Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Factors affecting depression and health-related quality of life in the elderly during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Deok-Ju Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(6):520-529. Published online November 16, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0166
- 812 View
- 40 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 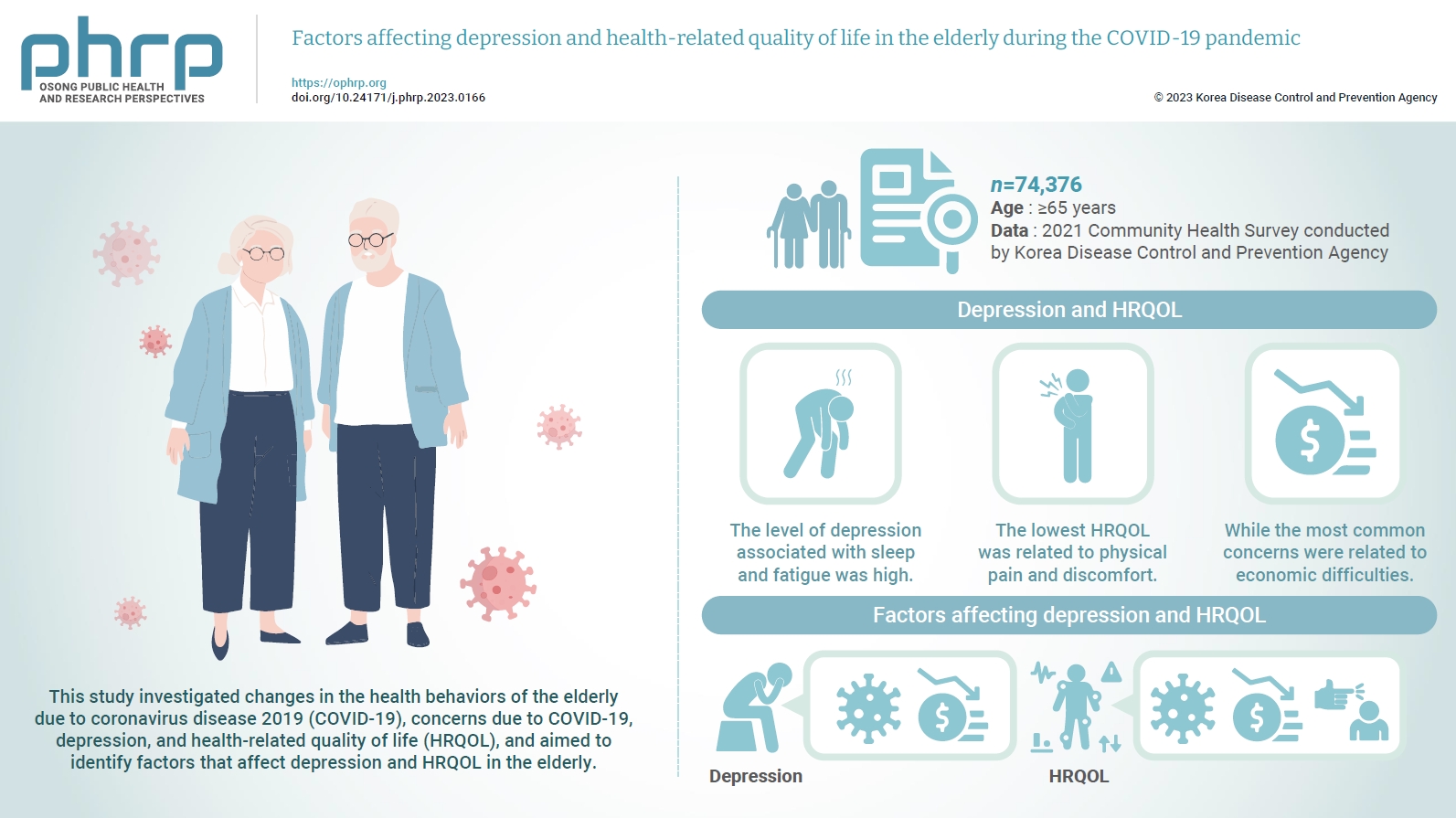
- Objectives
This study investigated changes in the health behaviors of the elderly due to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), concerns due to COVID-19, depression, and healthrelated quality of life (HRQOL), and aimed to identify factors that affect depression and HRQOL in the elderly. Methods: This study was conducted using data from the 2021 Community Health Survey of the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency. From a total sample size of 229,242 individuals, 74,376 elderly people aged 65 or older were selected as subjects, and changes in health behaviors, concerns due to COVID-19, depression, and HRQOL were measured and analyzed. Results: The level of depression associated with sleep and fatigue was high. The lowest HRQOL was related to physical pain and discomfort, while the most common concerns were related to economic difficulties. Factors influencing depression included worries about infection and economic harm, while factors impacting HRQOL encompassed concerns about infection, economic harm, and criticism from others. Conclusion: If an infectious disease situation such as COVID-19 reoccurs in the future, it will be necessary to encourage participation in hybrid online and offline programs at senior welfare centers. This should also extend to community counseling institutions like mental health welfare centers. Additionally, establishing connections with stable senior job projects can help to mitigate the effects of social interaction restrictions, physical and psychological health issues, and economic difficulties experienced by the elderly.
- Factors associated with the combination of general and abdominal obesity in middle-aged and older Korean women: a cross-sectional study
- Jin Suk Ra
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(5):379-387. Published online September 20, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0089
- 1,008 View
- 38 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 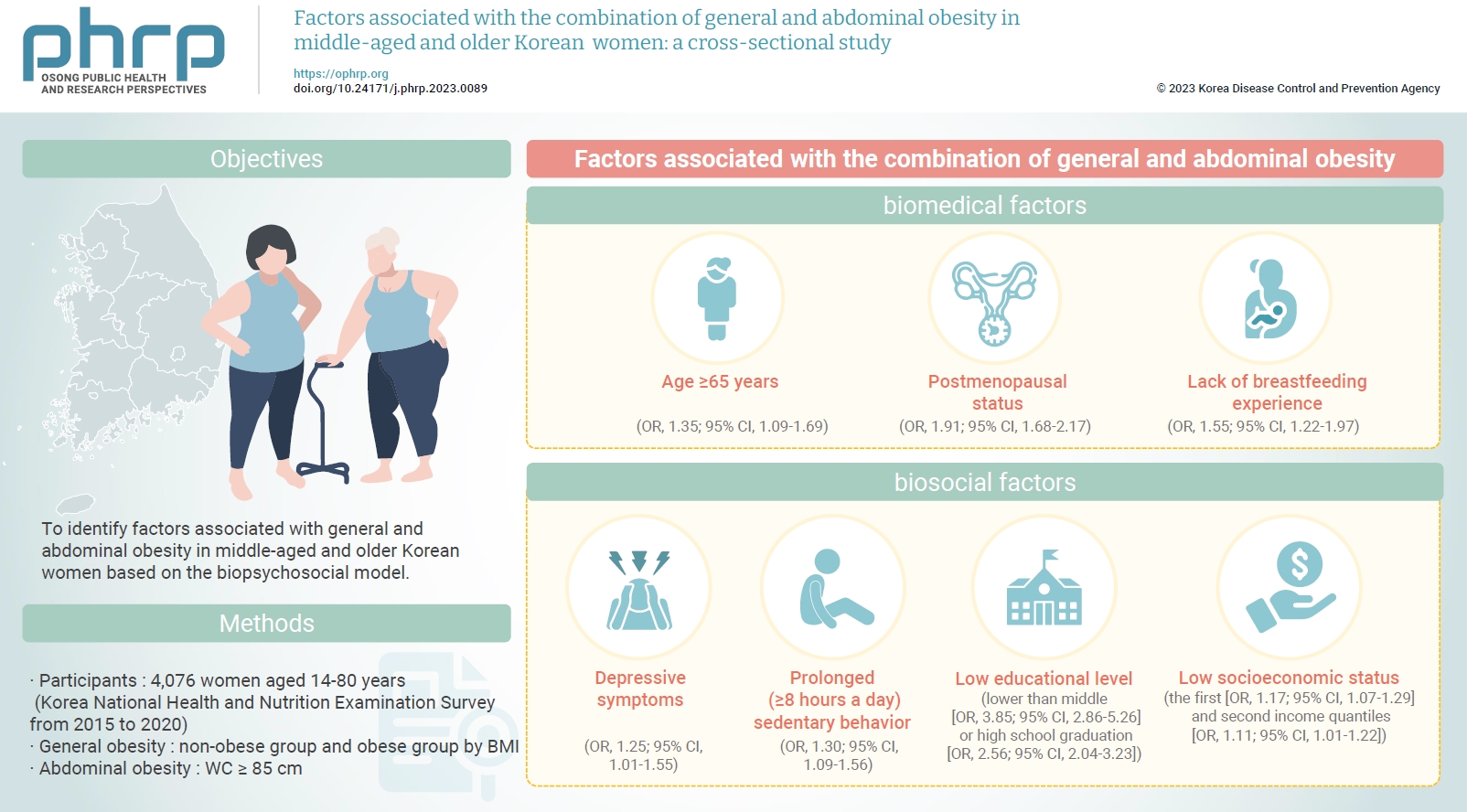
- Objectives
To identify factors associated with general and abdominal obesity in middle-aged and older Korean women based on the biopsychosocial model. Methods: Data from 4,076 women aged ≥45 years who participated in the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey from 2015 to 2020 were analyzed. Complex sampling analysis was performed using IBM SPSS ver. 26.0. Results: The combination of general and abdominal obesity was positively associated with age ≥65 years, postmenopausal status, and without breastfeeding experience among biomedical factors; depressive symptoms and prolonged (≥8 hours a day) sedentary behavior among psychosocial factors; and an educational level lower than middle or high school graduation and the first and second income quantiles among biosocial factors. Conclusion: Healthcare providers in communities and public societies should screen for risk factors for the combination of general and abdominal obesity while considering non-modifiable biomedical (e.g., age) and biosocial factors (e.g., educational level). In addition, intervention strategies should be developed by considering modifiable psychosocial factors such as sedentary behavior.
- Effects of medication adherence interventions for older adults with chronic illnesses: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Hae Ok Jeon, Myung-Ock Chae, Ahrin Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(5):328-340. Published online October 12, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0168
- 3,540 View
- 166 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to understand the characteristics of medication adherence interventions for older adults with chronic illnesses, and to investigate the average effect size by combining the individual effects of these interventions. Data from studies meeting the inclusion criteria were systematically collected in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis guidelines. The results showed that the average effect size (Hedges’ g) of the finally selected medication adherence interventions for older adults with chronic illnesses calculated using a random-effects model was 0.500 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.342−0.659). Of the medication adherence interventions, an implementation intention intervention (using face-to-face meetings and telephone monitoring with personalized behavioral strategies) and a health belief model–based educational program were found to be highly effective. Face-to-face counseling was a significantly effective method of implementing medication adherence interventions for older adults with chronic illnesses (Hedges’ g=0.531, 95% CI, 0.186−0.877), while medication adherence interventions through education and telehealth counseling were not effective. This study verified the effectiveness of personalized behavioral change strategies and cognitive behavioral therapy based on the health belief model, as well as face-to-face meetings, as medication adherence interventions for older adults with chronic illnesses.
- Factors Influencing Self-Rated Oral Health in Elderly People Residing in the Community: Results from the Korea Community Health Survey, 2016
- Jong-Hoon Moon, Sung-Jin Heo, Jin-Hwa Jung
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2020;11(4):245-250. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2020.11.4.14
- 5,797 View
- 91 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives The aim of this study was to examine the factors influencing perceived oral health in elderly individuals residing in the community.
Methods This study used raw data from the Korea community health survey, 2016. Of the 64,223 participants that were elderly (aged ≥ 65 years), 61,280 (95.4%) were included for analysis. Self-rated oral health was the dependent variable and 6 independent variables including age, gender, type of area of residence (metropolitan or provincial), educational level, income, and living status with spouse were assessed. Oral function was studied based on mastication, pronunciation, and use of dentures, and oral health behavior included brushing teeth after breakfast, after lunch, after dinner, and before sleep). The EQ-5D questionnaire measured health-related quality of life (mobility, self-care, usual activities, pain/discomfort and anxiety/depression).
Results Among the general characteristics, age, gender, educational level, income, and living status with spouse were the factors that affected self-rated oral health. Mastication, pronunciation, use of dentures, and brushing after lunch, dinner, and before sleep were the factors that influenced self-rated oral function. All domains of the EQ-5D (pain/discomfort, mobility, self-care, usual activities, and anxiety/depression) were factors that affected self-rated oral health.
Conclusion The results of the current investigation suggest that the development of management and education strategies for oral health promotion in the elderly, should focus on improving oral function and oral health behavior, taking into account the socio-economic and demographic characteristics that have been shown to be associated with poor self-rated oral function.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Older adults’ perceptions of oral health and its influence on general health: A deductive direct content analysis
Maria Snogren, Irene Eriksson, Maria Browall, Kristina Ek
Nordic Journal of Nursing Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Oral health status and behavior in elderly Koreans with periodontal disease
Sae‐Rom Lee, Mi Ah Han, Jong Park, So Yeon Ryu, So Yeong Kim
Journal of Public Health Dentistry.2022; 82(4): 378. CrossRef - Oral health-related quality of life, probable depression and probable anxiety: evidence from a representative survey in Germany
André Hajek, Hans-Helmut König
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Associated with Self‐reported Oral Health Among Community-Dwelling Older Adults in a Rural Province of Thailand
Yaowapa Chantaraboot, Nithimar Sermsuti-anuwat
Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare.2022; Volume 15: 2111. CrossRef - Self-rated oral health among elderly patients attending a university dental hospital in Thailand: a telephone-based cross-sectional survey study
Nithimar Sermsuti-anuwat, Narongrit Nampikul, Rawitsara Suwannimit, Weerachon Panthueng
PeerJ.2022; 10: e14191. CrossRef
- Older adults’ perceptions of oral health and its influence on general health: A deductive direct content analysis
- COVID-19 in Nursing Facilities: Experience in Republic of Korea
- Rok Song, Hee-Sook Kim, Seok-Ju Yoo, Kwan Lee, Ji-Hyuk Park, Joon Ho Jang, Gyoung-Sook Ahn, Jun-Nyun Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2020;11(4):164-169. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2020.11.4.04
- 7,236 View
- 146 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreaks in nursing facilities can easily lead to a high rate of infection and fatality. A surge in newly infected cases in the first quarter of 2020 in Gyeongsan-si, in the Republic of Korea, was followed by several outbreaks in nursing facilities in the same area. The aim of this study is to report on the epidemiological investigation and the management to reduce the infection rate in nursing facilities for older adults.
Methods The municipal government and the Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention performed an epidemiological investigation into 5 nursing facilities that reported a high number of COVID-19 infection cases from February to May 2020. COVID-19 infected cases in the facilities were investigated to identify the infection routes, and the fatality rate of the 5 facilities.
Results The 5 facilities had a combined fatality rate of 12.2% (9 deceased among the 74 infected cases). The median age of the deceased was 87 years old (range: 82–91). The infection was first identified on February 27th, 2020, peaked on March 6th, and was last detected on March 24th, 2020.
Conclusion Difficulties specific to such facilities included the delay in the recognition of symptoms and limitation in distancing. Tailored strategies such as daily monitoring of symptoms and proactive COVID-19 screening of quarantined residents, contributed to a decline in the infections in the facilities.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and corresponding control measures on long-term care facilities: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Jun Zhang, Yushan Yu, Mirko Petrovic, Xiaomei Pei, Qing-Bao Tian, Lei Zhang, Wei-Hong Zhang
Age and Ageing.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk factors for COVID-19 outbreaks in livestock slaughtering and processing facilities in Republic of Korea
Seongju Choi, Tae Jong Son, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2023; 14(3): 207. CrossRef - Using Non-Pharmaceutical Interventions and High Isolation of Asymptomatic Carriers to Contain the Spread of SARS-CoV-2 in Nursing Homes
Alec J. Schmidt, Yury García, Diego Pinheiro, Thomas A. Reichert, Miriam Nuño
Life.2022; 12(2): 180. CrossRef - An Experience of the Early Stage of COVID-19 Outbreak in Nursing Homes in Gyeonggi Province, Korea
Gawon Choi, Na-young Kim, Seon-young Lee, Hae Deun Noh, Heeyoung Lee
Korean Journal of Clinical Geriatrics.2022; 23(1): 27. CrossRef - Promising Best Practices Implemented in Long- Term Care Facilities During the COVID-19 Pandemic to Address Social Isolation and Loneliness: A Scoping Review
Idrissa Beogo, Nebila Jean-Claude Bationo, Stephanie Collin, Diane Tapp, Jean Ramdé, Marie-Pierre Gagnon, Eric Nguemeleu Tchouaket, Drissa Sia
Journal of Long-Term Care.2022; 0(2022): 298. CrossRef - Epidemiology and clinical features of COVID-19 outbreaks in aged care facilities: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Mohammad Rashidul Hashan, Nicolas Smoll, Catherine King, Hannah Ockenden-Muldoon, Jacina Walker, Andre Wattiaux, Julieanne Graham, Robert Booy, Gulam Khandaker
EClinicalMedicine.2021; 33: 100771. CrossRef - The experience of executing preventive measures to protect a nursing home in Taiwan from a COVID-19 outbreak
Chia-Yu Huang, Yu-Hung Kuo, Shu-Ting Chuang, Hung-Rong Yen, Sio-Ian Tou
European Geriatric Medicine.2021; 12(3): 609. CrossRef - Everyday life in a Swedish nursing home during the COVID-19 pandemic: a qualitative interview study with persons 85 to 100 years
Qarin Lood, Maria Haak, Synneve Dahlin-Ivanoff
BMJ Open.2021; 11(6): e048503. CrossRef
- Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and corresponding control measures on long-term care facilities: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Effect of Obesity on Blood Pressure and Arterial Stiffness in Middle-Aged Korean Women
- Won-Mok Son, Do-Yeon Kim, You-Sin Kim, Min-Seong Ha
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2017;8(6):369-372. Published online December 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2017.8.6.02
- 3,978 View
- 41 Download
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives Our study aims to provide basic scientific data on the importance of obesity management in middle-aged Korean women by analyzing its effects on blood pressure and arterial stiffness. In addition, we examined the correlations of these two parameters.
Methods The study participants were 40 middle-aged female volunteers, who were classified into obesity group (n = 20) and normal weight group (n = 20). Statistical analysis was performed using independent
t -test and the Pearson correlation coefficient was used to correlate blood pressure and arterial stiffness.Results This study evaluated the systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, and pulse wave velocity (PWV). These results were higher in the obesity group than the normal weight group. Furthermore, blood pressure and arterial stiffness (PWV, augmentation pressure) were static correlated.
Conclusion Obesity is closely related to blood pressure and arterial stiffness. Therefore, indices for blood pressure and arterial stiffness may play a vital role in predicting and preventing obesity and its sequelae.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Food readjustment plus exercise training improves cardiovascular autonomic control and baroreflex sensitivity in high‐fat diet‐fed ovariectomized mice
Bruno Nascimento‐Carvalho, Adriano Dos‐Santos, Nicolas Da Costa‐Santos, Sabrina L. Carvalho, Oscar A. de Moraes, Camila P. Santos, Katia De Angelis, Erico C. Caperuto, Maria‐Claudia Irigoyen, Katia B. Scapini, Iris C. Sanches
Physiological Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations between body composition and cardiovascular disease risk in pre- and postmenopausal women
Nirmala Rathnayake, Gayani Alwis, Janaka Lenora, Sarath Lekamwasam
Journal of Health, Population and Nutrition.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Vascular Function, Cardiometabolic Parameters, Hemorheological Function, and Cardiorespiratory Fitness Between Middle-Aged Korean Women With and Without Obesity—A Pilot Study
Hun-Young Park, Won-Sang Jung, Sung-Woo Kim, Kyounghwa Jung, Kiwon Lim
Frontiers in Physiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of femoral and carotid arteries in terms of pulse check in cardiopulmonary resuscitation: A prospective observational study
Gökhan Yılmaz, Oğuzhan Bol
Resuscitation.2021; 162: 56. CrossRef - Effect of yoga on pulse rate and blood pressure among women
G Kaleeswari, CVasantha Kalyani, JS Jayarani, KusumK Rohilla
Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.2021; 10(10): 3670. CrossRef - Association of obesity with arterial stiffness: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA)
Jeongok G. Logan, Hyojung Kang, Soyoun Kim, Daniel Duprez, Younghoon Kwon, David R. Jacobs, Nketi Forbang, Jennifer Mason Lobo, Min-Woong Sohn
Vascular Medicine.2020; 25(4): 309. CrossRef - The Feasibility and Applications of Non-invasive Cardiac Monitoring in Obese Patients Undergoing Day-case Surgery: Results of a Prospective Observational Study
P. Sansone, L.G. Giaccari, U. Colella, F. Coppolino, M.C. Pace, M.B. Passavanti, V. Pota, C. Aurilio
The Open Anesthesia Journal.2020; 14(1): 80. CrossRef - The Impact of Obesity on Nighttime Blood Pressure Dipping
Beata Moczulska, Maciej Zechowicz, Sylwia Leśniewska, Karolina Osowiecka, Leszek Gromadziński
Medicina.2020; 56(12): 700. CrossRef - Greater Adherence to Life’s Simple 7 Is Associated With Less Arterial Stiffness: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study
Abayomi O Oyenuga, Aaron R Folsom, Susan Cheng, Hirofumi Tanaka, Michelle L Meyer
American Journal of Hypertension.2019; 32(8): 769. CrossRef
- Food readjustment plus exercise training improves cardiovascular autonomic control and baroreflex sensitivity in high‐fat diet‐fed ovariectomized mice
- Different Effects of Cognitive and Non-exercise Physical Leisure Activities on Cognitive Function by Age in Elderly Korean Individuals
- Mi Sook Jung, Hyunli Kim, Yeji Lee, Mijung Kim, Eunyoung Chung
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2017;8(5):308-317. Published online October 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2017.8.5.04
- 4,405 View
- 44 Download
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives We aimed to examine the effects of various leisure activities on cognitive impairment in young-old (aged 65–74 years) and old-old (aged ≥ 75 years) adults.
Methods In total, 10,279 elderly Korean individuals from the 2014 Korean National Survey on Older Adults’ cohort were enrolled in our study. Cognitive impairment was assessed using the standardized score of the Mini-Mental State Examination for Dementia Screening, whereas leisure activities were recorded via self-reporting of the extent and type of leisure activity the subjects involved in over the past year. Multivariate logistic regression was used to assess the effect of leisure activities on cognitive impairment, while controlling for potential covariates.
Results The subjects were more likely to participate in cognitive activities than in non-exercise physical activities. After controlling for selected covariates, involvement in cognitive activities was found to be a significant predictor of cognitive impairment in both the groups, whereas involvement in non-exercise physical activities was not a predictor of cognitive impairment in individuals aged ≥ 75 years. Moreover, depressive symptoms, rural residence, and hearing difficulties were common predictors of cognitive impairment among elderly-Korean-individuals.
Conclusion Leisure activity involvement may help delay cognitive impairment, which is often concomitant with aging. Hence, an early intervention service may significantly benefit both young-old and old-old individuals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Leisure activity and cognitive function among Chinese old adults: The multiple mediation effect of anxiety and loneliness
Wenjun Li, Haiyan Sun, Wen Xu, Wenyuan Ma, Xin Yuan, Hao Wu, Changgui Kou
Journal of Affective Disorders.2021; 294: 137. CrossRef - Hearing Screening for Residents in Long-Term Care Homes Who Live with Dementia: A Scoping Review
Fiona Höbler, Katherine S. McGilton, Walter Wittich, Kate Dupuis, Marilyn Reed, Shirley Dumassais, Paul Mick, M. Kathleen Pichora-Fuller
Journal of Alzheimer's Disease.2021; 84(3): 1115. CrossRef - Effects of non‐pharmacological therapies for people with mild cognitive impairment. A Bayesian network meta‐analysis
Ying‐quan Wang, Rui‐xia Jia, Jing‐hong Liang, Jing Li, Sheng Qian, Jia‐yu Li, Yong Xu
International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry.2020; 35(6): 591. CrossRef - Do Musicians Have Better Mnemonic and Executive Performance Than Actors? Influence of Regular Musical or Theater Practice in Adults and in the Elderly
Mathilde Groussard, Renaud Coppalle, Thomas Hinault, Hervé Platel
Frontiers in Human Neuroscience.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Television Viewing and Cognitive Dysfunction of Korean Older Adults
Mi Sook Jung, Eunyoung Chung
Healthcare.2020; 8(4): 547. CrossRef - Associated factors for cognition of physically independent elderly people living in residential care facilities for the aged in Sri Lanka
Madushika Wishvanie Kodagoda Gamage, Chandana Hewage, Kithsiri Dedduwa Pathirana
BMC Psychiatry.2019;[Epub] CrossRef
- Leisure activity and cognitive function among Chinese old adults: The multiple mediation effect of anxiety and loneliness
- Age-differentiated Risk Factors of Suicidal Ideation among Young and Middle-aged Korean Adults
- Ahra Jo, Minho Jeon, Heeyoung Oh
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2017;8(3):201-210. Published online June 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2017.8.3.07
- 4,087 View
- 35 Download
- 17 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives This study aimed to determine the prevalence of suicidal ideation among young and middle-aged adults, and explore the risk factors that affect suicidal ideation.
Methods A descriptive study design was used for secondary data analysis. A total sample of 5,214 was drawn from two waves (2012–2013) of the 7th Korea Health Panel (KHP) survey. The KHP data were collected by a well-trained interviewer using the face-to-face method during home visits as well as self-report method. Descriptive statistics of frequency, percentage, chi-square test, and logistic regression analysis were performed using SPSS 22.0.
Results The prevalence of suicidal ideation in young and middle-aged adults was 4.4% and 5.6%, respectively. For young adults, suicidal ideation risk was higher among those with low income or heavy drinking habits. In middle-aged adults, low income, poor perceived health status, negative perception of peer-compared health status, and negative social perspective were the major risk factors.
Conclusion There is considerable risk of suicidal ideation in adulthood. Opportunities for increased income, avoidance of heavy drinking, and the construction of positive subjective health status and social perspective should be considered in suicide prevention interventions for Korean young and middle-aged adults.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Psychosocial risk factors of youth suicide in the Western Pacific: a scoping review
Mohammad Izzat Morshidi, Peter K. H. Chew, Lidia Suárez
Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology.2024; 59(2): 201. CrossRef - Spatial and temporal trends and risk factors for intentional carbon monoxide poisoning hospitalizations in England between 2002 and 2016
Aina Roca-Barceló, Helen Crabbe, Rebecca Close, Helena Fahie, Giovanni S. Leonardi, Frédéric B. Piel
Journal of Affective Disorders.2023; 329: 168. CrossRef - Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on intensive care
admissions and mortality due to self-poisoning:
A retrospective comparative study from a tertiary care
hospital
Aneela Α. Kidwai, Komal Fareed, Jamal Ara, Mahnoor Khalil, Shaista Ahmed, Syeda Urooj Riaz, Yumna Ahmed
Public Health and Toxicology.2023; 3(3): 1. CrossRef - Spectrum and predictors of suicidal risk among incarcerated youth in a correctional facility in Kaduna, Northern Nigeria
Marufah Dupe Lasisi, Folorunsho Tajudeen Nuhu, Femi Adebayo, Edwin Ehi Eseigbe, Taiwo Lateef Sheikh
Vulnerable Children and Youth Studies.2022; 17(2): 147. CrossRef - Alcohol use and its association with suicide attempt, suicidal thoughts and non-suicidal self-harm in two successive, nationally representative English household samples
Sarah Ledden, Paul Moran, David Osborn, Alexandra Pitman
BJPsych Open.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations between Suicidal Ideation and Relatives’ Physical and Mental Health among Community Residents: Differences between Family Members and Lineal Consanguinity
Caifeng Li, Zhen Wei, Yifan Wang, Long Sun
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2022; 19(23): 15997. CrossRef - Factors affecting suicidal ideation among premenopausal and postmenopausal women
Go‐Un Kim, Hae Kyoung Son, Mi‐Young Kim
Journal of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2021; 28(3): 356. CrossRef - Depression and suicidal ideation among HIV seropositive patients attending the special treatment clinic of the University of Calabar Teaching Hospital, Calabar, Nigeria
Elvis Mbu Bisong, Chidi John Okafor, Agam Ebaji Ayuk, Udeme Essien Asibong, Henry Ohem Okpa
Calabar Journal of Health Sciences.2021; 4: 64. CrossRef - The role of ageing in the wish to be dead: disentangling age, period and cohort effects in suicide ideation in European population
M. Cabello, L. A. Rico-Uribe, J. C. Martinez-Ávila, A. Sánchez-Niubò, F. F. Caballero, G. Borges, B. Mellor-Marsá, J. M. Haro, M. Prina, S. Koskinen, J. L. Ayuso-Mateos
Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Association Between Suicide Risk and Comorbidity of Mood Disorder and Alcohol Use Disorder: Using Common Data Model in Psychiatry
Yong Hyuk Cho, Eunyoung Lee, Eun Sil Her, Gyubeom Hwang, Ki-Young Lim, Jai Sung Noh, Yunmi Shin, Chang Hyung Hong, Hyun Woong Roh, Dongyun Lee, Heirim Lee, Doyeop Kim, Rae Woong Park, Bumhee Park, Sang Joon Son
Journal of Korean Neuropsychiatric Association.2021; 60(3): 232. CrossRef - Analysis of risk factors affecting suicidal ideation in South Korea by life cycle stage
Ji-Young Hwang, Il-Su Park
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2021; 12(5): 314. CrossRef - Association of chronic diseases and lifestyle factors with suicidal ideation among adults aged 18–69 years in Eswatini: evidence from a population-based survey
Mfundi President Sebenele Motsa, Hung-Yi Chiou, Yi-Hua Chen
BMC Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Cross-national prevalence and factors associated with suicide ideation and attempts in older and young-and-middle age people
Maria Cabello, Marta Miret, José Luis Ayuso-Mateos, Felix Feliz Caballero, Somnath Chatterji, Beata Tobiasz-Adamczyk, Josep Maria Haro, Seppo Koskinen, Matilde Leonardi, Guilherme Borges
Aging & Mental Health.2020; 24(9): 1533. CrossRef - Characteristics, causality, and suicidal behavior: a qualitative study of family members with suicide history in Wonogiri, Indonesia
Susana Nurtanti, Sri Handayani, Nita Yunianti Ratnasari, Putri Halimu Husna, Tantut Susanto
Frontiers of Nursing.2020; 7(2): 169. CrossRef - Risk Factors for Suicidal Ideation among Middle Class Korean: Focusing on Psychosocial Comparison - An Analysis of a Nationwide Survey of the 8th Korea Health Panel Data
Ahra Jo, Bora Kang, Youngju Seo, Eunha Gil, Heeyoung Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nurs.2018; 29(1): 1. CrossRef - The Function of Personality in Suicidal Ideation from the Perspective of the Interpersonal-Psychological Theory of Suicide
Marc Baertschi, Alessandra Costanza, Alessandra Canuto, Kerstin Weber
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2018; 15(4): 636. CrossRef - To Be or Not to Be
Hae-Wol Cho, Chaeshin Chu
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2017; 8(3): 157. CrossRef
- Psychosocial risk factors of youth suicide in the Western Pacific: a scoping review
- Experience of Late–Middle-Aged Women who Reside in Small and Medium-Sized Cities in Becoming Psychologically Mature Women
- Euna Park, Haeok Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2015;6(3):159-163. Published online June 30, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2015.04.002
- 2,835 View
- 17 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The purpose of this study is to search the inner world of postmenopausal women in late-middle age who are facing senescence and live in small and medium-sized cities.
Methods
The methods of the study were the investigation and classification of answers to questions according to a declarative ethnography analysis. The questions asked to late–middle-aged women living in small and medium-sized cities were “How do you interpret and recognize the changes in the body after menopause?” and “Which methods do you choose and practice to maintain your health in relation to aging during middle age?”.
Results
Four positive topics and two negative topics were drawn from the study. The four positive themes were: ambition; completion of a great mission; life with a sense of affection; and gratitude for maintaining health. The negative themes were: undulating emotion; and filling the emptiness.
Conclusion
The recognition of changes in the body after menopause in late–middle-aged women in small and medium-sized cities can affect their preparation processes towards senescence. It is critical to find the means to manage emergency health cases from early adulthood to middle age, based on the outcomes of the study. The study also emphasizes the importance of the woman's family's alternative strategies and supportive systems, which can fit into the cultural context of the community. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Trend of Women’s Health Research in Korea, 2012–2020: Topic and Text Network Analysis
Ji Eun Park, Saerom Kim, Myoung-Hee Kim, Taemi Kim, Seung-Ah Choe, Hye Sook Min
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The experiences and needs of Asian women experiencing menopausal symptoms: a meta-synthesis
Shefaly Shorey, Esperanza D. Ng
Menopause.2019; 26(5): 557. CrossRef - Effects of Aromatherapy on Menopausal Symptoms, Perceived Stress and Depression in Middle-aged Women: A Systematic Review
Shinmi Kim, Ji-Ah Song, Mi-Eun Kim, Myung-Haeng Hur
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2016; 46(5): 619. CrossRef
- Trend of Women’s Health Research in Korea, 2012–2020: Topic and Text Network Analysis
- Are There Spatial and Temporal Correlations in the Incidence Distribution of Scrub Typhus in Korea?
- Maengseok Noh, Youngjo Lee, Chaeshin Chu, Jin Gwack, Seung-Ki Youn, Sun Huh
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2013;4(1):39-44. Published online February 28, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2013.01.002
- 3,560 View
- 21 Download
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
A hierarchical generalized linear model (HGLM) was applied to estimate the transmission pattern of scrub typhus from 2001 to 2011 in the Republic of Korea, based on spatial and temporal correlation.
Methods
Based on the descriptive statistics of scrub typhus incidence from 2001 to 2011 reported to the Korean Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the spatial and temporal correlations were estimated by HGLM. Incidences according to age, sex, and year were also estimated by the best-fit model out of nine HGLMs. A disease map was drawn to view the annual regional spread of the disease.
Results
The total number of scrub typhus cases reported from 2001 to 2011 was 51,136: male, 18,628 (36.4%); female, 32,508 (63.6%). The best-fit model selected was a combination of the spatial model (Markov random-field model) and temporal model (first order autoregressive model) of scrub typhus transmission. The peak incidence was 28.80 per 100,000 persons in early October and the peak incidence was 40.17 per 100,000 persons in those aged 63.3 years old by the best-fit HGLM. The disease map showed the spread of disease from the southern central area to a nationwide area, excepting Gangwon-do (province), Gyeongsangbuk-do (province), and Seoul.
Conclusion
In the transmission of scrub typhus in Korea, there was a correlation to the incidence of adjacent areas, as well as that of the previous year. According to the disease map, we are unlikely to see any decrease in the incidence in the near future, unless ongoing aggressive measures to prevent the exposure to the vector, chigger mites, in rural areas, are put into place. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence of chigger mites and Orientia tsutsugamushi strains in northern regions of Gangwon-do, Korea
Soojin Kim, In Yong Lee, Sezim Monoldorova, Jiro Kim, Jang Hoon Seo, Tai-Soon Yong, Bo Young Jeon
Parasites, Hosts and Diseases.2023; 61(3): 263. CrossRef - Urine Metabolite of Mice with Orientia tsutsugamushi Infection
Sangho Choi, Do-Hwan Ahn, Min-Gyu Yoo, Hye-Ja Lee, Seong Beom Cho, Hee-Bin Park, Sung Soon Kim, Hyuk Chu
The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygi.2023; 108(2): 296. CrossRef - Spatiotemporal dynamics and environmental determinants of scrub typhus in Anhui Province, China, 2010–2020
Xianyu Wei, Junyu He, Wenwu Yin, Ricardo J. Soares Magalhaes, Yanding Wang, Yuanyong Xu, Liang Wen, Yehuan Sun, Wenyi Zhang, Hailong Sun
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Epidemiological characteristics of cases with scrub typhus and their correlation with chigger mite occurrence (2019–2021): A focus on case occupation and activity locations
Se‐Jin Jeong, Jin‐Hwan Jeon, Kyung won Hwang
Entomological Research.2023; 53(7): 247. CrossRef - Epidemiological characteristics and spatiotemporal patterns of scrub typhus in Yunnan Province from 2006 to 2017
Pei-Ying Peng, Lei Xu, Gu-Xian Wang, Wen-Yuan He, Ting-Liang Yan, Xian-Guo Guo
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical and Laboratory Predictors associated with Complicated Scrub Typhus
Mi-Hee Kim, Si-Hyun Kim, Jung-Hyun Choi, Seong-Heon Wie
Infection & Chemotherapy.2019; 51(2): 161. CrossRef - Awareness and Work-Related Factors Associated with Scrub Typhus: A Case-Control Study from South Korea
Dong-Seob Kim, Dilaram Acharya, Kwan Lee, Seok-Ju Yoo, Ji-Hyuk Park, Hyun-Sul Lim
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2018; 15(6): 1143. CrossRef - Estimating the burden of scrub typhus: A systematic review
Ana Bonell, Yoel Lubell, Paul N. Newton, John A. Crump, Daniel H. Paris, Janet Foley
PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases.2017; 11(9): e0005838. CrossRef - Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Scrub Typhus Transmission in Mainland China, 2006-2014
Yi-Cheng Wu, Quan Qian, Ricardo J. Soares Magalhaes, Zhi-Hai Han, Wen-Biao Hu, Ubydul Haque, Thomas A. Weppelmann, Yong Wang, Yun-Xi Liu, Xin-Lou Li, Hai-Long Sun, Yan-Song Sun, Archie C. A. Clements, Shen-Long Li, Wen-Yi Zhang, Mathieu Picardeau
PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases.2016; 10(8): e0004875. CrossRef - Larval Chigger Mites Collected from Small Mammals in 3 Provinces, Korea
In-Yong Lee, Hyeon-Je Song, Yeon-Joo Choi, Sun-Hye Shin, Min-Kyung Choi, So-Hyun Kwon, E-Hyun Shin, Chan Park, Heung-Chul Kim, Terry A. Klein, Kyung-Hee Park, Won-Jong Jang
The Korean Journal of Parasitology.2014; 52(2): 225. CrossRef
- Prevalence of chigger mites and Orientia tsutsugamushi strains in northern regions of Gangwon-do, Korea



 First
First Prev
Prev


