Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Mental health and its determinants among adolescents living in families with separated or divorced parents in an urban area of Vietnam
- Binh Thang Tran, Minh Tu Nguyen, Minh Tam Nguyen, Thanh Gia Nguyen, Vo Nu Hong Duc, Thi Tra My Tran
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(4):300-311. Published online August 9, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0110
- 2,183 View
- 171 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Objectives
We assessed the prevalence of stress, anxiety, and depression among adolescents living in families with separated or divorced parents in Hue City, Vietnam and identified factors associated with these conditions.
Methods
This cross-sectional study enrolled 309 adolescents, aged 12 to 17 years, living in families with separated or divorced parents in Hue City, Vietnam. The depression anxiety stress scale-21 (DASS-21) was used to measure stress, anxiety, and depression. Predictors of overall and individual mental health problems were identified using ordered and binary logistic regression, respectively.
Results
The DASS-21 scale revealed a 49.2% prevalence of stress, while anxiety and depression had s prevalence rates of 61.5%. Among participants, 42.4% experienced all 3 mental health issues. Several factors were identified as significant predictors of mental health problems, including poor to average economic status (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 2.00; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.21–3.31; p=0.007); being in high school (aOR, 5.02; 95% CI, 2.93–8.60; p<0.001); maternal occupation of teacher, healthcare professional, or official (aOR, 2.39; 95% CI, 1.13–5.03; p=0.022); longer duration of family separation or divorce (aOR, 1.24; 95% CI, 1.05–1.45; p=0.009); living with one’s mother (aOR, 1.69; 95% CI, 1.03–2.76; p=0.04); alcohol consumption (aOR, 1.70; 95% CI, 0.99–2.92; p=0.050); and being bullied (aOR, 5.33; 95% CI, 1.10–25.69; p=0.037). Most of these factors were associated with stress, anxiety, and depression. Additionally, smoking was associated with stress.
Conclusion
Adolescents with separated or divorced parents were at increased risk of stress, anxiety, and depression. The findings of this study provide important implications for prevention programs.
- Estimated impact of the national hepatitis B immunization program on acute viral hepatitis B among adolescents in Republic of Korea
- Chungman Chae, Sangwoo Tak
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(2):138-145. Published online March 24, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0321
- 1,523 View
- 62 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 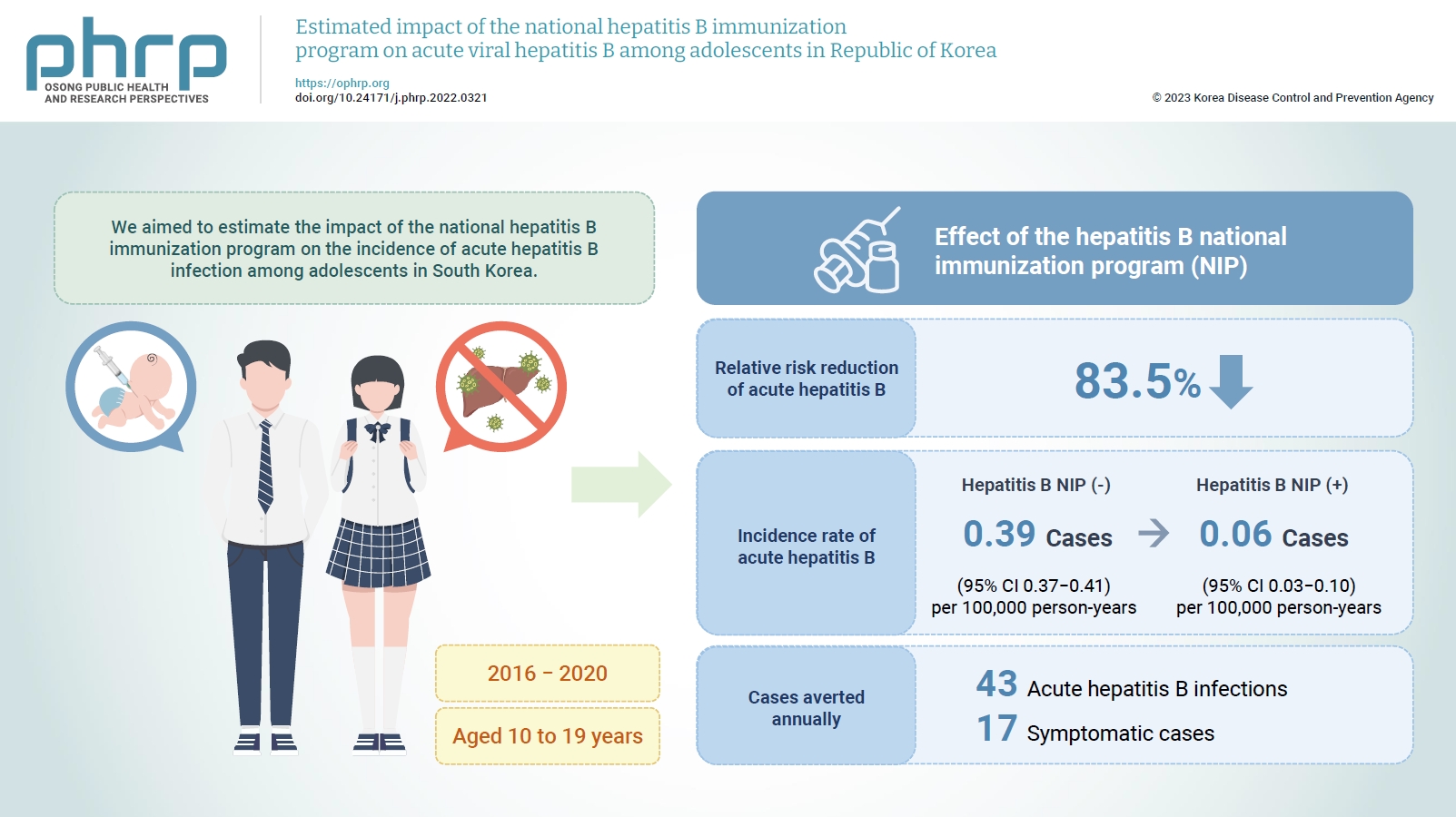
- Objectives
We aimed to estimate the impact of the national hepatitis B immunization program on the incidence of acute hepatitis B infection among adolescents in South Korea.
Methods
We estimated the counterfactual incidence rate of reported acute hepatitis B among adolescents from 2016 to 2020 compared to the assumption that the national hepatitis B immunization program for children had not been implemented since 1995. The impact of the national hepatitis B immunization program for adolescents was measured by estimating the absolute risk reduction and averted acute hepatitis B infections among adolescents from 2016 to 2020 attributed to the national immunization program.
Results
The relative risk reduction of acute hepatitis B among adolescents was estimated to be 83.5% after implementing the national hepatitis B immunization program. The incidence rate of reported acute hepatitis B infections among adolescents decreased from 0.39 to 0.06 per 100,000 person-years, and 43 acute hepatitis B infections, including 17 symptomatic cases, were averted annually from 2016 to 2020 by the national hepatitis B immunization program.
Conclusion
The national hepatitis B immunization program for children was effective in preventing acute hepatitis B infection among adolescents in South Korea.
- Adverse events of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine in Korean children and adolescents aged 5 to 17 years
- Seontae Kim, Yeseul Heo, Soon-Young Seo, Do Sang Lim, Enhi Cho, Yeon-Kyeng Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(5):382-390. Published online October 14, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0233
- 2,381 View
- 111 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to identify potential safety signals and adverse events following the primary Pfizer-BioNTech coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccination series among children and adolescents aged 5 to 17 years in the Republic of Korea. Methods: Adverse events reported through the COVID-19 vaccination management system (CVMS, a web-based passive vaccine safety surveillance system) and adverse events and health conditions collected from a text message-based survey were analyzed. Results: A total of 14,786 adverse events among 5 to 17-year-old children and adolescents were reported in the CVMS; 14,334 (96.9%) were non-serious and 452 (3.1%) were serious, including 125 suspected cases of acute cardiovascular injury and 101 suspected cases of anaphylaxis. The overall reporting rate was lower in 5 to 11-year-old children (64.5 per 100,000 doses) than in 12 to 17-year-old adolescents (300.5 per 100,000 doses). The text message survey identified that local and systemic adverse events after either dose were reported less frequently in 5 to 11-year-old children than in 12 to 17-year-old adolescents (p<0.001). The most commonly reported adverse events were pain at the injection site, myalgia, headache, and fatigue/tiredness. Conclusion: The overall results are consistent with the results of controlled trials; serious adverse events were extremely rare among 5 to 17-year-old children and adolescents following Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccination. Adverse events were less frequent in children aged 5 to 11 years than in adolescents aged 12 to 17 years. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Safety monitoring of COVID-19 vaccines: February 26, 2021, To June 4, 2022, Republic of Korea
Yeon-Kyeng Lee, Yunhyung Kwon, Yesul Heo, Eun Kyoung Kim, Seung Yun Kim, Hoon Cho, Seontae Kim, Mijeong Ko, Dosang Lim, Soon-Young Seo, Enhi Cho
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics.2023; 66(10): 415. CrossRef - Effectiveness of the BNT162b2 vaccine in preventing morbidity and mortality associated with COVID-19 in children aged 5 to 11 years: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Sumayyah Ebrahim, Ntombifuthi Blose, Natasha Gloeck, Ameer Hohlfeld, Yusentha Balakrishna, Rudzani Muloiwa, Andy Gray, Andy Parrish, Karen Cohen, Ruth Lancaster, Tamara Kredo, Julia Robinson
PLOS Global Public Health.2023; 3(12): e0002676. CrossRef
- Safety monitoring of COVID-19 vaccines: February 26, 2021, To June 4, 2022, Republic of Korea
- Factors influencing quality of life in caregivers of adolescents with developmental disabilities
- Joung Woo Joung
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(4):298-307. Published online August 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.0158
- 2,148 View
- 60 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Caring for adolescents with developmental disabilities (DD) is stressful and challenging, and mothers usually provide care for these children in Korea. This study aimed to identify factors influencing quality of life (QoL) in mothers of adolescents with DD.
Methods
A predictive design was used. Data were collected from a web-based survey administered to a convenience sample of 154 mothers of adolescents with DD from October to November 2020. Data were analyzed using the t-test, analysis of variance, Pearson correlation coefficients, and multiple regression.
Results
Perceived health, depression, and family strength were significantly correlated with QoL. Multiple regression showed that family strength, perceived health, depression, and monthly household income influenced the participants’ QoL, and these factors accounted for 69.2% of variance in QoL. Family strength was the factor most strongly affecting QoL (β=0.39).
Conclusion
The study results indicate that health professionals and policy-makers need to pay attention to the overall QoL and physical and psychological health of mothers of adolescents with DD. Since our findings raise the importance of family strength in the QoL of this population, programs to improve family strength need to be implemented and strengthened. Interventions to improve perceived health and decrease depression should be applied, and knowledge on adolescent characteristics and changes should be delivered to caregivers when providing education and consultations. The findings will be helpful for developing educational and counseling programs for this population.
- Safety monitoring of COVID-19 vaccination among adolescents aged 12 to 17 years old in the Republic of Korea
- Seontae Kim, Insob Hwang, Mijeong Ko, Yunhyung Kwon, Yeon-Kyeng Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(3):230-237. Published online June 10, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0122
- 4,128 View
- 139 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 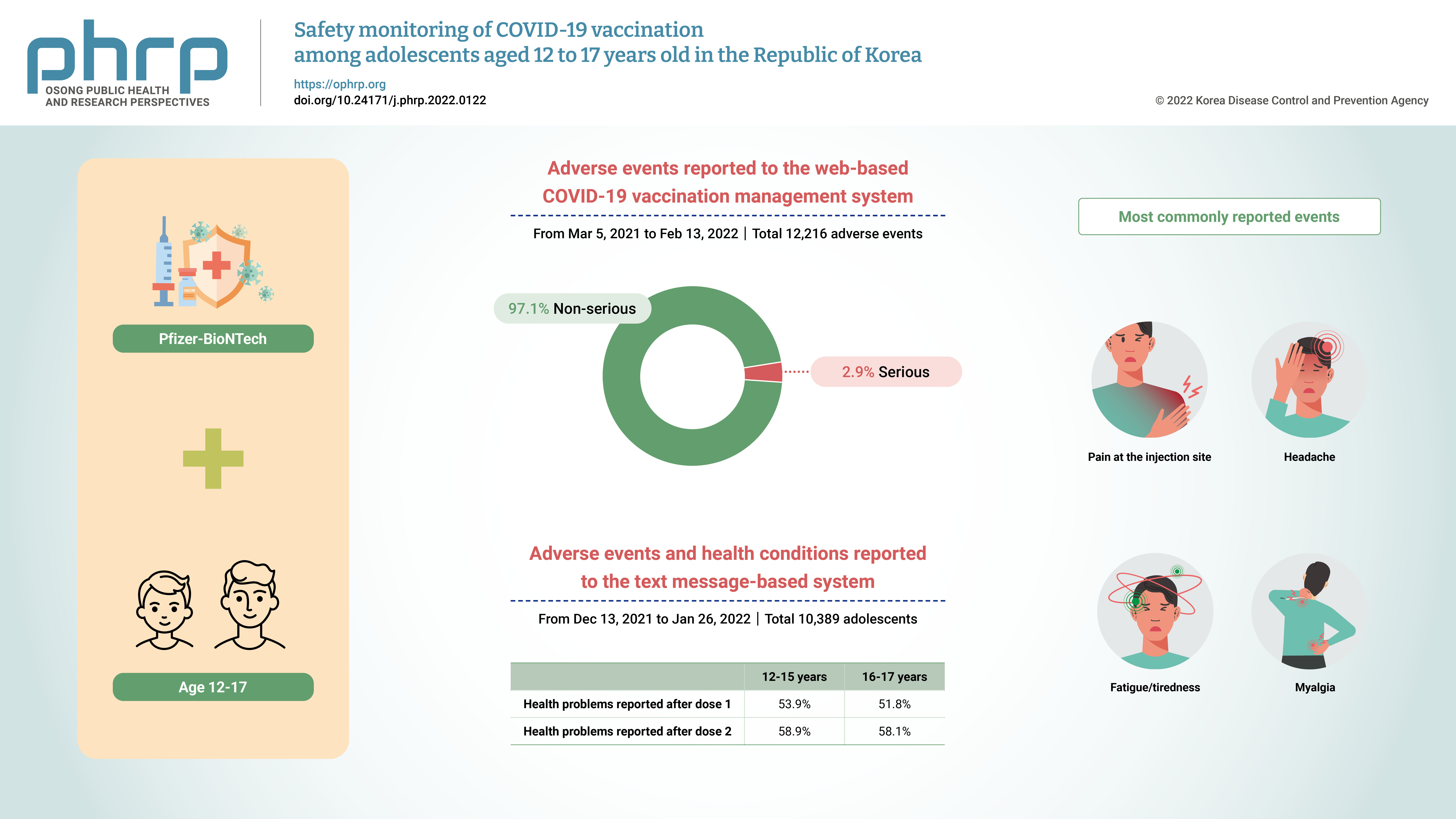
- Objectives
This study aimed to disseminate information on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccine safety among adolescents aged 12 to 17 years in the Republic of Korea. Methods: Two databases were used to assess COVID-19 vaccine safety in adolescents aged 12 to 17 years who completed the primary Pfizer-BioNTech vaccination series. Adverse events reported to the web-based COVID-19 vaccination management system (CVMS) and collected in the text message-based system were analyzed. Results: From March 5, 2021 to February 13, 2022, 12,216 adverse events among 12- to 17-yearolds were reported to the CVMS, of which 97.1% were non-serious adverse events and 2.9% were serious adverse events, including 85 suspected cases of anaphylaxis, 74 suspected cases of myocarditis and/or pericarditis, and 2 deaths. From December 13, 2021 to January 26, 2022, 10,389 adolescents responded to a text message survey, and local/systemic adverse events were more common after dose 2 than after dose 1. The most commonly reported events following either vaccine dose were pain at the injection site, headache, fatigue/tiredness, and myalgia. Conclusion: The overall results are consistent with previous findings; the great majority of adverse events were non-serious, and serious adverse events were rare among adolescents aged 12 to 17 years following Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccination. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Suspected Myocarditis after mRNA COVID-19 Vaccination among South Korean Adolescents
Mi Jin Kim, Jin Hee Kim, Hyun Ok Jun, Kyung Min Kim, Min Sub Jeung, Jun Sung Park
Journal of Pediatric Infectious Diseases.2024; 19(02): 075. CrossRef - Characterization of Brighton Collaboration criteria for myocarditis and pericarditis following COVID-19 vaccine in Korean adolescents
Jue Seong Lee, HyoSug Choi, Seung Hwan Shin, Myung-Jae Hwang, Sara Na, Jong Hee Kim, Sangshin Park, Yoonsun Yoon, Hyun Mi Kang, Bin Ahn, Kyoungsan Seo, Young June Choe
Vaccine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Immunogenicity, effectiveness, and safety of COVID-19 vaccines among children and adolescents aged 2–18 years: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis
Peng Gao, Liang-Yu Kang, Jue Liu, Min Liu
World Journal of Pediatrics.2023; 19(11): 1041. CrossRef - Incidence of myopericarditis after mRNA COVID-19 vaccination: A meta-analysis with focus on adolescents aged 12–17 years
Bao-Qiang Guo, Hong-Bin Li, Li-Qiang Yang
Vaccine.2023; 41(28): 4067. CrossRef - Safety monitoring of COVID-19 vaccines: February 26, 2021, To June 4, 2022, Republic of Korea
Yeon-Kyeng Lee, Yunhyung Kwon, Yesul Heo, Eun Kyoung Kim, Seung Yun Kim, Hoon Cho, Seontae Kim, Mijeong Ko, Dosang Lim, Soon-Young Seo, Enhi Cho
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics.2023; 66(10): 415. CrossRef - Risk of Coronavirus Disease 2019 Messenger RNA Vaccination-Associated Myocarditis and Pericarditis – A Systematic Review of Population-Based Data
Yen-Ching Lin, Chia-Hsuin Chang, Wei-Ju Su, Chin-Hui Yang, Jann-Tay Wang
Risk Management and Healthcare Policy.2023; Volume 16: 2085. CrossRef - COVID-19 Vaccination in Korea: Past, Present, and the Way Forward
Eliel Nham, Joon Young Song, Ji Yun Noh, Hee Jin Cheong, Woo Joo Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Suspected Myocarditis after mRNA COVID-19 Vaccination among South Korean Adolescents
- Prevalence and correlates of highly caffeinated beverage consumption among Korean adolescents
- Ho-Kyung Kwak, Jaesin Sa, Siyoung Choe, Jean-Philippe Chaput, Joon Chung, Gayle Cummings, Jounghee Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2021;12(6):374-384. Published online November 23, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.0013
- 10,147 View
- 94 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The purposes of this study were to (1) examine the multi-year prevalence of highly caffeinated beverage (HCB) consumption, (2) identify sex differences in the prevalence, and (3) investigate relationships between HCB consumption and behavioral characteristics in a nationally representative sample of Korean adolescents.
Methods
Data from the Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web-based Survey (2014–2017) were analyzed.
Results
HCB consumption was higher in 2017 than 2014 (23.9% vs. 12.0%), and higher among boys than girls (17.2% vs. 13.1%). HCB drinkers were more likely to (1) be boys, (2) be overweight or obese, (3) use alcohol and tobacco, (4) consume soda at least once per week, (5) consume sweetened beverages at least once per week, (6) have seriously considered suicide during the past 12 months, and (7) have attempted suicide during the past 12 months (p<0.05 for all).
Conclusion
Effective programs to curb HCB consumption among Korean adolescents need to be established. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Secondary School Students and Caffeine: Consumption Habits, Motivations, and Experiences
Sophie Turner, Ajmol Ali, Carol Wham, Kay Rutherfurd-Markwick
Nutrients.2023; 15(4): 1011. CrossRef
- Secondary School Students and Caffeine: Consumption Habits, Motivations, and Experiences
- The current status of sexually transmitted infections in South Korean children in the last 10 years
- Yumi Jang, Eunjung Oh
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2021;12(4):230-235. Published online August 4, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.0046
- 5,274 View
- 114 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Objectives
This study aimed to determine the status of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) in children in South Korea between 2010 and 2019), as well as to establish preventive maintenance guidelines to reduce the incidence of STIs in children.
Methods
Data reports from 590 STI surveillance systems in community clinics, hospital-level medical institutions with urology or obstetrics/gynecology departments and public hospitals between 2010 and 2019 in the integrative disease management system of the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency as of December 2020 were analyzed.
Results
A total of 172,645 cases of STIs were reported over the 10-year period (2010–2019), of which 2,179 cases (1.26%) represented STIs in children below the age of 18 years. A higher incidence of infections was observed in girls (1,499 cases, 68.79%) than in boys (680 cases, 31.21%). The STIs that had the highest incidence were, in descending order, chlamydia (997 cases, 45.75%), gonorrhea (592 cases, 27.17%), genital warts (338 cases, 15.51%), genital herpes (250 cases, 11.47%), and chancroid (2 cases, 0.09%). In adolescents aged 14 to 17 years, chlamydia, genital herpes, and gonorrhea were most frequently reported. Genital warts, in particular, have been consistently reported in children below the age of 14 years.
Conclusion
Children must be protected legally and institutionally from sexual abuse. Specific management protocols for STIs in children must be established by local governments and associated organizations. National human papillomavirus vaccination programs should be expanded to include boys, and anti-STI educational efforts using modern media should be implemented.
- Behavioral interventions for smoking cessation among adolescents: a rapid review and meta-analysis for the Korea Preventive Services Task Force
- Younglee Choi, Cheol Min Lee, Belong Cho, Eon Sook Lee, Seung-Won Oh, Naae Lee, Jae Moon Yun
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2021;12(3):177-186. Published online June 2, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.0018
- 9,379 View
- 162 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Objectives
The aim of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of behavioral smoking cessation interventions among adolescents.
Methods
MEDLINE, CENTRAL, Embase, CINAHL, KoreaMed, and KMbase were searched from inception to June 2020. Systematic reviews (SRs) or meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) were initially searched to perform a rapid SR. After selecting the final SR, RCTs after the publication year of the selected SR were searched. The primary outcome was smoking status after at least 6 months of follow-up, and the secondary outcome was smoking status at 4 weeks. Two reviewers independently assessed the selected studies’ quality using the Cochrane risk of bias tool. The meta-analysis utilized a Mantel-Haenszel fixed-effect model reporting the relative risk (RR) and 95% confidence interval (CI). The subgroup analysis utilized Cochrane’s Q.
Results
Thirty-two RCTs (11,637 participants) from a single SR were meta-analyzed. After 6 months of follow-up, the intervention group had significantly higher abstinence rates (RR, 1.30; 95% CI, 1.20−1.41; I2=26.46%). At 4 weeks of follow-up, the intervention group also had significantly higher abstinence rates (RR, 1.92; 95% CI, 1.49–2.47; I2=0.00%). The subgroup analysis indicated a significant difference in the abstinence rate according to the study setting and the period between intervention completion and follow-up.
Conclusion
This review showed that adolescent behavioral smoking cessation intervention programs significantly increased abstinence rates compared to the usual care. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of Healthcare Interventions on Smoking Cessation in Adolescents in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: A Narrative Review
Janhvi Thakur, Sonali G Choudhari
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Non-pharmacological interventions for smoking cessation: analysis of systematic reviews and meta-analyses
Tao Nian, Kangle Guo, Wendi Liu, Xinxin Deng, Xiaoye Hu, Meng Xu, Fenfen E, Ziyi Wang, Guihang Song, Kehu Yang, Xiuxia Li, Wenru Shang
BMC Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Behavioral Interventions for Smoking Cessation in Adolescents: Korea Preventive Services Task Force Guidance
Younglee Choi, Cheol Min Lee, Jae Moon Yun, Eon Sook Lee, Seung-Won Oh, Naae Lee, Belong Cho
Journal of the Korean Society for Research on Nico.2021; 12(1): 1. CrossRef - Tobacco Control Policy in Period of Epidemic “COVID 19”
Eon Sook Lee
Journal of the Korean Society for Research on Nico.2021; 12(1): 34. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of Healthcare Interventions on Smoking Cessation in Adolescents in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: A Narrative Review
- Noncommunicable Disease Risk Factors Among Adolescent Boys and Girls in Bangladesh: Evidence From a National Survey
- Nushrat Jahan Urmy, Md. Mokbul Hossain, Abu Ahmed Shamim, Md. Showkat Ali Khan, Abu Abdullah Mohammad Hanif, Mehedi Hasan, Fahmida Akter, Dipak Kumar Mitra, Moyazzam Hossaine, Mohammad Aman Ullah, Samir Kanti Sarker, SM Mustafizur Rahman, Md. Mofijul Islam Bulbul, Malay Kanti Mridha
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2020;11(6):351-364. Published online December 22, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2020.11.6.03
- 14,488 View
- 213 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives To assess the prevalence of noncommunicable disease (NCD) risk factors and the factors associated with the coexistence of multiple risk factors (≥ 2 risk factors) among adolescent boys and girls in Bangladesh.
Methods Data on selected NCD risk factors collected from face to face interviews of 4,907 boys and 4,865 girls in the national Nutrition Surveillance round 2018–2019, was used. Descriptive analysis and multivariable logistic regression were performed.
Results The prevalence of insufficient fruit and vegetable intake, inadequate physical activity, tobacco use, and being overweight/obese was 90.72%, 29.03%, 4.57%, and 6.04%, respectively among boys; and 94.32%, 50.33%, 0.43%, and 8.03%, respectively among girls. Multiple risk factors were present among 34.87% of boys and 51.74% of girls. Younger age (
p < 0.001), non-slum urban (p < 0.001) and slum residence (p < 0.001), higher paternal education (p = 0.001), and depression (p < 0.001) were associated with the coexistence of multiple risk factors in both boys and girls. Additionally, higher maternal education (p < 0.001) and richest wealth quintile (p = 0.023) were associated with the coexistence of multiple risk factors in girls.Conclusion The government should integrate specific services into the existing health and non-health programs which are aimed at reducing the burden of NCD risk factors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Co-occurrence of non-communicable disease risk factors among adolescents in Jos, Nigeria
Olutomi Y. Sodipo, Tolulope O. Afolaranmi, Hadiza A. Agbo, Esther A. Envuladu, Luret A. Lar, Emilia A. Udofia, Ayuba I. Zoakah
African Journal of Primary Health Care & Family Me.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparing Adolescents at Risk and Not at Risk of Non-Communicable Disease in Terms of Body Composition and Physical Activity in the Eastern Cape, South Africa
Sisanda Mvula, Maya Maria Van Gent, Rudolph Leon van Niekerk
Physical Activity and Health.2024; 8(1): 60. CrossRef - Dietary patterns and indicators of cardiometabolic risk among rural adolescents: A cross-sectional study at 15-year follow-up of the MINIMat cohort
Mohammad Redwanul Islam, Syed Moshfiqur Rahman, Katarina Selling, Pieta Näsänen-Gilmore, Maria Kippler, Eero Kajantie, Anisur Rahman, Jesmin Pervin, Eva-Charlotte Ekström
Frontiers in Nutrition.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Assuring Bangladesh’s future: non-communicable disease risk factors among the adolescents and the existing policy responses
Tuhin Biswas, Peter Azzopardi, Syeda Novera Anwar, Tim David de Vries, Luis Manuel Encarnacion-Cruz, Md. Mehedi Hasan, M. Mamun Huda, Sonia Pervin, Rajat Das Gupta, Dipak Kumar Mitra, Lal B. Rawal, Abdullah Al Mamun
Journal of Health, Population and Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Lifestyle practices predisposing adolescents to non communicable diseases in Delhi
Amod L. Borle, Navya Gangadharan, Saurav Basu
Dialogues in Health.2022; 1: 100064. CrossRef
- Co-occurrence of non-communicable disease risk factors among adolescents in Jos, Nigeria
- An Investigation into Chronic Conditions and Diseases in Minors to Determine the Socioeconomic Status, Medical Use and Expenditure According to Data from the Korea Health Panel, 2015
- Jong-Hoon Moon
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2019;10(6):343-350. Published online December 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2019.10.6.04
- 5,209 View
- 140 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives This study compared the socioeconomic status, medical use and expenditures for infants (1–5 years), juveniles (6–12 years), and adolescents (13–19 years) with a chronic condition or disease to determine factors affecting health spending.
Methods Data from 3,677 minors (< 20 years old, without disabilities) were extracted from the Korea Health Panel (2015) database.
Results Minors with chronic conditions or diseases were older (juveniles, and adolescents;
p < 0.001), and included a higher proportion of Medicaid recipients (p = 0.004), a higher use of hospital outpatient care (p < 0.001), and higher medical expenditure (p < 0.001) compared to minors without chronic conditions or diseases. Boys were more likely to have a chronic condition or disease than girls (p = 0.036). Adolescents and juveniles were more likely than infants to have a chronic condition or disease (p = 0.001). Medicaid recipients were more likely to have a chronic condition or disease than those who were not Medicaid recipients (p = 0.008). Minors who had been hospital outpatients were more likely to have a chronic condition or disease, compared with minors who had not been an outpatient (p = 0.001). Having a chronic condition or disease, was a factor increasing medical expenditure (p = 0.001). Medical expenditure was higher in infants than in juveniles and adolescents (p = 0.001). Infants had higher rates of medical use when compared with juveniles and adolescents (p = 0.001).Conclusion These findings suggest that systematic health care management for minors with chronic conditions or diseases, is needed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Household income and maternal education in early childhood and activity-limiting chronic health conditions in late childhood: findings from birth cohort studies from six countries
Nicholas James Spencer, Johnny Ludvigsson, Yueyue You, Kate Francis, Yara Abu Awad, Wolfgang Markham, Tomas Faresjö, Jeremy Goldhaber-Fiebert, Pär Andersson White, Hein Raat, Fiona Mensah, Lise Gauvin, Jennifer J McGrath
Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health.2022; 76(11): 939. CrossRef
- Household income and maternal education in early childhood and activity-limiting chronic health conditions in late childhood: findings from birth cohort studies from six countries
- Percentage Body Fat is As a Good Indicator for Determining Adolescents Who Are Overweight or Obese: A Cross-Sectional Study in Vietnam
- Le Thu Trang, Nguyen Nam Trung, Dinh-Toi Chu, Nguyen Thi Hong Hanh
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2019;10(2):108-114. Published online April 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2019.10.2.10
- 6,243 View
- 75 Download
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives To identify trends in percentage body fat (PBF) in adolescents to determine gender-specific classification thresholds for being overweight and obese.
Methods A cross-sectional study of 899 adolescents (11 to 14.5 years) from Hanoi and Nam Dinh was conducted in Vietnam. PBF, subcutaneous fat and percentage of lean mass were measured directly using OMRON HBF 375 scales to measure bioelectrical impedance.
Results PBF decreased in boys with increasing age (
p < 0.001). The difference in PBF between boys and girls, significantly increased with age after 12.5 years (p < 0.001). There was a stronger correlation between PBF and fat content (Pearson’sr =0.860 ,p <0.0001 ) than that between (BMI) and fat content (Pearson’sr =0.521 ,p <0.0001 ). The prevalence of being overweight or obese in girls was similar when determined by PBF or BMI. Hanoi had higher rates of adolescents being overweight or obese compared with Nam Dinh.Conclusion PBF provides a more accurate body assessment for being overweight or obese in adolescents compared with BMI.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Quadriceps muscle reaction time in obese children
Eduardo Guzmán-Muñoz, Guillermo Mendez-Rebolledo, Sergio Sazo-Rodriguez, Joaquín Salazar-Méndez, Pablo Valdes-Badilla, Cristian Nuñez-Espinosa, Tomas Herrera-Valenzuela
PeerJ.2024; 12: e17050. CrossRef - Blood Concentration of Macro- and Microelements in Women Who Are Overweight/Obesity and Their Associations with Serum Biochemistry
Zuzana Knazicka, Maros Bihari, Ivona Janco, Lubos Harangozo, Julius Arvay, Anton Kovacik, Peter Massanyi, Branislav Galik, Jorge M. A. Saraiva, Marta Habanova
Life.2024; 14(4): 465. CrossRef - Association of Anthropometric Adiposity Indices and Hand Grip Strength among Male Industrial Workers in Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India: A Cross-Sectional Study
R. Durga Priyadarshini, D. Annette Beatrice
Indian Journal of Occupational and Environmental M.2024; 28(1): 56. CrossRef - Changes in the prevalence of underweight, overweight, obesity and excessive adiposity among adolescents from Kraków (Poland) in the years 1983–2020
Paulina Artymiak, Magdalena Żegleń, Małgorzata Kowal, Agnieszka Woronkowicz, Łukasz Kryst
American Journal of Human Biology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Tri-ponderal mass index as a screening tool for obesity prediction in children aged 6–9 years
Yang Niu, Yajie Zhang, Jinye Sheng, Wenyi Lu, Ji Li, Xiaomeng Mao, Wei Cai, Qingya Tang, Xiuhua Shen, Yi Feng
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations Between Body Composition, Leptin, and Vitamin D Varied by the Body Fat Percentage in Adolescents
Rapheeporn Khwanchuea, Chuchard Punsawad
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychiatric symptoms are not associated with circulating CRP concentrations after controlling for medical, social, and demographic factors
Leandra K. Figueroa-Hall, Bohan Xu, Rayus Kuplicki, Bart N. Ford, Kaiping Burrows, T. Kent Teague, Sandip Sen, Hung-Wen Yeh, Michael R. Irwin, Jonathan Savitz, Martin P. Paulus
Translational Psychiatry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of School-Based Physical Activity Programs on Health-Related Physical Fitness of Korean Adolescents: A Preliminary Study
Eui-Jae Lee, Wi-Young So, Hyun-Su Youn, Jooyoung Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2021; 18(6): 2976. CrossRef - Bone Health and Its Positive Relationships with Body Composition in Malaysian Schoolchildren: Findings from a Cross-Sectional Study
Hui Chin Koo, Geok Pei Lim, Satvinder Kaur, Kai Quin Chan, Keh En Chan, Casey Chung, Michelle Wong, Ugunesh Danaselvam
Children.2021; 8(7): 569. CrossRef - Obesity parameters in relation to lung function levels in a large Chinese rural adult population
Xiang Zeng, Dongling Liu, Zhen An, Huijun Li, Jie Song, Weidong Wu
Epidemiology and Health.2021; 43: e2021047. CrossRef - Современные подходы к оценке физического развития детей и подростков
Zh.V. Sotnikova-Meleshkina, O.H. Zinchuk, O.Ya. Mikhalchuk
CHILD`S HEALTH.2021; 16(1): 33. CrossRef - Changes to cardiovascular risk factors over 7 years: a prospective cohort study of in situ urbanised residents in the Chaoyang District of Beijing
Zhe Li, Shicheng Yu, Xiaoyan Han, Jianjun Liu, Hongyan Yao
BMJ Open.2020; 10(3): e033548. CrossRef - Effect of Body Fat Percentage on Muscle Damage Induced by High-Intensity Eccentric Exercise
Eun-Jung Yoon, Jooyoung Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2020; 17(10): 3476. CrossRef - Body mass index and waist-to-hip ratio misclassification of overweight and obesity in Chinese military personnel
Qingqing Zhu, Binbin Huang, Qiaoli Li, Liqian Huang, Wenbo Shu, Lin Xu, Qiongying Deng, Ziliang Ye, Chunyan Li, Peng Liu
Journal of Physiological Anthropology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Identification of the most appropriate existing anthropometric index for home-based obesity screening in children and adolescents
X.F. Ye, W. Dong, L.L. Tan, Z.R. Zhang, Y.L. Qiu, J. Zhang
Public Health.2020; 189: 20. CrossRef
- Quadriceps muscle reaction time in obese children
- Health Related Nutritional Knowledge and Dietary Behavior Regarding Caffeine Intake among High School Students in Yongin Region
- Seong Yeong Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2018;9(6):299-308. Published online December 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2018.9.6.03
- 5,256 View
- 38 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives We aimed to examine health-related nutritional knowledge and dietary behavior related to caffeine intake among high school students (
n = 310) in the Yongin region of Korea.Methods Data were collected using a face-to-face survey, and analyzed using chi-square test,
t - test, and logistic regression analysis.Results The level of caffeine intake in respondents was divided into low (< 30 mg/d;
n = 208) and high caffeine intake groups (> 30 mg/d;n = 102). Total nutritional knowledge related to bone disease was higher in the low intake group (score 2.75) than the high intake group (score 2.39;p < 0.05). The high intake group had lower scores for nutritional knowledge (score 0.70;p < 0.05) related to how caffeinated beverages affect sleep and for dietary behavior (score 3.25;p < 0.001), based on “I avoid caffeinated foods before sleep,” than the low intake group (nutritional knowledge score, 0.80; dietary behavior score, 3.76).Conclusion In the overall analysis, the low caffeine intake group had better nutritional knowledge related to bone and sleep health, and healthier dietary behavior related to sleep health compared with the high intake group.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Caffeine intake and its association with nutrition, sleep, and physical activity among schoolchildren in the United Arab Emirates: a national cross-sectional study
MoezAlIslam E. Faris, Eman Rashid Saif, Eman Ali Turki, Dana N. Abdelrahim, Salma Abu-Qiyas, Katia Abi Shihab, Falak Zeb, Haydar Hasan, Mona S. Hashim, Hadia M. Radwan, Farah Naja, Leila Cheikh Ismail, Tareq M. Osaili, Hanin Kassem, Radhiya Al Rajaby, Kha
European Journal of Nutrition.2024; 63(2): 549. CrossRef - TINGKAT PENGETAHUAN EFEK KONSUMSI KAFEIN DAN ASUPAN KAFEIN PADA MAHASISWA
Sarah Stephanie Br Ginting, Yunisa Astiarani, Bryany Titi Santi, Vetinly Vetinly
Journal of Nutrition College.2022; 11(4): 264. CrossRef - Caffeine Consumption in a Group of Adolescents from South East Poland—A Cross Sectional Study
Ewa Błaszczyk-Bębenek, Paweł Jagielski, Małgorzata Schlegel-Zawadzka
Nutrients.2021; 13(6): 2084. CrossRef
- Caffeine intake and its association with nutrition, sleep, and physical activity among schoolchildren in the United Arab Emirates: a national cross-sectional study
- Multilevel Analysis of the Risk Factors in High-Risk Health Behavior among Korean Adolescents
- Eun Gyeong Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2018;9(1):3-8. Published online December 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2018.9.1.02
- 5,204 View
- 77 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives To examine health behaviors among Korean adolescents with a focus on both individual and school-based factors, specifically in relation to predictors of high-risk groups.
Methods Secondary data analysis was conducted with data from the 8th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web-Based Survey, using descriptive statistics, t tests, χ2 test, and multilevel logistic regression analysis. Health Practice Index was calculated and a range of 0 to 2 was classified as a high-risk group.
Results The results revealed that the individual-level variables of sex, age, stress, depression, subjective health status, school performance, health education, father’s level of education, and living situation were significant predictors of high-risk behaviors. The risk was greater in girls, greater with higher age and higher stress scores, greater in adolescents with depression, greater with lower paternal educational level, and greater in adolescents who did not live with both parents, as were the school-level variables of school grade and school affluence score. The possibility of being in the high-risk group in health behavior was greater if a student attended a school where the Family Affluence Score (FAS) was lower.
Conclusion School health education should be expanded to manage students’ high-risk health behaviors, especially in schools that have many students from families with a low affluence status.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mental health and its determinants among adolescents living in families with separated or divorced parents in an urban area of Vietnam
Binh Thang Tran, Minh Tu Nguyen, Minh Tam Nguyen, Thanh Gia Nguyen, Vo Nu Hong Duc, Thi Tra My Tran
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2023; 14(4): 300. CrossRef - Prevalence of and Factors Associated with Club Drug Use among Secondary Vocational Students in China
Jincong Yu, Qingfeng Wu, Yuqin Wu, Jiang Li, Qinxuan Wu, Huiping Cao, Zengzhen Wang
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2021; 18(19): 10408. CrossRef - Problematic Gaming Is Associated with Some Health-Related Behaviors Among Finnish Vocational School Students
Niko Männikkö, Heidi Ruotsalainen, Asko Tolvanen, Maria Kääriäinen
International Journal of Mental Health and Addicti.2020; 18(4): 993. CrossRef - The relationship between social participation and self-rated health in persons with psychiatric disabilities: Is the health behavior mediation model useful
Ji Hye Park, Sun Hae Lee
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2020; 37(2): 69. CrossRef
- Mental health and its determinants among adolescents living in families with separated or divorced parents in an urban area of Vietnam
- Korean Adolescents’ Health Behavior and Psychological Status according to Their Mother’s Nationality
- Yunjeong Yi, Ji-Soo Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2017;8(6):377-383. Published online December 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2017.8.6.04
- 4,303 View
- 24 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives This study was conducted to compare adolescents’ health behaviors and psychological status according to whether or not their mother was born in Korea.
Methods This secondary analysis used nationally representative data from the 2015 Korean Youth Risk Behavior Web-based Survey. The self-administered questionnaire included computer measured socio-demographic variables, 15 health behaviors, and psychological status. Data from 65,426 middle school and high school students were analyzed. Multiple logistic regression, adjusting for socio-demographic variables, was used to analyze differences in health behaviors and psychological status between adolescents with a foreign-born mother and those with a Korean mother.
Results Adolescents who have foreign-born mothers had a lower level of current drinking and subjective happiness, but a higher stress level.
Conclusion The stress levels of the adolescents with foreign-born mothers could be affected by their multicultural background. It is necessary to analyze stress-influencing factors of multicultural adolescents by comparing them to adolescents from Korean parents. Additionally, our society should pay more attention to the mental health of multicultural adolescents. Schools should also make various efforts to protect multicultural adolescents by adopting mental health management programs led by school nurses and counselors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Measuring Happiness in Adolescent Samples: A Systematic Review
Justė Lukoševičiūtė, Gita Argustaitė-Zailskienė, Kastytis Šmigelskas
Children.2022; 9(2): 227. CrossRef - Factors Related to Depressive Symptoms Among Multicultural Adolescents in Korea
Kyoung Hwa Joung, Sung Suk Chung
The Journal of School Nursing.2022; 38(2): 138. CrossRef - The Mental Health of Ethnic Minority Youths in South Korea and Its Related Environmental Factors: A Literature Review
Yeeun Lee, Minji Lee, Subin Park
Journal of the Korean Academy of Child and Adolesc.2019; 30(3): 88. CrossRef - Adolescents in Multi-Ethnic Families under Korean Ethnic Nationalism
Hae-Wol Cho, Chaeshin Chu
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2017; 8(6): 367. CrossRef
- Measuring Happiness in Adolescent Samples: A Systematic Review
- Development of a Food Safety and Nutrition Education Program for Adolescents by Applying Social Cognitive Theory
- Jounghee Lee, Soyeon Jeong, Gyeongah Ko, Hyunshin Park, Youngsook Ko
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2016;7(4):248-260. Published online August 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2016.05.005
- 3,198 View
- 20 Download
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The purpose of this study was to develop an educational model regarding food safety and nutrition. In particular, we aimed to develop educational materials, such as middle- and high-school textbooks, a teacher’s guidebook, and school posters, by applying social cognitive theory.
Methods
To develop a food safety and nutrition education program, we took into account diverse factors influencing an individual’s behavior, such as personal, behavioral, and environmental factors, based on social cognitive theory. We also conducted a pilot study of the educational materials targeting middle-school students (n = 26), high-school students (n = 24), and dietitians (n = 13) regarding comprehension level, content, design, and quality by employing the 5-point Likert scale in May 2016.
Results
The food safety and nutrition education program covered six themes: (1) caffeine; (2) food additives; (3) foodborne illness; (4) nutrition and meal planning; (5) obesity and eating disorders; and (6) nutrition labeling. Each class activity was created to improve self-efficacy by setting one’s own goal and to increase self-control by monitoring one’s dietary intake. We also considered environmental factors by creating school posters and leaflets to educate teachers and parents. The overall evaluation score for the textbook was 4.0 points among middle- and high-school students, and 4.5 points among dietitians.
Conclusion
This study provides a useful program model that could serve as a guide to develop educational materials for nutrition-related subjects in the curriculum. This program model was created to increase awareness of nutrition problems and self-efficacy. This program also helped to improve nutrition management skills and to promote a healthy eating environment in middle- and high-school students. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Chinese families' knowledge, attitudes, and practices regarding seizure management for children with epilepsy: a mixed-methods study
Cui Cui, Shuangzi Li, Wenjin Chen, Hengyu Zhou, Xianlan Zheng
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of a Health-Related Education Program on Food-Related Behaviors of Vulnerable Women in Zanjan: A Pilot Randomized Clinical Trial
Jalal Hejazi, Sahar Nazari Darab Khani, Mohammad Masoud Vakili, Majid Aminzare
Journal of Human Environment and Health Promotion.2023; 9(3): 146. CrossRef - Analyzing consumer behaviour towards food and nutrition labeling: A comprehensive review
K.M. Priya, Sivakumar Alur
Heliyon.2023; 9(9): e19401. CrossRef - The effect of a nutrition program based on the Health Behavior Interaction Model on primary school students’ nutritional attitudes and behaviors
Ayşe Burcu Başçı, Oya Nuran Emiroğlu, Bilge Kalanlar
Journal of Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluating the Consistency Between Conceptual Frameworks and Factors Influencing the Safe Behavior of Iranian Workers in the Petrochemical Industry: Mixed Methods Study
Azita Zahiri Harsini, Philip Bohle, Lynda R Matthews, Fazlollah Ghofranipour, Hormoz Sanaeinasab, Farkhondeh Amin Shokravi, Krishan Prasad
JMIR Public Health and Surveillance.2021; 7(5): e22851. CrossRef - Critical Consciousness of Food Systems as a Potential Lifestyle Intervention on Health Issues
Sothy Eng, Carli Donoghue, Tricia Khun, Whitney Szmodis
American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine.2020; 14(3): 258. CrossRef - Development, Implementation, and Process Evaluation of a Theory-Based Nutrition Education Programme for Adults Living With HIV in Abeokuta, Nigeria
Temitope K. Bello, Gerda J. Gericke, Una E. MacIntyre
Frontiers in Public Health.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - What matters for higher education success of private educational institutions? Senior students’ perceptions in Malaysia
Jayaraman Krishnaswamy, Zarif Hossain, Mohan Kumar Kavigtha, Annamalai Nagaletchimee
Journal of Applied Research in Higher Education.2019; 11(3): 616. CrossRef - Augmented reality of traditional food for nutrition education
Cica Yulia, H Hasbullah, E.E. Nikmawati, S.R. Mubaroq, Cep Ubad Abdullah, Isma Widiaty, Ade Gafar Abdullah, Asep Bayu Dani Nandiyanto
MATEC Web of Conferences.2018; 197: 16001. CrossRef - Decreasing the use of edible oils in China using WeChat and theories of behavior change: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Rui Zhu, Xianglong Xu, Yong Zhao, Manoj Sharma, Zumin Shi
Trials.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Chemicals as additives in food processing -a review
KUMARESAN D, NITHYA SERMUGAPANDIAN, HEMASHREE S, RUBINI K R
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Science.2017;[Epub] CrossRef
- Chinese families' knowledge, attitudes, and practices regarding seizure management for children with epilepsy: a mixed-methods study



 First
First Prev
Prev


