Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- The role of lipids in the pathophysiology of coronavirus infections
- Milad Zandi, Parastoo Hosseini, Saber Soltani, Azadeh Rasooli, Mona Moghadami, Sepideh Nasimzadeh, Farzane Behnezhad
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2021;12(5):278-285. Published online October 15, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.0153
- 5,502 View
- 164 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 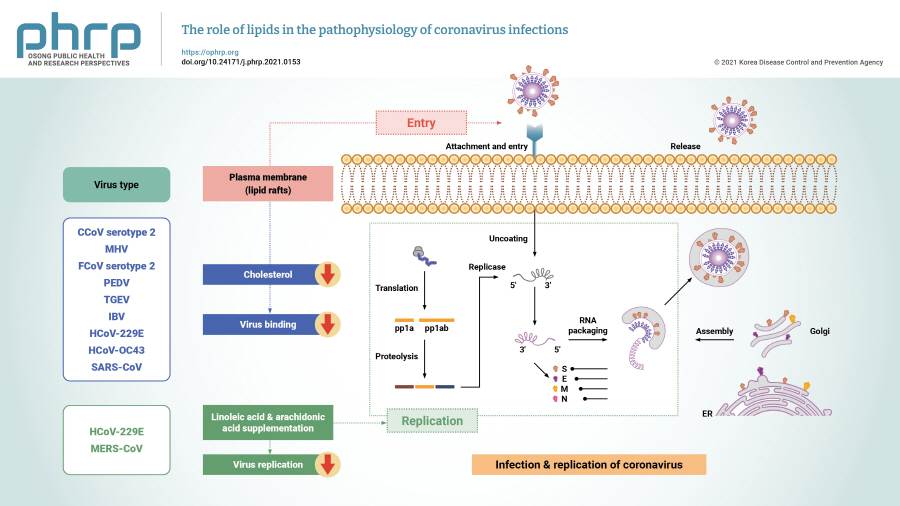
- Coronaviruses, which have been known to cause diseases in animals since the 1930s, utilize cellular components during their replication cycle. Lipids play important roles in viral infection, as coronaviruses target cellular lipids and lipid metabolism to modify their host cells to become an optimal environment for viral replication. Therefore, lipids can be considered as potential targets for the development of antiviral agents. This review provides an overview of the roles of cellular lipids in different stages of the life cycle of coronaviruses.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- PEDV inhibits HNRNPA3 expression by miR-218-5p to enhance cellular lipid accumulation and promote viral replication
Xiaojie Shi, Qi Zhang, Naling Yang, Quanqiong Wang, Yanxia Zhang, Xingang Xu, Xiang-Jin Meng, Ying Fang
mBio.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Orsay Virus Infection of Caenorhabditis elegans Is Modulated by Zinc and Dependent on Lipids
Luis Alberto Casorla-Perez, Ranya Guennoun, Ciro Cubillas, Bo Peng, Kerry Kornfeld, David Wang, Rebecca Ellis Dutch
Journal of Virology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- PEDV inhibits HNRNPA3 expression by miR-218-5p to enhance cellular lipid accumulation and promote viral replication
- Enrolment Phase Results of the Tabari Cohort Study: Comparing Family History, Lipids and Anthropometric Profiles Among Diabetic Patients
- Mahmood Moosazadeh, Mahdi Afshari, Kaveh Jafari, Motahareh Kheradmand, Zahra Kashi, Mohsen Aarabi, Adeleh Bahar, Mohammad Khademloo
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2019;10(5):289-294. Published online October 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2019.10.5.05
- 5,275 View
- 62 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives Different factors are responsible for the silent epidemic of diabetes mellitus in developing and developed countries. This study aimed to determine the role of demographic factors, lipid profile, family history (the estimation of genetic association) and anthropometric factors on diabetes onset.
Methods Data from the enrolment phase of the Tabari Cohort study was applied for this study and included 10,255 participants aged between 35–70 years. Anthropometric variables were measured by trained staff using standard tools. Blood specimens were collected for lipid profile and blood glucose measurements. Data analyses were performed using SPSS version 24, with univariate and multivariate logistic regression.
Results The prevalence of diabetes mellitus was estimated to be 17.2% in the cohort population, 15.6% in men, and 18.3% in women. The adjusted odds ratios (95% confidence intervals) for age groups 40–49, 50–59 and over 60 were 2.58 (2.20–3.69), 5.80 (4.51–7.48) and 8.72 (6.67–11.39), respectively. In addition, the odds ratios (95% confidence intervals) for 2 (or more), and 1 affected family member were 4.12 (3.55–4.90) and 2.34 (2.07–2.65), respectively. Triglyceride concentrations more than 500, and abnormal high-density lipoprotein levels increased the odds of diabetes mellitus by 3.29- and 1.18-fold, respectively.
Conclusion The current study showed that old age and a family history were strong predictors for diabetes mellitus.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The relationship between spiritual intelligence and self-management in patients with diabetes type 1
Sima Rafiei, Saber Souri, Zahra Nejatifar, Mohammad Amerzadeh
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence and determinants of diabetes and prediabetes in southwestern Iran: the Khuzestan comprehensive health study (KCHS)
Sanam Hariri, Zahra Rahimi, Nahid Hashemi-Madani, Seyyed Ali Mard, Farnaz Hashemi, Zahra Mohammadi, Leila Danehchin, Farhad Abolnezhadian, Aliasghar Valipour, Yousef Paridar, Mohammad Mahdi Mir-Nasseri, Alireza Khajavi, Sahar Masoudi, Saba Alvand, Bahman
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- The relationship between spiritual intelligence and self-management in patients with diabetes type 1



 First
First Prev
Prev


