Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- The role of lipids in the pathophysiology of coronavirus infections
- Milad Zandi, Parastoo Hosseini, Saber Soltani, Azadeh Rasooli, Mona Moghadami, Sepideh Nasimzadeh, Farzane Behnezhad
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2021;12(5):278-285. Published online October 15, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.0153
- 5,500 View
- 164 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 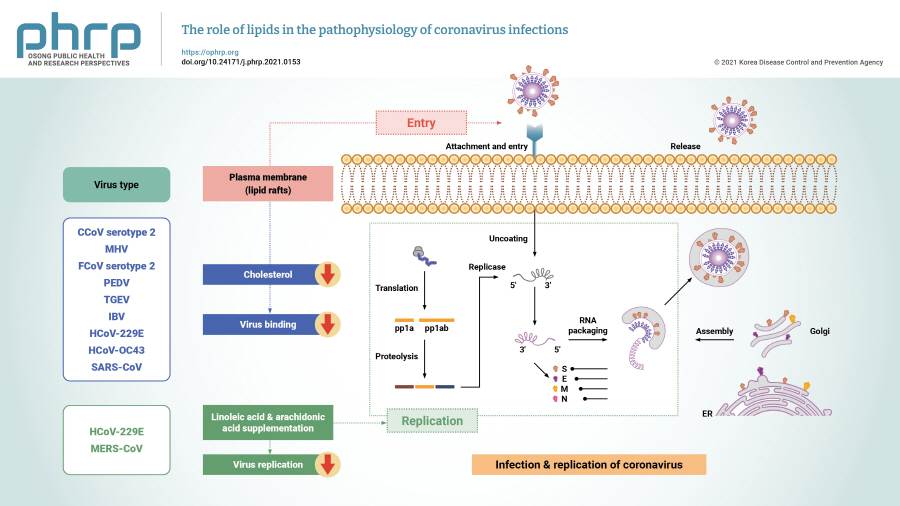
- Coronaviruses, which have been known to cause diseases in animals since the 1930s, utilize cellular components during their replication cycle. Lipids play important roles in viral infection, as coronaviruses target cellular lipids and lipid metabolism to modify their host cells to become an optimal environment for viral replication. Therefore, lipids can be considered as potential targets for the development of antiviral agents. This review provides an overview of the roles of cellular lipids in different stages of the life cycle of coronaviruses.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- PEDV inhibits HNRNPA3 expression by miR-218-5p to enhance cellular lipid accumulation and promote viral replication
Xiaojie Shi, Qi Zhang, Naling Yang, Quanqiong Wang, Yanxia Zhang, Xingang Xu, Xiang-Jin Meng, Ying Fang
mBio.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Orsay Virus Infection of Caenorhabditis elegans Is Modulated by Zinc and Dependent on Lipids
Luis Alberto Casorla-Perez, Ranya Guennoun, Ciro Cubillas, Bo Peng, Kerry Kornfeld, David Wang, Rebecca Ellis Dutch
Journal of Virology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- PEDV inhibits HNRNPA3 expression by miR-218-5p to enhance cellular lipid accumulation and promote viral replication
- Effects of Timely Control Intervention on the Spread of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Infection
- Ilsu Choi, Dong Ho Lee, Yongkuk Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2017;8(6):373-376. Published online December 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2017.8.6.03
- 4,270 View
- 29 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives The 2015 Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV) outbreak in Korea caused major economic and social problems. The control intervention was conducted during the MERS-CoV outbreak in Korea immediately after the confirmation of the index case. This study investigates whether the early risk communication with the general public and mass media is an effective preventive strategy.
Methods The SEIR (Susceptible, Exposed, Infectious, Recovered) model with estimated parameters for the time series data of the daily MERS-CoV incidence in Korea was considered from May to December 2015. For 10,000 stochastic simulations, the SEIR model was computed using the Gillespie algorithm. Depending on the time of control intervention on the 20th, 40th, and 60th days after the identification of the index case, the box plots of MERS-CoV incidences in Korea were computed, and the results were analyzed via ANOVA.
Results The box plots showed that there was a significant difference between the non-intervention and intervention groups (the 20th day, 40th day, and 60th day groups) and seemed to show no significant difference based on the time of intervention. However, the ANOVA revealed that early intervention was a good strategy to control the disease.
Conclusion Appropriate risk communication can secure the confidence of the general public in the public health authorities.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Healthcare-associated infections: the hallmark of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus with review of the literature
J.A. Al-Tawfiq, P.G. Auwaerter
Journal of Hospital Infection.2019; 101(1): 20. CrossRef
- Healthcare-associated infections: the hallmark of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus with review of the literature



 First
First Prev
Prev


