Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Special Article
- The COVID-19 Vaccine Safety Research Center: a cornerstone for strengthening safety evidence for COVID-19 vaccination in the Republic of Korea
- Na-Young Jeong, Hyesook Park, Sanghoon Oh, Seung Eun Jung, Dong-Hyun Kim, Hyoung-Shik Shin, Hee Chul Han, Jong-Koo Lee, Jun Hee Woo, Jaehun Jung, Joongyub Lee, Ju-Young Shin, Sun-Young Jung, Byung-Joo Park, Nam-Kyong Choi
- Received November 16, 2023 Accepted February 22, 2024 Published online April 4, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0343 [Epub ahead of print]
- 247 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The COVID-19 Vaccine Safety Research Committee (CoVaSC) was established in November 2021 to address the growing need for independent, in-depth scientific evidence on adverse events (AEs) following coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccination. This initiative was requested by the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency and led by the National Academy of Medicine of Korea. In September 2022, the COVID-19 Vaccine Safety Research Center was established, strengthening CoVaSC’s initiatives. The center has conducted various studies on the safety of COVID-19 vaccines. During CoVaSC’s second research year, from September 29, 2022 to July 19, 2023, the center was restructured into 4 departments: Epidemiological Research, Clinical Research, Communication & Education, and International Cooperation & Policy Research. Its main activities include (1) managing CoVaSC and the COVID-19 Vaccine Safety Research Center, (2) surveying domestic and international trends in AE causality investigation, (3) assessing AEs following COVID-19 vaccination, (4) fostering international collaboration and policy research, and (5) organizing regular fora and training sessions for the public and clinicians. Causality assessments have been conducted for 27 diseases, and independent research has been conducted after organizing ad hoc committees comprising both epidemiologists and clinical experts on each AE of interest. The research process included protocol development, data analysis, interpretation of results, and causality assessment. These research outcomes have been shared transparently with the public and healthcare experts through various fora. The COVID-19 Vaccine Safety Research Center plans to continue strengthening and expanding its research activities to provide reliable, high-quality safety information to the public.
Review Article
- Psychiatric adverse events associated with the COVID-19 vaccines approved in the Republic of Korea: a systematic review
- Seungeun Ryoo, Miyoung Choi, Nam-Kyong Choi, Hyoung-Shik Shin, Jun Hee Woo, Byung-Joo Park, Sanghoon Oh
- Received October 31, 2023 Accepted January 16, 2024 Published online March 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0325 [Epub ahead of print]
- 302 View
- 21 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This systematic review evaluated psychiatric adverse events (AEs) following vaccination against coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). We included studies that reported or investigated psychiatric AEs in individuals who had received an approved COVID-19 vaccine in the Republic of Korea. Systematic electronic searches of Ovid-Medline, Embase, CENTRAL, and KoreaMed databases were conducted on March 22, 2023. Risk of bias was assessed using the Risk of Bias Assessment Tool for Non-randomized Studies 2.0. The study protocol was registered in the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (CRD42023449422). Of the 301 articles initially selected, 7 were included in the final analysis. All studies reported on sleep disturbances, and 2 highlighted anxiety-related AEs. Sleep disorders like insomnia and narcolepsy were the most prevalent AEs, while depression was not reported. Our review suggests that these AEs may have been influenced by biological mechanisms as well as the broader psychosocial context of the COVID-19 pandemic. Although this study had limitations, such as a primary focus on the BNT162b2 vaccine and an observational study design, it offered a systematic, multi-vaccine analysis that fills a critical gap in the existing literature. This review underscores the need for continued surveillance of psychiatric AEs and guides future research to investigate underlying mechanisms, identify risk factors, and inform clinical management.
Original Articles
- COVID-19 infection among people with disabilities in 2021 prior to the Omicron-dominant period in the Republic of Korea: a cross-sectional study
- Seul-Ki Kang, Bryan Inho Kim
- Received July 11, 2023 Accepted January 16, 2024 Published online March 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0194 [Epub ahead of print]
- 339 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study investigated the characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) among individuals with disabilities on a nationwide scale in the Republic of Korea, as limited research has examined this population.
Methods
Between January 1 and November 30, 2021, a total of 5,687 confirmed COVID-19 cases among individuals with disabilities were reported through the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency’s COVID-19 web reporting system. Follow-up continued until December 24, and demographic, epidemiological, and clinical characteristics were analyzed.
Results
Individuals with disabilities represented approximately 1.5% of confirmed cases, with a mean age of 58.1 years. Most resided in or near metropolitan areas (86.6%) and were male (60.6%). Frequent sources of infection included home (33.4%) and contact with confirmed cases (40.7%). Many individuals (75.9%) had underlying conditions, and 7.7% of cases were severe. People with disabilities showed significantly elevated risk of severe infection (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.63; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.47–1.81) and mortality (aOR, 1.65; 95% CI, 1.43–1.91). Vaccination against COVID-19 was associated with significantly lower risk of severe infection (aORs for the first, second, and third doses: 0.6 [95% CI, 0.42–0.85], 0.28 [95% CI, 0.22–0.35], and 0.16 [95% CI, 0.05–0.51], respectively) and death (adjusted hazard ratios for the first and second doses: 0.57 [95% CI, 0.35–0.93] and 0.3 [95% CI, 0.23–0.40], respectively).
Conclusion
Individuals with disabilities showed higher risk of severe infection and mortality from COVID-19. Consequently, it is critical to strenghthenCOVID-19 vaccination initiatives and provide socioeconomic assistance for this vulnerable population.
- Evaluation of COVID-19 vaccine effectiveness in different high-risk facility types during a period of Delta variant dominance in the Republic of Korea: a cross-sectional study
- Min Jei Lee, Myung-Jae Hwang, Dong Seob Kim, Seon Kyeong Park, Jihyun Choi, Ji Joo Lee, Jong Mu Kim, Young-Man Kim, Young-Joon Park, Jin Gwack, Sang-Eun Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(5):418-426. Published online October 19, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0188
- 1,247 View
- 43 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 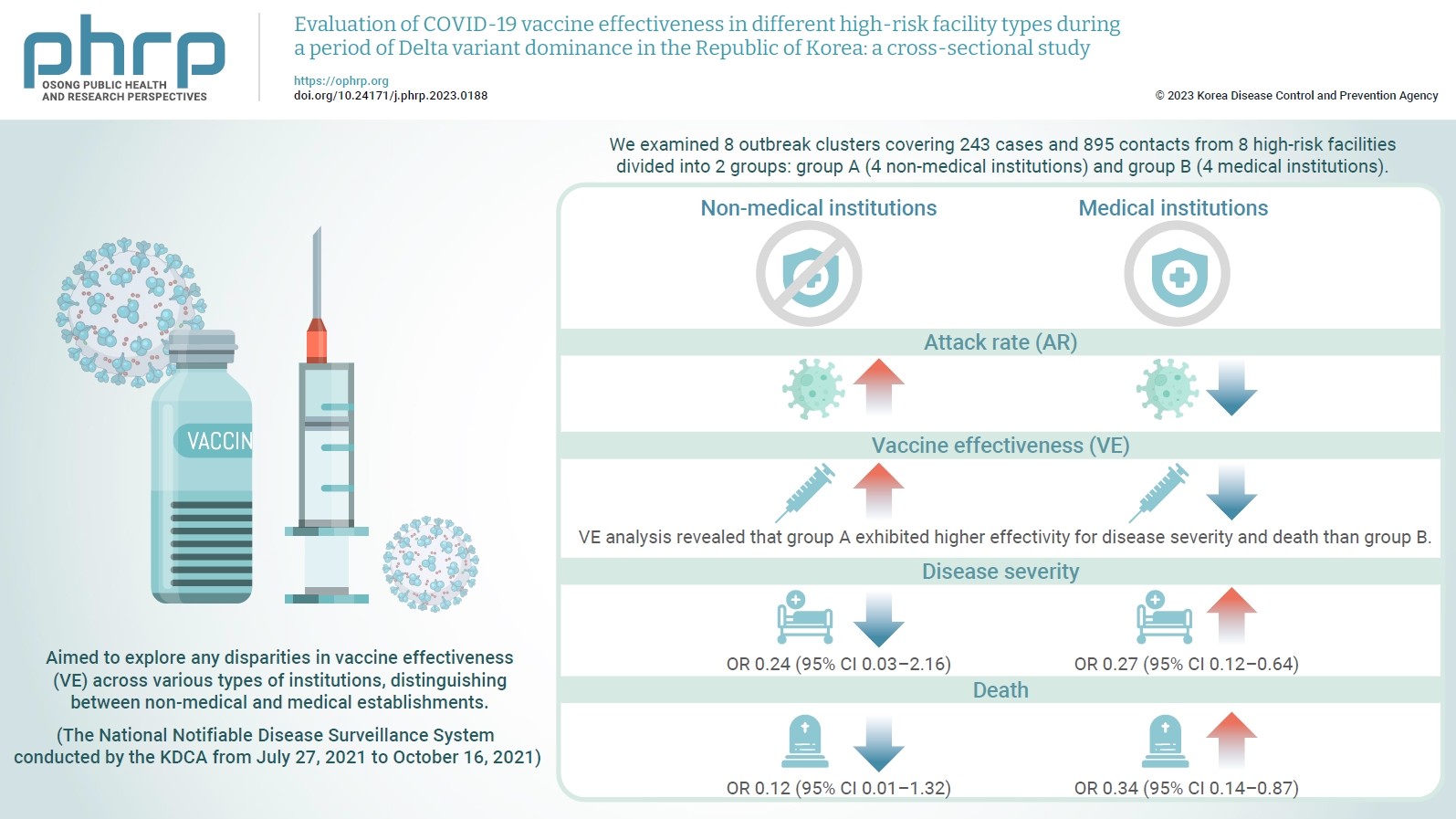
- Objectives
We evaluated the effectiveness of coronavirus disease 2019 vaccination in high-risk facilities in the Republic of Korea during the period when the highly transmissible Delta variant was prevalent. Additionally, we aimed to explore any disparities in vaccine effectiveness (VE) across various types of institutions, specifically distinguishing between non-medical and medical establishments. Methods: We examined 8 outbreak clusters covering 243 cases and 895 contacts from 8 high-risk facilities divided into 2 groups: group A (4 non-medical institutions) and group B (4 medical institutions). These clusters were observed from July 27, 2021 to October 16, 2021 for the attack rate (AR) and VE with respect to disease severity. A generalized linear model with a binomial distribution was used to determine the odds ratio (OR) for disease severity and death. Results: AR was notably lower in group B (medical institutions). Furthermore, VE analysis revealed that group A exhibited higher effectivity for disease severity and death than group B. The OR for disease severity was 0.24 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.03–2.16) for group A and 0.27 (95% CI, 0.12–0.64) for group B, with the OR for death at 0.12 (95% CI, 0.01–1.32) in group A and 0.34 (95% CI, 0.14–0.87) in group B. Conclusion: Although VE may vary across institutions, our findings underscore the importance of implementing vaccinations in high-risk facilities. Customized vaccination programs, tailored response plans, and competent management personnel are essential for effectively addressing and mitigating public health challenges.
Brief Report
- JYNNEOS vaccine safety monitoring in the Republic of Korea, 2022: a cross-sectional study
- Jaeeun Lee, Seunghyun Lewis Kwon, Jinhee Park, Hyuna Bae, Hyerim Lee, Geun-Yong Kwon
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(5):433-438. Published online October 18, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0182
- 853 View
- 37 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 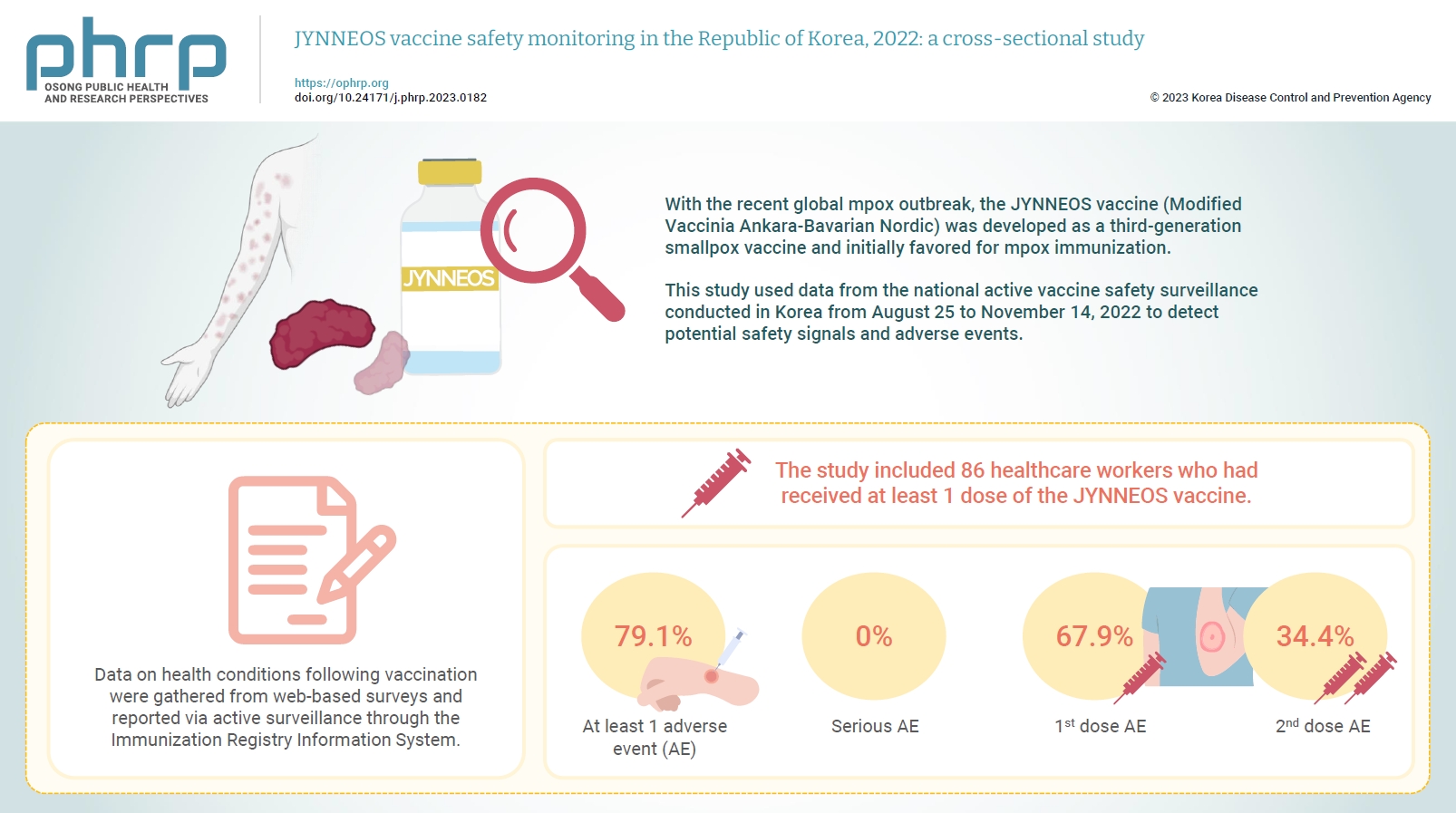
- Objectives
With the recent global mpox outbreak, the JYNNEOS vaccine (Modified Vaccinia Ankara-Bavarian Nordic) was developed as a third-generation smallpox vaccine and initially favored for mpox immunization. Vaccine-associated side effects contribute to vaccine hesitancy. Consequently, tracking adverse events post-immunization is crucial for safety management. This study used data from the national active vaccine safety surveillance conducted in Korea from August 25 to November 24, 2022 to detect potential safety signals and adverse events. Methods: Data on health conditions following vaccination were gathered from web-based surveys and reported via active surveillance through the Immunization Registry Information System. This follow-up system functioned via a text message link, surveying adverse events and health conditions beginning on the second day post-vaccination. Information about specific adverse events, including both local and systemic reactions, was collected. Results: The study included 86 healthcare workers who had received at least 1 dose of the JYNNEOS vaccine. Among the respondents, 79.1% reported experiencing at least 1 adverse event, with the majority being local reactions at the injection site. The incidence of adverse events was higher following the first dose (67.9%) than after the second dose (34.4%). The most frequently reported adverse event for both doses was mild pain at the injection site. Conclusion: The study provides crucial information on the safety of the JYNNEOS vaccine, demonstrating that most adverse events were manageable and predominantly localized to the injection site. Nonetheless, additional research is needed on the safety of various vaccine administration techniques and the vaccine’s effects on broader demographics. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Adverse Reactions After Intradermal Vaccination With JYNNEOS for Mpox in Korea
So Yun Lim, Yu Mi Jung, Yeonjae Kim, Gayeon Kim, Jaehyun Jeon, BumSik Chin, Min-Kyung Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Adverse Reactions After Intradermal Vaccination With JYNNEOS for Mpox in Korea
Original Article
- Prevalence and patterns of adverse events following childhood immunization and the responses of mothers in Ile-Ife, South West Nigeria: a facility-based cross-sectional survey
- Olorunfemi Akinbode Ogundele, Funmito Omolola Fehintola, Mubarak Salami, Rahmat Usidebhofoh, Mary Aderemi Abaekere
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(4):291-299. Published online July 27, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0071
- 2,184 View
- 132 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 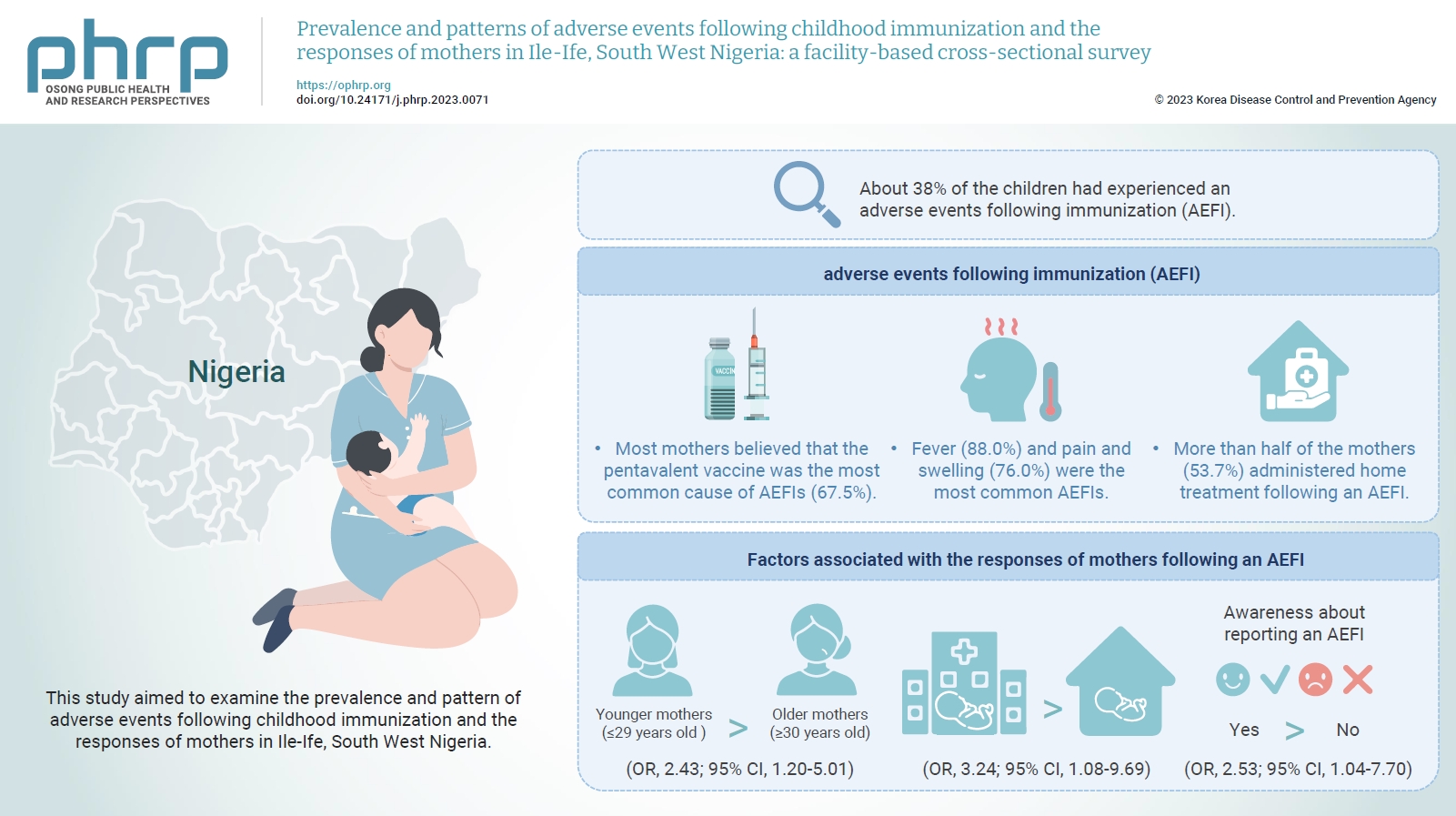
- Objectives
This study aimed to examine the prevalence and pattern of adverse events following childhood immunization and the responses of mothers in Ile-Ife, South West Nigeria.
Methods
This descriptive cross-sectional study was conducted among 422 mothers of children aged 0 to 24 months attending any of the 3 leading immunization clinics in Ile-Ife, Nigeria. The respondents were selected using the multi-stage sampling technique. Data were collected using a pretested structured interviewer-administered questionnaire and analyzed using IBM SPSS ver. 26.0. The chi-square test was used to test associations, while binary logistic regression was used to determine the predictors of mothers’ responses to adverse events following immunization (AEFIs). A p-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
The mean age of the respondents was 29.99±5.74 years. About 38% of the children had experienced an AEFI. Most mothers believed that the pentavalent vaccine was the most common cause of AEFIs (67.5%). Fever (88.0%) and pain and swelling (76.0%) were the most common AEFIs. More than half of the mothers (53.7%) administered home treatment following an AEFI. Younger mothers (odds ratio [OR], 2.43; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.20–5.01), mothers who delivered their children at a healthcare facility (OR, 3.24; 95% CI, 1.08–9.69), and mothers who were knowledgeable about reporting AEFIs (OR, 2.53; 95% CI, 1.04–7.70) were most likely to respond appropriately to AEFIs.
Conclusion
The proportion of mothers who responded poorly to AEFIs experienced by their children was significant. Therefore, strategies should be implemented to improve mothers’ knowledge about AEFIs to improve their responses.
Brief Report
- Temporal association between the age-specific incidence of Guillain-Barré syndrome and SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in Republic of Korea: a nationwide time-series correlation study
- Hyunju Lee, Donghyok Kwon, Seoncheol Park, Seung Ri Park, Darda Chung, Jongmok Ha
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(3):224-231. Published online June 22, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0050
- 2,015 View
- 88 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 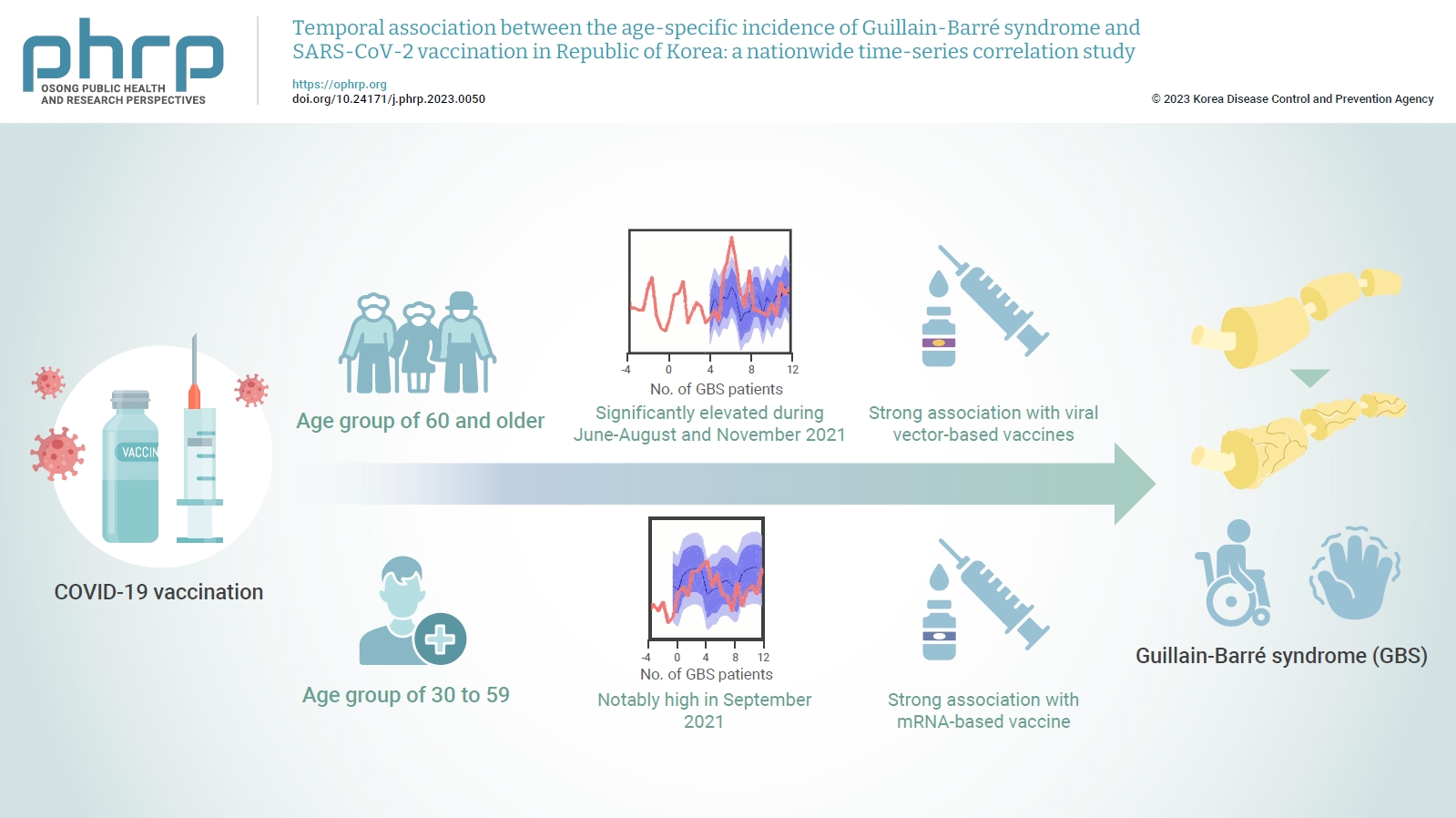
- Objectives
The incidence of Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) changed significantly during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. Emerging reports suggest that viral vector-based vaccines may be associated with an elevated risk of GBS.
Methods
In this nationwide time-series correlation study, we examined the age-specific incidence of GBS from January 2011 to August 2022, as well as data on severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) vaccinations and infections from February 2021 to August 2022. We compared the forecasted estimates of age-specific GBS incidence, using the pre-SARS-CoV-2 period as a benchmark, with the actual incidence observed during the post-vaccination period of the pandemic. Furthermore, we assessed the temporal association between GBS, SARS-CoV-2 vaccinations, and COVID-19 for different age groups.
Results
In the age group of 60 and older, the rate ratio was significantly elevated during June-August and November 2021. A significant, strong positive association was observed between viral vector-based vaccines and GBS incidence trends in this age group (r=0.52, p=0.022). For the 30 to 59 years age group, the rate ratio was notably high in September 2021. A statistically significant, strong positive association was found between mRNA-based vaccines and GBS incidence in this age group (r=0.61, p=0.006).
Conclusion
Viral vector-based SARS-CoV-2 vaccines were found to be temporally associated with an increased risk of GBS, particularly in older adults. To minimize age-specific and biological mechanism-specific adverse events, future vaccination campaigns should adopt a more personalized approach, such as recommending homologous mRNA-based SARS-CoV-2 vaccines for older adults to reduce the heightened risk of GBS. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- mRNA-LNP COVID-19 Vaccine Lipids Induce Complement Activation and Production of Proinflammatory Cytokines: Mechanisms, Effects of Complement Inhibitors, and Relevance to Adverse Reactions
Tamás Bakos, Tamás Mészáros, Gergely Tibor Kozma, Petra Berényi, Réka Facskó, Henriette Farkas, László Dézsi, Carlo Heirman, Stefaan de Koker, Raymond Schiffelers, Kathryn Anne Glatter, Tamás Radovits, Gábor Szénási, János Szebeni
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(7): 3595. CrossRef - Guillain–Barre syndrome following COVID-19 vaccination: a study of 70 case reports
Biki Kumar Sah, Zahra Fatima, Rajan Kumar Sah, Bushra Syed, Tulika Garg, Selia Chowdhury, Bikona Ghosh, Binita Kunwar, Anagha Shree, Vivek Kumar Sah, Anisha Raut
Annals of Medicine & Surgery.2024; 86(4): 2067. CrossRef
- mRNA-LNP COVID-19 Vaccine Lipids Induce Complement Activation and Production of Proinflammatory Cytokines: Mechanisms, Effects of Complement Inhibitors, and Relevance to Adverse Reactions
Original Article
- The incidence and clinical characteristics of myocarditis and pericarditis following mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccination in Republic of Korea adolescents from July 2021 to September 2022
- Ju-Young Sim, Seung-Yun Kim, Eun-Kyoung Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(2):76-88. Published online April 18, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0032
- 3,861 View
- 230 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 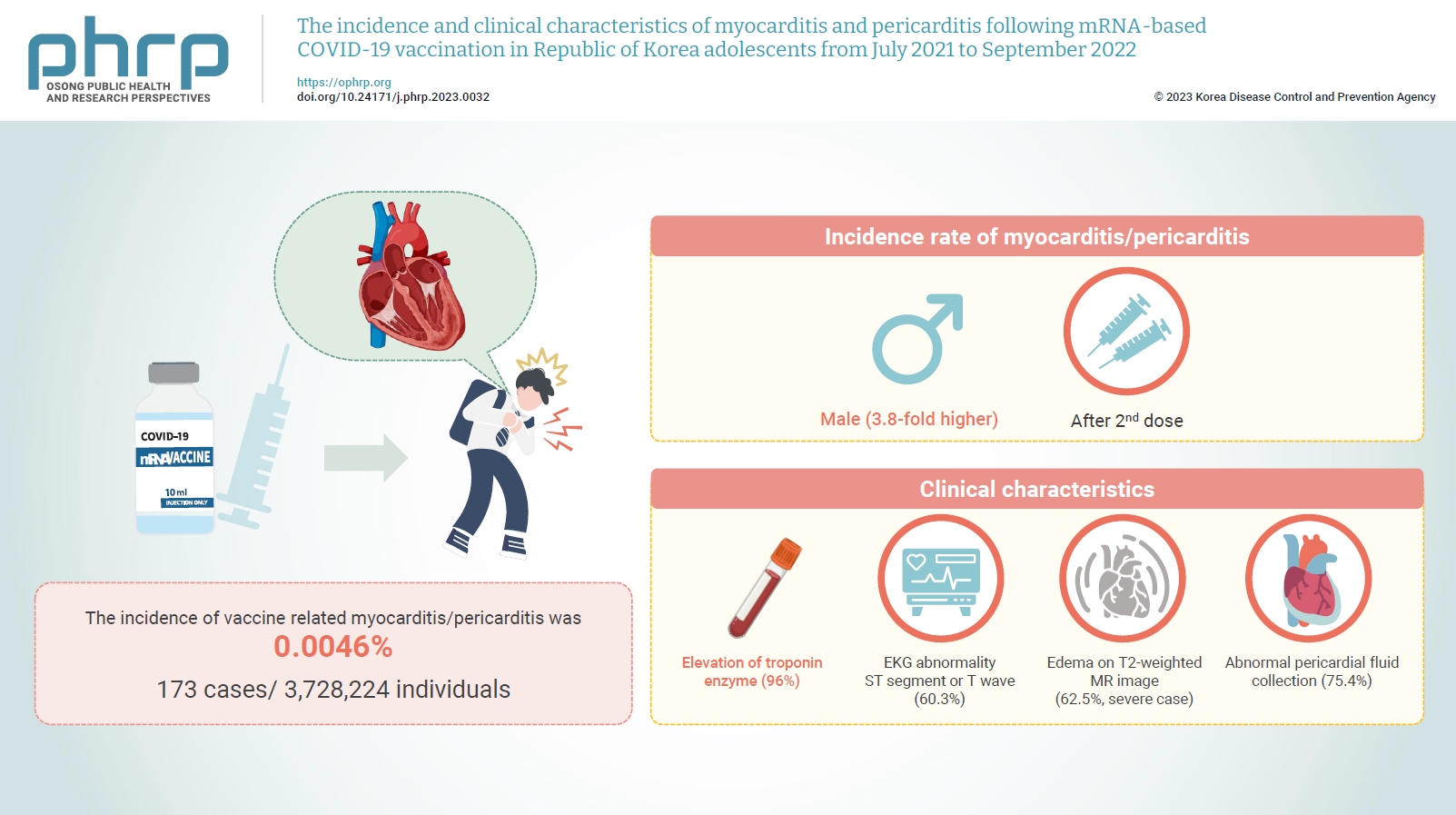
- Objectives
Age-specific information regarding myocarditis/pericarditis in adolescents following mRNA-based coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccination in Asia remains insufficient. This study investigated the incidence and clinical characteristics of myocarditis/pericarditis in Republic of Korea adolescents after mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccination.
Methods
This retrospective descriptive study utilized patient data from the Korea Immunization Management System. Incidence rates were calculated according to age and sex. Clinical characteristics (symptoms/signs, laboratory values, and imaging results) were compared between mild and severe cases.
Results
Between July 19, 2021 and September 30, 2022, 3,728,224 individuals aged 12 to 19 years received 6,484,165 mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines, and 173 cases met the case definition for myocarditis/pericarditis: 151 mild (87.3%) and 22 severe (12.7%). The incidence was 3.8-fold higher in males than in females. Troponin I/ troponin T was elevated in 96% of myocarditis cases, demonstrating higher sensitivity than creatine kinase-myocardial band (67.6%) or C-reactive protein (75.2%). ST-segment or Twave on electrography abnormalities were found in 60.3% (85/141). Paroxysmal/sustained atrial/ventricular arrhythmias were more common in severe than in mild cases (45.5% vs. 16.8%, p=0.008). Edema on T2-weighted magnetic imaging occurred in 21.6% (8/37) and 62.5% (5/8) of mild and severe cases, respectively (p=0.03). Abnormal pericardial fluid collection or pericardial inflammation was found in 75.4% of pericarditis cases (49/65).
Conclusion
Myocarditis/pericarditis occurred in rare cases following mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccination. Most cases were mild, but the incidence was higher in adolescent males and after the second dose. As bivalent severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 mRNA vaccination started in Republic of Korea in October 2022, the post-vaccination incidence of myocarditis/pericarditis should be closely monitored, considering clinical characteristics. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Responses to Common Misconceptions Relating to COVID-19 Variant-Adapted mRNA Vaccines
George Kassianos, Pauline MacDonald, Ivan Aloysius, Shanti Pather
Vaccines.2024; 12(1): 57. CrossRef - To become a more stronger and safer country
Jong-Koo Lee
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2023; 14(2): 67. CrossRef
- Responses to Common Misconceptions Relating to COVID-19 Variant-Adapted mRNA Vaccines
Special Article
- A framework for nationwide COVID-19 vaccine safety research in the Republic of Korea: the COVID-19 Vaccine Safety Research Committee
- Na-Young Jeong, Hyesook Park, Sanghoon Oh, Seung Eun Jung, Dong-Hyun Kim, Hyoung-Shik Shin, Hee Chul Han, Jong-Koo Lee, Jun Hee Woo, Byung-Joo Park, Nam-Kyong Choi
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(1):5-14. Published online February 28, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0026
- 2,974 View
- 150 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- With the introduction of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccines, the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency (KDCA) commissioned the National Academy of Medicine of Korea to gather experts to independently assess post-vaccination adverse events. Accordingly, the COVID-19 Vaccine Safety Research Committee (CoVaSC) was launched in November 2021 to perform safety studies and establish evidence for policy guidance. The CoVaSC established 3 committees for epidemiology, clinical research, and communication. The CoVaSC mainly utilizes pseudonymized data linking KDCA’s COVID-19 vaccination data and the National Health Insurance Service’s claims data. The CoVaSC’s 5-step research process involves defining the target diseases and organizing ad-hoc committees, developing research protocols, performing analyses, assessing causal relationships, and announcing research findings and utilizing them to guide compensation policies. As of 2022, the CoVaSC completed this research process for 15 adverse events. The CoVaSC launched the COVID-19 Vaccine Safety Research Center in September 2022 and has been reorganized into 4 divisions to promote research including international collaborative studies, long-/short-term follow-up studies, and education programs. Through these enhancements, the CoVaSC will continue to swiftly provide scientific evidence for COVID-19 vaccine research and compensation and may serve as a model for preparing for future epidemics of new diseases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk of encephalitis and meningitis after COVID-19 vaccination in South Korea: a self-controlled case series analysis
Ju Hwan Kim, Dongwon Yoon, Hwa Yeon Ko, Kyungyeon Jung, Jun-Sang Sunwoo, Won Chul Shin, Jung-Ick Byun, Ju-Young Shin
BMC Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - To become a more stronger and safer country
Jong-Koo Lee
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2023; 14(2): 67. CrossRef - Risk of lymphadenopathy from SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in Korea: a self-controlled case series analysis
Mi-Sook Kim, Bongyoung Kim, Jeong Pil Choi, Nam-Kyong Choi, Jung Yeon Heo, Jun Yong Choi, Joongyub Lee, Sang Il Kim
Epidemiology and Health.2023; 45: e2023090. CrossRef
- Risk of encephalitis and meningitis after COVID-19 vaccination in South Korea: a self-controlled case series analysis
Brief Reports
- Adverse events of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine in Korean children and adolescents aged 5 to 17 years
- Seontae Kim, Yeseul Heo, Soon-Young Seo, Do Sang Lim, Enhi Cho, Yeon-Kyeng Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(5):382-390. Published online October 14, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0233
- 2,350 View
- 110 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to identify potential safety signals and adverse events following the primary Pfizer-BioNTech coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccination series among children and adolescents aged 5 to 17 years in the Republic of Korea. Methods: Adverse events reported through the COVID-19 vaccination management system (CVMS, a web-based passive vaccine safety surveillance system) and adverse events and health conditions collected from a text message-based survey were analyzed. Results: A total of 14,786 adverse events among 5 to 17-year-old children and adolescents were reported in the CVMS; 14,334 (96.9%) were non-serious and 452 (3.1%) were serious, including 125 suspected cases of acute cardiovascular injury and 101 suspected cases of anaphylaxis. The overall reporting rate was lower in 5 to 11-year-old children (64.5 per 100,000 doses) than in 12 to 17-year-old adolescents (300.5 per 100,000 doses). The text message survey identified that local and systemic adverse events after either dose were reported less frequently in 5 to 11-year-old children than in 12 to 17-year-old adolescents (p<0.001). The most commonly reported adverse events were pain at the injection site, myalgia, headache, and fatigue/tiredness. Conclusion: The overall results are consistent with the results of controlled trials; serious adverse events were extremely rare among 5 to 17-year-old children and adolescents following Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccination. Adverse events were less frequent in children aged 5 to 11 years than in adolescents aged 12 to 17 years. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Safety monitoring of COVID-19 vaccines: February 26, 2021, To June 4, 2022, Republic of Korea
Yeon-Kyeng Lee, Yunhyung Kwon, Yesul Heo, Eun Kyoung Kim, Seung Yun Kim, Hoon Cho, Seontae Kim, Mijeong Ko, Dosang Lim, Soon-Young Seo, Enhi Cho
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics.2023; 66(10): 415. CrossRef - Effectiveness of the BNT162b2 vaccine in preventing morbidity and mortality associated with COVID-19 in children aged 5 to 11 years: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Sumayyah Ebrahim, Ntombifuthi Blose, Natasha Gloeck, Ameer Hohlfeld, Yusentha Balakrishna, Rudzani Muloiwa, Andy Gray, Andy Parrish, Karen Cohen, Ruth Lancaster, Tamara Kredo, Julia Robinson
PLOS Global Public Health.2023; 3(12): e0002676. CrossRef
- Safety monitoring of COVID-19 vaccines: February 26, 2021, To June 4, 2022, Republic of Korea
- Presumed population immunity to SARS-CoV-2 in South Korea, April 2022
- Eun Jung Jang, Young June Choe, Seung Ah Choe, Yoo-Yeon Kim, Ryu Kyung Kim, Jia Kim, Do Sang Lim, Ju Hee Lee, Seonju Yi, Sangwon Lee, Young-Joon Park
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(5):377-381. Published online October 14, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0209
- 2,323 View
- 70 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 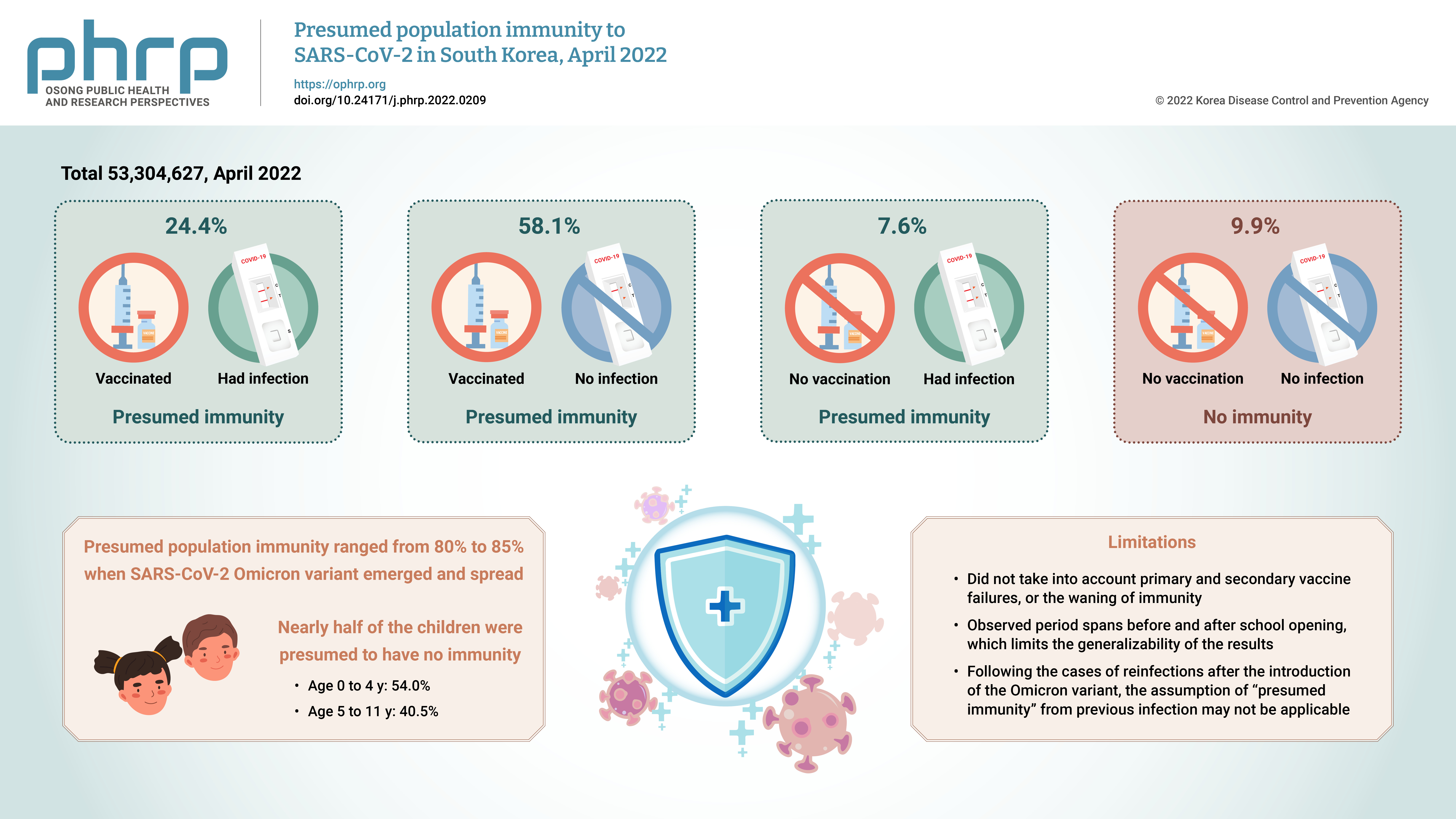
- Objectives
We estimated the overall and age-specific percentages of the Korean population with presumed immunity against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARSCoV-2) as of April 2022 using the national registry.
Methods
We used the national coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection and vaccination registry from South Korea, as described to define individuals with a previous history of COVID-19 infection, vaccination, or both, as persons with presumed immunity.
Results
Of a total of 53,304,627 observed persons, 24.4% had vaccination and infection, 58.1% had vaccination and no infection, 7.6% had infection and no vaccination, and 9.9% had no immunity. The SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant emerged at a time when the presumed population immunity ranged from 80% to 85%; however, nearly half of the children were presumed to have no immunity.
Conclusion
We report a gap in population immunity, with lower presumed protection in children than in adults. The approach presented in this work can provide valuable informed tools to assist vaccine policy-making at a national level. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Realistic Estimation of COVID-19 Infection by Seroprevalence Surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies: An Experience From Korea Metropolitan Area From January to May 2022
In Hwa Jeong, Jong-Hun Kim, Min-Jung Kwon, Jayoung Kim, Hee Jin Huh, Byoungguk Kim, Junewoo Lee, Jeong-hyun Nam, Eun-Suk Kang
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Epidemiology of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Infants and Toddlers, Seoul, South Korea
JiWoo Sim, Euncheol Son, Young June Choe
Pediatric Infection & Vaccine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Predicting adherence to COVID-19 preventive measures among South Korean adults aged 40 to 69 Years using the expanded health empowerment model
Su-Jung Nam, Tae-Young Pak
SSM - Population Health.2023; 22: 101411. CrossRef - Acute COVID-19 in unvaccinated children without a history of previous infection during the delta and omicron periods
Jee Min Kim, Ji Yoon Han, Seung Beom Han
Postgraduate Medicine.2023; 135(7): 727. CrossRef
- Realistic Estimation of COVID-19 Infection by Seroprevalence Surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies: An Experience From Korea Metropolitan Area From January to May 2022
Review Article
- India’s efforts to achieve 1.5 billion COVID-19 vaccinations: a narrative review
- Kapil Singh, Ashwani Verma, Monisha Lakshminarayan
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(5):316-327. Published online October 14, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0104
- 3,423 View
- 89 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 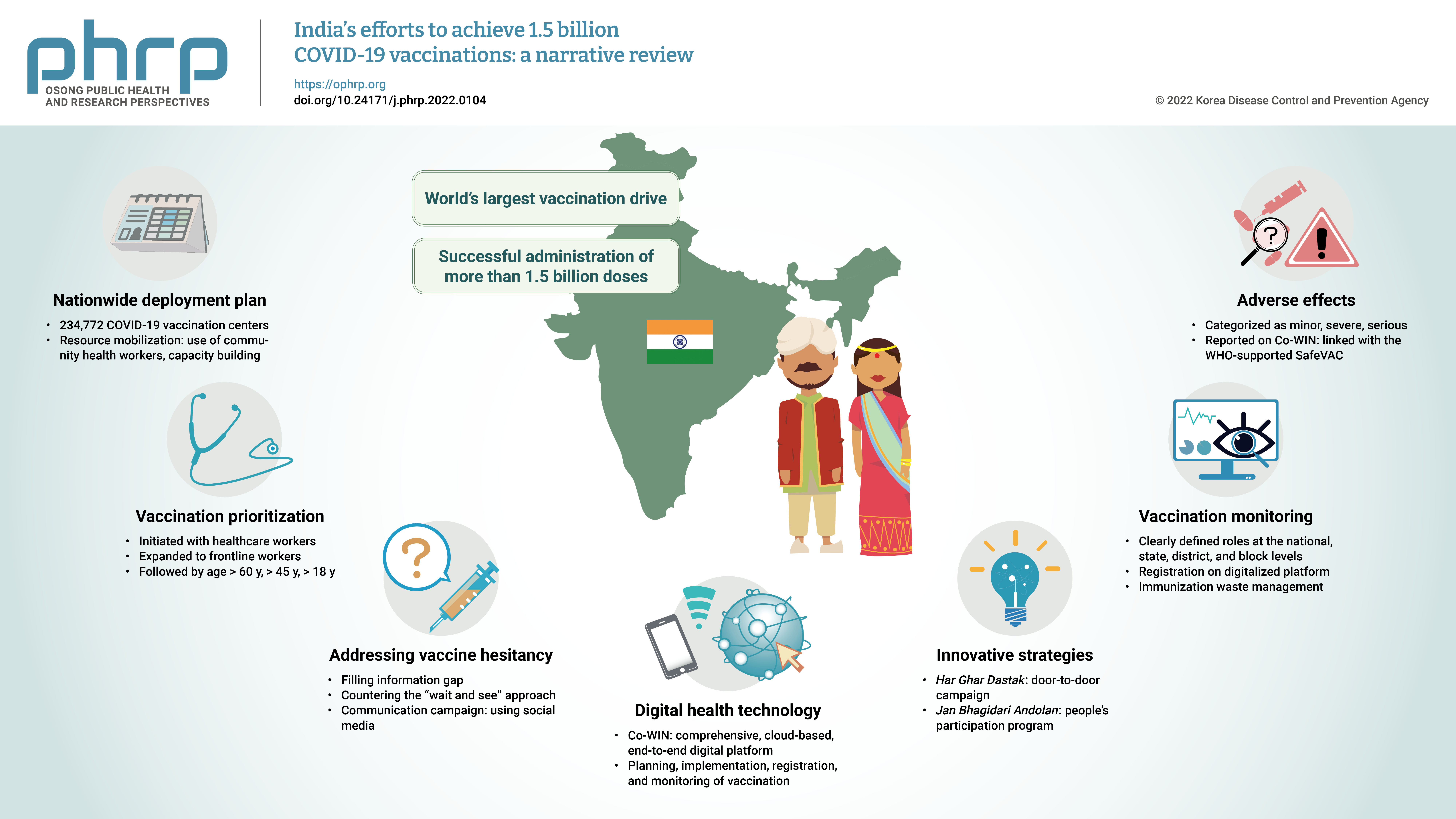
- The initial case of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in India was reported on January 30, 2020, and subsequently, the number of COVID-19-infected patients surged during the first wave of April 2020 and the second wave in the same month of 2021. The government of India imposed a strict nationwide lockdown in April 2020 and extended it until May 2020. The second wave of COVID-19 in India overwhelmed the country’s health facilities and exhausted its medical and paramedical workforce. This narrative review was conducted with the aim of summarizing the evidence drawn from policy documents of governmental and non-governmental organizations, as well as capturing India's COVID-19 vaccination efforts. The findings from this review cover the Indian government's vaccination initiatives, which ranged from steps taken to combat vaccine hesitancy to vaccination roadmaps, deployment plans, the use of digital health technology, vaccination monitoring, adverse effects, and innovative strategies such as Har Ghar Dastak and Jan Bhagidari Andolan (people’s participation). These efforts collectively culminated in the successful administration of more than 1.8 billion doses of COVID-19 vaccines in India. This review also provides insights into other countries’ responses to COVID-19 and guidance for future pandemics.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Digital health technology used in emergency large-scale vaccination campaigns in low- and middle-income countries: a narrative review for improved pandemic preparedness
Paula Mc Kenna, Lindsay A. Broadfield, Annik Willems, Serge Masyn, Theresa Pattery, Ruxandra Draghia-Akli
Expert Review of Vaccines.2023; 22(1): 243. CrossRef - Media Reporting Relating to COVID-19 Vaccination as a Driver of Vaccine Hesitancy Prior to the Second Wave of the COVID-19 Pandemic in India: A Content Analysis of Newspaper and Digital Media Reports
Saurav Basu, Himanshi Sharma
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - An assessment of the strategy and status of COVID-19 vaccination in India
Sneh Lata Gupta, Surbhi Goswami, Ananya Anand, Namrata Naman, Priya Kumari, Priyanka Sharma, Rishi K. Jaiswal
Immunologic Research.2023; 71(4): 565. CrossRef - Development of a Choice-framework for Covid vaccines in India using a multi-criteria decision analysis approach
Tarun K. George, Nayana P. Nair, Awnish Kumar Singh, A. Dilesh Kumar, Arup Deb Roy, Varshini Neethi Mohan, Gagandeep Kang
Vaccine.2023; 41(25): 3755. CrossRef - COVID-19 Booster Dose Coverage and Hesitancy among Older Adults in an Urban Slum and Resettlement Colony in Delhi, India
Nandini Sharma, Saurav Basu, Heena Lalwani, Shivani Rao, Mansi Malik, Sandeep Garg, Rahul Shrivastava, Mongjam Meghachandra Singh
Vaccines.2023; 11(7): 1177. CrossRef - Review of the unmet medical need for vaccination in adults with immunocompromising conditions: An Indian perspective
Ashok Vaid, Neha Rastogi, T. Mark Doherty, Peter San Martin, Yashpal Chugh
Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Translating the COVID-19 experience in widening the HPV vaccination campaign for cervical cancer in India
Aruni Ghose, Anisha Agarwal, Bhawna Sirohi, Shona Nag, Linus Chuang, Swarupa Mitra
Gynecologic Oncology Reports.2023; 48: 101247. CrossRef - Symptomatic prevalence of covid-19 in vaccinated and non-vaccinated population
Jay Bhupesh Pandya, Nirali Milind Shethia, Divya Bangera, Shailaja Gada Saxena
IP International Journal of Medical Microbiology a.2023; 9(2): 110. CrossRef - Active surveillance of adverse events following COVID-19 vaccines in a tertiary care hospital
Naveena Mary Cherian, Dravya Anna Durai, Muhammed Jaisel, Divyansh Sharma, Juny Sebastian, Chetak Kadabasal Basavaraja, Merrin Mathew
Therapeutic Advances in Vaccines and Immunotherapy.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of ayurvedic formulation, NAOQ19 along with standard care in the treatment of mild-moderate COVID-19 patients: A double blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, multicentric trial
Pankaj Bhardwaj, Kalaiselvan Ganapathy, Monika Pathania, K.H. Naveen, Jaykaran Charan, Siddhartha Dutta, Ravisekhar Gadepalli, Srikanth Srinivasan, Manoj Kumar Gupta, Akhil D. Goel, Naresh Midha, Bharat Kumar, Meenakshi Sharma, Praveen Sharma, Mithu Baner
Journal of Ayurveda and Integrative Medicine.2023; 14(6): 100778. CrossRef - Balancing Routine and Pandemic: The Synergy of India’s Universal Immunization Program and COVID-19 Vaccination Program
Pawan Kumar, Ashish Birendra Chakraborty, Suhas Dhandore, Pritu Dhalaria, Ajeet Kumar Singh, Disha Agarwal, Kapil Singh, Pretty Priyadarshini, Paras Jain, Vidushi Bahl, Gunjan Taneja
Vaccines.2023; 11(12): 1776. CrossRef - Unveiling vaccine safety: a narrative review of pharmacovigilance in India's COVID-19 vaccination
Megha Hegde, Saurav Raj, Dhananjay Tikadar, Sanatkumar B Nyamagoud
Monaldi Archives for Chest Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Digital health technology used in emergency large-scale vaccination campaigns in low- and middle-income countries: a narrative review for improved pandemic preparedness
Brief Report
- Safety monitoring of COVID-19 vaccination among adolescents aged 12 to 17 years old in the Republic of Korea
- Seontae Kim, Insob Hwang, Mijeong Ko, Yunhyung Kwon, Yeon-Kyeng Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(3):230-237. Published online June 10, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0122
- 4,099 View
- 138 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 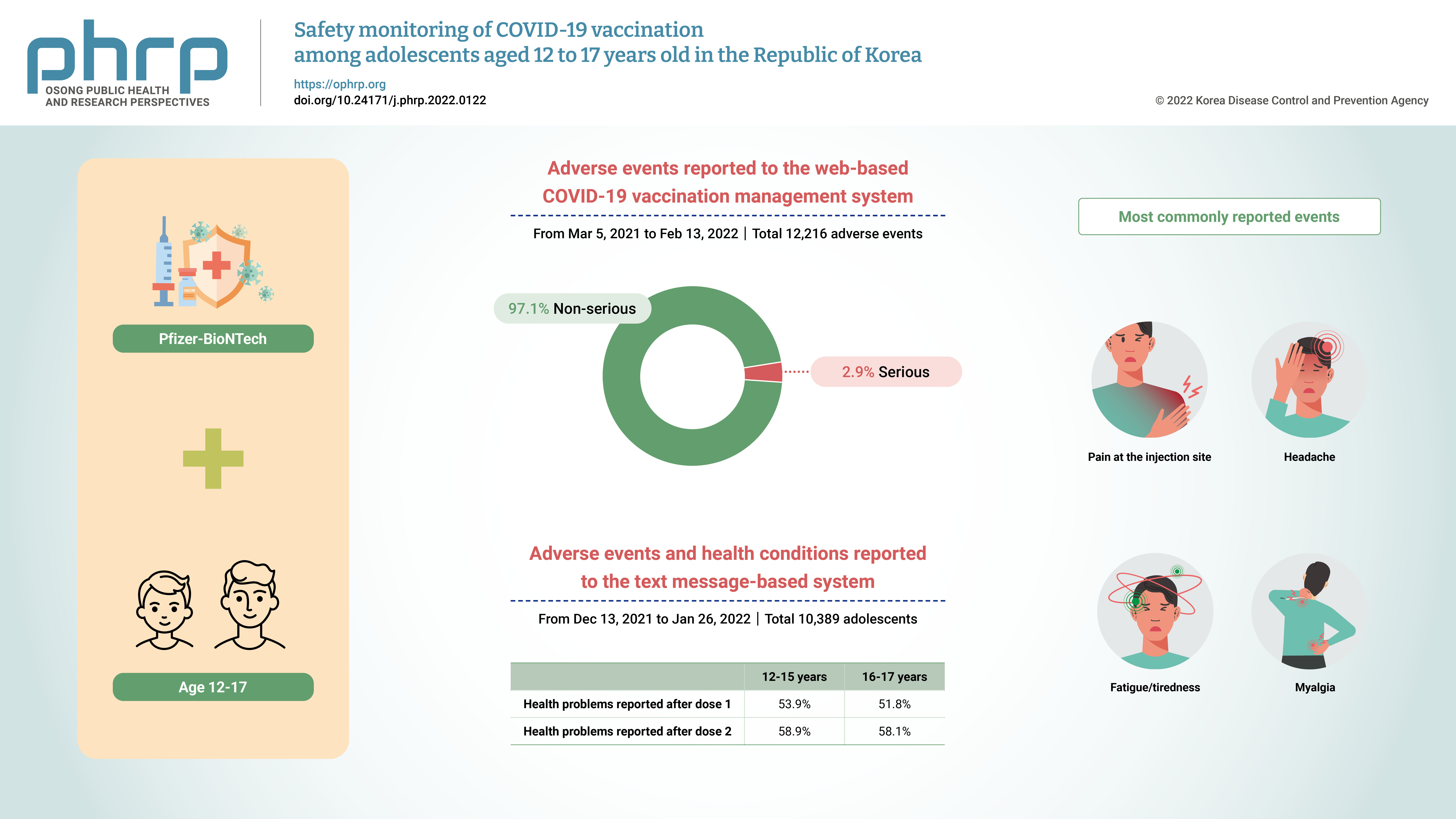
- Objectives
This study aimed to disseminate information on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccine safety among adolescents aged 12 to 17 years in the Republic of Korea. Methods: Two databases were used to assess COVID-19 vaccine safety in adolescents aged 12 to 17 years who completed the primary Pfizer-BioNTech vaccination series. Adverse events reported to the web-based COVID-19 vaccination management system (CVMS) and collected in the text message-based system were analyzed. Results: From March 5, 2021 to February 13, 2022, 12,216 adverse events among 12- to 17-yearolds were reported to the CVMS, of which 97.1% were non-serious adverse events and 2.9% were serious adverse events, including 85 suspected cases of anaphylaxis, 74 suspected cases of myocarditis and/or pericarditis, and 2 deaths. From December 13, 2021 to January 26, 2022, 10,389 adolescents responded to a text message survey, and local/systemic adverse events were more common after dose 2 than after dose 1. The most commonly reported events following either vaccine dose were pain at the injection site, headache, fatigue/tiredness, and myalgia. Conclusion: The overall results are consistent with previous findings; the great majority of adverse events were non-serious, and serious adverse events were rare among adolescents aged 12 to 17 years following Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccination. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Immunogenicity, effectiveness, and safety of COVID-19 vaccines among children and adolescents aged 2–18 years: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis
Peng Gao, Liang-Yu Kang, Jue Liu, Min Liu
World Journal of Pediatrics.2023; 19(11): 1041. CrossRef - Incidence of myopericarditis after mRNA COVID-19 vaccination: A meta-analysis with focus on adolescents aged 12–17 years
Bao-Qiang Guo, Hong-Bin Li, Li-Qiang Yang
Vaccine.2023; 41(28): 4067. CrossRef - Safety monitoring of COVID-19 vaccines: February 26, 2021, To June 4, 2022, Republic of Korea
Yeon-Kyeng Lee, Yunhyung Kwon, Yesul Heo, Eun Kyoung Kim, Seung Yun Kim, Hoon Cho, Seontae Kim, Mijeong Ko, Dosang Lim, Soon-Young Seo, Enhi Cho
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics.2023; 66(10): 415. CrossRef - Risk of Coronavirus Disease 2019 Messenger RNA Vaccination-Associated Myocarditis and Pericarditis – A Systematic Review of Population-Based Data
Yen-Ching Lin, Chia-Hsuin Chang, Wei-Ju Su, Chin-Hui Yang, Jann-Tay Wang
Risk Management and Healthcare Policy.2023; Volume 16: 2085. CrossRef - Suspected Myocarditis after mRNA COVID-19 Vaccination among South Korean Adolescents
Mi Jin Kim, Jin Hee Kim, Hyun Ok Jun, Kyung Min Kim, Min Sub Jeung, Jun Sung Park
Journal of Pediatric Infectious Diseases.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - COVID-19 Vaccination in Korea: Past, Present, and the Way Forward
Eliel Nham, Joon Young Song, Ji Yun Noh, Hee Jin Cheong, Woo Joo Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Immunogenicity, effectiveness, and safety of COVID-19 vaccines among children and adolescents aged 2–18 years: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis
Review Article
- Immune-related therapeutics: an update on antiviral drugs and vaccines to tackle the COVID-19 pandemic
- Iqra Mir, Sania Aamir, Syed Rizwan Hussain Shah, Muhammad Shahid, Iram Amin, Samia Afzal, Amjad Nawaz, Muhammad Umer Khan, Muhammad Idrees
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(2):84-100. Published online April 27, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0024
- 5,048 View
- 96 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 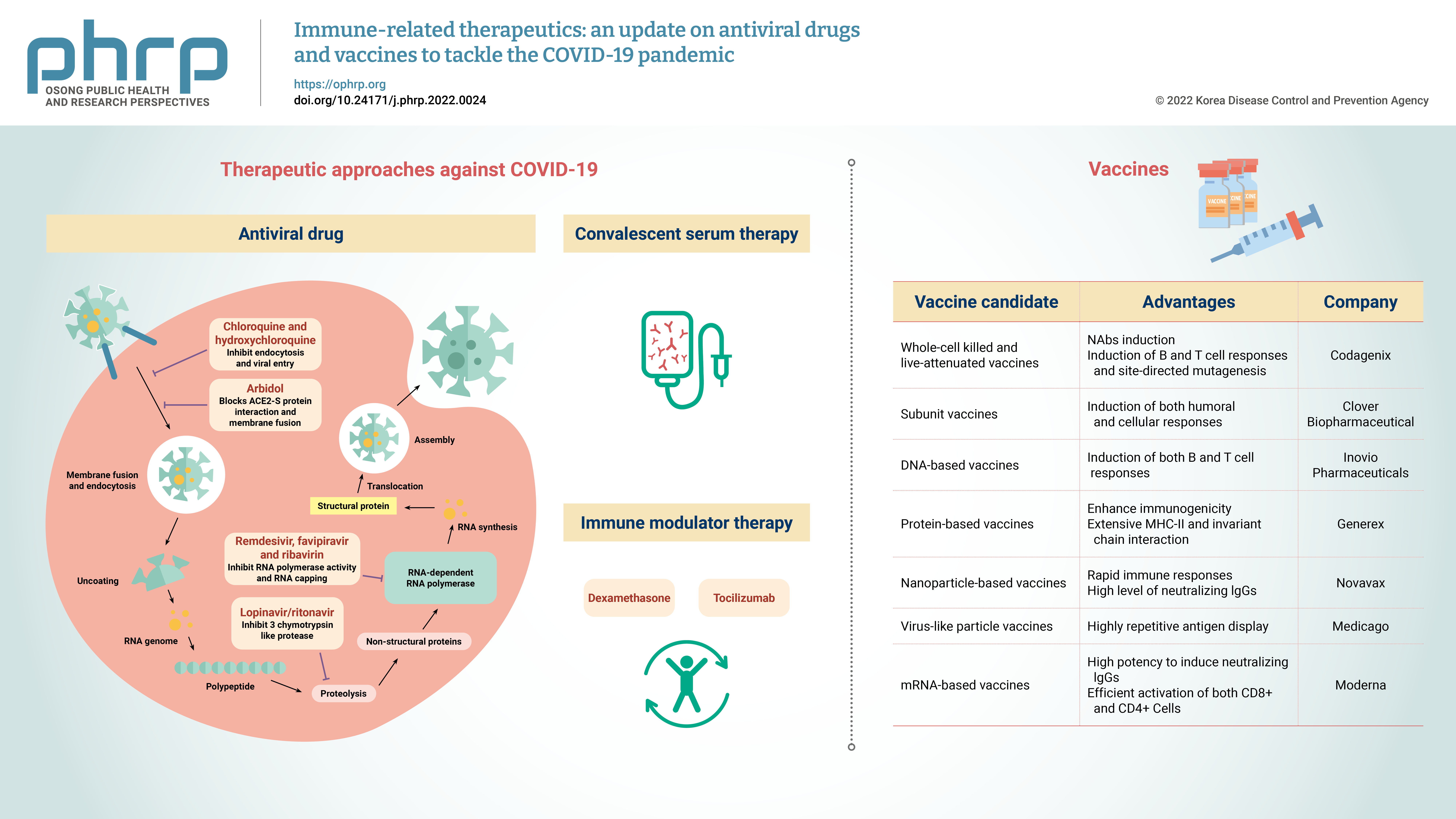
- The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic rapidly spread globally. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), which causes COVID-19, is a positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus with a reported fatality rate ranging from 1% to 7%, and people with immune-compromised conditions, children, and older adults are particularly vulnerable. Respiratory failure and cytokine storm-induced multiple organ failure are the major causes of death. This article highlights the innate and adaptive immune mechanisms of host cells activated in response to SARS-CoV-2 infection and possible therapeutic approaches against COVID-19. Some potential drugs proven to be effective for other viral diseases are under clinical trials now for use against COVID-19. Examples include inhibitors of RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (remdesivir, favipiravir, ribavirin), viral protein synthesis (ivermectin, lopinavir/ ritonavir), and fusion of the viral membrane with host cells (chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine, nitazoxanide, and umifenovir). This article also presents the intellectual groundwork for the ongoing development of vaccines in preclinical and clinical trials, explaining potential candidates (live attenuated-whole virus vaccines, inactivated vaccines, subunit vaccines, DNAbased vaccines, protein-based vaccines, nanoparticle-based vaccines, virus-like particles and mRNA-based vaccines). Designing and developing an effective vaccine (both prophylactic and therapeutic) would be a long-term solution and the most effective way to eliminate the COVID-19 pandemic.
Original Article
- COVID-19 outbreak response at a nursing hospital in South Korea in the post-vaccination era, including an estimation of the effectiveness of the first shot of the Oxford-AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine (ChAdOx1-S)
- Chanhee Kim, Geon Kang, Sun Gu Kang, Heeyoung Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(2):114-122. Published online April 26, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.0262
- 4,133 View
- 91 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
We descriptively reviewed a coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak at a nursing hospital in Gyeonggi Province (South Korea) and assessed the effectiveness of the first dose of the Oxford-AstraZeneca vaccine in a real-world population. Methods: The general process of the epidemiological investigation included a public health intervention. The relative risk (RR) of vaccinated and unvaccinated groups was calculated and compared to confirm the risk of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARSCoV-2) infection, and vaccine effectiveness was evaluated based on the calculated RR. Results: The population at risk was confined to ward E among 8 wards of Hospital X, where the outbreak occurred. This population comprised 55 people, including 39 patients, 12 nurses, and 4 caregivers, and 19 cases were identified. The RR between the vaccinated and unvaccinated groups was 0.04, resulting in a vaccine effectiveness of 95.3%. The vaccination rate of the nonpatients in ward E was the lowest in the entire hospital, whereas the overall vaccination rate of the combined patient and non-patient groups in ward E was the third lowest. Conclusion: The first dose of the Oxford-AstraZeneca vaccine (ChAdOx1-S) was effective in preventing SARS-CoV-2 infection. To prevent COVID-19 outbreaks in medical facilities, it is important to prioritize the vaccination of healthcare providers. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- COVID-19 Vaccination in Korea: Past, Present, and the Way Forward
Eliel Nham, Joon Young Song, Ji Yun Noh, Hee Jin Cheong, Woo Joo Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- COVID-19 Vaccination in Korea: Past, Present, and the Way Forward



 First
First Prev
Prev


