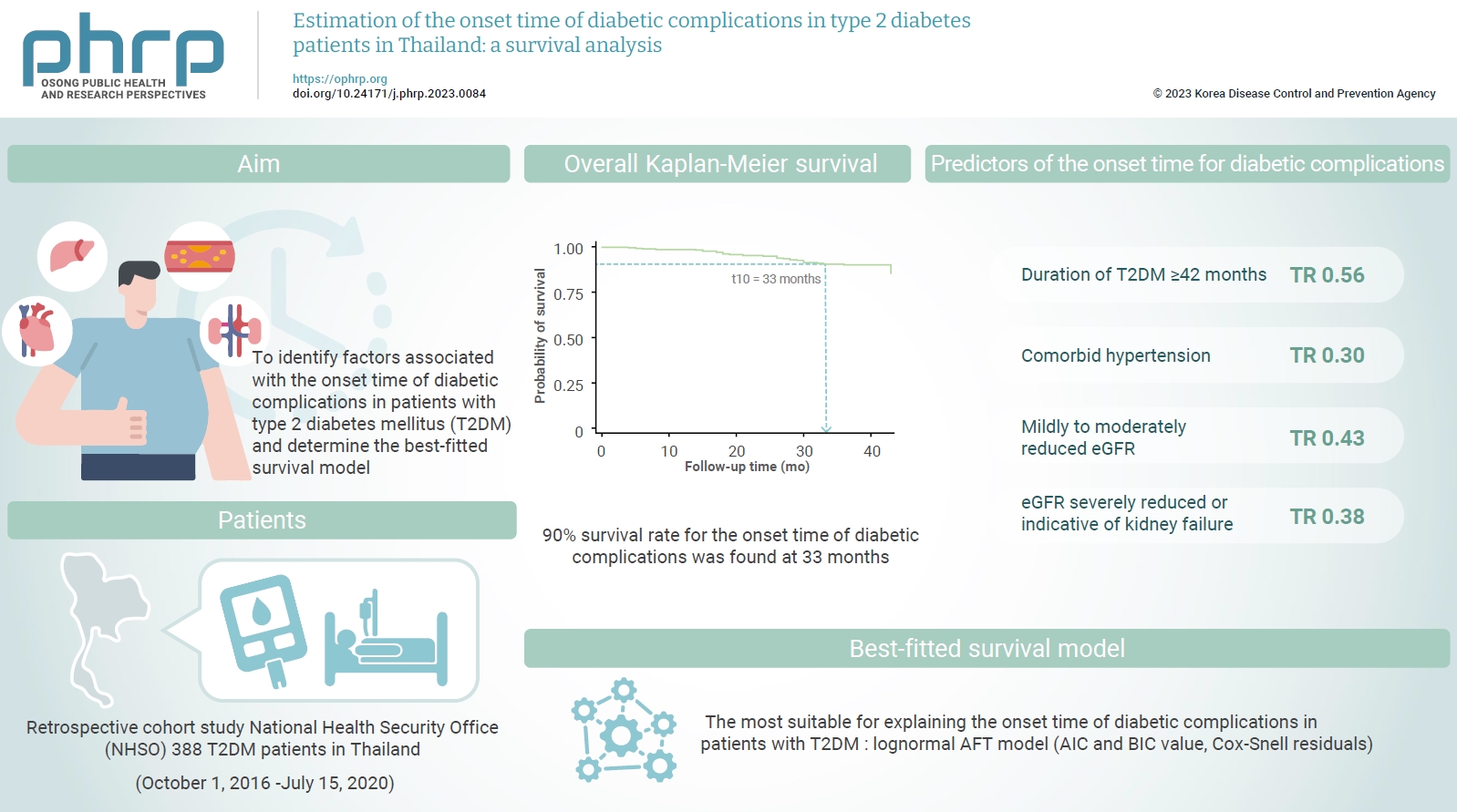
- Objectives
This study aimed to identify factors associated with the onset time of diabetic complications in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and determine the best-fitted survival model. Methods: A retrospective cohort study was conducted among T2DM patients enrolled from October 1, 2016 to July 15, 2020 at the National Health Security Office (NHSO). In total, 388 T2DM patients were included. Cox proportional-hazard and parametric models were used to identify factors related to the onset time of diabetic complications. The Akaike information criterion, Bayesian information criterion, and Cox-Snell residual were compared to determine the best-fitted survival model. Results: Thirty diabetic complication events were detected among the 388 patients (7.7%). A 90% survival rate for the onset time of diabetic complications was found at 33 months after the first T2DM diagnosis. According to multivariate analysis, a duration of T2DM ≥42 months (time ratio [TR], 0.56; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.33–0.96; p=0.034), comorbid hypertension (TR, 0.30; 95% CI, 0.15–0.60; p=0.001), mildly to moderately reduced levels of the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) (TR, 0.43; 95% CI, 0.24–0.75; p=0.003) and an eGFR that was severely reduced or indicative of kidney failure (TR, 0.38; 95% CI, 0.16–0.88; p=0.025) were significantly associated with the onset time of diabetic complications (p<0.05). Conclusion: Patients with T2DM durations of more than 42 months, comorbid hypertension, and decreased eGFR were at risk of developing diabetic complications. The NHSO should be aware of these factors to establish a policy to prevent diabetic complications after the diagnosis of T2DM.
- Risk factors for transmission in a COVID-19 cluster infection in a high school in the Republic of Korea
- Jin-Hwan Jeon, Su Jin Kang, Se-Jin Jeong, Hyeon-Cheol Jang, Young-Joon Park, Sang-Eun Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(4):252-262. Published online July 27, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0125
- 3,399 View
- 191 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 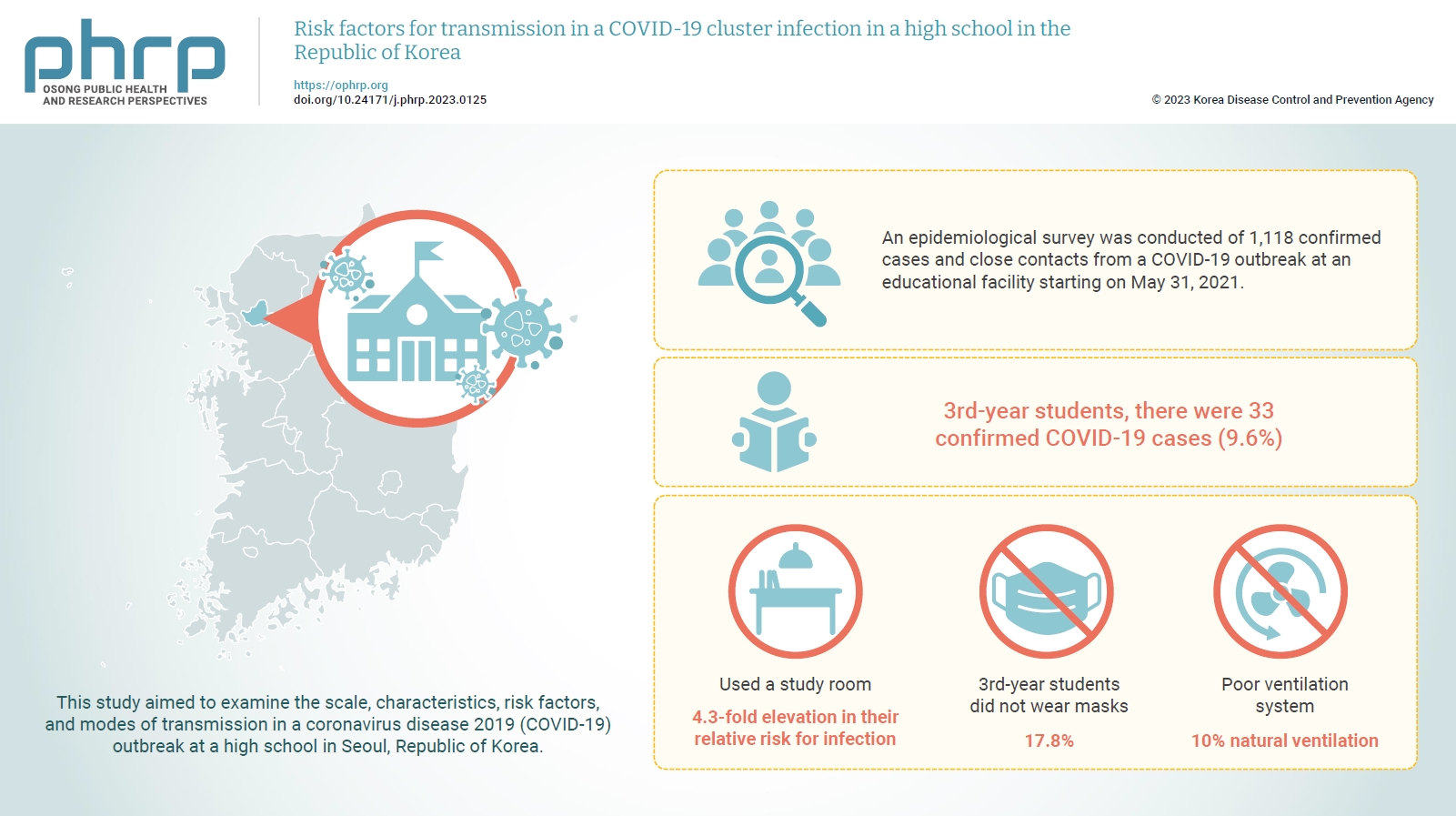
- Objectives
This study aimed to examine the scale, characteristics, risk factors, and modes of transmission in a coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak at a high school in Seoul, Republic of Korea.
Methods
An epidemiological survey was conducted of 1,118 confirmed cases and close contacts from a COVID-19 outbreak at an educational facility starting on May 31, 2021. In-depth interviews, online questionnaires, flow evaluations, and CCTV analyses were used to devise infection prevention measures. Behavioral and spatial risk factors were identified, and statistical significance was tested.
Results
Among 3rd-year students, there were 33 confirmed COVID-19 cases (9.6%). Students who used a study room in the annex building showed a statistically significant 4.3-fold elevation in their relative risk for infection compared to those who did not use the study room. Moreover, CCTV facial recognition analysis confirmed that 17.8% of 3rd-year students did not wear masks and had the lowest percentage of mask-wearers by grade. The air epidemiological survey conducted in the study room in the annex, which met the 3 criteria for a closed space, confirmed that there was only 10% natural ventilation due to the poor ventilation system.
Conclusion
To prevent and manage the spread of COVID-19 in educational facilities, advance measures that consider the size, operation, and resources of each school are crucial. In addition, various survey methodologies should be used in future studies to quickly analyze a wider range of data that can inform an evidence-based quarantine response. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Detection of a cluster of Omicron's BA.4 sublineage in Northern Senegal and identification of the first XAS recombinant variant in Senegal
Martin Faye, Modeste Name Faye, Babacar Ndiaye, Moussa Moïse Diagne, Safietou Sankhe, Ndeye Marième Top, Amadou Diallo, Cheikh Loucoubar, Ndongo Dia, Amadou Alpha Sall, Ousmane Faye
Virus Research.2024; 339: 199259. CrossRef
- Detection of a cluster of Omicron's BA.4 sublineage in Northern Senegal and identification of the first XAS recombinant variant in Senegal
- Time-series comparison of COVID-19 case fatality rates across 21 countries with adjustment for multiple covariates
- Yongmoon Kim, Bryan Inho Kim, Sangwoo Tak
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(6):424-434. Published online November 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0212
- 2,686 View
- 110 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Objectives
Although it is widely used as a measure for mortality, the case fatality rate (CFR) ofcoronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) can vary over time and fluctuate for many reasons otherthan viral characteristics. To compare the CFRs of different countries in equal measure, weestimated comparable CFRs after adjusting for multiple covariates and examined the mainfactors that contributed to variability in the CFRs among 21 countries.Methods: For statistical analysis, time-series cross-sectional data were collected from OurWorld in Data, CoVariants.org, and GISAID. Biweekly CFRs of COVID-19 were estimated bypooled generalized linear squares regression models for the panel data. Covariates includedthe predominant virus variant, reproduction rate, vaccination, national economic status,hospital beds, diabetes prevalence, and population share of individuals older than age 65. Intotal, 21 countries were eligible for analysis.Results: Adjustment for covariates reduced variation in the CFRs of COVID-19 across countriesand over time. Regression results showed that the dominant spread of the Omicron variant,reproduction rate, and vaccination were associated with lower country-level CFRs, whereasage, the extreme poverty rate, and diabetes prevalence were associated with higher countrylevel CFRs.Conclusion: A direct comparison of crude CFRs among countries may be fallacious, especiallyin a cross-sectional analysis. Our study presents an adjusted comparison of CFRs over timefor a more proper comparison. In addition, our findings suggest that comparing CFRs amongdifferent countries without considering their context, such as the epidemic phase, medicalcapacity, surveillance strategy, and socio-demographic traits, should be avoided. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comments on the article "Time-series comparison of COVID-19 case fatality rates across 21 countries with adjustment for multiple covariates"
Gaetano Perone
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2023; 14(2): 146. CrossRef
- Comments on the article "Time-series comparison of COVID-19 case fatality rates across 21 countries with adjustment for multiple covariates"
- Effects of medication adherence interventions for older adults with chronic illnesses: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Hae Ok Jeon, Myung-Ock Chae, Ahrin Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(5):328-340. Published online October 12, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0168
- 3,540 View
- 166 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to understand the characteristics of medication adherence interventions for older adults with chronic illnesses, and to investigate the average effect size by combining the individual effects of these interventions. Data from studies meeting the inclusion criteria were systematically collected in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis guidelines. The results showed that the average effect size (Hedges’ g) of the finally selected medication adherence interventions for older adults with chronic illnesses calculated using a random-effects model was 0.500 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.342−0.659). Of the medication adherence interventions, an implementation intention intervention (using face-to-face meetings and telephone monitoring with personalized behavioral strategies) and a health belief model–based educational program were found to be highly effective. Face-to-face counseling was a significantly effective method of implementing medication adherence interventions for older adults with chronic illnesses (Hedges’ g=0.531, 95% CI, 0.186−0.877), while medication adherence interventions through education and telehealth counseling were not effective. This study verified the effectiveness of personalized behavioral change strategies and cognitive behavioral therapy based on the health belief model, as well as face-to-face meetings, as medication adherence interventions for older adults with chronic illnesses.
- Phylogenetic and genome-wide mutational analysis of SARS-CoV-2 strains circulating in Nigeria: no implications for attenuated COVID-19 outcomes
- Daniel B. Kolawole, Malachy I. Okeke
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(2):101-113. Published online April 22, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.0329
- 3,302 View
- 64 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Objectives
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is the causative agent of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). The COVID-19 incidence and mortality rates are low in Nigeria compared to global trends. This research mapped the evolution of SARS-CoV-2 circulating in Nigeria and globally to determine whether the Nigerian isolates are genetically distinct from strains circulating in regions of the world with a high disease burden. Methods: Bayesian phylogenetics using BEAST 2.0, genetic similarity analyses, and genomewide mutational analyses were used to characterize the strains of SARS-CoV-2 isolated in Nigeria. Results: SARS-CoV-2 strains isolated in Nigeria showed multiple lineages and possible introductions from Europe and Asia. Phylogenetic clustering and sequence similarity analyses demonstrated that Nigerian isolates were not genetically distinct from strains isolated in other parts of the globe. Mutational analysis demonstrated that the D614G mutation in the spike protein, the P323L mutation in open reading frame 1b (and more specifically in NSP12), and the R203K/ G204R mutation pair in the nucleocapsid protein were most prevalent in the Nigerian isolates. Conclusion: The SARS-CoV-2 strains in Nigeria were neither phylogenetically nor genetically distinct from virus strains circulating in other countries of the world. Thus, differences in SARS-CoV-2 genomes are not a plausible explanation for the attenuated COVID-19 outcomes in Nigeria.
- Spatiotemporal analysis of environmental and physiographic factors related to malaria in Bareilly district, India
- Shikhar Chaudhary, Biju Soman
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(2):123-132. Published online March 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.0304
- 4,970 View
- 91 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 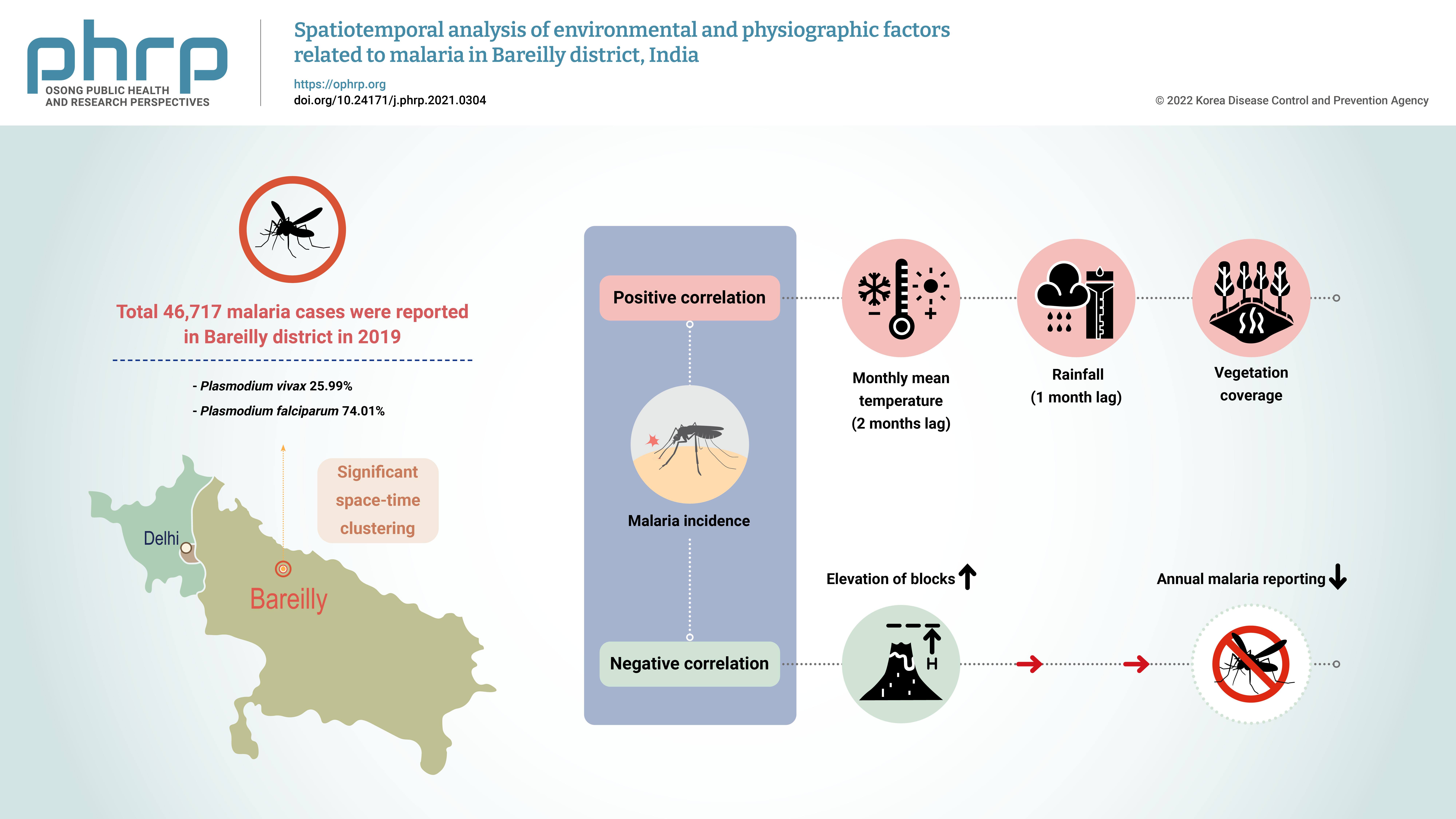
- Objectives
The aim of this study was to explore the spatiotemporal clustering of reported malaria cases and to study the effects of various environmental and physiographic factors on malaria incidence in Bareilly district, Uttar Pradesh, India. Methods: Malaria surveillance data were collected from the state health department and cleaned into an analyzable format. These data were analyzed along with meteorological, physiographic, and 2019 population data, which were obtained from the Indian Meteorological Department, National Aeronautics and Space Administration web portal, the Bhuvan platform of the Indian Space Research Organization, and the 2011 Census of India. Results: In total, 46,717 malaria cases were reported in Bareilly district in 2019, of which 25.99% were Plasmodium vivax cases and 74.01% were P. falciparum cases. The reported malaria cases in the district showed clustering, with significant spatial autocorrelation (Moran’s I value=0.63), and space-time clustering (p<0.01). A significant positive correlation was found between monthly malaria incidence and the monthly mean temperature (with a lag of 1−2 months) and rainfall (with a lag of 1 month). A significant negative correlation was detected between the elevation of blocks (i.e., intermediate-level administrative districts) and annual malaria reporting. Conclusion: The presence of space-time clustering of malaria cases and its correlation with meteorological and physiographic factors indicate that routine spatial analysis of the surveillance data could help control and manage malaria outbreaks in the district. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Digital health: trends, opportunities and challenges in medical devices, pharma and bio-technology
Naresh Kasoju, N. S. Remya, Renjith Sasi, S. Sujesh, Biju Soman, C. Kesavadas, C. V. Muraleedharan, P. R. Harikrishna Varma, Sanjay Behari
CSI Transactions on ICT.2023; 11(1): 11. CrossRef
- Digital health: trends, opportunities and challenges in medical devices, pharma and bio-technology
- Worldwide prevalence of fungal coinfections among COVID-19 patients: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis
- Saber Soltani, Milad Zandi, Samireh Faramarzi, Ramin Shahbahrami, Mohebat Vali, Sara Akhavan Rezayat, Reza Pakzad, Pooneh Malekifar, Iraj Pakzad, Neda Jahandoost, Jalal Moludi
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(1):15-23. Published online February 8, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.0293
- 7,456 View
- 117 Download
- 5 Web of Science
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Microbial coinfections can increase the morbidity and mortality rates of viral respiratory diseases. Therefore, this study aimed to determine the pooled prevalence of fungal coinfections in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients. Web of Science, Medline, Scopus, and Embase were searched without language restrictions to identify the related research on COVID-19 patients with fungal coinfections from December 1, 2019, to December 30, 2020. A random-effects model was used for analysis. The sample size included 2,246 patients from 8 studies. The pooled prevalence of fungal coinfections was 12.60%. The frequency of fungal subtype coinfections was 3.71% for Aspergillus, 2.39% for Candida, and 0.39% for other. The World Health Organization’s Regional Office for Europe and Regional Office for Southeast Asia had the highest (23.28%) and lowest (4.53%) estimated prevalence of fungal coinfection, respectively. Our findings showed a high prevalence of fungal coinfections in COVID-19 cases, which is a likely contributor to mortality in COVID-19 patients. Early identification of fungal pathogens in the laboratory for COVID-19 patients can lead to timely treatment and prevention of further damage by this hidden infection.
- A spatial analysis of the association between social vulnerability and the cumulative number of confirmed deaths from COVID-19 in United States counties through November 14, 2020
- Baksun Sung
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2021;12(3):149-157. Published online June 2, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2020.0372
- 6,635 View
- 150 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 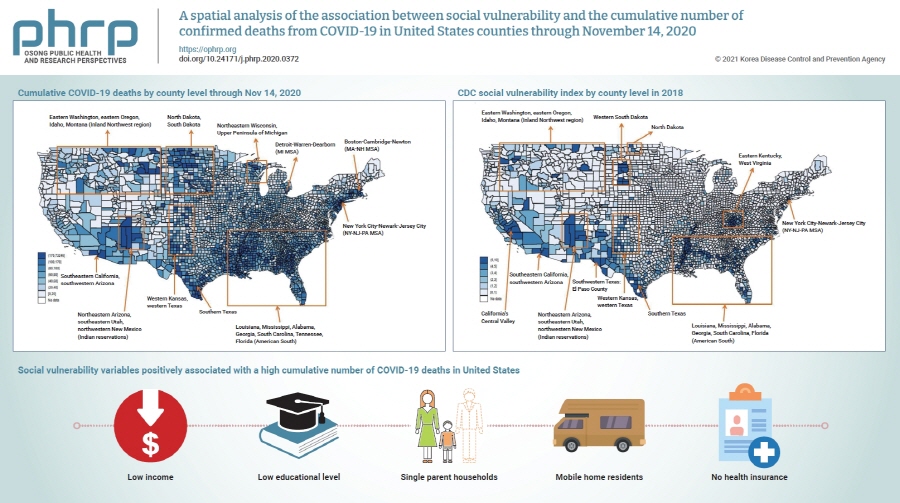
- Objectives
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is classified as a natural hazard, and social vulnerability describes the susceptibility of social groups to potential damages from natural hazards. Therefore, the objective of this study was to examine the association between social vulnerability and the cumulative number of confirmed COVID-19 deaths (per 100,000) in 3,141 United States counties.
Methods
The cumulative number of COVID-19 deaths was obtained from USA Facts. Variables related to social vulnerability were obtained from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Social Vulnerability Index and the 2018 5-Year American Community Survey. Data were analyzed using spatial autoregression models.
Results
Lowest income and educational level, as well as high proportions of single parent households, mobile home residents, and people without health insurance were positively associated with a high cumulative number of COVID-19 deaths.
Conclusion
In conclusion, there are regional differences in the cumulative number of COVID-19 deaths in United States counties, which are affected by various social vulnerabilities. Hence, these findings underscore the need to take social vulnerability into account when planning interventions to reduce COVID-19 deaths. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ecological comparison of six countries in two waves of COVID-19
Meiheng Liu, Leiyu Shi, Manfei Yang, Jun Jiao, Junyan Yang, Mengyuan Ma, Wanzhen Xie, Gang Sun
Frontiers in Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Social vulnerability and COVID-19 in Maringá, Brazil
Matheus Pereira Libório, Oseias da Silva Martinuci, Patrícia Bernardes, Natália Cristina Alves Caetano Chav Krohling, Guilherme Castro, Henrique Leonardo Guerra, Eduardo Alcantara Ribeiro, Udelysses Janete Veltrini Fonzar, Ícaro da Costa Francisco
Spatial Information Research.2023; 31(1): 51. CrossRef - A county-level analysis of association between social vulnerability and COVID-19 cases in Khuzestan Province, Iran
Mahmoud Arvin, Shahram Bazrafkan, Parisa Beiki, Ayyoob Sharifi
International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction.2023; 84: 103495. CrossRef - Global mapping of epidemic risk assessment toolkits: A scoping review for COVID-19 and future epidemics preparedness implications
Bach Xuan Tran, Long Hoang Nguyen, Linh Phuong Doan, Tham Thi Nguyen, Giang Thu Vu, Hoa Thi Do, Huong Thi Le, Carl A. Latkin, Cyrus S. H. Ho, Roger C. M. Ho, Md Nazirul Islam Sarker
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(9): e0272037. CrossRef - COVID-19 mortality and deprivation: pandemic, syndemic, and endemic health inequalities
Victoria J McGowan, Clare Bambra
The Lancet Public Health.2022; 7(11): e966. CrossRef
- Ecological comparison of six countries in two waves of COVID-19
- The 100 top-cited articles on scrub typhus: a bibliometric analysis
- Taha Hussein Musa, Wei Li, Joseph Kawuki, Pingmin Wei
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2021;12(2):126-135. Published online April 29, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.12.2.10
- 5,624 View
- 115 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Objectives
The aims of this study were to analyze the characteristics of the 100 top-cited articles on scrub typhus (ST), and to assess the present research landscape and future research directions using bibliometric analysis.
Methods
Web of Science was used to conduct a bibliometric analysis of the 100 top-cited articles on ST. The articles were analyzed by publication year, number of citations, document type, journals, keywords, institutions, country of origin, and authorship.
Results
The top 100 articles on ST were published between 1945 to 2017. The number of citations ranges from 39 to 227 and the interquartile range was 35.5. The United States published the highest number (n =21) of articles. Mahidol University was the most prolific institution in terms of articles (n =14). TheAmerican Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene was the journal with the most articles (n =14), and Paris DH was the most productive author in terms of the Hirsh-index, which was 10 for that author. The study revealed a significant correlation between the total number of citations and the number of authors (r=0.668,p <0.001), number of institutions (r=0.692,p <0.001), number of years since publication (r=0.869,p <0.001), and number of countries involved (r=0.963,p <0.001).
Conclusion
The findings of this study provide landmarks in the publication and citation frequency of the most influential articles on ST. In addition, this study provides useful information for readers and health policy-makers in evaluating the literature on ST. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Top-50 cited articles on cysticercosis and neurocysticercosis
Gregorio Gonzalez-Alcaide, Nestor Sosa, Fatima Valero-Samper, Isabel Belinchon-Romero, Jose-Manuel Ramos-Rincon
Medicine.2024; 103(9): e37268. CrossRef - Cancer and COVID-19 research studies with team science: a bibliometric study
Arezoo Ghamgosar, Sirous Panahi, Leila Nemati-Anaraki
Journal of Interprofessional Care.2023; 37(4): 568. CrossRef - Investigating Empirical evidence on the Epidemiology, Diagnosis and Bibliometric analysis of the 100 topmost cited publications on Tuberculosis Disease
Taha Hussein Musa, Lovel Fornah, Tosin Yinka Akintunde, Idriss Hussein Musa, Hassan Hussein Musa, Gabriel Maxwell Turay , Maram Abdulhakim Abdulkarem Al-sharai
PAN AFRICA SCIENCE JOURNAL.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Gum: Sytamatic and thematic analysis of the top 100 most-cited articles indexed in the Scopus database
Hassan Hussein Musa, Akintunde Tosin Yinka, Olayinka Oderinde, Taha Hussein Musa, Abdelkareem A. Ahmed, Jaafar Sulieman Fedail, Adriano Mollica, Azzurra Stefanucci, Demin Cai
Bioactive Carbohydrates and Dietary Fibre.2023; 30: 100359. CrossRef - Knowledge mapping and visualization of current sarcopenia and cancer research: a bibliometric analysis
Marwa Mohammed, Jianan Li
Beni-Suef University Journal of Basic and Applied .2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The 100 top-cited articles on childhood obesity: a bibliometric analysis
Joseph Kawuki, Taha Hussein Musa, Upama Ghimire, Nathan Obore, Shireen Salome Papabathini
Global Health Journal.2022; 6(3): 136. CrossRef - The associations between scientific collaborations of LIS research and its policy impact
Zhihong Huang, Qianjin Zong, Xuerui Ji
Scientometrics.2022; 127(11): 6453. CrossRef - A systematic and thematic analysis of the top 100 cited articles on mRNA vaccine indexed in Scopus database
Hassan H. Musa, Taha H. Musa
Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The 100 Most Cited Articles on Dental Anomalies: a bibliometric analysis
Glenda VİEİRA DE SOUSA, Maria Eduarda FERREİRA DE SOUZA, Eloísa CESÁRİO, Patrícia SANTOS
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2022; 25(4): 330. CrossRef
- Top-50 cited articles on cysticercosis and neurocysticercosis
- COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Laboratory Findings, Comorbidities, and Clinical Outcomes Comparing Medical Staff versus the General Population
- Mina Ebrahimi, Amal Saki Malehi, Fakher Rahim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2020;11(5):269-279. Published online October 22, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2020.11.5.02
- 8,396 View
- 124 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material This review compared coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) laboratory findings, comorbidities, and clinical outcomes in patients from the general population versus medical staff to aid diagnosis of COVID-19 in a more timely, efficient, and accurate way. Electronic databases were searched up to 23rd March, 2020. The initial search yielded 6,527 studies. Following screening, 24 studies were included [18 studies (11,564 cases) of confirmed COVID-19 cases in the general public, and 6 studies (394 cases) in medical staff] in this review. Significant differences were observed in white blood cell counts (
p < 0.001), lymphocyte counts (p < 0.001), platelet counts (p = 0.04), procalcitonin levels (p < 0.001), lactate dehydrogenase levels (p < 0.001), and creatinine levels (p = 0.03) when comparing infected medical staff with the general public. The mortality rate was higher in the general population than in medical staff (8% versus 2%). This review showed that during the early stages of COVID-19, laboratory findings alone may not be significant predictors of infection and may just accompany increasing C-reactive protein levels, erythrocyte sedimentation rates, and lactate dehydrogenase levels. In the symptomatic stage, the lymphocyte and platelet counts tended to decrease. Elevated D-dimer fibrin degradation product was associated with poor prognosis.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- microRNA-185 Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Infection through the Modulation of the Host’s Lipid Microenvironment
Nadine Ahmed, Magen E. Francis, Noreen Ahmed, Alyson A. Kelvin, John Paul Pezacki
Viruses.2023; 15(9): 1921. CrossRef - Protective action of natural and induced immunization against the occurrence of delta or alpha variants of SARS-CoV-2 infection: a test-negative case-control study
Giovanni Corrao, Matteo Franchi, Federico Rea, Danilo Cereda, Antonio Barone, Catia Rosanna Borriello, Petra Giulia Della Valle, Michele Ercolanoni, Ida Fortino, Jose Jara, Olivia Leoni, Francesco Mazziotta, Elisabetta Pierini, Giuseppe Preziosi, Marcello
BMC Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Balancing Benefits and Harms of COVID-19 Vaccines: Lessons from the Ongoing Mass Vaccination Campaign in Lombardy, Italy
Giovanni Corrao, Federico Rea, Matteo Franchi, Danilo Cereda, Antonio Barone, Catia Rosanna Borriello, Giulia Petra Della Valle, Michele Ercolanoni, Jose Jara, Giuseppe Preziosi, Manuel Maffeo, Francesco Mazziotta, Elisabetta Pierini, Francesco Lecis, Pie
Vaccines.2022; 10(4): 623. CrossRef - Vulnerability Predictors of Post-Vaccine SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Disease—Empirical Evidence from a Large Population-Based Italian Platform
Giovanni Corrao, Matteo Franchi, Danilo Cereda, Francesco Bortolan, Olivia Leoni, Catia Rosanna Borriello, Petra Giulia Della Valle, Marcello Tirani, Giovanni Pavesi, Antonio Barone, Michele Ercolanoni, Jose Jara, Massimo Galli, Guido Bertolaso
Vaccines.2022; 10(6): 845. CrossRef - Factors associated with severe or fatal clinical manifestations of SARS‐CoV‐2 infection after receiving the third dose of vaccine
Giovanni Corrao, Matteo Franchi, Danilo Cereda, Francesco Bortolan, Olivia Leoni, Jose Jara, Giuseppina Valenti, Giovanni Pavesi
Journal of Internal Medicine.2022; 292(5): 829. CrossRef - Role of multiresolution vulnerability indices in COVID-19 spread in India: a Bayesian model-based analysis
Rupam Bhattacharyya, Anik Burman, Kalpana Singh, Sayantan Banerjee, Subha Maity, Arnab Auddy, Sarit Kumar Rout, Supriya Lahoti, Rajmohan Panda, Veerabhadran Baladandayuthapani
BMJ Open.2022; 12(11): e056292. CrossRef - A novel multi-omics-based highly accurate prediction of symptoms, comorbid conditions, and possible long-term complications of COVID-19
Debmalya Barh, Sandeep Tiwari, Bruno Silva Andrade, Marianna E. Weener, Aristóteles Góes-Neto, Vasco Azevedo, Preetam Ghosh, Kenneth Blum, Nirmal Kumar Ganguly
Molecular Omics.2021; 17(2): 317. CrossRef - Clinical and laboratory factors associated with coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid‐19): A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Le Huu Nhat Minh, Ali Ahmed‐Fouad Abozaid, Nam Xuan Ha, Loc Le Quang, Abdelrahman Gamil Gad, Ranjit Tiwari, Tran Nhat‐Le, Dinh Kim Quyen, Balqees AL‐Manaseer, Nguyen Dang Kien, Nguyen Lam Vuong, Ahmad Helmy Zayan, Le Huu Hanh Nhi, Kadek Agus Surya Dila, J
Reviews in Medical Virology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Epidemiologic and Clinic Characteristics of the First Wave of the COVID-19 Pandemic in Hospitalized Patients from Galați County
Mihaela-Camelia Vasile, Anca-Adriana Arbune, Gabriela Lupasteanu, Constantin-Marinel Vlase, George-Cosmin Popovici, Manuela Arbune
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(18): 4210. CrossRef - Human Amniotic Fluid for the Treatment of Hospitalized, Symptomatic, and Laboratory-verified SARS-CoV-2 Patients
Mojgan Barati, Fakher Rahim
The Open Biology Journal.2021; 9(1): 36. CrossRef - Stratification of the risk of developing severe or lethal Covid-19 using a new score from a large Italian population: a population-based cohort study
Giovanni Corrao, Federico Rea, Flavia Carle, Salvatore Scondotto, Alessandra Allotta, Vito Lepore, Antonio D'Ettorre, Cinzia Tanzarella, Patrizia Vittori, Sabrina Abena, Marica Iommi, Liana Spazzafumo, Michele Ercolanoni, Roberto Blaco, Simona Carbone, Cr
BMJ Open.2021; 11(11): e053281. CrossRef
- microRNA-185 Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Infection through the Modulation of the Host’s Lipid Microenvironment
- Meta-Analysis of the Effects of Physical Modality Therapy and Exercise Therapy on Neck and Shoulder Myofascial Pain Syndrome
- Chan-Myeong Kim, Ji-Won Park
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2020;11(4):251-258. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2020.11.4.15
- 6,497 View
- 144 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives The main purpose of this study was to identify the effects of physical therapy modalities and exercise therapy on myofascial pain syndrome by assessing the degree of effect size (ES) and related variables.
Methods Related studies published between 1st January 2008 and 31st December 2019were retrieved from national [KCI, RISS, National Assembly Library and DBpia (
n = 405)] and international [PubMed, Embase, Google Scholar and Cochrane library (n = 1,600)] databases. According to the selection criteria, 25 studies were selected for review.Results The degree of ES in the physical therapy and exercise therapy combined group (1.83) showed the largest mean ES. The size of the effect according to the number of people to be treated was 41 or more (1.64), and showed the largest mean ES. The size of the effect according to treatment period was 16 to 30 days (1.41). The size of the effect for 6 to 10 treatments (1.51) showed the largest mean ES. Trim and fill results showed that the calibration ES was 0.67.
Conclusion Physical therapy modalities and exercise therapy had a great effect on myofascial pain syndrome in the neck and shoulders, and the effect differed according to the methods of intervention, and the methods of evaluation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Impact of Dry Needling With Electrical Stimulation on Pain and Disability in Patients With Musculoskeletal Shoulder Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Anthony N Baumann, Andrew Fiorentino, Caleb J Oleson, John Martin Leland
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Meta-Analysis of the Effects of Various Physical Therapy Method about Shoulder Adhesive Capsulitis: The Cases of Domestic Research
Chan Myeong Kim
The Journal of Korean Physical Therapy.2020; 32(5): 277. CrossRef
- The Impact of Dry Needling With Electrical Stimulation on Pain and Disability in Patients With Musculoskeletal Shoulder Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- Neighborhood Deprivation and Unmet Health Care Needs: A Multilevel Analysis of Older Individuals in South Korea
- Seung Eun Lee, Miyeon Yeon, Chul-Woung Kim, Tae-Ho Yoon, Dongjin Kim, Jihee Choi
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2019;10(5):295-306. Published online October 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2019.10.5.06
- 12,219 View
- 64 Download
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives In this study the relationship between neighborhood deprivation and the unmet health care needs of elderly individuals (≥ 65 years) was examined. Some previous studies suggested that neighborhood characteristics affect access to health care, yet research on the unmet needs of older individuals is limited.
Methods Multilevel logistic regression analysis was used to assess the relationship of neighborhood-level factors with unmet health care needs due to costs, adjusting for individual-level factors, in individuals ≥ 65 years in the 2017 Korean Community Health Survey (
n = 63,388).Results There were 2.6% of elderly individuals who experienced unmet health care needs due to costs. Following adjustment for individual and neighborhood characteristics, the neighborhood deprivation in urban areas was found to have an inverse association with unmet needs (odds ratio = 0.50; 95% confidence interval = 0.24–1.06) for the most deprived quartile versus the least deprived quartile). However, in rural areas neighborhood deprivation was not a significant variable. Among the individual-level variables, household income was one of the strongest correlates with unmet needs in both urban and rural areas.
Conclusion The present findings suggest that targeted policy interventions reflecting both neighborhood and individual characteristics, should be implemented to reduce the unmet health care needs of elderly individuals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- What are the factors affecting older adults’ experience of unmet healthcare needs amid the COVID-19 pandemic in Korea?
Sujin Kim, Jongnam Hwang
BMC Geriatrics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Linking neighbourhood safety and children's internalizing and externalizing problems: Mediating role of maternal depression
Youngmin Cho
Child & Family Social Work.2023; 28(4): 1089. CrossRef - Urban-Rural Differences in the Prevalence of Depressive Symptoms in Korean Adults
Ji-An Jeong, Sun A Kim, Jung Ho Yang, Min-Ho Shin
Chonnam Medical Journal.2023; 59(2): 128. CrossRef - PhaVIP: Phage VIrion Protein classification based on chaos game representation and Vision Transformer
Jiayu Shang, Cheng Peng, Xubo Tang, Yanni Sun
Bioinformatics.2023; 39(Supplement): i30. CrossRef - Dashboard to analyze associations of socio-economic and environmental inequality of regions with health indicators. Guidelines
A. A. Zelenina, S. A. Shalnova, S. A. Maksimov
Cardiovascular Therapy and Prevention.2023; 22(7): 3652. CrossRef - The Older Persons' Index of Multiple Deprivation: Measuring the deprivation circumstances of older populations in Aotearoa New Zealand
Daniel J. Exeter, Michael Browne, Tommi Robinson-Chen, Jessie Colbert, Ngaire Kerse, Arier Lee
Health & Place.2022; 76: 102850. CrossRef - The Contribution of Material, Behavioral, Psychological, and Social-Relational Factors to Income-Related Disparities in Cardiovascular Risk Among Older Adults
Chiyoung Lee, Qing Yang, Eun-Ok Im, Eleanor Schildwachter McConnell, Sin-Ho Jung, Hyeoneui Kim
Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing.2021; 36(4): E38. CrossRef - Association between community deprivation and practising health behaviours among South Korean adults: a survey-based cross-sectional study
Bich Na Jang, Hin Moi Youn, Doo Woong Lee, Jae Hong Joo, Eun-Cheol Park
BMJ Open.2021; 11(6): e047244. CrossRef
- What are the factors affecting older adults’ experience of unmet healthcare needs amid the COVID-19 pandemic in Korea?
- Therapeutic Intervention for Visuo-Spatial Neglect after Stroke: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- Jae-Sung Kwon
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2018;9(2):59-65. Published online April 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2018.9.2.04
- 5,981 View
- 72 Download
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives The aims of this meta-analysis were to examine intervention methods of qualitatively, well-designed studies from the past 10 years for treating visuo-spatial neglect (VSN) in patients who had suffered a stroke, and to evaluate the combined effects of intervention.
Methods Studies published between 2008 and 2017 on the theme of VSN were collected from PubMed, CINAHL, and MEDLINE, representative academic databases and search engines. The PEDro scale was used for evaluating the quality of methodology. The sample size, mean, and standard deviation of identified studies were used for meta-analysis.
Results Eight studies were selected for analysis. The PEDro scores of the selected studies were ≥ 7, with 237 subjects analyzed. The results of intervention were classified into “mental function” and “activity and participation” based on the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health. The analyzed effect sizes for combined outcomes, mental function and, activity and participation, were 0.728 (medium effect size), 0.850 (large effect size), and 0.536 (medium effect size), respectively.
Conclusion Intervention methods for treating VSN had a short-term effect on cognitive function (visual perception). In particular, non-invasive brain stimulation therapy showed a large effect size for VSN treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Non-pharmacological interventions for spatial neglect or inattention following stroke and other non-progressive brain injury
Verity Longley, Christine Hazelton, Calvin Heal, Alex Pollock, Kate Woodward-Nutt, Claire Mitchell, Gorana Pobric, Andy Vail, Audrey Bowen
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Neural Mechanisms of Spatial Attention Deficits in Trauma
Stefanie R. Russman Block, Daniel H. Weissman, Chandra Sripada, Mike Angstadt, Elizabeth R. Duval, Anthony P. King, Israel Liberzon
Biological Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and .2020; 5(10): 991. CrossRef - Updated Approach to Stroke Rehabilitation
Leroy R. Lindsay, Diane A. Thompson, Michael W. O’Dell
Medical Clinics of North America.2020; 104(2): 199. CrossRef - Implementing a Rehabilitation Protocol for Spatial Neglect Assessment and Treatment in an Acute Care Hospital
Kimberly Hreha, Peii Chen, Jennifer LaRosa, Christopher Santos, Cindy Gocon, A.M. Barrett
Journal of Acute Care Physical Therapy.2020; 11(2): 59. CrossRef - Alertness Training Improves Spatial Bias and Functional Ability in Spatial Neglect
Thomas Van Vleet, Paolo Bonato, Eric Fabara, Sawsan Dabit, Sarah‐Jane Kim, Christopher Chiu, Antonio Luigi Bisogno, Michael Merzenich, Maurizio Corbetta, Joseph DeGutis
Annals of Neurology.2020; 88(4): 747. CrossRef
- Non-pharmacological interventions for spatial neglect or inattention following stroke and other non-progressive brain injury
- Associations between Social and Physical Environments, and Physical Activity in Adults from Urban and Rural Regions
- Bongjeong Kim, Hye Sun Hyun
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2018;9(1):16-24. Published online December 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2018.9.1.04
- 4,881 View
- 48 Download
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives This study investigates investigated the relationship between social and physical environments, and moderate to vigorous physical activity (MVPA) amongst adults in both rural and urban areas within Korea.
Methods A sample of 128,735 adults from the 2013 Community Health Survey (CHS) was analyzed using a multilevel logistic analysis.
Results Urban residents with higher satisfaction in public transportation satisfaction and rural residents with more access to sports parks, hiking trails, and bike cycle paths were more likely to be active. The MVPA of adults from rural areas correlated urban adults was uncorrelatedwith neighborhood factors, but that of rural adults was whereas no correlations were observed in adults from urban areas.
Conclusion These differences should be considered when developing interventions strategies to enhance adult physical activity in different communities.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Neighborhood Environmental Factors and Physical Activity Status among Rural Older Adults in Japan
Kenta Okuyama, Takafumi Abe, Xinjun Li, Yuta Toyama, Kristina Sundquist, Toru Nabika
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2021; 18(4): 1450. CrossRef - Youth’s Physical Activity and Fitness from a Rural Environment of an Azores Island
João Pedro Gouveia, Pedro Forte, Eduarda Coelho
Social Sciences.2021; 10(3): 96. CrossRef - The Changes in Obesity Prevalence and Dietary Habits in Korean Adults by Residential Area during the Last 10 Years — Based on the 4th (2007–2009) and the 7th (2016–2018) Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data
Da-Mee Kim, Kyung-Hee Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2021; 26(1): 37. CrossRef - Regional Disparity in Adult Obesity Prevalence, and Its Determinants
Bongjeong Kim
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2021; 46(4): 410. CrossRef -
Factors Affecting Activity Limitation in the Elderly: Data Processed from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2016
Jong-Hoon Moon
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2019; 10(3): 117. CrossRef - Corrigendum to “Associations between Social and Physical Environments, and Physical Activity in Adults from Urban and Rural Regions”[Osong Public Health Res Perspect 2018;9(1):16–24]
Bongjeong Kim, Hye Sun Hyun
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2018; 9(5): 283. CrossRef
- Neighborhood Environmental Factors and Physical Activity Status among Rural Older Adults in Japan



 First
First Prev
Prev


