Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- The COVID-19 pandemic and healthcare utilization in Iran: evidence from an interrupted time series analysis
- Monireh Mahmoodpour-Azari, Satar Rezaei, Nasim Badiee, Mohammad Hajizadeh, Ali Mohammadi, Ali Kazemi-Karyani, Shahin Soltani, Mehdi Khezeli
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(3):180-187. Published online June 22, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0041
- 1,341 View
- 66 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 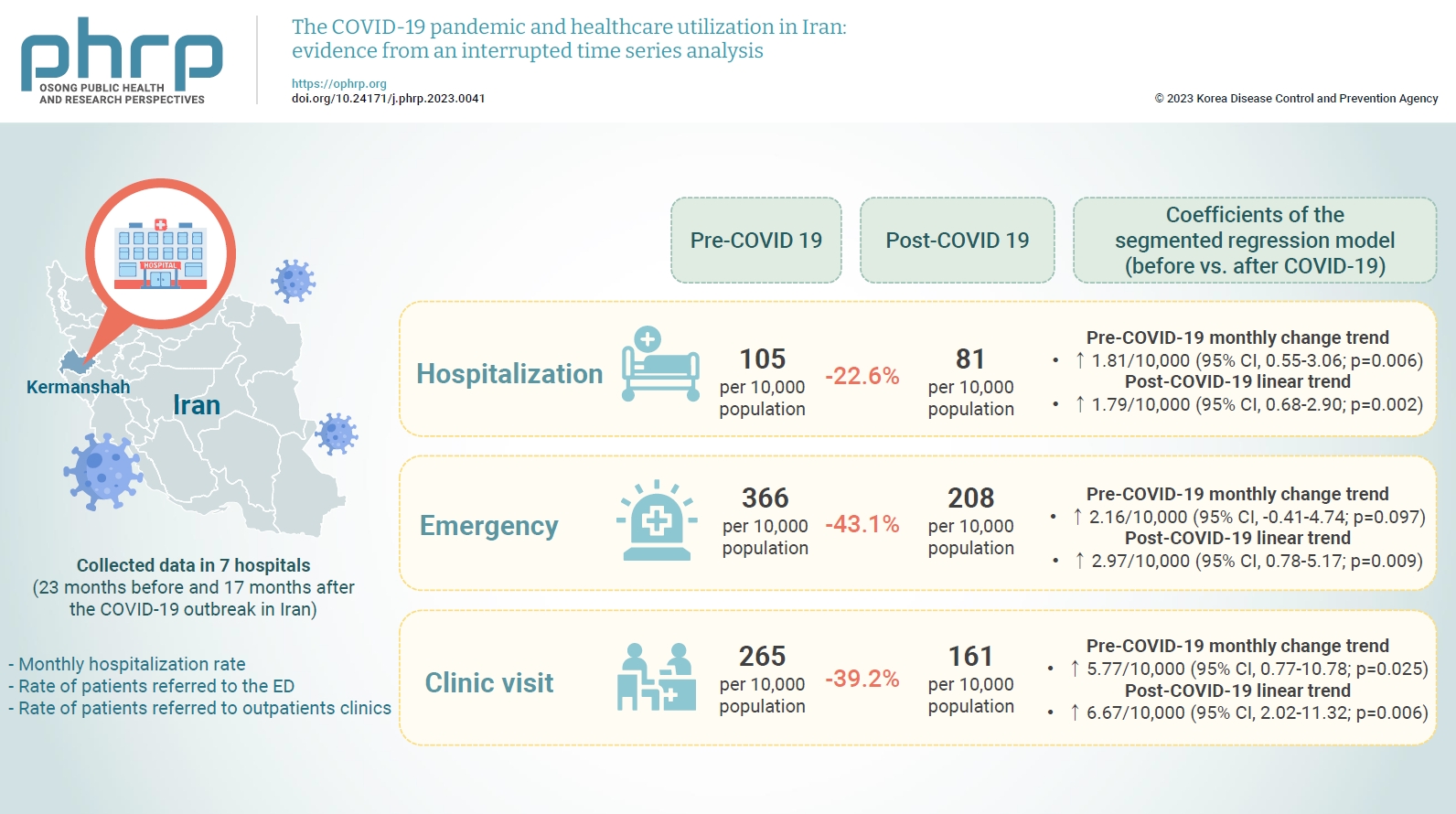
- Objectives
This study aimed to examine the effect of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak on the hospitalization rate, emergency department (ED) visits, and outpatient clinic visits in western Iran.
Methods
We collected data on the monthly hospitalization rate, rate of patients referred to the ED, and rate of patients referred to outpatient clinics for a period of 40 months (23 months before and 17 months after the COVID-19 outbreak in Iran) from all 7 public hospitals in the city of Kermanshah. An interrupted time series analysis was conducted to examine the impact of COVID-19 on the outcome variables in this study.
Results
A statistically significant decrease of 38.11 hospitalizations per 10,000 population (95% confidence interval [CI], 24.93–51.29) was observed in the first month of the COVID-19 outbreak. The corresponding reductions in ED visits and outpatient visits per 10,000 population were 191.65 (95% CI, 166.63–216.66) and 168.57 (95% CI, 126.41–210.73), respectively. After the initial reduction, significant monthly increases in the hospitalization rate (an increase of 1.81 per 10,000 population), ED visits (an increase of 2.16 per 10,000 population), and outpatient clinic visits (an increase of 5.77 per 10,000 population) were observed during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Conclusion
Our study showed that the utilization of outpatient and inpatient services in hospitals and clinics significantly declined after the COVID-19 outbreak, and use of these services did not return to pre-outbreak levels as of June 2021.
- The Occurrence and Risk Assessment of Exposure to Aflatoxin M1 in Ultra-High Temperature and Pasteurized Milk in Hamadan Province of Iran
- Amir Sasan Mozaffari Nejad, Ali Heshmati, Tayebe Ghiasvand
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2019;10(4):228-233. Published online August 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2019.10.4.05
- 7,002 View
- 151 Download
- 24 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives Aflatoxins are a category of poisonous compounds found in most plants, milk and dairy products. The present research was carried out to detect the presence of aflatoxin M1 (AFM1) in samples of milk collected from Hamadan province, Iran.
Methods Twenty five samples of ultra-high temperature (UHT) and 63 samples of pasteurized milk were collected and the amount of AFM1 was measured by an Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay method. In addition, the estimated daily intake (EDI) and hazard index (HI) of AFM1 was determined by the following equations:(EDI= mean concentration of AFM1 × daily consumption of milk/body weight; HI= EDI/Tolerance Daily Intake).
Results AFM1 was detected in 21 (84%) UHT milk samples and in 55 (87.30%) pasteurized milk samples. Seven (28%) samples of UHT and 21 (33.33%) pasteurized milk samples had higher AFM1 content than the limit allowed in the European Union and Iranian National Standard Limits (0.05 μg/kg). None of the samples exceeded the US Food and Drug Administration limit (0.5 μg/kg) for AFM1. EDI and HI for AM1 through milk were 0.107 ng/kg body weight/day, and 0.535, respectively.
Conclusion A significant percentage of milk produced by different factories in Iran (84% of UHT and 87.3% of pasteurized milk) was contaminated with AFM1. Therefore, more control and monitoring of livestock feeding in dairy companies may help reduce milk contamination with AFM1. As the HI value was lower than 1, it can be assumed that there was no risk of developing liver cancer due to milk consumption.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Seasonal variation and risk assessment of exposure to aflatoxin M1 in milk, yoghurt, and cheese samples from Ilam and Lorestan Provinces of Iran
Kousar Aghebatbinyeganeh, Mohammadhosein Movassaghghazani, Mohamed Fathi Abdallah
Journal of Food Composition and Analysis.2024; 128: 106083. CrossRef - Review, meta-analysis and carcinogenic risk assessment of aflatoxin M1 in different types of milks in Iran
Fatemeh Mortezazadeh, Fathollah Gholami-Borujeni
Reviews on Environmental Health.2023; 38(3): 511. CrossRef - Molecular identification and biocontrol of ochratoxigenic fungi and ochratoxin A in animal feed marketed in the state of Qatar
Fatma Ali Alsalabi, Zahoor Ul Hassan, Roda F. Al-Thani, Samir Jaoua
Heliyon.2023; 9(1): e12835. CrossRef - Risk assessments for the dietary intake aflatoxins in food: A systematic review (2016–2022)
Kiran Bhardwaj, Julie P. Meneely, Simon A. Haughey, Moira Dean, Patrick Wall, Guangtao Zhang, Bob Baker, Christopher T. Elliott
Food Control.2023; 149: 109687. CrossRef - A systematic literature review for aflatoxin M1 of various milk types in Iran: Human health risk assessment, uncertainty, and sensitivity analysis
Tooraj Massahi, Amir Kiani, Kiomars Sharafi, Behzad Karami Matin, Abdullah Khalid Omer, Gholamreza Ebrahimzadeh, Jalil Jaafari, Nazir Fattahi
Food Control.2023; 150: 109733. CrossRef - The occurrence of aflatoxin M1 in milk samples of Iran: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Neda Mollakhalili-Meybodi, Amene Nematollahi
Environmental Monitoring and Assessment.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of basil seed and xanthan gum on physicochemical, textural, and sensory characteristics of low‐fat cream cheese
Jalal Portaghi, Ali Heshmati, Mehdi Taheri, Ebrahim Ahmadi, Amin Mousavi Khaneghah
Food Science & Nutrition.2023; 11(10): 6060. CrossRef - Evaluation of aflatoxin M1 content in milk and dairy products by high-performance liquid chromatography in Tehran, Iran
Nazanin SHABANSALMANİ, Mohammadhosein MOVASSAGHGHAZANİ
Harran Tarım ve Gıda Bilimleri Dergisi.2023; 27(3): 435. CrossRef - Seasonal Study of Aflatoxin M1 Contamination in Cow Milk on the Retail Dairy Market in Gorgan, Iran
Hadi Rahimzadeh Barzoki, Hossein Faraji, Somayeh Beirami, Fatemeh Zahra Keramati, Gulzar Ahmad Nayik, Zahra Izadi Yazdanaabadi, Amir Sasan Mozaffari Nejad
Dairy.2023; 4(4): 571. CrossRef - Aflatoxin M1 in milk and dairy products: global occurrence and potential decontamination strategies
Khurram Muaz, Muhammad Riaz, Carlos Augusto Fernandes de Oliveira, Saeed Akhtar, Shinawar Waseem Ali, Habibullah Nadeem, Sungkwon Park, Balamuralikrishnan Balasubramanian
Toxin Reviews.2022; 41(2): 588. CrossRef - Feed to fork risk assessment of mycotoxins under climate change influences - recent developments
Rhea Sanjiv Chhaya, John O'Brien, Enda Cummins
Trends in Food Science & Technology.2022; 126: 126. CrossRef - The behavior of aflatoxin M1 during lactic cheese production and storage
Mahtab Einolghozati, Ali Heshmati, Freshteh Mehri
Toxin Reviews.2022; 41(4): 1163. CrossRef - Exposure assessment on aflatoxin M1 from milk and dairy products-relation to public health
Eleni Malissiova, Georgia Soultani, Konstantina Tsokana, Mary Alexandraki, Athanasios Manouras
Clinical Nutrition ESPEN.2022; 47: 189. CrossRef - Aflatoxin M1 in distributed milks in northwestern Iran: occurrence, seasonal variation, and risk assessment
Seyyed Ahmad Mokhtari, Ali Nemati, Mehdi Fazlzadeh, Eslam Moradi-Asl, Vahid Taefi Ardabili, Anoshirvan Seddigh
Environmental Science and Pollution Research.2022; 29(27): 41429. CrossRef - Brucellosis in Humans with the Approach of Brucella Species Contamination in Unpasteurized Milk and Dairy Products from Hamadan, Iran
Mohammad Mahdi Majzobi, Pejman Karami, Amir Khodavirdipour, Mohammad Yousef Alikhani
Iranian Journal of Medical Microbiology.2022; 16(4): 282. CrossRef - Probabilistic modeling and risk characterization of the chronic aflatoxin M1 exposure of Hungarian consumers
Zsuzsa Farkas, Kata Kerekes, Árpád Ambrus, Miklós Süth, Ferenc Peles, Tünde Pusztahelyi, István Pócsi, Attila Nagy, Péter Sipos, Gabriella Miklós, Anna Lőrincz, Szilveszter Csorba, Ákos Bernard Jóźwiak
Frontiers in Microbiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The occurrence of aflatoxin M1 in doogh, kefir, and kashk in Hamadan, Iran
Mina KHORSHIDI, Ali HESHMATI, Zahra HADIAN, Slim SMAOUI, Amin MOUSAVI KHANEGHAH
Food Science and Technology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Characterization and mechanism of aflatoxin degradation by a novel strain of Trichoderma reesei CGMCC3.5218
Xiaofeng Yue, Xianfeng Ren, Jiayun Fu, Na Wei, Claudio Altomare, Miriam Haidukowski, Antonio F. Logrieco, Qi Zhang, Peiwu Li
Frontiers in Microbiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Simultaneous multi-determination of pesticide residues in black tea leaves and infusion: a risk assessment study
Ali Heshmati, Fereshteh Mehri, Amin Mousavi Khaneghah
Environmental Science and Pollution Research.2021; 28(11): 13725. CrossRef - Development of a specific anti-idiotypic nanobody for monitoring aflatoxin M1 in milk and dairy products
Chong Cai, Qi Zhang, Seyni Nidiaye, Honglin Yan, Wen Zhang, Xiaoqian Tang, Peiwu Li
Microchemical Journal.2021; 167: 106326. CrossRef - Prevalence of aflatoxin M1 in pasteurized and ultra-high temperature (UHT) milk marketed in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania
F. Mwakosya Hilda, K. Mugula Jovin
African Journal of Microbiology Research.2021; 15(9): 461. CrossRef - Multi-mycotoxin occurrence in feed, metabolism and carry-over to animal-derived food products: A review
J. Tolosa, Y. Rodríguez-Carrasco, M.J. Ruiz, P. Vila-Donat
Food and Chemical Toxicology.2021; 158: 112661. CrossRef - Presence of Aflatoxin M1 in Commercial Milk in Paraguay
Andrea Alejandra Arrúa, Pablo David Arrúa, Juliana Moura-Mendes, Cinthia Cazal, Francisco Paulo Ferreira, Cristhian Javier Grabowski, Horacio Daniel Lopez-Nicora, Danilo Fernández Rios
Journal of Food Protection.2021; 84(12): 2128. CrossRef - The Occurrence and Risk Assessment of Aflatoxin M1 in Yoghurt Samples from Hamadan, Iran
Ali Heshmati, Amir Sasan Mozaffari Mozaffari Nejad, Tayebeh Ghyasvand
The Open Public Health Journal.2020; 13(1): 512. CrossRef
- Seasonal variation and risk assessment of exposure to aflatoxin M1 in milk, yoghurt, and cheese samples from Ilam and Lorestan Provinces of Iran
- Seroprevalence of
Toxocara in Children from Urban and Rural Areas of Ilam Province, West Iran - Sahar Shokouhi, Jahangir Abdi
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2018;9(3):101-104. Published online June 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2018.9.3.03
- 11,095 View
- 101 Download
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives The present study was performed to determine the seroprevalence of
Toxocara in children ≤ 10 years old, from rural and urban areas of Ilam.Methods Serum samples from 383 children ≤ 10 years old, were selected randomly from rural and urban areas of Ilam province and surveyed using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays.
Results The total rate of infection with
Toxocara was 22% (31% with a history of contact with dogs and cats, and 14% without a history of contact). Of those infected, 23% were male and 18% were female, 36% lived a rural life and 20% had an urban life. A significant correlation was found between the incidence of disease, and urban and rural life, as well as exposure to dogs and cats. There was no correlation between prevalence and gender or age.Conclusion Given the high prevalence of infection with
Toxocara amongst children in Ilam province, preventive work in the community such as education in risk management and periodic treatment with anti-parasitic drugs and elimination of stray dogs and cats is an appropriate measure.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Seroprevalence and Potential Risk Factors of Toxocariasis among General Population in Southwest Iran: Implications on the One Health Approach
Masoud Foroutan, Aida Vafae Eslahi, Shahrzad Soltani, Naser Kamyari, Ehsan Moradi-Joo, Jean-Francois Magnaval, Milad Badri, Rahul Shivahare
Journal of Immunology Research.2024; 2024: 1. CrossRef - Maternal COVID-19 infection and the fetus: Immunological and neurological perspectives
Shahab Falahi, Amir Abdoli, Azra Kenarkoohi
New Microbes and New Infections.2023; 53: 101135. CrossRef - Seroprevalence of Toxocariasis and Its Associated Risk Factors among Adult Population in Kavar District, Fars Province, South of Iran: A Cross-Sectional Community-Based Seroepidemiological Survey
Fatemehsadat Pezeshkian, Ali Pouryousef, Mostafa Omidian, Fattaneh Mikaeili, Ali Reza Safarpour, Sara Shojaei-Zarghani, Bahador Sarkari, Payam Behzadi
Interdisciplinary Perspectives on Infectious Disea.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Real‐time impact of COVID‐19 pandemic on cutaneous leishmaniasis case finding and strategic planning, preventive interventions, control and epidemiology in a region with a high burden of cutaneous leishmaniasis and COVID‐19: A cross‐sectional descriptive
Morteza Shams, Ayoub Rashidi, Jasem Mohamadi, Mohamad Moradi, Reza Pakzad, Razi Naserifar, Jahangir Abdi, Fariba Ghelichi, Arezoo Bozorgomid, Nahid Maspi, Azra Kenarkoohi, Yasin Mohammadi, Amir Abdoli, Shahab Falahi
Health Science Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Presence of CRISPR CAS-Like Sequences as a Proposed Mechanism for Horizontal Genetic Exchanges between Trichomonas vaginalis and Its Associated Virus: A Comparative Genomic Analysis with the First Report of a Putative CRISPR CAS Structures in Eukaryotic C
Azra Kenarkoohi, Amir Abdoli, Arman Rostamzad, Mahmoud Rashnavadi, Razi Naserifar, Jahangir Abdi, Morteza Shams, Arezoo Bozorgomid, Sepideh Saeb, Dhurgham Al-Fahad, Kosar Khezri, Shahab Falahi, Shibiao Wan
BioMed Research International.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Seroprevalence and risk factors of Toxocara canis infection in children aged 2–15 years from the southwest Iran
Masoud Foroutan, Shahrzad Soltani, Samaneh Bahadoram, Fatemeh Maghsoudi, Naser Kamyari, Shekoufe Haddadi
Comparative Immunology, Microbiology and Infectiou.2022; 85: 101801. CrossRef - Seroprevalence of Toxocara spp. in children (3–13 years old) in Zahedan, Southeast of Iran
Alireza Salimi Khorashad, Majid Shahraki, Mansour Rahmati Balaghaleh, Samaneh Abdolahi Khabisi, Sangeetha Rala, Reza Shafiei, Hadi Mirahmadi
Journal of Parasitic Diseases.2021; 45(2): 449. CrossRef - The global prevalence of Toxocara spp. in pediatrics: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Behnam Abedi, Mehran Akbari, Sahar KhodaShenas, Alireza Tabibzadeh, Ali Abedi, Reza Ghasemikhah, Marzieh Soheili, Shnoo Bayazidi, Yousef Moradi
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics.2021; 64(11): 575. CrossRef - Seroprevalence and associated risk factors of toxocariasis among nomads in Boyer-Ahmad County, southwest Iran
Nasir Arefkhah, Mohammad Reza Shadzi, Fattaneh Mikaeili, Bahador Sarkari, Farideh Esfandiari, Fatemeh Goudarzi
Transactions of The Royal Society of Tropical Medi.2020; 114(5): 372. CrossRef - Seroprevalence of anti-Toxocara antibody among multiple sclerosis patients: a case–control study
Nastaran Khalili, Neda Khalili, Ali Nickhah, Bahman Khalili
Journal of Parasitic Diseases.2020; 44(1): 145. CrossRef - Seroprevalence of toxocariasis and its related risk factors among municipal street sweepers in Shiraz District in Fars Province, southern Iran
Amirhossein Erfani, Ali Pouryousef, Nasir Arefkhah, Reza Shahriarirad, Mohammad Rastegarian, Ali Zeighami, Fattaneh Mikaeili, Seyed Younes Hosseini, Bahador Sarkari
Clinical Epidemiology and Global Health.2020; 8(2): 643. CrossRef - Toxocara infection: seroprevalence and associated risk factors among primary school children in central China
Shuai Wang, Haoran Li, Zhijun Yao, Pengju Li, Dong Wang, Haizhu Zhang, Qing Xie, Zhenchao Zhang, Xiangrui Li
Parasite.2020; 27: 30. CrossRef - Status of human toxocariasis, a neglected parasitic zoonosis in Iran: a systematic review from past to current
Reza Shafiei, Mohammad T Rahimi, Reza Zolfaghari Emameh, Mehdi Mirzaei, Gregorio Perez-Cordon, Ehsan Ahmadpour
Tropical Doctor.2020; 50(4): 285. CrossRef
- Seroprevalence and Potential Risk Factors of Toxocariasis among General Population in Southwest Iran: Implications on the One Health Approach
- Factors Associated with Cesarean Section in Tehran, Iran using Multilevel Logistic Regression Model
- Payam Amini, Maryam Mohammadi, Reza Omani-Samani, Amir Almasi-Hashiani, Saman Maroufizadeh
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2018;9(2):86-92. Published online April 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2018.9.2.08
- 5,525 View
- 62 Download
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives Over the past few decades, the prevalence of cesarean sections (CS) have risen dramatically worldwide, particularly in Iran. The aim of this study was to determine the prevalence of CS in Tehran, and to examine the associated risk factors.
Methods A cross-sectional study of 4,308 pregnant women with singleton live-births in Tehran, Iran, between July 6–21, 2015 was performed. Multilevel logistic regression analysis was performed using demographic and obstetrical variables at the first level, and hospitals as a variable at the second level.
Results The incidence of CS was 72.0%. Multivariate analysis showed a significant relationship between CS and the mother’s age, socioeconomic status, body mass index, parity, type of pregnancy, preeclampsia, infant height, and baby’s head circumference. The intra-class correlation using the second level variable, the hospital was 0.292, indicating approximately 29.2% of the total variation in the response variable accounted for by the hospital.
Conclusion The incidence of CS was substantially higher than other countries. Therefore, educational and psychological interventions are necessary to reduce CS rates amongst pregnant Iranian women.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Determinants of cesarean mode of childbirth among Rwandan women of childbearing age: Evidence from the 2019–2020 Rwanda Demographic and Health Survey (RDHS)
Nsereko Etienne, Uwase Aline, Mpinganzima Ornella, Usanzineza Henriette, Niyitegeka Jean Pierre, Turabayo Jean Léonard, Mwiseneza Marie Josee, Mugeni Girimpundu Candide, Moreland Patricia
Public Health Challenges.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Virtual Reality, Fear of Pain and Labor Pain Intensity: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Halimeh Mohammadi, Javad Rasti, Elham Ebrahimi
Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The double burden of maternal overweight and short stature and the likelihood of cesarean deliveries in South Asia: An analysis of national datasets from Bangladesh, India, Maldives, Nepal, and Pakistan
Mosiur Rahman, Syed Emdadul Haque, Md. Jahirul Islam, Nguyen Huu Chau, Izzeldin Fadl Adam, Md. Nuruzzaman Haque
Birth.2022; 49(4): 661. CrossRef - Geospatial analysis of cesarean section in Iran (2016–2020): exploring clustered patterns and measuring spatial interactions of available health services
Alireza Mohammadi, Elahe Pishgar, Zahra Salari, Behzad Kiani
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors associated with cesarean delivery in Bangladesh: A multilevel modeling
Md. Akhtarul Islam, Mst. Tanmin Nahar, Md. Ashfikur Rahman, Sutapa Dey Barna, S.M. Farhad Ibn Anik
Sexual & Reproductive Healthcare.2022; 34: 100792. CrossRef - The Birth Satisfaction Scale-Revised Indicator (BSS-RI): a validation study in Iranian mothers
Reza Omani-Samani, Caroline J. Hollins Martin, Colin R. Martin, Saman Maroufizadeh, Azadeh Ghaheri, Behnaz Navid
The Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine.2021; 34(11): 1827. CrossRef - The effect of familiarization with preoperative care on anxiety and vital signs in the patient’s cesarean section: A randomized controlled trial
Mehrnush Mostafayi, Behzad Imani, Shirdel Zandi, Faeze Jongi
European Journal of Midwifery.2021; 5(June): 1. CrossRef - Dynamic prediction of liver cirrhosis risk in chronic hepatitis B patients using longitudinal clinical data
Ying Wang, Xiang-Yong Li, Li-Li Wu, Xiao-Yan Zheng, Yu Deng, Meng-Jie Li, Xu You, Yu-Tian Chong, Yuan-Tao Hao
European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology.2020; 32(1): 120. CrossRef - Factors Contributing to Iranian Pregnant Women’s Tendency to Choice Cesarean Section
Soraya Nouraei Motlagh, Zahra Asadi-piri, Razyeh Bajoulvand, Fatemeh Seyed Mohseni, Katayoun Bakhtiar, Mehdi Birjandi, Maryam Mansouri
Medical - Surgical Nursing Journal.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Trends and correlates of cesarean section rates over two decades in Nepal
Aliza K. C. Bhandari, Bibha Dhungel, Mahbubur Rahman
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Symptoms of Discomfort and Problems Associated with Mode of Delivery During the Puerperium: An Observational Study
Martínez-Galiano, Delgado-Rodríguez, Rodríguez-Almagro, Hernández-Martínez
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2019; 16(22): 4564. CrossRef
- Determinants of cesarean mode of childbirth among Rwandan women of childbearing age: Evidence from the 2019–2020 Rwanda Demographic and Health Survey (RDHS)
- Profiling of Virulence-associated Factors in
Shigella Species Isolated from Acute Pediatric Diarrheal Samples in Tehran, Iran - Sajad Yaghoubi, Reza Ranjbar, Mohammad Mehdi Soltan Dallal, Somayeh Yasliani Fard, Mohammad Hasan Shirazi, Mahmood Mahmoudi
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2017;8(3):220-226. Published online June 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2017.8.3.09
- 4,480 View
- 61 Download
- 17 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives The genus
Shigella comprises the most infectious and diarrheagenic bacteria causing severe diseases, mostly in children under five years of age. This study aimed to detect nine virulence genes (ipaBCD ,VirA ,sen ,set1A ,set1B ,ial ,ipaH ,stx , andsat ) inShigella species (spp.) using multiplex polymerase chain reaction (MPCR) and to determine the relation ofShigella spp. from pediatric diarrheal samples with hospitalization and bloody diarrhea in Tehran, Iran.Methods Shigella spp. were isolated and identified using standard microbiological and serological methods. The virulence genes were detected using MPCR.Results Seventy-five
Shigella spp. (40S. sonnei , 33S. flexneri , 1S. dysenteriae , and 1S. boydii ) were isolated in this study. The prevalence ofial ,sen ,sat ,set1A , andset1B was 74.7%, 45.4%, 28%, 24%, and 24%, respectively. AllS. flexneri isolates, while noS. sonnei ,S. dysenteriae , orS. boydii isolates, containedsat ,set1A , andset1B . All isolates were positive foripaH ,ipaBCD , andvirA , while one (1.4%) of the isolates containedstx . The highest prevalence of virulence determinants was found inS. flexneri serotype IIa. Nineteen (57.6%) of 33S. flexneri isolates were positive foripaBCD ,ipaH ,virA ,ial , andsat . Thesen determinants were found to be statistically significantly associated with hospitalization and bloody diarrhea (p = 0.001).Conclusion This study revealed a high prevalence of enterotoxin genes in
S. flexneri , especially in serotype 2a, and has presented relations between a few clinical features of shigellosis and numerous virulence determinants of clinical isolates ofShigella spp.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Epidemiological analysis and prevention strategies in response to a shigellosis cluster outbreak: a retrospective case series in an alternative school in the Republic of Korea, 2023
Yeongseo Ahn, Sunmi Jin, Gemma Park, Hye Young Lee, Hyungyong Lee, Eunkyung Shin, Junyoung Kim, Jaeil Yoo, Yuna Kim
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2024; 15(1): 68. CrossRef - Invasion of HeLa Cells by Shigella Species Clinical Isolates Recovered from Pediatric Diarrhea
Zohreh Ghalavand, Marzieh Taheri, Gita Eslami, Mohammadmahdi Karimi-Yazdi, Mehrzad Sadredinamin
Foodborne Pathogens and Disease.2023; 20(11): 509. CrossRef - Plant-derived nanoparticles as alternative therapy against Diarrheal pathogens in the era of antimicrobial resistance: A review
Tesleem Olatunde Abolarinwa, Daniel Jesuwenu Ajose, Bukola Opeyemi Oluwarinde, Justine Fri, Kotsoana Peter Montso, Omolola Esther Fayemi, Adeyemi Oladapo Aremu, Collins Njie Ateba
Frontiers in Microbiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Distribution of genes encoding virulence factors of Shigella strains isolated from children with diarrhea in southwest Iran
Nabi Jomehzadeh, Khadijah Ahmadi, Hazhir Javaherizadeh, Maryam Afzali
Molecular Biology Reports.2021; 48(2): 1645. CrossRef - Evaluate the distribution of virulence genes and to investigate antibiotic resistance pattern among Shigella species isolated from children with shigellosis in Iran
Samane Mohebi, Hossein Hosseini Nave, Kasra Javadi, Ali Amanati, Soudeh Kholdi, Mahtab Hadadi, Zahra Hashemizadeh, Mohammad Motamedifar
Gene Reports.2021; 23: 101189. CrossRef - Burden, Antibiotic Resistance, and Clonality of Shigella spp. Implicated in Community-Acquired Acute Diarrhoea in Lilongwe, Malawi
Abel F.N.D. Phiri, Akebe Luther King Abia, Daniel Gyamfi Amoako, Rajab Mkakosya, Arnfinn Sundsfjord, Sabiha Y. Essack, Gunnar Skov Simonsen
Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease.2021; 6(2): 63. CrossRef - Frequency and Antimicrobial Resistance of Shigella Species in Iran During 2000-2020
Farhad Moradi, Nahal Hadi, Maryam Akbari, Zahra Hashemizadeh, Reyhaneh Rouhi Jahromi
Jundishapur Journal of Health Sciences.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Virulence factors and molecular characteristics of Shigella flexneri isolated from calves with diarrhea
Zhen Zhu, Weiwei Wang, Mingze Cao, Qiqi Zhu, Tenghe Ma, Yongying Zhang, Guanhui Liu, Xuzheng Zhou, Bing Li, Yuxiang Shi, Jiyu Zhang
BMC Microbiology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef -
Development of quinolone resistance and prevalence of different virulence genes among
Shigella flexneri
and
Shigella dysenteriae
in environmental water samples
B. Roy, S.K. Tousif Ahamed, B. Bandyopadhyay, N. Giri
Letters in Applied Microbiology.2020; 71(1): 86. CrossRef High Rates of Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence Gene Distribution Among Shigella spp. Isolated from Pediatric Patients in Tehran, Iran
Mohammadmahdi Karimi-Yazdi, Zohreh Ghalavand, Mahdi Shabani, Hamidreza Houri, Mehrzad Sadredinamin, Marzieh Taheri, Gita Eslami
Infection and Drug Resistance.2020; Volume 13: 485. CrossRef- Molecular characterization of Shigella species isolated from diarrheal patients in Tehran, Iran: phylogenetic typing and its association with virulence gene profiles and a novel description of Shigella invasion associated locus
Sina Arabshahi, Aytak Novinrooz, Reza Ranjbar, Abbas Ali Imani Fooladi
European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infect.2020; 39(9): 1727. CrossRef - Case report on a swift shift in uropathogens from Shigella flexneri to Escherichia coli: a thin line between bacterial persistence and reinfection
Kukwah Anthony Tufon, Djike Puepi Yolande Fokam, Youmbi Sylvain Kouanou, Henry Dilonga Meriki
Annals of Clinical Microbiology and Antimicrobials.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Virulence-related genes are associated with clinical and nutritional outcomes of Shigella/Enteroinvasive Escherichia coli pathotype infection in children from Brazilian semiarid region: A community case-control study
Mariana Bona, Pedro Henrique Medeiros, Ana Karolina Santos, Thiago Freitas, Mara Prata, Herlice Veras, Marília Amaral, Daniel Oliveira, Alexandre Havt, Aldo Ângelo Lima
International Journal of Medical Microbiology.2019; 309(2): 151. CrossRef - Genotyping and diversity of virulence genes among Shigella sonnei isolated from children with diarrhoea
Hamed Memariani, Mojtaba Memariani
Reviews in Medical Microbiology.2019; 30(4): 217. CrossRef - Virulence gene profiles of Shigella species isolated from stool specimens in India: its association with clinical manifestation and antimicrobial resistance
Dhiviya Prabaa Muthuirulandi Sethuvel, Shalini Anandan, Joy Sarojini Michael, Dhivya Murugan, Ayyanraj Neeravi, Valsan Philip Verghese, Kamini Walia, Balaji Veeraraghavan
Pathogens and Global Health.2019; 113(4): 173. CrossRef - Prevalence of enterotoxin-encoding genes among diverse Shigella strains isolated from patients with diarrhea, southwest Iran
Mojtaba Moosavian, Sakineh Seyed-Mohammadi, Ahmad Farajzadeh Sheikh, Saeed Khoshnood, Aram Asarehzadegan Dezfuli, Morteza Saki, Gholamreza Ghaderian, Fatemeh Shahi, Mahtab Abdi, Fariba Abbasi
Acta Microbiologica et Immunologica Hungarica.2018; 66(1): 91. CrossRef - Frequency of Mutations in Quinolone Resistance-Determining Regions and Plasmid-Mediated Quinolone Resistance in Shigella Isolates Recovered from Pediatric Patients in Tehran, Iran: An Overlooked Problem
Sajad Yaghoubi, Reza Ranjbar, Mohammad Mehdi Soltan Dallal, Mohammad Hasan Shirazi, Mohammad Kazem Sharifi-Yazdi
Microbial Drug Resistance.2018; 24(6): 699. CrossRef
- Epidemiological analysis and prevention strategies in response to a shigellosis cluster outbreak: a retrospective case series in an alternative school in the Republic of Korea, 2023
- Factors Influencing Animal Bites in Iran: A Descriptive Study
- Rouhullah Dehghani, Alireza Sharif, Mahla Madani, Hamed H. Kashani, Mohammad R. Sharif
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2016;7(4):273-277. Published online August 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2016.06.004
- 3,004 View
- 19 Download
- 26 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Animal bite is a significant health economic challenge worldwide. In Iran, there has been an increase in the number of animal bites in recent years. This study was performed to investigate the epidemiology of animal bites and their influencing factors in Semirom, Iran, from 2008 to 2012.
Methods
This was a descriptive study conducted for 5 years. The data were based on the information sheets presented in health-care centers concerning how to combat against rabies caused by animal bites. The data obtained were classified and analyzed statistically.
Results
During the 5-year study period, 1,246 animal bite cases were reported; 60% of the victims belonged to rural areas and the remaining 40% to urban areas. Among various aggressive animals, dogs had the highest rate of attacks (63.4%). The highest rate of animal bite (23.19%) was reported in the age group of 10–19 years and the lowest one (2.32%) was reported in the age group of 0–4 years. The animal bite rates among men and women were 76% and 24%; respectively. The highest and lowest rates were found among students (23.5%) and employees (5.5%), respectively. Regarding the commonly injured organ, the highest (67%) and lowest rates (23%) were for lower extremities and head and face, respectively. Regarding the nationality of the victims, 98% were Iranians and the rest were Afghan.
Conclusion
Given the increasing number of animal bites reported, there is a need to implement strategies to prevent bite-related complications, which may have health and financial burden on the country. It is also necessary to increase awareness among target groups and to formulate preventive strategies with the help of various authorities to control animal bites. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Medically important snakes and snakebite envenoming in Iran
Rouhullah Dehghani, Seyed Mostafa Monzavi, Omid Mehrpour, Farshad M. Shirazi, Hossein Hassanian-Moghaddam, Daniel E. Keyler, Wolfgang Wüster, Alexander Westerström, David A. Warrell
Toxicon.2023; 230: 107149. CrossRef - Epidemiologic Aspects of Animal Bite, Rabies, and Predictors of Delay in Post-exposure Prophylaxis: A National Registry-based Study in Iran
Salman Khazaei, Mohammad Reza Shirzadi, Behzad Amiri, Jamshid Pourmozafari, Erfan Ayubi
Journal of Research in Health Sciences.2023; 23(2): e583. CrossRef - Serum interleukin-6 level and its association with pulmonary involvement in progressive systemic sclerosis; a case-control study
Ahmad Piroozmand, Batool Zamani, Hamed Haddad Kashani, Javad Amini Mahabadi
Clinical and Molecular Allergy.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Epidemiology of animal bite injuries in North of Fars province in Iran
Hamed Karami, Fatemeh Jafari, AliKhani Jeihooni, Sanaz Amiri, Tahereh Hashemifard, Asadollah Niknam
Journal of Acute Disease.2023; 12(4): 157. CrossRef - Decadal trend analysis and epidemiological pattern of animal bite cases in a tertiary care hospital of North India
Babita Rani, Sanjay Kumar Jha, Anita Punia, Sanjeet Singh, Mansi Mehta, Alka Kumari
D Y Patil Journal of Health Sciences.2023; 11(4): 178. CrossRef - Epidemiology of Dog Bite Incidents in Chile: Factors Related to the Patterns of Human-Dog Relationship
Carmen Luz Barrios, Carlos Bustos-López, Carlos Pavletic, Alonso Parra, Macarena Vidal, Jonathan Bowen, Jaume Fatjó
Animals.2021; 11(1): 96. CrossRef - Toxicity and protein composition of venoms of Hottentotta saulcyi, Hottentotta schach and Androctonus crassicauda, three scorpion species collected in Iran
Ani Boghozian, Habibollah Nazem, Mohammad Fazilati, Seyed Hossein Hejazi, Mohammadreza Sheikh Sajjadieh
Veterinary Medicine and Science.2021; 7(6): 2418. CrossRef - The wound severity of animal bite victims visiting rabies prevention clinics and the influencing factors in Central China: a cross-sectional investigation
Dandan Li, Hanlin Liao, Fan Chen, Qingqing Jiang, Tiantian Wang, Zuxun Lu, Qiaoyan Liu, Shiyi Cao
BMC Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - A Brief Review on Biting/Stinging of Animals and Its Risk of Infection
Rouhullah Dehghani, Hamid Kassiri, Mousa Dehghani
Archives of Clinical Infectious Diseases.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Epidemiological study on animal bite cases referred to Haji Daii health Center in Kermanshah province, Iran during 2013–2017
Maryam Janatolmakan, Mojtaba Delpak, Alireza Abdi, Sabah Mohamadi, Bahare Andayeshgar, Alireza Khatony
BMC Public Health.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Using phylogeographic approaches to analyse the dispersal history, velocity and direction of viral lineages — Application to rabies virus spread in Iran
Simon Dellicour, Cécile Troupin, Fatemeh Jahanbakhsh, Akram Salama, Siamak Massoudi, Madjid K. Moghaddam, Guy Baele, Philippe Lemey, Alireza Gholami, Hervé Bourhy
Molecular Ecology.2019; 28(18): 4335. CrossRef - Comparison of a novel herbal skin care ointment with regular ointments to treat skin around the abdominal stoma: A clinical trial study
Maryam Hajikari, Soheila Mojdeh, Mohsen Shariari
Polish Annals of Medicine.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk of human exposure to animal bites in China: a clinic‐based cross‐sectional study
Fan Chen, Qiaoyan Liu, Qingqing Jiang, Jun Shi, Tegene Regassa Luba, Asefa Deressa Hundera, Pengqian Fang, Shiyi Cao, Zuxun Lu
Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences.2019; 1452(1): 78. CrossRef - Epidemiological characterization of bites: A retrospective study of dog bites to humans in Chile during 2009
C.L. Barrios, M. Vidal, A. Parra, C. Valladares, C. González, C. Pavletic
Journal of Veterinary Behavior.2019; 33: 31. CrossRef - Comparison of Various Methods of Collecting Scorpions (Arachnida, Scorpiones) in Khuzestan Province, Southwestern Iran
Rouhullah Dehghani, Hamid Kassiri, Narges Mohammadzadeh
Archives of Clinical Infectious Diseases.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - The protective effect of coenzyme Q10 and berberine on sperm parameters, with and without varicocelectomy in rats with surgically induced varicoceles
Hamed Najaran, Hamid Rashtbari, Abouzar Mohammadi, Fatemeh Soleimanifar, Fatemeh Izadpanah, Hamed Haddad Kashani, Hassan Hassani Bafrani
Comparative Clinical Pathology.2019; 28(2): 479. CrossRef -
Comparison of Purgative Manna Drop and Phototherapy with Phototherapy Treatment of Neonatal Jaundice: A Randomized Double-Blind Clinical Trial
Amirreza Monsef, Fatemeh Eghbalian, Neda Rahimi
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2019; 10(3): 152. CrossRef - Epidemiological patterns of animal bites in Abadeh district of central Iran from 2012 to 2018: A cross-sectional study
Ahmad Karimi, Behnam Karimi, Ahmad Karimifard, Nabiollah Taherimotlagh, Amin Kasraei, Mohammad Yandarani, Fatemeh Safikhani, Fatemeh Majidpour
Journal of Acute Disease.2019; 8(6): 265. CrossRef - Effect of melatonin in reducing second-generation antipsychotic metabolic effects: A double blind controlled clinical trial
Mansour Agahi, Negar Akasheh, Afshin Ahmadvand, Hossein Akbari, Fatemeh Izadpanah
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research &.2018; 12(1): 9. CrossRef - Dog bites in a U.S. county: age, body part and breed in paediatric dog bites
Sriram Ramgopal, Lauren Bealafeld Brungo, Michael R. Bykowski, Raymond D. Pitetti, Robert W. Hickey
Acta Paediatrica.2018; 107(5): 893. CrossRef - Scorpionism by Hemiscorpius spp. in Iran: a review
Rouhullah Dehghani, Fatemeh Kamiabi, Malihe Mohammadi
Journal of Venomous Animals and Toxins including T.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Immune Responses following Intradermal and Intramuscular Rabies Vaccination Methods
Mahsa Golahdooz, Sana Eybpoosh, Rouzbeh Bashar, Mahsa Taherizadeh, Behzad Pourhossein, Mohamadreza Shirzadi, Behzad Amiri, Maryam Fazeli
Journal of Medical Microbiology and Infectious Dis.2018; 6(4): 77. CrossRef - Epidemiology of Animal Bites and Associated Factors with Delay in Post-Exposure Prophylaxis; A Cross-Sectional Study
Salman Khazaei, Manoochehr Karami, Yousef Veisani, Manoochehr Solgi, Shahram Goodarzi
Bulletin of Emergency and Trauma.2018; 6(3): 239. CrossRef - Introducing of a New Sting Agent of Velvet Ant Dentilla sp. (Hymenoptera: Mutillidae) in Kashan, Centerl of Iran (2014 - 2015)
Rouhullah Dehghani, Hamid Kassiri, Babak Gharali, Gholamreza Hoseindoost, Elahe Chimehi, Seyedmahdi Takhtfiroozeh, Mehdi Moameni
Archives of Clinical Infectious Diseases.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - The lowering of bilirubin levels in patients with neonatal jaundice using massage therapy: A randomized, double-blind clinical trial
Fatemeh Eghbalian, Haneyeh Rafienezhad, Javad Farmal
Infant Behavior and Development.2017; 49: 31. CrossRef - Solpugidophobia in Iran: Real or Illusion
R. Dehghani
Journal of Biology and Today's World.2017;[Epub] CrossRef
- Medically important snakes and snakebite envenoming in Iran
- Epidemiological and Clinical Features of People with Malta Fever in Iran: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Mahmood Moosazadeh, Roja Nikaeen, Ghasem Abedi, Motahareh Kheradmand, Saeid Safiri
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2016;7(3):157-167. Published online June 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2016.04.009
- 3,341 View
- 22 Download
- 17 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Numerous studies have reported the epidemiological and clinical features of Malta fever incidence in Iran. Review and synthesis of the related literature through meta-analysis can provide an appropriate measurement for aforementioned indices. Therefore, the present study aimed to determine the epidemiological and clinical features of people with Malta fever in Iran.
Methods
The required documents were obtained through searching national and international databases. In each study, standard deviation of the indices was calculated using binomial distribution formulas. Finally, the heterogeneity index was determined between studies using Cochran (Q) and I2 tests.
Results
Combining the results of 47 articles in the meta-analysis indicated that 57.6% (55.02–60.1%) and 42.3% (49.8–44.9%) of the patients were male and female, respectively. Most of the patients lived in rural areas; 68.4% (63.6–73.2%) compared to 31.4% (26.7–36.3%). In addition, 20.8% (17.4–24.2%) of the patients were ranchers and farmers, 16.9% (14.5–19.4%) were students, and 31.6% (27–36.2%) were housewives. Of the patients studies, 50.5% (35.6–65.2%) experienced contact with animals and 57.1% (46.4–67.9%) used unpasteurized dairy products. Fever, joint pain, and sweating were detected among 65.7% (53.7–77.8%) and 55.3% (44.4–66.2%), respectively.
Conclusion
The present study revealed that the frequency of male patients with brucellosis was considerably more than that of female patients. The number of patients with Malta fever in rural areas was significantly more than in urban areas. High-risk behavior, unprotected contact with animals, and using unpasteurized dairy products were among the most significant factors affecting Malta fever incidence in Iran. Fever, joint pain, and sweating were detected among most of the patients with Malta fever. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A study of rural populations’ knowledge, attitude, and practice about brucellosis: a descriptive, cross-sectional, multicenter study
Zahra Montaseri, Zahra Mohebi, Rahil Masoumi, Azizallah Dehghan, Mostafa Bijani
BMC Research Notes.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic significance of hematological parameters in brucellosis
Mehmet Çelik, Mehmet Reşat Ceylan, Deniz Altındağ, Nevin Güler Dinçer, Sevil Alkan
Journal of Clinical Medicine of Kazakhstan.2023; 20(1): 50. CrossRef - Presence of Brucella spp. in Milk and Dairy Products: A Comprehensive Review and Its Perspectives
Md. Sadequl Islam, Md. Ariful Islam, Md. Moshiur Rahman, Khaleda Islam, Md. Mominul Islam, Md. Murtuza Kamal, Md. Nazrul Islam, Gianfranco Picone
Journal of Food Quality.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Predicting of Bacteremia in Patients with Brucellosis Using Machine Learning Methods
Mehmet ÇELİK, Mehmet Reşat CEYLAN, Deniz ALTINDAĞ, Sait Can YÜCEBAŞ, Nevin GÜLER DİNCER, Sevil ALKAN
Journal of Contemporary Medicine.2023; 13(3): 459. CrossRef - Toponyms in dermatology
Heera Ramesh, Sachin Somashekar
Indian Journal of Dermatology.2022; 67(3): 279. CrossRef - Brucella pleurisy: An extremely rare complication of brucellosis
Ahmad Alikhani, Hamideh Abbaspour Kasgari, Haadi Majidi, Zahra Nekoukar
Clinical Case Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Design and validation of brucellosis prevention questionnaire focused on animal vaccination
Farhad Bahadori, Fazlollah Ghofranipour, Saeideh Ghaffarifar, Reza Ziaei
BMC Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Forecasting the monthly incidence rate of brucellosis in west of Iran using time series and data mining from 2010 to 2019
Hadi Bagheri, Leili Tapak, Manoochehr Karami, Zahra Hosseinkhani, Hamidreza Najari, Safdar Karimi, Zahra Cheraghi, Esteban Tlelo-Cuautle
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(5): e0232910. CrossRef - Epidemiologically characteristics of human brucellosis and antimicrobial susceptibility pattern of Brucella melitensis in Hinggan League of the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
Hai-Tao Yuan, Cheng-Ling Wang, Li-Na Liu, Dan Wang, Dan Li, Zhen-Jun Li, Zhi-Guo Liu
Infectious Diseases of Poverty.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Brucellosis: Evaluation of Two Hundred and Ten Cases with Different Clinical Features
Esma Eroglu, Bahar Kandemir
Annals of the Academy of Medicine, Singapore.2020; 49(7): 462. CrossRef - A comparison of three data mining time series models in prediction of monthly brucellosis surveillance data
Nasrin Shirmohammadi‐Khorram, Leili Tapak, Omid Hamidi, Zohreh Maryanaji
Zoonoses and Public Health.2019; 66(7): 759. CrossRef - Human brucellosis caused by raw dairy products: A review on the occurrence, major risk factors and prevention
Maryam Dadar, Youcef Shahali, Adrian M. Whatmore
International Journal of Food Microbiology.2019; 292: 39. CrossRef - Epidemiological, Clinical and Paraclinical Evaluation of Recorded Cases with Brucellosis in Kermanshah Province Health Center 2012 - 2016
Hossein Hatami, Ali Ramezankhani, Farahnaz Shekarchi
Journal of Kermanshah University of Medical Scienc.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Epidemiological, risk factors, clinical, and laboratory features of brucellosis in the Southwest of Iran within 2009–2015
Mahmood Nabavi, Hossein Hatami, Hedayatollah Jamaliarand
International Journal of Preventive Medicine.2019; 10(1): 108. CrossRef - Meta-Analysis of the Changes of Peripheral Blood T Cell Subsets in Patients with Brucellosis
Rongjiong Zheng, Songsong Xie, Shaniya Niyazi, Xiaobo Lu, Lihua Sun, Yan Zhou, Yuexin Zhang, Kai Wang
Journal of Immunology Research.2018; 2018: 1. CrossRef - A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Epidemiology and Clinical Manifestations of Human Brucellosis in China
Rongjiong Zheng, Songsong Xie, Xiaobo Lu, Lihua Sun, Yan Zhou, Yuexin Zhang, Kai Wang
BioMed Research International.2018; 2018: 1. CrossRef - The clinical features of 590 patients with brucellosis in Xinjiang, China with the emphasis on the treatment of complications
Bin Jia, Fengbo Zhang, Ying Lu, Wenbao Zhang, Jun Li, Yuexin Zhang, Jianbing Ding, Mazin Barry
PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases.2017; 11(5): e0005577. CrossRef
- A study of rural populations’ knowledge, attitude, and practice about brucellosis: a descriptive, cross-sectional, multicenter study
- Antibiotic Resistance of
Acinetobacter baumannii in Iran: A Systemic Review of the Published Literature - Jale Moradi, Farhad B. Hashemi, Abbas Bahador
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2015;6(2):79-86. Published online April 30, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2014.12.006
- 2,984 View
- 28 Download
- 50 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Acinetobacter baumannii is a bacterium responsible for health care-associated infections, and it frequently develops multiple drug resistance (MDR). The prevalence of antibiotic-resistant A. baumannii in Iran has increased, and this may cause significant clinical problems. Therefore, in order to elucidate the development of antibiotic resistance, we performed a systematic review of the literature published on antibiotic-resistant A. baumannii reported in Iran.
Methods
Thirty-six publications that met the criteria for inclusion were reviewed from an initial 87 papers. Selected papers published between 2008 and September 2014, were categorized on the basis of the sample collecting year been between 2001 and 2013.
Results
Analysis of data revealed that, in general, there was an increase in antimicrobial resistance. During the initial time point of these studies (2001–2007) there was a high rate of resistance to all antibiotics, with the exception of carbapenems, lipopeptides, and aminoglycosides that had a low resistance rate in comparison with the others. Also, the resistance rate was increased in one group of these three antimicrobial groups from 2010 to 2013. In particular, there was an increase in resistance to carbapenems (imipenem and meropenem) from 2010–2011 and 2012–2013, whereas no significant change in the resistance rate of the other two antimicrobial groups (lipopeptides and aminoglycosides) during the study time was observed, although we did observe certain trends in amikacin (aminoglycoside group antibiotic) between 2011–2012 and 2012–2013.
Conclusion
These findings indicate that antimicrobial resistance of A. baumannii in Iran has increased, which may very well affect the antimicrobial resistance of this organism worldwide. Based on these results, novel prevention and treatment strategies against A. baumannii infections are warranted. Furthermore, these data may assist in revising treatment guidelines and regional policies in care units to slow the emergence of antimicrobial resistance. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Isolation and Identification of Effective Probiotics on Drug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Strains and Their Biofilms
Zahra Abbasi, Seyed Mahdi Ghasemi, Yasaman Ahmadi, Dariush Shokri, Tingtao Chen
Canadian Journal of Infectious Diseases and Medica.2024; 2024: 1. CrossRef - A bioinformatic approach to identify confirmed and probable CRISPR–Cas systems in the Acinetobacter calcoaceticus–Acinetobacter baumannii complex genomes
Jetsi Mancilla-Rojano, Víctor Flores, Miguel A. Cevallos, Sara A. Ochoa, Julio Parra-Flores, José Arellano-Galindo, Juan Xicohtencatl-Cortes, Ariadnna Cruz-Córdova
Frontiers in Microbiology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The prevalence of antibiotic-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii infections among the Iranian ICU patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Masoud Keikha, Mohsen Karbalaei, Farid Rahimi, Amin Talebi Bezmin Abadi
Gene Reports.2023; 30: 101731. CrossRef - Prevalence and Phenotypic and Genotypic Patterns of Antibiotic Resistance of Acinetobacter baumannii Strains Isolated from Fish, Shrimp, and Lobster Samples
Zahra Hasiri, Ebrahim Rahimi, Hassan Momtaz, Amir Shakerian, Ali Akbar
Journal of Food Processing and Preservation.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Effect of photodynamic therapy on multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: A scoping review
Vanessa Bustamante, Christian Erick Palavecino
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2023; 43: 103709. CrossRef - Meropenem inhibits Acinetobacter baumannii biofilm formation by downregulating pgaA gene expression
Mir Mahdi Najafi
Journal of Medical Microbiology and Infectious Dis.2023; 11(2): 86. CrossRef - High Frequency of Class I and II Integrons and the Presence of aadA2 and dfrA12 Gene Cassettes in the Clinical Isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii from Shiraz, Southwest of Iran
Seyed Sajjad Khoramrooz, Saba Eslami, Mohammad Motamedifar, Abdoolah Bazargani, Kamiar Zomorodian
Jundishapur Journal of Microbiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Evasion of Antimicrobial Activity in Acinetobacter baumannii by Target Site Modifications: An Effective Resistance Mechanism
Arturo Martínez-Trejo, Juan Manuel Ruiz-Ruiz, Luis Uriel Gonzalez-Avila, Andrés Saldaña-Padilla, Cecilia Hernández-Cortez, Miguel Angel Loyola-Cruz, Juan Manuel Bello-López, Graciela Castro-Escarpulli
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(12): 6582. CrossRef - Mechanisms involved in resistance to carbapenems among Acinetobacter baumannii isolates recovered in Brazil: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Adrielle Pieve de Castro, William Gustavo de Lima, Cristina Sanches, Magna Cristina de Paiva
Revista Colombiana de Ciencias Químico-Farmacéutic.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Production of bla oxa-23 type genes carrying by Acinetobacter baumannii isolated from hospitalized patients in Tehran, Iran
Maryam Rezaei, Jalil vand Yousefi, Naser Harzandi, Monireh Sharifizadeh, Abed Zahedi bialvaei, Mohammad Rahbar
Reviews in Medical Microbiology.2021; 32(2): 102. CrossRef - Acinetobacter baumannii as a community foodborne pathogen: Peptide mass fingerprinting analysis, genotypic of biofilm formation and phenotypic pattern of antimicrobial resistance
Ayman Elbehiry, Eman Marzouk, Ihab M. Moussa, Turki M. Dawoud, Ayman S. Mubarak, Dalia Al-Sarar, Roua A. Alsubki, Jwaher H. Alhaji, Mohamed Hamada, Adil Abalkhail, Hassan A. Hemeg, Rasha N. Zahran
Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences.2021; 28(1): 1158. CrossRef - Mapping Global Prevalence of Acinetobacter baumannii and Recent Vaccine Development to Tackle It
Chaoying Ma, Siobhán McClean
Vaccines.2021; 9(6): 570. CrossRef - Evaluation of Antibiotic Resistance to Colistin in Nosocomial Infections with Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter
Fariba Keramat, Hamid Reza Ghasemi Basir, Abbas Taher, Abbas Moradi, Ali Saadatmand, Pooria Owji Nejad
Avicenna Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 27(4): 211. CrossRef - Syzygium aromaticum Extracts as a Potential Antibacterial Inhibitors against Clinical Isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii: An In-Silico-Supported In-Vitro Study
Abdelhamed Mahmoud, Magdy M. Afifi, Fareed El Shenawy, Wesam Salem, Basem H. Elesawy
Antibiotics.2021; 10(9): 1062. CrossRef - Detection of blaOXA-23 and blaNDM-1 carbapenemase among clinical isolates of A. baumannii in Tabriz, north-west of Iran
Leila Rahbarnia, Safar Farajnia, Hajar Khaneshi, Hadi Farajnia, Behrooz Naghili, Asghar Tanomand
Gene Reports.2020; 18: 100555. CrossRef - Prevalence and phenotypic pattern of antibiotic resistance of Acinetobacter baumannii isolated from different types of raw meat samples in Isfahan, Iran
Neda Askari, Hassan Momtaz, Elahe Tajbakhsh
Veterinary Medicine and Science.2020; 6(1): 147. CrossRef Trend and Characteristics of Acinetobacter baumannii Infections in Patients Attending Universal College of Medical Sciences, Bhairahawa, Western Nepal: A Longitudinal Study of 2018
Shristi Raut, Komal Raj Rijal, Sulochana Khatiwada, Subhash Karna, Rita Khanal, Janak Adhikari, Bipin Adhikari
Infection and Drug Resistance.2020; Volume 13: 1631. CrossRef- Evaluating the frequency of carbapenem and aminoglycoside resistance genes among clinical isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii from Ahvaz, south-west Iran
S.M. Mortazavi, Z. Farshadzadeh, S. Janabadi, M. Musavi, F. Shahi, M. Moradi, S. Khoshnood
New Microbes and New Infections.2020; 38: 100779. CrossRef - Evaluation of Antibiotic Resistance Pattern of Meropenem and Piperacillin- Tazobactam in Multi Drug Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Isolates by Flow Cytometry Method
Nahid Rahimi, Sahar Honarmand Jahromy, Shohreh Zare Karizi
Iranian Journal of Medical Microbiology.2019; 13(3): 194. CrossRef - Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy against clinical isolates of carbapenem-susceptible and carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii
Mirian Marcolan De Mello, Patrícia Pimentel De Barros, Renata de Cassia Bernardes, Silvio Rubens Alves, Naiara Pires Ramanzini, Lívia Mara Alves Figueiredo-Godoi, Ana Carolina Chipoletti Prado, Antonio Olavo Cardoso Jorge, Juliana Campos Junqueira
Lasers in Medical Science.2019; 34(9): 1755. CrossRef - Antibacterial Resistance Pattern of Acinetobacter baumannii in Burn Patients in Northeast of Iran
Alireza Sedaghat, Majid Khadem-Rezaiyan, Ali Ahmadabadi, Hassan Abbaspour, Masoud Youssefi, Mohammad Moein Shirzad, Mohammad Hossein Esfahani, Mohammad Mirzaei, Mohammad Ramezani
Jundishapur Journal of Microbiology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Amikacin resistance due to the aphA6 gene in multi-antibiotic resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolates belonging to global clone 1 from Iran
Parisa Aris, Mohammad Ali Boroumand, Masoumeh Douraghi
BMC Microbiology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Highly Synergistic Effects of Melittin with Conventional Antibiotics Against Multidrug-Resistant Isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Reza Akbari, Mojdeh Hakemi-Vala, Fatemeh Pashaie, Parvaneh Bevalian, Ali Hashemi, Kamran Pooshang Bagheri
Microbial Drug Resistance.2019; 25(2): 193. CrossRef - Seven-Year Trend of Antimicrobial Resistance of Acinetobacter and Pseudomonas spp. Causing Bloodstream Infections: A Retrospective Study from Shiraz, Southern Iran
Amir Hossein Babaei, Gholamreza Pouladfar, Bahman Pourabbas, Zahra Jafarpour, Samin Ektesabi, Pejman Abbasi
Jundishapur Journal of Microbiology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Antibacterial Effect Leaf Extract of Avicennia marina on Standard and Clinical Strains of Acinetobacter baumannii
Mehdi Mahmudpour, Azam Askari, Forough Yousefi
Iranian South Medical Journal.2019; 22(3): 150. CrossRef - Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain 1 is dispensable for host immune responses against pulmonary infection of Acinetobacter baumannii in mice
Min-Jung Kang, Jin-A Choi, Joo-Hee Choi, Ah-Ra Jang, Ji-Yeon Park, Jae-Hun Ahn, Tae-Sung Lee, Dong-Yeon Kim, Jong-Hwan Park
Laboratory Animal Research.2018; 34(4): 295. CrossRef - Survey of aminoglycoside acetyl transferase genes in multi-drug resistance acinetobacter
Seyyed mohammad atyabi
MOJ Toxicology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Cloning and expression of nlpA gene as DNA vaccine candidate against Acinetobacter baumannii
Rassoul Hashemzehi, Abbas Doosti, Mohammad Kargar, Mojtaba Jaafarinia
Molecular Biology Reports.2018; 45(4): 395. CrossRef - Association of virulence gene expression with colistin-resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii: analysis of genotype, antimicrobial susceptibility, and biofilm formation
Abbas Bahador, Zahra Farshadzadeh, Reza Raoofian, Masoumeh Mokhtaran, Babak Pourakbari, Maryam Pourhajibagher, Farhad B. Hashemi
Annals of Clinical Microbiology and Antimicrobials.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Distribution and Genotyping of Aquatic Acinetobacter baumannii Strains Isolated from the Puzi River and Its Tributaries Near Areas of Livestock Farming
Hsin-Chi Tsai, Ming-Yuan Chou, Yi-Jia Shih, Tung-Yi Huang, Pei-Yu Yang, Yi-Chou Chiu, Jung-Sheng Chen, Bing-Mu Hsu
Water.2018; 10(10): 1374. CrossRef - Antibiotic resistance of Klebsiella�pneumoniae through β-arrestin recruitment-induced β-lactamase signaling pathway
Jiang Wei, Yang Wenjie, Liu Ping, Wang Na, Ren Haixia, Zhao Xuequn
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical Isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii From Tehran Hospitals: Pulsed-field Gel Electrophoresis Characterization, Clonal Lineages, Antibiotic Susceptibility, and Biofilm-forming Ability
Mahdi Akbari Dehbalaei, Shahin Najar-Peerayeh, Morovat Taherikalani, Mehrdad Behmanesh
Jundishapur Journal of Microbiology.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring the resistance mechanism of imipenem in carbapenem hydrolysing class D beta-lactamases OXA-143 and its variant OXA-231 (D224A) expressing Acinetobacter baumannii: An in-silico approach
Kullappan Malathi, Anand Anbarasu, Sudha Ramaiah
Computational Biology and Chemistry.2017; 67: 1. CrossRef - A national framework for an antimicrobial resistance surveillance system within Iranian healthcare facilities: Towards a global surveillance system
Reza Safdari, Marjan GhaziSaeedi, Hossein Masoumi-Asl, Peyman Rezaei-Hachesu, Kayvan Mirnia, Taha Samad-Soltani
Journal of Global Antimicrobial Resistance.2017; 10: 59. CrossRef - Polyclonal Distribution of blaOXA-23 Gene Among Acinetobacter baumannii Isolated from Intensive Care Unit Patients in Tehran; Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis Analysis
Mahdi Akbari Dehbalaei, Shahin Najar-Peerayeh, Mehrdad Behmanesh, Morovat Taherikalani
Jundishapur Journal of Microbiology.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Antimicrobial activity of photodynamic therapy in combination with colistin against a pan-drug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolated from burn patient
Ebrahim Boluki, Hossein Kazemian, Hadi Peeridogaheh, Mohammad Yousef Alikhani, Sima Shahabi, Leili Beytollahi, Roghayeh Ghorbanzadeh
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2017; 18: 1. CrossRef - Acinetobacter baumannii strains isolated from patients in intensive care units in Goiânia, Brazil: Molecular and drug susceptibility profiles
Suellen Rocha Araújo Castilho, Cássia Silva de Miranda Godoy, Adriana Oliveira Guilarde, Juliana Lamaro Cardoso, Maria Cláudia Porfirio André, Ana Paula Junqueira-Kipnis, André Kipnis, Patrick Butaye
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(5): e0176790. CrossRef - Acquisition of Tn6018-3′ CS regions increases colistin MICs against Acinetobacter baumannii isolates harboring new variants of AbaRs
Mohammad Savari, Alireza Ekrami, Saeed Shoja, Abbas Bahador
Folia Microbiologica.2017; 62(5): 373. CrossRef - Systematic Review of Antimicrobial Resistance of ClinicalAcinetobacter baumanniiIsolates in Iran: An Update
Hadi Razavi Nikoo, Abdollah Ardebili, Jalal Mardaneh
Microbial Drug Resistance.2017; 23(6): 744. CrossRef - Plasmid borne Carbapenem-Hydrolyzing Class D β-Lactamases (CHDLs) and AdeABC efflux pump conferring carbapenem-tigecycline resistance among Acinetobacter baumannii isolates harboring TnAbaRs
Mohammad Savari, Alireza Ekrami, Saeed Shoja, Abbas Bahador
Microbial Pathogenesis.2017; 104: 310. CrossRef - Evaluation of photodynamic therapy effect along with colistin on pandrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii
Maryam Pourhajibagher, Hosein Kazemian, Nasim Chiniforush, Abbas Bahador
LASER THERAPY.2017; 26(2): 97. CrossRef - Regional differences and trends in antimicrobial susceptibility of Acinetobacter baumannii
Sibylle H. Lob, Daryl J. Hoban, Daniel F. Sahm, Robert E. Badal
International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents.2016; 47(4): 317. CrossRef -
Acinetobacter baumannii Infection Should be Considered as the Most Troublesome Pathogens for Health Care Institutions in Karaj
Enayatollah Kalantar, Amir Hatami, Fatemeh Rahimi, Sadegh Saedi, Aliehsan Heidari, Parviz Fallah, Morteza Qoghaei, Morteza Nazari, Soheila Beiranvand, Mohsen Arabi, Mohammad Hossein Dehghan
Avicenna Journal of Clinical Microbiology and Infe.2016; 4(1): 39368. CrossRef - AcinetobacterInfections among Adult Patients in Qatar: A 2-Year Hospital-Based Study
Musaed Saad Al Samawi, Fahmi Yousef Khan, Yasser Eldeeb, Muna Almaslamani, Abdullatif Alkhal, Hussam Alsoub, Wissam Ghadban, Faraj Howady, Samar Hashim
Canadian Journal of Infectious Diseases and Medica.2016; 2016: 1. CrossRef - Prevalence of Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria on Fresh Vegetables Collected from Farmers' Markets in Connecticut
Deepti Prasad Karumathil, Hsin-Bai Yin, Anup Kollanoor-Johny, Kumar Venkitanarayanan
Journal of Food Protection.2016; 79(8): 1446. CrossRef - Antimicrobial resistance profiles and genetic elements involved in carbapenem resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii isolates from a referral hospital in Southern Iran
Najmeh Alaei, Masoud Aziemzadeh, Abbas Bahador
Journal of Global Antimicrobial Resistance.2016; 5: 75. CrossRef - Characterization of integrons and associated gene cassettes in Acinetobacter baumannii strains isolated from intensive care unit in Tehran, Iran
Hossein Goudarzi, Mehdi Azad, Sima Sadat Seyedjavadi, Hadi Azimi, Alireza Salimi Chirani, Vahid Fallah Omrani, Mehdi Goudarzi
Journal of Acute Disease.2016; 5(5): 386. CrossRef - Genotypic and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: Analysis of is Aba Elements and blaOXA-23-like Genes Including a New Variant
Abbas Bahador, Reza Raoofian, Babak Pourakbari, Mohammad Taheri, Zahra Hashemizadeh, Farhad B. Hashemi
Frontiers in Microbiology.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Bacterial Etiology and Antibacterial Susceptibility Patterns of Pediatric Bloodstream Infections: A Two Year Study From Nemazee Hospital, Shiraz, Iran
Hadi Sedigh Ebrahim-Saraie, Mohammad Motamedifar, Davood Mansury, Mehrdad Halaji, Zahra Hashemizadeh, Yosef Ali-Mohammadi
Journal of Comprehensive Pediatrics.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Wide distribution of carbapenem resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in burns patients in Iran
Zahra Farshadzadeh, Farhad B. Hashemi, Sara Rahimi, Babak Pourakbari, Davoud Esmaeili, Mohammad A. Haghighi, Ali Majidpour, Saeed Shojaa, Maryam Rahmani, Samira Gharesi, Masoud Aziemzadeh, Abbas Bahador
Frontiers in Microbiology.2015;[Epub] CrossRef
- Isolation and Identification of Effective Probiotics on Drug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Strains and Their Biofilms
- Acute Human Cytomegalovirus Infection with Bleeding in Iran
- Behzad Pourhossein, Farhad Yaghmaei, Saber Esmaeili, Omid Banafshi, Shahla Afrasiabian, Mohammad Reza Shirzadi, Mark Schleiss, Ehsan Mostafavi
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2014;5(6):383-386. Published online December 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2014.10.003
- 2,508 View
- 27 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In December 2011, a 42-year-old male farmer was admitted to a hospital in Sanandaj (Western Iran) with fever and anemia in order to check whether he suffered from some infectious diseases. During the first 3 days after admission, the patient gradually developed progressive oliguria, fever, abdominal pain in the right upper quadrant, leukocytosis with toxic granulation, petechiae and ecchymosis, oral bleeding, and vomiting. The sonographic findings revealed splenomegaly and an increase in the thickness of the gall bladder wall. In order to manage the patient and taking into consideration the most probable differential diagnoses, diagnostic tests were performed on two blood samples collected from him, and real-time polymerase chain reaction for human cytomegalovirus was positive.
- Characterization of Plasmid-Mediated AmpC and Carbapenemases among Iranain Nosocomial Isolates of
Klebsiella pneumoniae Using Phenotyping and Genotyping Methods - Alireza Japoni-Nejad, Ehsanollah Ghaznavi-Rad, Alex van Belkum
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2014;5(6):333-338. Published online December 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2014.09.003
- 2,791 View
- 27 Download
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Plasmid-mediated AmpC β-lactamases (PMABLs) and carbapenemases are emerging groups of antimicrobial-resistance determinants. The aims of the study were to evaluate the occurrence of PMABLs and carbapenemases in clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae and compare the test performance of various phenotypic methods for detection of these enzymes in Iran.
Methods
A total of 100 K. pneumoniae isolates were collected from clinical specimens obtained in Valiasr Hospital. AmpC production in all isolates was determined using the AmpC disk test, the cephamycin Hodge test, the AmpC Etest, and the boronic acid combined-disk test. In addition, carbapenemase production was determined using the modified Hodge test, the EDTA disk synergy test, and the boronic acid combined-disk test. The performances of various phenotypic methods were evaluated by the comparison of their results with polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method as the gold standard.
Results
Of the 100 isolates, 19 (19%) were demonstrated to harbor the PMABL-resistance gene by the multiplex PCR method. The PCR result indicated the presence of carbapenemase genes in 12 isolates. The performance of various phenotypic tests carried out for detection of carbapenemase-producing isolates varied widely, ranging in sensitivity from 30% to 100% and in specificity from 90.8% to 100%.
Conclusion
This is the first report of MOX-type AmpC β-lactamase and blaGES in K. pneumoniae in Iran. A comparison of the phenotypic methods showed that a combination of cefoxitin plus boronic acid is optimal for detecting plasmid-mediated AmpC enzymes in K. pneumoniae, whereas the implementation of molecular methods is often complex, requires specially trained personnel, and is associated with higher costs. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Global and Regional Prevalence of Hospital-Acquired Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Xing-chen Lin, Chang-li Li, Shao-yang Zhang, Xiao-feng Yang, Meng Jiang
Open Forum Infectious Diseases.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - High frequency of NDM-1 and OXA-48 carbapenemase genes among Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates in central Iran
Elnaz Abbasi, Ehsanollah Ghaznavi-Rad
BMC Microbiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Detection of ESBL and AmpC producing Klebsiella pneumoniae ST11 and ST147 from urinary tract infections in Iran
Shaghayegh Shahkolahi, Pegah Shakibnia, Shahla Shahbazi, Samira Sabzi, Farzad Badmasti, Mohammad Reza Asadi Karam, Mehri Habibi
Acta Microbiologica et Immunologica Hungarica.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Plasmid-mediated AmpC β-Lactamase gene analysis in Klebsiella Pneumoniae clinical isolates
Nabi Jomehzadeh, Khadijeh Ahmadi, Hasti Shaabaninejad, Gholamali Eslami
Biomedical and Biotechnology Research Journal (BBR.2022; 6(4): 582. CrossRef - Characterization of Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns of Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates Obtained from Wound Infections
Roya Ghanavati, Hossein Kazemian, Parisa Asadollahi , Hamid Heidari, Gholamreza Irajian, Fatemeh Navab-Moghadam, Shabnam Razavi
Infectious Disorders - Drug Targets .2021; 21(1): 119. CrossRef - An investigation of extended-spectrum β-lactamases (ESBLs) in Klebsiella isolated from foodborne outbreaks in Iran
Farnaz Hajikarim, Mohammad Mehdi Soltan Dallal, Mohammad Reza Pourmand, Milad Abdi
Gene Reports.2020; 19: 100632. CrossRef - Prevalence and Mechanisms of Carbapenem Resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae and Escherichia coli: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Cross-Sectional Studies from Iran
Mohammad Javad Nasiri, Mehdi Mirsaeidi, Seyyed Mohammad Javad Mousavi, Mania Arshadi, Fatemeh Fardsanei, Behnaz Deihim, Sara Davoudabadi, Samin Zamani, Bahareh Hajikhani, Hossein Goudarzi, Mehdi Goudarzi, Zahra Sadat Seghatoleslami, Hossein Dabiri, Payam
Microbial Drug Resistance.2020; 26(12): 1491. CrossRef - Characterization of β-lactam resistance in K. pneumoniae associated with ready-to-eat processed meat in Egypt
Shaymaa H. Abdel-Rhman, Grzegorz Woźniakowski
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(9): e0238747. CrossRef - Multiplex PCR to detect pAmpC β-lactamases among enterobacteriaceae at a tertiary care laboratory in Mumbai, India
Mubin Kazi, Kanchan Ajbani, Jeffrey A. Tornheim, Anjali Shetty, Camilla Rodrigues
Microbiology.2019; 165(2): 246. CrossRef - AmpC β lactamases in Urinary Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates: First Report of ACC Type AmpC β-lactamase Resistance in Iran
Maryam Ghane, Laleh Babaeekhou, Mahdi Jafar Shanjani
Journal of Advances in Medical and Biomedical Rese.2019; 27(123): 23. CrossRef - The Molecular and Clinical Epidemiology of Extended-Spectrum Cephalosporin– and Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae at 4 US Pediatric Hospitals
Danielle M Zerr, Scott J Weissman, Chuan Zhou, Matthew P Kronman, Amanda L Adler, Jessica E Berry, Jaipreet Rayar, Jeff Myers, Wren L Haaland, Carey-Ann D Burnham, Alexis Elward, Jason Newland, Rangaraj Selvarangan, Kaede V Sullivan, Theoklis Zaoutis, Xua
Journal of the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Socie.2017; 6(4): 366. CrossRef - Previous Antibiotic Exposure Increases Risk of Infection with Extended-Spectrum-β-Lactamase- and AmpC-Producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae in Pediatric Patients
Danielle M. Zerr, Arianna Miles-Jay, Matthew P. Kronman, Chuan Zhou, Amanda L. Adler, Wren Haaland, Scott J. Weissman, Alexis Elward, Jason G. Newland, Theoklis Zaoutis, Xuan Qin
Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy.2016; 60(7): 4237. CrossRef - Molecular characterization of extended-spectrum β-lactamase, plasmid-mediated AmpC cephalosporinase and carbapenemase genes among Enterobacteriaceae isolates in five medical centres of East and West Azerbaijan, Iran
Mohammad Reza Sadeghi, Reza Ghotaslou, Mohammad Taghi Akhi, Mohammad Asgharzadeh, Alka Hasani
Journal of Medical Microbiology .2016; 65(11): 1322. CrossRef - High Prevalence of AmpC β-Lactamases in Clinical Isolates of Escherichia coli in Ilam, Iran
Abbas Maleki, Afra Khosravi, Sobhan Ghafourian, Iraj Pakzad, Shiva Hosseini, Rashid Ramazanzadeh, Nourkhoda Sadeghifard
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2015; 6(3): 201. CrossRef
- The Global and Regional Prevalence of Hospital-Acquired Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- Evidence Gap on the Prevalence of Non-conventional Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes in Iran
- Abdolreza Shaghaghi, Ali Ahmadi
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2014;5(5):292-297. Published online October 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2014.08.002
- 2,744 View
- 18 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Robust scientific evidence exists about the role of non-conventional risk factors in type 2 diabetes worldwide. The current epidemiological pattern of the disease in Iran suggests a precipitating role for these non-conventional risk factors. This review was performed to examine the research evidence suggesting a higher prevalence of non-conventional type 2 diabetes risk factors in Iran.
Methods
MeSH keywords were applied to search several databases, including PUBMED, MEDLINE, AMED, EMBASE, Iran DOC, and the Scientific Information Database without a time limit from inception to September 2011. The quality of the non-interventional and population-based studies on Iranians included in these databases was assessed by the authors and any disagreement was resolved with consensus.
Results
The literature search yielded 1847 publications, of which 62 were included in this study after eliminating non-relevant and overlapping papers. No study was found that verified a higher prevalence of the non-conventional type 2 diabetes risk factors in the Iranian population.
Conclusion
The identified evidence gap about the role of prominent non-conventional risk factors of type 2 diabetes in the Iranian population could be a major caveat in the application of an evidence-based approach to endorse or reject existing hypothesis about these risk factors. Studies on the prevalence of non-conventional biomarkers of type 2 diabetes among Iranians could be a promising area of research. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Application of Pender’s health promotion model for type 2 diabetes treatment adherence: protocol for a mixed methods study in southern Iran
Nahid Shahabi, Zahra Hosseini, Teamur Aghamolaei, Amin Ghanbarnejad, Ahmad Behzad
Trials.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence and determinants of diabetes and prediabetes in southwestern Iran: the Khuzestan comprehensive health study (KCHS)
Sanam Hariri, Zahra Rahimi, Nahid Hashemi-Madani, Seyyed Ali Mard, Farnaz Hashemi, Zahra Mohammadi, Leila Danehchin, Farhad Abolnezhadian, Aliasghar Valipour, Yousef Paridar, Mohammad Mahdi Mir-Nasseri, Alireza Khajavi, Sahar Masoudi, Saba Alvand, Bahman
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of modified Nordic diet with cardiovascular risk factors among type 2 diabetes patients: a cross-sectional study
Elnaz Daneshzad, Shaghayegh Emami, Manije Darooghegi Mofrad, Sahar Saraf-Bank, Pamela J. Surkan, Leila Azadbakht
Journal of Cardiovascular and Thoracic Research.2018; 10(3): 153. CrossRef
- Application of Pender’s health promotion model for type 2 diabetes treatment adherence: protocol for a mixed methods study in southern Iran
- High Prevalence of Class 1 to 3 Integrons Among Multidrug-Resistant Diarrheagenic
Escherichia coli in Southwest of Iran - Mohammad Kargar, Zahra Mohammadalipour, Abbas Doosti, Shahrokh Lorzadeh, Alireza Japoni-Nejad
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2014;5(4):193-198. Published online August 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2014.06.003
- 3,186 View
- 24 Download
- 44 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Horizontal transfer of integrons is one of the important factors that can contribute to the occurrence of multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacteria. This study aimed to determine the prevalence of integrons among MDR Escherichia coli strains isolated from stool specimens and investigate the associations between the existence of integrons and MDR properties in the southwest of Iran.
Methods
There were 164 E. coli strains isolated from January 2012 to June 2012. Fecal specimens identified as E. coli by the conventional methods. Subsequently the antibiotic resistance was assessed using Clinical and Laboratory Standard Institute criteria. The presence of class 1–3 integrons and embedded gene cassettes was verified using specific primers by multiplex polymerase chain reaction assay.
Results
Among a total of 164 studied samples, 69 (42.07%) isolates were multidrug resistant. Class 1 and class 2 integrons were present in 78.26% and 76.81% MDR isolates, respectively. For the first time in Iran, class 3 integron was observed in 26.09% MDR isolates. Significant correlations were identified between: class 1 integron and resistance to amikacin, gentamicin, chloramphenicol, ampicillin, tetracycline, nalidixic acid, and co-trimoxazole; class 2 integron and resistance to aminoglycosides, co-trimoxazole, cefalexin, ampicillin, and chloramphenicol; and class 3 integron and resistance to gentamicin, kanamycin, and streptomycin.
Conclusion
Our results indicate that integrons are common among MDR isolates and they can be used as a marker for the identification of MDR isolates. Therefore, due to the possibility of a widespread outbreak of MDR isolates, molecular surveillance and sequencing of the integrons in other parts of the country is recommended. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Municipal wastewater treatment plant showing a potential reservoir for clinically relevant MDR bacterial strains co-occurrence of ESBL genes and integron-integrase genes
Kuldeep Soni, David Kothamasi, Ram Chandra
Journal of Environmental Management.2024; 351: 119938. CrossRef - Detection of virulence factor genes, antibiotic resistance genes and biofilm formation in clinical Gram-negative bacteria and first report from Türkiye of K.oxytoca carrying both blaOXA-23 and blaOXA-51 genes
Azer Özad Düzgün, Gamze Yüksel
Biologia.2023; 78(8): 2245. CrossRef - Antimicrobial Resistance in Romania: Updates on Gram-Negative ESCAPE Pathogens in the Clinical, Veterinary, and Aquatic Sectors
Ilda Czobor Barbu, Irina Gheorghe-Barbu, Georgiana Alexandra Grigore, Corneliu Ovidiu Vrancianu, Mariana Carmen Chifiriuc
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(9): 7892. CrossRef - Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli Isolated from Food-Producing Animals in Tamaulipas, Mexico
Antonio Mandujano, Diana Verónica Cortés-Espinosa, José Vásquez-Villanueva, Paulina Guel, Gildardo Rivera, Karina Juárez-Rendón, Wendy Lizeth Cruz-Pulido, Guadalupe Aguilera-Arreola, Abraham Guerrero, Virgilio Bocanegra-García, Ana Verónica Martínez-Vázqu
Antibiotics.2023; 12(6): 1010. CrossRef - Antimicrobial susceptibility and integrons detection among extended-spectrum β-lactamase producing Enterobacteriaceae isolates in patients with urinary tract infection
Karzan Taha Abubaker, Khanda Abdulateef Anwar
PeerJ.2023; 11: e15429. CrossRef - Brucella abortus antigen omp25 vaccines: Development and targeting based on Lactococcus lactis
Somaye Tirbakhsh Gouran, Abbas Doosti, Mohammad Saeid Jami
Veterinary Medicine and Science.2023; 9(4): 1908. CrossRef - Integrons in the development of antimicrobial resistance: critical review and perspectives
Basharat Ahmad Bhat, Rakeeb Ahmad Mir, Hafsa Qadri, Rohan Dhiman, Abdullah Almilaibary, Mustfa Alkhanani, Manzoor Ahmad Mir
Frontiers in Microbiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Tracing the Evolutionary Pathways of Serogroup O78 Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli
Eun-Jin Ha, Seung-Min Hong, Seung-Ji Kim, Sun-Min Ahn, Ho-Won Kim, Kang-Seuk Choi, Hyuk-Joon Kwon
Antibiotics.2023; 12(12): 1714. CrossRef - Molecular Detection of Integrons, Colistin and β-lactamase Resistant Genes in Salmonella enterica Serovars Enteritidis and Typhimurium Isolated from Chickens and Rats Inhabiting Poultry Farms
Tsepo Ramatla, Kealeboga Mileng, Rendani Ndou, Nthabiseng Mphuti, Michelo Syakalima, Kgaugelo E. Lekota, Oriel M.M. Thekisoe
Microorganisms.2022; 10(2): 313. CrossRef - Prevalence of the Integrons and ESBL Genes in Multidrug-Resistant Strains of Escherichia coli Isolated from Urinary Tract Infections, Ardabil, Iran
Soheyla Barzegar, Mohsen Arzanlou, Amir Teimourpour, Majid Esmaelizad, Mehdi Yousefipour, Jafar MohammadShahi, Roghayeh Teimourpour
Iranian Journal of Medical Microbiology.2022; 16(1): 56. CrossRef - Migration of antibiotic resistance genes and evolution of flora structure in the Xenopus tropicalis intestinal tract with combined exposure to roxithromycin and oxytetracycline
Xiaojun Lin, Yanbin Xu, Ruiqi Han, Wenshi Luo, Li Zheng
Science of The Total Environment.2022; 820: 153176. CrossRef - Investigation of class 1 integrons and biofilm formation in multi-drug resistance uropathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from patients with urinary tract infection in shohadaye qom hospital, Iran
Ahmad Khorshidi, NadiaMohammad Zadeh, Azad Khaledi, GholamAbbas Moosavi, Ali Shakerimoghaddam, Azade Matinpur
International Archives of Health Sciences.2022; 9(1): 47. CrossRef - Prevalence and characterisation of antimicrobial resistance genes and class 1 and 2 integrons in multiresistant Escherichia coli isolated from poultry production
Przemysław Racewicz, Michał Majewski, Hanna Biesiada, Sebastian Nowaczewski, Jarosław Wilczyński, Danuta Wystalska, Magdalena Kubiak, Marcin Pszczoła, Zofia E. Madeja
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of integrons in multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli isolates from waters and vegetables in Nsukka and Enugu, Southeast Nigeria
Chinyere B. Chigor, Ini-Abasi I. Ibangha, Nkechinyere O. Nweze, Valentino C. Onuora, Chizoba A. Ozochi, Yinka Titilawo, Matthew C. Enebe, Tatyana N. Chernikova, Peter N. Golyshin, Vincent N. Chigor
Environmental Science and Pollution Research.2022; 29(40): 60945. CrossRef - Antimicrobial resistance and genetic diversity of Staphylococcus aureus collected from livestock, poultry and humans
Sangeeta Rao, Lyndsey Linke, Roberta Magnuson, Linzy Jauch, Doreene R. Hyatt
One Health.2022; 15: 100407. CrossRef - The Emergence of Carbapenem-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria in Mizoram, Northeast India
Vanlalruati S. C. Ralte, Archana Loganathan, Prasanth Manohar, Christine Vanlalbiakdiki Sailo, Zothan Sanga, Lalremruata Ralte, John Zothanzama, Sebastian Leptihn, Ramesh Nachimuthu, Nachimuthu Senthil Kumar
Microbiology Research.2022; 13(3): 342. CrossRef - Common Etiological Agents in Adult Patients with Gastroenteritis from Central Iran
Elnaz Abbasi, Alex van Belkum, Ehsanollah Ghaznavi-Rad
Microbial Drug Resistance.2022; 28(11): 1043. CrossRef - Antibiotic Resistance in Proteus mirabilis: Mechanism, Status, and Public Health Significance
Ebtehal Alqurashi, Khaled Elbanna, Iqbal Ahmad, Hussein H. Abulreesh
Journal of Pure and Applied Microbiology.2022; 16(3): 1550. CrossRef - Antibiotic Susceptibility Profiles and Resistance Mechanisms to β-Lactams and Polymyxins of Escherichia coli from Broilers Raised under Intensive and Extensive Production Systems
Mariana Ferreira, Célia Leão, Lurdes Clemente, Teresa Albuquerque, Ana Amaro
Microorganisms.2022; 10(10): 2044. CrossRef - Antimicrobial Resistance, Integron Carriage, and Fluoroquinolone Resistance Genes in Acinetobacte baumannii Isolates
Parastoo Ashouri, Jafar Mohammadshahi, Vajihe Sadat Nikbin, Hadi Peeridogaheh, Behnam Mohammadi-Ghalehbin, Soheila Refahi, Amir Teimourpour, Majid Esmaelizad, Hafez Mirzaneghad, Roghayeh Teimourpour
Archives of Clinical Infectious Diseases.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Multidrug resistance-encoding gene in Citrobacter freundii isolated from healthy laying chicken in Blitar District, Indonesia
Adiana Mutamsari Witaningrum, Freshinta Jellia Wibisono, Dian Ayu Permatasari, Mustofa Helmi Effendi, Emmanuel Nnabuike Ugbo
International Journal of One Health.2022; : 161. CrossRef - Evaluation of Retail Meat as a Source of ESBL Escherichia coli in Tamaulipas, Mexico
Ana Verónica Martínez-Vázquez, Antonio Mandujano, Eduardo Cruz-Gonzalez, Abraham Guerrero, Jose Vazquez, Wendy Lizeth Cruz-Pulido, Gildardo Rivera, Virgilio Bocanegra-García
Antibiotics.2022; 11(12): 1795. CrossRef - Characterization of Integrons and Quinolone Resistance in Clinical Escherichia coli Isolates in Mansoura City, Egypt
Shaymaa H. Abdel-Rhman, Rehab M. Elbargisy, Dina E. Rizk, Ahmed Majeed Al-Shammari
International Journal of Microbiology.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Prevalence and Characterization of ESBL/AmpC Producing Escherichia coli from Fresh Meat in Portugal
Lurdes Clemente, Célia Leão, Laura Moura, Teresa Albuquerque, Ana Amaro
Antibiotics.2021; 10(11): 1333. CrossRef - Association of phylogenetic distribution and presence of integrons with multidrug resistance in Escherichia coli clinical isolates from children with diarrhoea
Yesmi Patricia Ahumada-Santos, María Elena Báez-Flores, Sylvia Páz Díaz-Camacho, Magdalena de Jesús Uribe-Beltrán, Carlos Alberto Eslava-Campos, Jesús Ricardo Parra-Unda, Francisco Delgado-Vargas
Journal of Infection and Public Health.2020; 13(5): 767. CrossRef - Class 1 Integrons in Clinical Multi Drug Resistance E. coli, Sana’a Hospitals, Yemen
Mukhtar A. Al-Hammadi, Hassan A. Al-Shamahy, Abdulaziz Q. Ali, Mahfoudh A.M. Abdulghani, Hassan Pyar, Ibrahim AL-Suboal
Pakistan Journal of Biological Sciences.2020; 23(3): 231. CrossRef - Occurrence, Phenotypic and Molecular Characterization of Extended-Spectrum- and AmpC- β-Lactamase Producing Enterobacteriaceae Isolated From Selected Commercial Spinach Supply Chains in South Africa
Loandi Richter, Erika M. du Plessis, Stacey Duvenage, Lise Korsten
Frontiers in Microbiology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Staphylococcus aureus biofilms: Structures, antibiotic resistance, inhibition, and vaccines
Raziey Parastan, Mohammad Kargar, Kavous Solhjoo, Farshid Kafilzadeh
Gene Reports.2020; 20: 100739. CrossRef - Dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) via integrons in Escherichia coli: A risk to human health
Shaqiu Zhang, Muhammad Abbas, Mujeeb Ur Rehman, Yahui Huang, Rui Zhou, Siyue Gong, Hong Yang, Shuling Chen, Mingshu Wang, Anchun Cheng
Environmental Pollution.2020; 266: 115260. CrossRef Multi-Drug-Resistant Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli Pathotypes in Pediatric Patients with Gastroenteritis from Central Iran
Elnaz Abbasi, Mahdieh mondanizadeh, Alex van Belkum, Ehsanollah Ghaznavi-Rad
Infection and Drug Resistance.2020; Volume 13: 1387. CrossRef- The Relationship of Class I Integron Gene Cassettes and the Multidrug-Resistance in Extended -Spectrum β-Lactamase Producing Isolates of Escherichia coli
Alisha Akya, Roya Chegene Lorestani, Mosayeb Rostamian, Azam Elahi, Shokofe Baakhshii, Minoo Aliabadi, Keyghobad Ghadiri
Archives of Pediatric Infectious Diseases.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Integrons in Enterobacteriaceae : diversity, distribution and epidemiology
Megha Kaushik, Sanjay Kumar, Rajeev Kumar Kapoor, Jugsharan Singh Virdi, Pooja Gulati
International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents.2018; 51(2): 167. CrossRef - Molecular analysis of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O157:H7 and non-O157 strains isolated from calves
Maryam Kohansal, Ali Ghanbari Asad
Onderstepoort Journal of Veterinary Research.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of Integrons and Insertion Sequences in ESBL-Producing E. coli Isolated from Different Sources in Navarra, Spain
Lara Pérez-Etayo, Melibea Berzosa, David González, Ana Vitas
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2018; 15(10): 2308. CrossRef - Frequency of antimicrobial resistance and integron gene cassettes in Escherichia coli isolated from giant pandas (Ailuropoda melanoleuca) in China
Wencheng Zou, Caiwu Li, Xin Yang, Yongxiang Wang, Guangyang Cheng, Jinxin Zeng, Xiuzhong Zhang, Yanpeng Chen, Run Cai, Qianru Huang, Lan Feng, Hongning Wang, Desheng Li, Guiquan Zhang, Yanxi Chen, Zhizhong Zhang, Heming Zhang
Microbial Pathogenesis.2018; 116: 173. CrossRef - Colistin-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: Prevalence of Integrons and Synergistic Out Turn for Colistin-Meropenem
Prasanth Manohar, Thamaraiselvan Shanthini, Pandey Ekta, Mahesan J B, Kodiveri Muthukaliannan Gothandam, Bulent Bozdogan, Nachimuthu Ramesh
Archives of Clinical Infectious Diseases.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of integrons classes 1–3 in extended spectrum beta-lactamases and multi drug resistant Escherichia coli isolates in the North of Iran
Shahla Asgharzadeh Kangachar, Ali Mojtahedi
Gene Reports.2018; 12: 299. CrossRef - Association of Glycerol Kinase Gene with Class 3 Integrons: A Novel Cassette Array within Escherichia coli
Rajkumari Elizabeth, Debadatta Dhar Chanda, Atanu Chakravarty, Deepjyoti Paul, Shiela Chetri, Deepshikha Bhowmik, Jayalaxmi Wangkheimayum, Amitabha Bhattacharjee
Indian Journal of Medical Microbiology.2018; 36(1): 104. CrossRef - Emergence of class 1 to 3 integrons among members of Enterobacteriaceae in Egypt
Dina E. Rizk, Areej M. El-Mahdy
Microbial Pathogenesis.2017; 112: 50. CrossRef - Detection of Class I and II integrons for the assessment of antibiotic and multidrug resistance amongEscherichia coliisolates from agricultural irrigation waters in Bulacan, Philippines
Cielo Emar M. Paraoan, Windell L. Rivera, Pierangeli G. Vital
Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part .2017; 52(5): 306. CrossRef - Distribution of Integrons and Phylogenetic Groups among Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli Isolates from Children <5 Years of Age in Delhi, India
Taru Singh, Shukla Das, V. G. Ramachandran, Sayim Wani, Dheeraj Shah, Khan A. Maroof, Aditi Sharma
Frontiers in Microbiology.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - The distribution of carbapenem- and colistin-resistance in Gram-negative bacteria from the Tamil Nadu region in India
Prasanth Manohar, Thamaraiselvan Shanthini, Ramankannan Ayyanar, Bulent Bozdogan, Aruni Wilson, Ashok J. Tamhankar, Ramesh Nachimuthu, Bruno S. Lopes
Journal of Medical Microbiology .2017; 66(7): 874. CrossRef - Multidrug-Resistant Escherichia coli Strains Isolated from Patients Are Associated with Class 1 and 2 Integrons
Hamid Lavakhamseh, Parviz Mohajeri, Samaneh Rouhi, Pegah Shakib, Rashid Ramazanzadeh, Afshin Rasani, Majid Mansouri
Chemotherapy.2016; 61(2): 72. CrossRef - Variability in gene cassette patterns of class 1 and 2 integrons associated with multi drug resistance patterns in Staphylococcus aureus clinical isolates in Tehran-Iran
Mahdi Mostafa, Seyed Davar Siadat, Fereshteh Shahcheraghi, Farzam Vaziri, Alireza Japoni-Nejad, Jalil Vand Yousefi, Bahareh Rajaei, Elnaz Harifi Mood, Nayyereh Ebrahim zadeh, Arfa Moshiri, Seyed Alireza Seyed Siamdoust, Mohamad Rahbar
BMC Microbiology.2015;[Epub] CrossRef
- Municipal wastewater treatment plant showing a potential reservoir for clinically relevant MDR bacterial strains co-occurrence of ESBL genes and integron-integrase genes



 First
First Prev
Prev


