Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- The effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on the trends and characteristics of natural and unnatural deaths in an urban Sri Lankan cohort viewed through retrospective analysis of forensic death investigations from 2019 to 2022
- Sameera Anuruddha Gunawardena, Nishani Dassanayake, Buddhika Indeewarie Keerawelle, Shivasankarie Kanthasamy, Hasini Ranganatha, Jayani Wathsala Gunawardana
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(6):468-482. Published online November 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0175
- 1,112 View
- 43 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 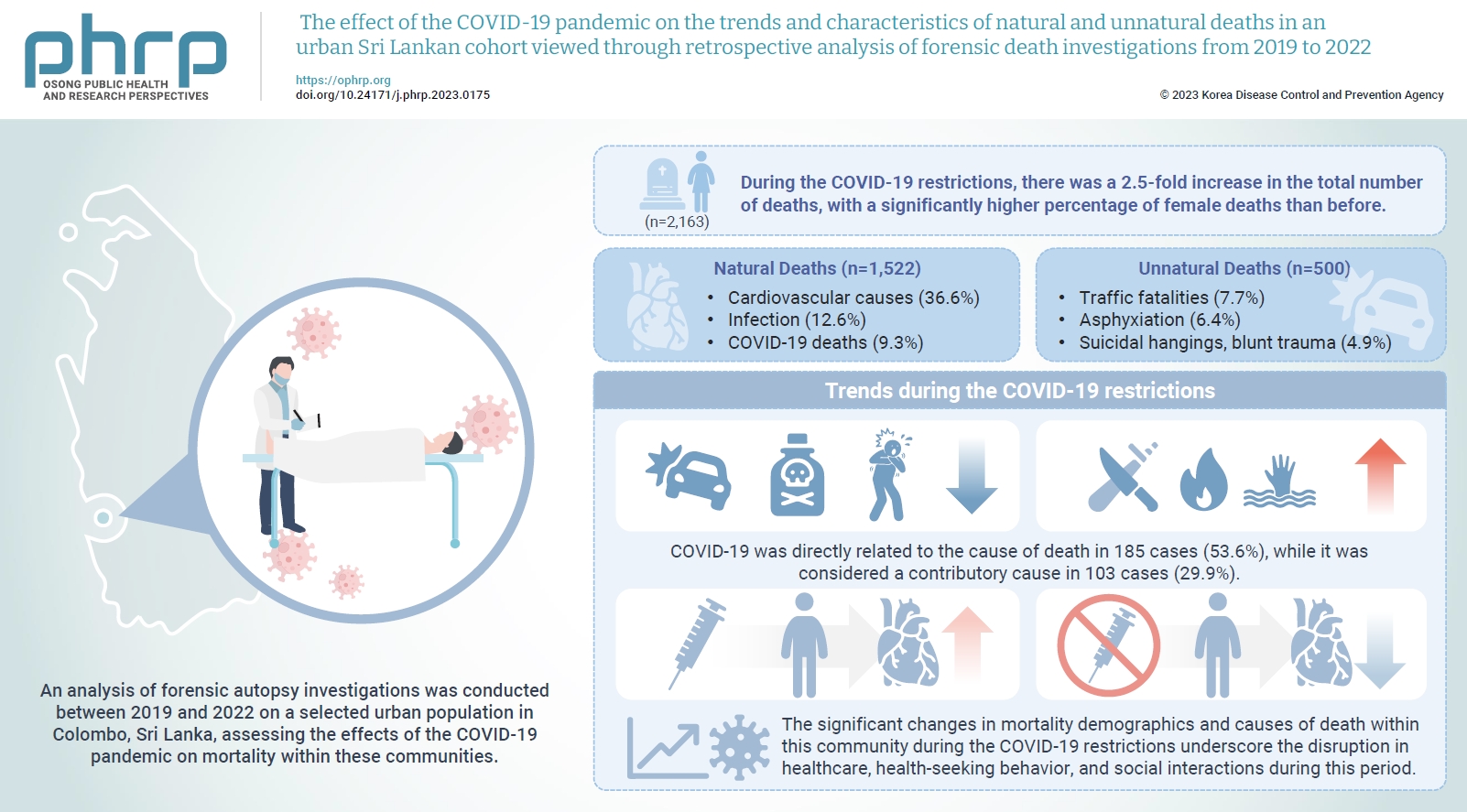
- Objectives
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has had a severe impact on global health. Apart from the disease itself, the strict restrictions and lockdowns enforced to minimize its spread have also substantially disrupted personal and public health. Methods: An analysis of forensic autopsy investigations was conducted between 2019 and 2022 on a selected urban population in Colombo, Sri Lanka, assessing the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on mortality within these communities. Results: During the COVID-19 restrictions, there was a 2.5-fold increase in the total number of deaths, with a significantly higher percentage of female deaths than before. The majority of these deaths were due to cardiovascular causes, while COVID-19-related deaths ranked third overall. The highest proportion of COVID-19 deaths occurred among unvaccinated females. The monthly frequency of deaths from traffic accidents, poisoning, and asphyxiation decreased, while deaths from blunt trauma, sharp trauma, burns, and immersion increased. There was also a rise in blunt homicides and a greater number of femicides during the COVID-19 restrictions than in the pre-pandemic period. A significantly higher percentage of males who received the COVID-19 vaccine died from cardiovascular causes compared to those in the unvaccinated group. Conclusion: The significant changes in mortality demographics and causes of death within this community during the COVID-19 restrictions underscore the disruption in healthcare, healthseeking behavior, and social interactions during this period. The vulnerability of individuals residing in highly urbanized areas with lower socioeconomic status, particularly women, is brought into sharp focus.
- Epidemiological characteristics of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae outbreaks in the Republic of Korea between 2017 and 2022
- Hyoseon Jeong, Junghee Hyun, Yeon-Kyeng Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(4):312-320. Published online August 21, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0069
- 1,049 View
- 143 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Objectives
We aimed to describe the epidemiological characteristics of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae (CPE) outbreaks in healthcare settings in the Republic of Korea between 2017 and 2022.
Methods
Under the national notifiable disease surveillance system, we obtained annual descriptive statistics regarding the isolated species, carbapenemase genotype, healthcare facility type, outbreak location and duration, and number of patients affected and recommended interventions. We used epidemiological investigation reports on CPE outbreaks reported to Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency from June 2017 to September 2022.
Results
Among the 168 reports analyzed, Klebsiella pneumoniae (85.1%) was the most frequently reported species, while K. pneumoniae carbapenemase (KPC, 82.7%) was the most common carbapenemase genotype. Both categories increased from 2017 to 2022 (p<0.01). General hospitals had the highest proportion (54.8%), while tertiary general hospitals demonstrated a decreasing trend (p<0.01). The largest proportion of outbreaks occurred exclusively in intensive care units (ICUs, 44.0%), and the frequency of concurrent outbreaks in ICUs and general wards increased over time (p<0.01). The median outbreak duration rose from 43.5 days before the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic (2017–2019) to 79.5 days during the pandemic (2020–2022) (p=0.01), and the median number of patients associated with each outbreak increased from 5.0 to 6.0 (p=0.03). Frequently recommended interventions included employee education (38.1%), and 3 or more measures were proposed for 45.2% of outbreaks.
Conclusion
In the Republic of Korea, CPE outbreaks have been consistently dominated by K. pneumoniae and KPC. The size of these outbreaks increased during the COVID-19 pandemic. Our findings highlight the need for continuing efforts to control CPE outbreaks using a multimodal approach, while considering their epidemiology. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of clinical outcomes of patients with serial negative surveillance cultures according to a subsequent polymerase chain reaction test for carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales
H. Seo, S. Kim, Y.W. Lee, H.S. Oh, H-S. Kim, Y.K. Kim
Journal of Hospital Infection.2024; 146: 93. CrossRef - Identifying Contact Time Required for Secondary Transmission of Clostridioides difficile Infections by Using Real-Time Locating System
Min Hyung Kim, Jaewoong Kim, Heejin Ra, Sooyeon Jeong, Yoon Soo Park, Dongju Won, Hyukmin Lee, Heejung Kim
Emerging Infectious Diseases.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Comparison of clinical outcomes of patients with serial negative surveillance cultures according to a subsequent polymerase chain reaction test for carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales
- Public health agencies’ use of social media for communication during pandemics: a scoping review of the literature
- Babatunde Abiodun Balogun, Anne Hogden, Nenagh Kemp, Lin Yang, Maria Agaliotis
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(4):235-251. Published online August 9, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0095
- 1,651 View
- 146 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Public health agencies (PHAs) have increasingly incorporated social media into their communication mix during successive pandemics in the 21st century. However, the quality, timing, and accuracy of their health messages have varied significantly, resulting in mixed outcomes for communication, audience engagement, and pandemic management. This study aimed to identify factors influencing the effectiveness of pandemic-related health messages shared by PHAs on social media and to report their impact on public engagement as documented in the literature. A scoping literature review was conducted following a predefined protocol. An electronic search of 7 relevant databases and 5 grey literature repositories yielded 9,714 papers published between January 2003 and November 2022. Seventy-three papers were deemed eligible and selected for review. The results underscored the insufficiency of social media guidance policies for PHAs. Six themes were identified: message source, message topic, message style, message timing, content credibility and reliability, and message recipient profile. These themes encompassed 20 variables that could inform PHAs’ social media public health communication during pandemics. Additionally, the findings revealed potential interconnectedness among the variables, and this study concluded by proposing a conceptual model that expands upon existing theoretical foundations for developing and evaluating pandemic-related health messaging.
- Neck circumference and incidence of cerebrovascular disease over 12 years among Korean adults
- Jae-Seon Han, Yun-Hee Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(1):71-79. Published online February 8, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.0277
- 3,228 View
- 57 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Neck circumference is associated with a distinctive fat storage process that confers additional metabolic risk. Hence, this study aimed to investigate the correlation between baseline neck circumference and the incidence of cerebrovascular disease using a prospective community-based sample of Korean adults over 12 years of follow-up, after controlling for selected covariates. Methods: Participants with non-cerebrovascular disease were divided into 4 groups (Q1–Q4) based on their baseline neck circumference. Cox proportional hazards analysis was used to calculate hazard ratios and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) to evaluate the relationship between neck circumference and cerebrovascular disease incidence over a 12-year period. Results: Among this study’s 3,662 participants, 128 (3.50%) developed cerebrovascular disease. The incidence of cerebrovascular disease increased from 2.2% in Q1 to 4.3% in Q2, 2.5% in Q3, and 5.0% in Q4. When compared to Q1, the relative risks of cerebrovascular disease development were 0.57 (95% CI, 0.25–1.31), 0.86 (95% CI, 0.38–1.96), and 0.79 (95% CI, 0.30–2.07) in man and 1.86 (95% CI, 0.66–5.20), 3.50 (95% CI, 1.25–9.86), and 4.71 (95% CI, 1.50–14.77) in woman in Q2, Q3, and Q4, respectively, after adjusting for most risk factors related to cerebrovascular disease. Conclusion: The relationship between neck circumference and cerebrovascular disease was stronger in woman than in man, indicating potential differences between the sexes. These results are meaningful for evaluating and surveilling neck circumference as a promising tool for identifying subgroups of vulnerable and at-risk populations. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Neck circumference as a predictor of all-cause mortality in middle-aged and older adults in rural Ecuador
Oscar H Del Brutto, Denisse A Rumbea, Maitri Patel, Robertino M Mera
International Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The association of Carbohydrate Quality Index with cardiovascular disease risk factors among women with overweight and obesity: A cross-sectional study
Darya Khosravinia, Farideh Shiraseb, Atieh Mirzababaei, Elnaz Daneshzad, Shahin Jamili, Cain C. T. Clark, Khadijeh Mirzaei
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Neck circumference as a predictor of all-cause mortality in middle-aged and older adults in rural Ecuador
- Global variation of COVID-19 mortality rates in the initial phase
- Saman Hasan Siddiqui, Azza Sarfraz, Arjumand Rizvi, Fariha Shaheen, Mohammad Tahir Yousafzai, Syed Asad Ali
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2021;12(2):64-72. Published online April 29, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.12.2.03
- 6,536 View
- 149 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Objectives
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has caused devastation in over 200 countries. Italy, Spain, and the United States (US) were most severely affected by the first wave of the pandemic. The reasons why some countries were more strongly affected than others remain unknown. We identified the most-affected and less-affected countries and states and explored environmental, host, and infrastructure risk factors that may explain differences in the SARS-CoV-2 mortality burden.
Methods
We identified the top 10 countries/US states with the highest deaths per population until May 2020. For each of these 10 case countries/states, we identified 6 control countries/states with a similar population size and at least 3 times fewer deaths per population. We extracted data for 30 risk factors from publicly available, trusted sources. We compared case and control countries/states using the non-parametric Wilcoxon rank-sum test, and conducted a secondary cluster analysis to explore the relationship between the number of cases per population and the number of deaths per population using a scalable EM (expectation–maximization) clustering algorithm.
Results
Statistically significant differences were found in 16 of 30 investigated risk factors, the most important of which were temperature, neonatal and under-5 mortality rates, the percentage of under-5 deaths due to acute respiratory infections (ARIs) and diarrhea, and tuberculosis incidence (p <0.05)
Conclusion
Countries with a higher burden of baseline pediatric mortality rates, higher pediatric mortality from preventable diseases like diarrhea and ARI, and higher tuberculosis incidence had lower rates of coronavirus disease 2019-associated mortality, supporting the hygiene hypothesis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prediction models of COVID-19 fatality in nine Peruvian provinces: A secondary analysis of the national epidemiological surveillance system
Wendy Nieto-Gutierrez, Jaid Campos-Chambergo, Enrique Gonzalez-Ayala, Oswaldo Oyola-Garcia, Alberti Alejandro-Mora, Eliana Luis-Aguirre, Roly Pasquel-Santillan, Juan Leiva-Aguirre, Cesar Ugarte-Gil, Steev Loyola, Sizulu Moyo
PLOS Global Public Health.2024; 4(1): e0002854. CrossRef - The effect of the urban exposome on COVID-19 health outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Laura Houweling, Anke-Hilse Maitland-Van der Zee, Judith C.S. Holtjer, Somayeh Bazdar, Roel C.H. Vermeulen, George S. Downward, Lizan D. Bloemsma
Environmental Research.2024; 240: 117351. CrossRef - Demographic Characteristics and Status of Vaccinated Individuals with a History of COVID-19 Infection Pre- or Post-Vaccination: A Descriptive Study of a Nationally Representative Sample in Saudi Arabia
Yazed AlRuthia, Haya F. Al-Salloum, Omar A. Almohammed, Amani S. Alqahtani, Hana A. Al-Abdulkarim, Yousef M. Alsofayan, Sami S. Almudarra, Sara H. AlQahtani, Abdullah Almutlaq, Khaled Alabdulkareem, Bander Balkhi, Hamoud T. Almutairi, Abdullah S. Alanazi,
Vaccines.2022; 10(2): 323. CrossRef - Temporal variation, socioeconomic status, and out‐of‐hospital deaths as factors that influence mortality rates among hospitalized COVID‐19 patients receiving ACEIs/ARBs
Owais M. Aftab, Anurag Modak, Jai C. Patel
The Journal of Clinical Hypertension.2022; 24(4): 519. CrossRef - Coinfection of leptospirosis and coronavirus disease 2019: A retrospective case series from a coastal region in South India
Nitin Gupta, William Wilson, Prithvishree Ravindra, Roshini Raghu, Kavitha Saravu
Journal of Medical Virology.2022; 94(9): 4508. CrossRef - Dietary, comorbidity, and geo-economic data fusion for explainable COVID-19 mortality prediction
Milena Trajanoska, Risto Trajanov, Tome Eftimov
Expert Systems with Applications.2022; 209: 118377. CrossRef - Paraoxonase 1 rs662 polymorphism, its related variables, and COVID-19 intensity: Considering gender and post-COVID complications
Zohreh-Al-Sadat Ghoreshi, Mojtaba Abbasi-jorjandi, Gholamreza Asadikaram, Mohsen Sharif-zak, Fatemeh Seyedi, Mohammad Khaksari Haddad, Mohammadreza Zangouey
Experimental Biology and Medicine.2022; : 153537022211285. CrossRef - Clinical Effect of Q192R Paraoxonase 1 Polymorphism and its Related Variables on the COVID-19 Intensity Considering Gender and Post-COVID Complications
Zohreh-al-sadat Ghoreshi, Mojtaba abasi, Gholamreza Asadikaram, Mohsen sharif-zak, Mitra Rezazadeh-Jabalbarzi, Hamidreza rashidinejad, Mohammadreza Zangouey
SSRN Electronic Journal .2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk Factors and a Novel Score (CARI-65) Predicting Mortality in COVID-19 Patients
Fayaz Ahmad Sofi, Umar Hafiz Khan, Sonaullah Shah, Nazia Mehfooz, Farhana Siraj, Afshan Shabir, Tajamul Hussain Shah, Muzaffar Bindroo, Mushtaq Ahmad, Rafi Ahmed Jan, Asma Shah, Faizan Wani
Indian Journal of Respiratory Care.2022; 11(2): 154. CrossRef - Variances in BCG protection against COVID-19 mortality: A global assessment
Zouina Sarfraz, Azza Sarfraz, Krunal Pandav, Sarabjot Singh Makkar, Saman Hasan Siddiqui, Gaurav Patel, Tania Platero-Portillo, Bishnu Mohan Singh, Mohamed Iburahim Haja Maideen, Deepika Sarvepalli, Muzna Sarfraz, Jose Cardona-Guzman, Marcos A. Sanchez-Go
Journal of Clinical Tuberculosis and Other Mycobac.2021; 24: 100249. CrossRef
- Prediction models of COVID-19 fatality in nine Peruvian provinces: A secondary analysis of the national epidemiological surveillance system
- KCDC Risk Assessments on the Initial Phase of the COVID-19 Outbreak in Korea
- Inho Kim, Jia Lee, Jihee Lee, Eensuk Shin, Chaeshin Chu, Seon Kui Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2020;11(2):67-73. Published online April 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2020.11.2.02
- 13,049 View
- 621 Download
- 17 Web of Science
- 17 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives This study aims to evaluate the risk assessments of coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) in the Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (KCDC), from the point of detection to the provision of basic information to the relevant public health authorities.
Methods To estimate the overall risk of specific public health events, probability, and impact at the country-level were evaluated using available information. To determine the probability of particular public health events, the risk of importation and risk of transmission were taken into consideration. KCDC used 5 levels (“very low,” “low,” “moderate,” “high,” and “very high”) for each category and overall risk was eventually decided.
Results A total of 8 risk assessments were performed on 8 separate occasions between January 8th to February 28th, 2020, depending on the detection and report of COVID-19 cases in other countries. The overall risk of the situation in each assessment increased in severity over this period: “low” (first), “moderate” (second), “high” (third), “high” (fourth), “high” (fifth), “high” (sixth), “high” (seventh), and “very high” (eighth).
Conclusion The KCDC’s 8 risk assessments were utilized to activate national emergency response mechanisms and eventually prepare for the pandemic to ensure the containment and mitigation of COVID-19 with non-pharmaceutical public health measures.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- COVID-19 Pandemic Risk Assessment: Systematic Review
Amanda Chu, Patrick Kwok, Jacky Chan, Mike So
Risk Management and Healthcare Policy.2024; Volume 17: 903. CrossRef - COVID-19 Cases and Deaths among Healthcare Personnel with the Progression of the Pandemic in Korea from March 2020 to February 2022
Yeonju Kim, Sung-Chan Yang, Jinhwa Jang, Shin Young Park, Seong Sun Kim, Chansoo Kim, Donghyok Kwon, Sang-Won Lee
Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease.2023; 8(6): 308. CrossRef - A resposta da Coreia do Sul à pandemia de COVID-19: lições aprendidas e recomendações a gestores
Thais Regis Aranha Rossi, Catharina Leite Matos Soares, Gerluce Alves Silva, Jairnilson Silva Paim, Lígia Maria Vieira-da-Silva
Cadernos de Saúde Pública.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Nursing Experience of New Nurses Caring for COVID-19 Patients in Military Hospitals: A Qualitative Study
Young-Hoon Kwon, Hye-Ju Han, Eunyoung Park
Healthcare.2022; 10(4): 744. CrossRef - South Korea’s fast response to coronavirus disease: implications on public policy and public management theory
Pan Suk Kim
Public Management Review.2021; 23(12): 1736. CrossRef - Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in Fecal Samples From Patients With Asymptomatic and Mild COVID-19 in Korea
Soo-kyung Park, Chil-Woo Lee, Dong-Il Park, Hee-Yeon Woo, Hae Suk Cheong, Ho Cheol Shin, Kwangsung Ahn, Min-Jung Kwon, Eun-Jeong Joo
Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2021; 19(7): 1387. CrossRef - Systematic assessment of South Korea’s capabilities to control COVID-19
Katelyn J. Yoo, Soonman Kwon, Yoonjung Choi, David M. Bishai
Health Policy.2021; 125(5): 568. CrossRef - Environmental risk assessment and comprehensive index model of disaster loss for COVID-19 transmission
Sulin Pang, Xiaofeng Hu, Zhiming Wen
Environmental Technology & Innovation.2021; 23: 101597. CrossRef - Transmission dynamics and control of two epidemic waves of SARS-CoV-2 in South Korea
Sukhyun Ryu, Sheikh Taslim Ali, Eunbi Noh, Dasom Kim, Eric H. Y. Lau, Benjamin J. Cowling
BMC Infectious Diseases.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Identifying and Prioritizing Ways to Improve Oman’s Tourism Sector in the Corona Period
Zakiya Salim Al-Hasni
Journal of Intercultural Management.2021; 13(1): 144. CrossRef - Decreased Use of Broad-Spectrum Antibiotics During the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Epidemic in South Korea
Sukhyun Ryu, Youngsik Hwang, Sheikh Taslim Ali, Dong-Sook Kim, Eili Y Klein, Eric H Y Lau, Benjamin J Cowling
The Journal of Infectious Diseases.2021; 224(6): 949. CrossRef - COVID-19 and Cancer Therapy: Interrelationships and Management of Cancer Cases in the Era of COVID-19
Simon N. Mbugua, Lydia W. Njenga, Ruth A. Odhiambo, Shem O. Wandiga, Martin O. Onani, Nenad Ignjatovic
Journal of Chemistry.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Challenges to manage pandemic of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in Iran with a special situation: a qualitative multi-method study
Hamidreza Khankeh, Mehrdad Farrokhi, Juliet Roudini, Negar Pourvakhshoori, Shokoufeh Ahmadi, Masoumeh Abbasabadi-Arab, Nader Majidi Bajerge, Babak Farzinnia, Pirhossain Kolivand, Vahid Delshad, Mohammad Saeed Khanjani, Sadegh Ahmadi-Mazhin, Ali Sadeghi-Mo
BMC Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Nonpharmaceutical Interventions on Transmission of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2, South Korea, 2020
Sukhyun Ryu, Seikh Taslim Ali, Cheolsun Jang, Baekjin Kim, Benjamin J. Cowling
Emerging Infectious Diseases.2020; 26(10): 2406. CrossRef - Early Trend of Imported COVID-19 Cases in South Korea
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2020; 11(3): 140. CrossRef - Effect of Underlying Comorbidities on the Infection and Severity of COVID-19 in Korea: a Nationwide Case-Control Study
Wonjun Ji, Kyungmin Huh, Minsun Kang, Jinwook Hong, Gi Hwan Bae, Rugyeom Lee, Yewon Na, Hyoseon Choi, Seon Yeong Gong, Yoon-Hyeong Choi, Kwang-Pil Ko, Jeong-Soo Im, Jaehun Jung
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Innovative countermeasures can maintain cancer care continuity during the coronavirus disease-2019 pandemic in Korea
Soohyeon Lee, Ah-reum Lim, Min Ja Kim, Yoon Ji Choi, Ju Won Kim, Kyong Hwa Park, Sang Won Shin, Yeul Hong Kim
European Journal of Cancer.2020; 136: 69. CrossRef
- COVID-19 Pandemic Risk Assessment: Systematic Review
- Enhancing ‘Whole-of-Government’ Response to Biological Events in Korea: Able Response 2014
- Sangwoo Tak, Anton Jareb, Suon Choi, Marvin Sikes, Yeon Hwa Choi, Hyeong-wook Boo
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2018;9(1):32-35. Published online December 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2018.9.1.06
- 5,097 View
- 40 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Since 2011, the Republic of Korea (ROK) and United States (U.S.) have been collaborating to conduct inter- and intra-governmental exercises to jointly respond to biological events in Korea. These exercises highlight U.S. interest in increasing its global biosurveillance capability and the ROK’s interest in improving cooperation among ministries to respond to crises. With Able Response (AR) exercises, the ROK and U.S. have improved coordination among US and ROK government and defense agencies responding to potential bio-threats and identified additional areas on which to apply refinements in policies and practices. In 2014, the AR exercise employed a Biosurveillance Portal (BSP) to facilitate more effective communication among participating agencies and countries including Australia. In the present paper, we seek to provide a comprehensive assessment of the AR 2014 (AR14) exercise and make recommendations for future improvements. Incorporating a more realistic response in future scenarios by integrating a tactical response episode in the exercise is recommended.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Artificial intelligence in public health: the potential of epidemic early warning systems
Chandini Raina MacIntyre, Xin Chen, Mohana Kunasekaran, Ashley Quigley, Samsung Lim, Haley Stone, Hye-young Paik, Lina Yao, David Heslop, Wenzhao Wei, Ines Sarmiento, Deepti Gurdasani
Journal of International Medical Research.2023; 51(3): 030006052311593. CrossRef - Whole of government and whole of society approaches: call for further research to improve population health and health equity
Flaminia Ortenzi, Robert Marten, Nicole B Valentine, Aku Kwamie, Kumanan Rasanathan
BMJ Global Health.2022; 7(7): e009972. CrossRef - Biodefence research two decades on: worth the investment?
Carrie M Long, Andrea Marzi
The Lancet Infectious Diseases.2021; 21(8): e222. CrossRef
- Artificial intelligence in public health: the potential of epidemic early warning systems
- Cost of Tuberculosis Treatment: Evidence from Iran’s Health System
- Vahid Bay, Payam Tabarsi, Aziz Rezapour, Sima Marzban, Ehsan Zarei
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2017;8(5):351-357. Published online October 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2017.8.5.09
- 4,671 View
- 39 Download
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives This study aimed to estimate the cost of smear-positive drug-susceptible pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) treatment of the patients in the Azadshahr district, Golestan Province, Iran.
Methods In this retrospective study, all new smear positive pulmonary TB patients who had been registered at the district’s health network between April, 2013 and December, 2015 and had successfully completed their treatment were entered into the study (45 patients). Treatment costs were estimated from the provider’s perspective using an activity-based costing (ABC) method.
Results The cost of treating a new smear-positive pulmonary TB patient was US dollar (USD) 1,409.00 (Iranian Rial, 39,438,260), which can be divided into direct and indirect costs (USD 1,226.00 [87%] and USD 183.00 [13%], respectively). The highest cost (58.1%) was related to care and management of TB patients (including 46.1% human resources costs and 12% directly-observed treatment, short course implementation) and then respectively related to hospitalization (12.1%), supportive activity centers (11.4%), transportation (6.5%), medicines (5.3%), and laboratory tests and radiography (3.2%).
Conclusion Using disease-specific cost studies can help the healthcare system management to have correct insight into the financial burden created by the disease. This can subsequently be used in prioritization, planning, operational budgeting, economic evaluation of programs, interventions, and ultimately in disease management.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Costs of services and funding gap of the Bangladesh National Tuberculosis Control Programme 2016–2022: An ingredient based approach
Md. Zahid Hasan, Sayem Ahmed, Zeenat Islam, Farzana Dorin, Md. Golam Rabbani, Gazi Golam Mehdi, Mohammad Wahid Ahmed, Tazeen Tahsina, Shehrin Shaila Mahmood, Ziaul Islam, Kevin Schwartzman
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(6): e0286560. CrossRef - Distribution incidence, mortality of tuberculosis and human development index in Iran: estimates from the global burden of disease study 2019
Hossien Fallahzadeh, Zaher Khazaei, Moslem Lari Najafi, Sajjad Rahimi Pordanjani, Elham Goodarzi
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Spatio-temporal epidemiology of the tuberculosis incidence rate in Iran 2008 to 2018
Behzad Kiani, Amene Raouf Rahmati, Robert Bergquist, Soheil Hashtarkhani, Neda Firouraghi, Nasser Bagheri, Elham Moghaddas, Alireza Mohammadi
BMC Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - An Analysis of the Survival Probability of Tuberculosis Patients with Right Censored and Interval Censored Observation in Zahedan during 2014 - 2016
Mohammad Hossein Dehghan, Seyyed Mohammad Hashemi Shahri, Mojgan Salari
Zahedan Journal of Research in Medical Sciences.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Extent and determinants of catastrophic health expenditure for tuberculosis care in Chongqing municipality, China: a cross-sectional study
Weixia Duan, Wen Zhang, Chengguo Wu, Qingya Wang, Ya Yu, Hui Lin, Ying Liu, Daiyu Hu
BMJ Open.2019; 9(4): e026638. CrossRef - Demographic, socio-economic and behavior as risk factors of tuberculosis in Malaysia: a systematic review of the literature
Nur Adibah Mohidem, Zailina Hashim, Malina Osman, Rafiza Shaharudin, Farrah Melissa Muharam, Punitha Makeswaran
Reviews on Environmental Health.2018; 33(4): 407. CrossRef
- Costs of services and funding gap of the Bangladesh National Tuberculosis Control Programme 2016–2022: An ingredient based approach
- Trends and Characteristics of HIV Infection among Suspected Tuberculosis Cases in Public Health Centers in Korea: 2001–2013
- Meekyung Kee, Kyoung-Ho Lee, Sae-Young Lee, Chun Kang, Chaeshin Chu
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2014;5(Suppl):S37-S42. Published online December 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2014.11.002
- 2,856 View
- 18 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The Republic of Korea reports approximately 35,000 new tuberculosis (TB) patients each year, and the number of HIV-infected individuals is steadily increasing. Public health centers (PHCs) conduct TB diagnosis and treatment for risk groups in communities. This study aimed to identify possible trends and characteristics of HIV infection among suspected TB cases in PHCs.
Methods
Study subjects were suspected TB cases in PHCs who agreed to be tested for HIV from 2001 to 2013. Trends in HIV seroprevalence were assessed through a series of annual cross-sectional analyses. We analyzed suspected TB cases, and HIV-infected individuals among suspected TB cases, by gender, age, nationality, and region.
Results
The number of suspected tuberculosis cases who took an HIV test in PHCs was approximately 6,000 each year from 2001 to 2013. Among the suspected TB cases who took an HIV test, the number of those aged 20–39 is gradually decreasing, while the number of those aged 50–69 is increasing. During this period, 32 HIV-infected individuals were identified; the majority were men (94%), aged 30–49 (68%), Korean (94%), and residents in a metropolitan area (53%). HIV seroprevalence decreased from 8.2 per 10,000 persons in 2001 to 1.9 per 10,000 persons in 2013.
Conclusion
This study has identified trends and characteristics of HIV infection among suspected tuberculosis cases in PHCs. This national data provides a basis for public health policy for HIV and tuberculosis infections. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Is Tuberculosis Still the Number One Infectious Disease in Korea?
Hae-Wol Cho, Chaeshin Chu
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2014; 5: S1. CrossRef
- Is Tuberculosis Still the Number One Infectious Disease in Korea?
- Public Health Crisis Preparedness and Response in Korea
- Hye-Young Lee, Mi-Na Oh, Yong-Shik Park, Chaeshin Chu, Tae-Jong Son
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2013;4(5):278-284. Published online October 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2013.09.008
- 3,294 View
- 19 Download
- 21 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Since the 2006 Pandemic Influenza Preparedness and Response Plan according to the World Health Organization’s recommendation, the Republic of Korea has prepared and periodically evaluated the plan to respond to various public health crises including pandemic influenza. Korea has stockpiled 13,000,000 doses of antiviral drugs covering 26% of the Korean population and runs 519 isolated beds in 16 medical institutions. The division of public health crisis response in Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention are in charge of responding to public health crises caused by emerging infectious diseases including severe acute respiratory syndrome, avian influenza human infection, and pandemic influenza. Its job description includes preparing for emerging infectious diseases, securing medical resources during a crisis, activating the emergency response during the crisis, and fortification of capabilities of public health personnel. It could evolve into a comprehensive national agency to deal with public health crisis based on the experience of previous national emerging infectious diseases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Viral Entanglements
Timothy Gitzen
Current Anthropology.2023; 64(2): 172. CrossRef - No one left behind: risk communication to the street vendors during COVID-19 social distancing
Pham Tien Thanh, Hanh Thi Hong Nguyen, Le Thi Bao Ngan, Doan My Duyen Nguyen, Gia Han Phan, Thi My Nhung Nguyen
Library Hi Tech.2022; 40(2): 357. CrossRef - Spatial Variation in Risk for Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Subtype H5N6 Viral Infections in South Korea: Poultry Population-Based Case–Control Study
Saleem Ahmad, Kye-Young Koh, Dae-Sung Yoo, Jae-Il Lee
Veterinary Sciences.2022; 9(3): 135. CrossRef - The Evolution of Vigilance and Its Atrophy Preceding the COVID-19 Global Pandemic
Theodore J. Witek, Robert Schwartz
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Healthcare Workers’ Knowledge, Attitude, Practice and Perceived Health Facility Preparedness Regarding COVID-19 in Sierra Leone
Sulaiman Kanu, Peter Bai James, Abdulai Jawo Bah, John Alimamy Kabba, Musa Salieu Kamara, Christine Ellen Elleanor Williams, Joseph Sam Kanu
Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare.2021; Volume 14: 67. CrossRef - COVID-19 Pandemic in Hong Kong and Gaza Strip: Lessons Learned from Two Densely Populated Locations in the World
Hammoda Abu-Odah, Sheena Ramazanu, Eslam Saleh, Jonathan Bayuo, Yehia Abed, Motasem Said Salah
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2021; 12(1): 44. CrossRef - Citizens’ Opinion on Governmental Response to COVID-19 Outbreak: A Qualitative Study from Iran
Kamran Bagheri Lankarani, Behnam Honarvar, Ahmad Kalateh Sadati, Mohammad Reza Rahmanian Haghighi
INQUIRY: The Journal of Health Care Organization, .2021; 58: 004695802110249. CrossRef - The Korean government’s public health responses to the COVID-19 epidemic through the lens of industrial policy
Hee-Young Shin
International Review of Applied Economics.2021; 35(6): 851. CrossRef - Preparedness of Frontline Doctors in Jordan Healthcare Facilities to COVID-19 Outbreak
Aiman Suleiman, Isam Bsisu, Hasan Guzu, Abeer Santarisi, Murad Alsatari, Ala’ Abbad, Ahmad Jaber, Taima’a Harb, Ahmad Abuhejleh, Nisreen Nadi, Abdelkarim Aloweidi, Mahmoud Almustafa
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2020; 17(9): 3181. CrossRef - Lessons learned from Korea: COVID-19 pandemic
Hazhir Moradi, Atefeh Vaezi
Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology.2020; 41(7): 873. CrossRef - Lesson Learned from the Power of Open Data: Resolving the Mask Shortage Problem Caused by COVID-19 in South Korea
Haklae Kim
Sustainability.2020; 13(1): 278. CrossRef - A Systematic Narrative Review of Comprehensive Preparedness Strategies of Healthcare Resources for a Large Resurgence of COVID-19 Nationally, with Local or Regional Epidemics: Present Era and Beyond
Young Kyung Yoon, Jacob Lee, Sang Il Kim, Kyong Ran Peck
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Metapopulation model using commuting flow for national spread of the 2009 H1N1 influenza virus in the Republic of Korea
Jonggul Lee, Bo Youl Choi, Eunok Jung
Journal of Theoretical Biology.2018; 454: 320. CrossRef - Enhancing ‘Whole-of-Government’ Response to Biological Events in Korea: Able Response 2014
Sangwoo Tak, Anton Jareb, Suon Choi, Marvin Sikes, Yeon Hwa Choi, Hyeong-wook Boo
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2018; 9(1): 32. CrossRef - Mathematical model of transmission dynamics and optimal control strategies for 2009 A/H1N1 influenza in the Republic of Korea
Soyoung Kim, Jonggul Lee, Eunok Jung
Journal of Theoretical Biology.2017; 412: 74. CrossRef - Syndromic Surveillance System for Korea–US Joint Biosurveillance Portal: Design and Lessons Learned
Chulwoo Rhee, Howard Burkom, Chang-gyo Yoon, Miles Stewart, Yevgeniy Elbert, Aaron Katz, Sangwoo Tak
Health Security.2016; 14(3): 152. CrossRef - Changes of Global Infectious Disease Governance in 2000s: Rise of Global Health Security and Transformation of Infectious Disease Control System in South Korea
Eun Kyung CHOI, Jong-Koo LEE
Korean Journal of Medical History.2016; 25(3): 489. CrossRef - Crisis prevention and management by infection control nurses during the Middle East respiratory coronavirus outbreak in Korea
Jeong Sil Choi, Kyung Mi Kim
American Journal of Infection Control.2016; 44(4): 480. CrossRef - Ebola virus disease in nonendemic countries
Samson Sai-Yin Wong, Sally Cheuk-Ying Wong
Journal of the Formosan Medical Association.2015; 114(5): 384. CrossRef - A spatial–temporal transmission model and early intervention policies of 2009 A/H1N1 influenza in South Korea
Jonggul Lee, Eunok Jung
Journal of Theoretical Biology.2015; 380: 60. CrossRef - How to Manage a Public Health Crisis and Bioterrorism in Korea
Hae-Wol Cho, Chaeshin Chu
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2013; 4(5): 223. CrossRef
- Viral Entanglements
- Epidemic Intelligence Service Officers and Field Epidemiology Training Program in Korea
- Geun-Yong Kwon, Shinje Moon, Wooseok Kwak, Jin Gwack, Chaeshin Chu, Seung-Ki Youn
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2013;4(4):215-221. Published online August 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2013.07.001
- 3,446 View
- 22 Download
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Korea has adopted Epidemic Intelligence Service (EIS) officers through the Field Epidemiology Training Program (FETP) since 1999 for systematic control of emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases. Graduates of medical schools in Korea are selected and serve as public health doctors (PHDs) for their mandatory military service. The duration of service is 3 years and PHDs comprise general practitioners and specialists. Some PHDs are selected as EIS officers with 3 weeks basic FETP training and work for central and provincial public health authorities to conduct epidemiological investigations. The total number of EIS officers is 31 as of 2012. The Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (KCDC) has 12 specialists, whereas specialists and each province has one or two EIS officers to administer local epidemiological investigations in 253 public health centers. The Korean EIS officers have successfully responded and prevented infectious diseases, but there is a unique limitation: the number of PHDs in Korea is decreasing and PHDs are not allowed to stay outside Korea, which makes it difficult to cope with overseas infectious diseases. Furthermore, after 3 years service, they quit and their experiences are not accumulated. KCDC has hired full-time EIS officers since 2012 to overcome this limitation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A resposta da Coreia do Sul à pandemia de COVID-19: lições aprendidas e recomendações a gestores
Thais Regis Aranha Rossi, Catharina Leite Matos Soares, Gerluce Alves Silva, Jairnilson Silva Paim, Lígia Maria Vieira-da-Silva
Cadernos de Saúde Pública.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Turnover Intention among Field Epidemiologists in South Korea
Sukhyun Ryu
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2020; 17(3): 949. CrossRef - National Response to COVID-19 in the Republic of Korea and Lessons Learned for Other Countries
Juhwan Oh, Jong-Koo Lee, Dan Schwarz, Hannah L. Ratcliffe, Jeffrey F. Markuns, Lisa R. Hirschhorn
Health Systems & Reform.2020; 6(1): e1753464. CrossRef - Steering the Private Sector in COVID-19 Diagnostic Test Kit Development in South Korea
Sora Lee
Frontiers in Public Health.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Experience of 16 years and its associated challenges in the Field Epidemiology Training Program in Korea
Moo-Sik Lee, Eun-Young Kim, Sang-Won Lee
Epidemiology and Health.2017; 39: e2017058. CrossRef - The direction of restructuring of a Korea field epidemiology training program through questionnaire survey among communicable disease response staff in Korea
Moo Sik Lee, Kwan Lee, Jee-Hyuk Park, Jee-Young Hong, Min-Young Jang, Byoung-Hak Jeon, Sang-Yun Cho, Sun-Ja Choi, JeongIk Hong
Epidemiology and Health.2017; 39: e2017032. CrossRef - Review for the Korean Health Professionals and International Cooperation Doctors Dispatched to Peru by the Korea International Cooperation Agency (KOICA)
Bongyoung Kim
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2015; 6(2): 133. CrossRef - From Seoul to Lima: Korean Doctors in Peru
Hae-Wol Cho, Chaeshin Chu
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2015; 6(2): 71. CrossRef - Emerging Pathogens and Vehicles of Food- and Water-borne Disease Outbreaks in Korea, 2007–2012
Shinje Moon, Il-Woong Sohn, Yeongseon Hong, Hyungmin Lee, Ji-Hyuk Park, Geun-Yong Kwon, Sangwon Lee, Seung-Ki Youn
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2014; 5(1): 34. CrossRef
- A resposta da Coreia do Sul à pandemia de COVID-19: lições aprendidas e recomendações a gestores
- The Effects of Religious Attendance and Obesity on Health by Race/Ethnicity
- Sanggon Nam
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2013;4(2):81-88. Published online April 30, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2013.03.002
- 2,505 View
- 13 Download
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The objectives of this paper are to examine the effects of religion and obesity on health and determine how the relationship varies by racial/ethnic groups with data from the Panel Study of American Race and Ethnicity (PS-ARE).
Methods
Using ordinal logistic regression, the effects of religion and obesity on self-rated health and how the relationship varies by racial/ethnic groups are investigated. Additionally, to determine whether certain ethnic groups are more impacted by the frequency of religious attendance and obesity, whites, blacks, and Hispanics are analyzed separately with ordinal logistic regression.
Results
When obesity was added in focal relationship between religious services attendance and self-rated health strengthened this focal relationship which is a suppression effect between religious services attending and self-rated health adding obesity. For BMI is also significantly associated with decreased odds of reporting better health–normal weight (OR = 2.99; 95% CI = 2.43–3.67) and overweight (OR = 2.19; 95% CI = 1.79–2.68) compared to obese. Subjects who attend religious services 1–2 time a year (OR = 1.30; 95% CI = 1.04–1.62) and 1–3 times a month (OR = 1.28; 95% CI = 1.05–1.57) are associated with increased odds of reporting better health. In whites, attending religious services 1–2 times a year are associated with increased odds of reporting better health (OR = 1.48; 95% CI = 1.09–2.00) and 1–3 times a month are also associated with increased odds of reporting health (OR = 1.34; 95% CI = 1.02–1.78) compared to never attending religious attendance. The frequency of religious services attendance of blacks and Hispanics are not associated with self-rated health. For BMI, being white is more positively associated with increased odds of reporting better health than black and Hispanic subjects. Although white subjects are less likely to attend religious services more frequently than black and Hispanic subjects, the influence on self-rated health in white subjects is more evidenced than other racial/ethnic groups.
Conclusions
Although it was not proven that the association between participation in religious services and self-rated health is mediated by obesity, the research shows the suppression effect of obesity between participation in religious services and self-rated health. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Metabolically Healthy Obesity: Are Interventions Useful?
Bryan J. Mathis, Kiyoji Tanaka, Yuji Hiramatsu
Current Obesity Reports.2023; 12(1): 36. CrossRef - Racial/ethnic differences in the beneficial effect of social support on sleep duration
Dayna A. Johnson, Radhika Prakash-Asrani, Billye D. Lewis, Donald L. Bliwise, Tené T. Lewis
Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine.2023; 19(7): 1231. CrossRef - The Effect of Hajj Trip on Mental Health: A Longitudinal Study
Mansooreh Fateh, Seyed Abbas Mousavi, Mohammad Bagher Sohrabi, Mohsen Arabi, Mohammad Hassan Emamian
Journal of Religion and Health.2020; 59(3): 1319. CrossRef - The Role of Religious Behavior in Health Self-Management: A Community-Based Participatory Research Study
Jane Pfeiffer, Hong Li, Maybelline Martez, Tim Gillespie
Religions.2018; 9(11): 357. CrossRef - Impact of religious attendance on psychosocial outcomes for individuals with traumatic brain injury: A NIDILRR funded TBI Model Systems study
Angela Philippus, David Mellick, Therese O’Neil-Pirozzi, Thomas Bergquist, Yelena Guller Bodien, Angelle M. Sander, Laura E. Dreer, Joseph Giacino, Thomas Novack
Brain Injury.2016; 30(13-14): 1605. CrossRef
- Metabolically Healthy Obesity: Are Interventions Useful?



 First
First Prev
Prev


