Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Seroprevalence of immunoglobulin G antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 in children and adolescents in Delhi, India, from January to October 2021: a repeated cross-sectional analysis
- Pragya Sharma, Saurav Basu, Suruchi Mishra, Mongjam Meghachandra Singh
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(3):184-190. Published online June 10, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0014
- 5,151 View
- 76 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 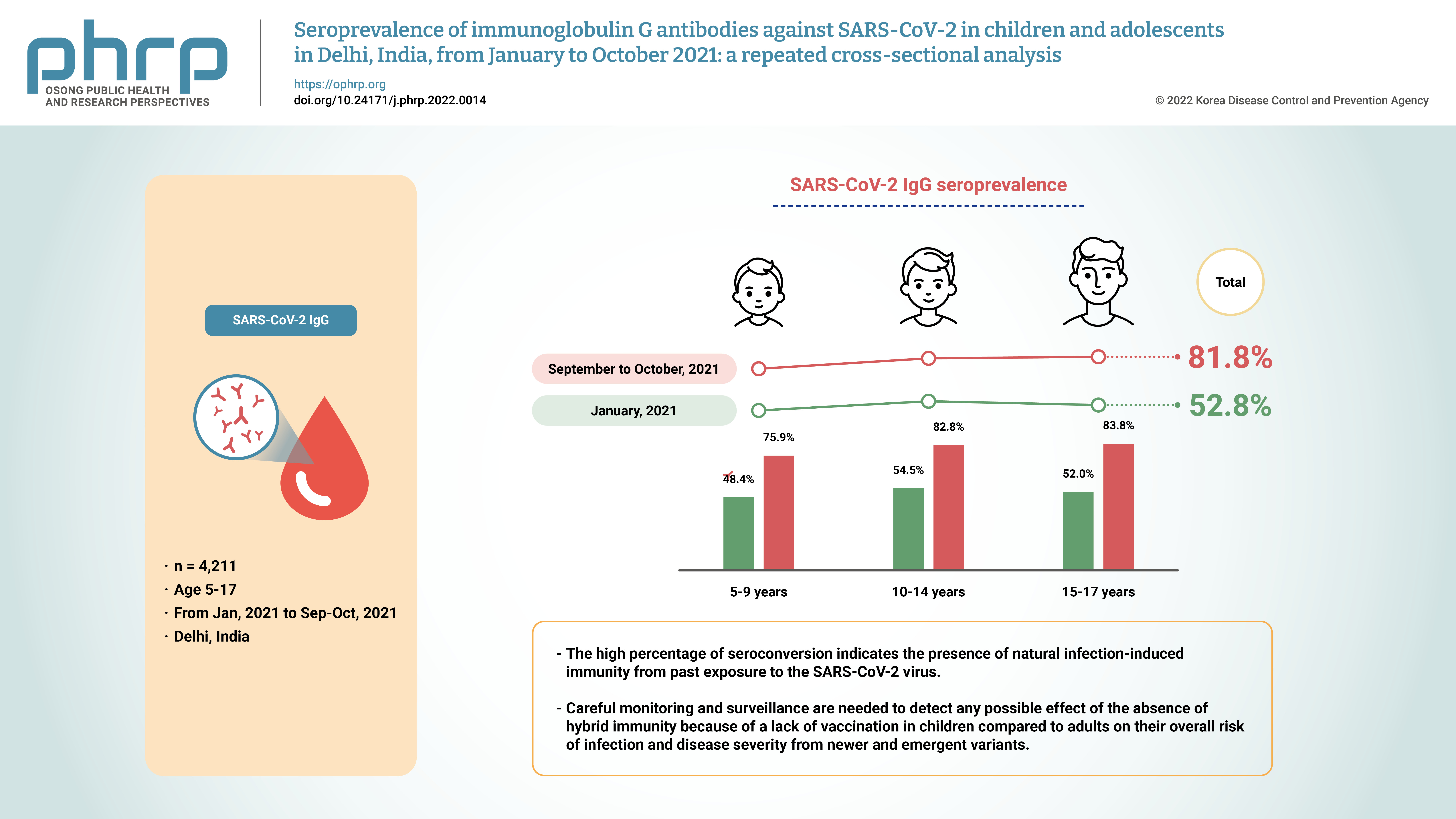
- Objectives
The aim of this study was to assess changes in the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) immunoglobulin G (IgG) seroprevalence among children and adolescents in Delhi, India from January 2021 to October 2021. Methods: This was a repeated cross-sectional analysis of participants aged 5 to 17 years from 2 SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence surveys conducted in Delhi, India during January 2021 and September to October 2021. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibodies were detected by using the VITROS assay (90% sensitivity, 100% specificity). Results: The seroprevalence among 5- to 17-year-old school-age children and adolescents increased from 52.8% (95% confidence interval [CI], 51.3%−54.3%) in January 2021 to 81.8% (95% CI, 80.9%−82.6%) in September to October 2021. The assay-adjusted seroprevalence was 90.8% (95% CI, 89.8%−91.7%). Seropositivity positively correlated with participants’ age (p<0.001), but not sex (p=0.388). A signal to cut-off ratio ≥4.00, correlating with the presence of neutralization antibodies, was observed in 4,814 (57.9%) participants. Conclusion: The high percentage of seroconversion among children and adolescents indicates the presence of natural infection-induced immunity from past exposure to the SARS-CoV-2 virus. However, the lack of hybrid immunity and the concomitant likelihood of lower levels of neutralization antibodies than in adults due to the absence of vaccination warrants careful monitoring and surveillance of infection risk and disease severity from newer and emergent variants. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Severe Acute Hepatitis of Unknown Etiology Presenting as Pediatric Acute Liver Failure: Analysis of Likely Etiology, Clinical Course and Outcome
Bikrant B. Lal, Vikrant Sood, Ekta Gupta, Reshu Agarwal, Rajeev Khanna, Seema Alam
Journal of Clinical and Experimental Hepatology.2023; 13(5): 912. CrossRef - Anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody kinetics up to 6 months of follow-up: Result from a nation-wide population-based, age stratified sero-epidemiological prospective cohort study in India
Puneet Misra, Arvind Kumar Singh, Baijayantimala Mishra, Bijayini Behera, Binod Kumar Patro, Guruprasad R. Medigeshi, Hari Shanker Joshi, Mohammad Ahmad, Pradeep Kumar Chaturvedi, Palanivel Chinnakali, Partha Haldar, Mohan Bairwa, Pradeep Kharya, Rahul Dh
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(12): e0287807. CrossRef - Seroprevalence of SARS CoV-2 among children after the second surge (June 2021) in a rural district of South India: Findings and lessons from a population-based survey
Carolin Elizabeth George, Leeberk Raja Inbaraj, Shon Rajukutty, Roshni Florina Joan, Sangeetha Muthuraj, Sindhulina Chandrasingh
Frontiers in Pediatrics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Severe Acute Hepatitis of Unknown Etiology Presenting as Pediatric Acute Liver Failure: Analysis of Likely Etiology, Clinical Course and Outcome
- AIDS Awareness: Indispensible Prerequisite Among Fishermen Population
- Swapna B. Shetty, Darshan D. Divakar, M.H.N. Dalati, Sajith Vellappally, Sukumaran Anil, Marey A. Alshehry, Baher Felemban, Al S. Mamdouh, Obaid A. Alshahrani
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2016;7(5):327-333. Published online October 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2016.09.003
- 2,943 View
- 28 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Fishermen are among the most vulnerable groups for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)/AIDS with reported high prevalence. Poor knowledge base has been evidenced by a few studies. The present study was conducted to assess the knowledge regarding HIV/AIDS among fishermen of the Kutch coast, Gujarat, India.
Methods
A descriptive cross-sectional study was conducted among 950 fishermen of the Kutch coast, in the months of January–February 2015. Knowledge of HIV/AIDS of fishermen was assessed using structured interview schedules with 12 questions. The information on socio-demographic characteristics was also obtained. Chi-square test and multivariate logistic regression analysis were used for statistical analysis. The confidence level and level of significance were fixed at 95% and 5%, respectively.
Results
A major proportion of participants (57.2%) had no access to any potential source of information and had never heard about HIV/AIDS (65.1%). Some of them were aware of modes of transmission of AIDS but only a few of them knew about the methods of prevention. Only 23.1% of participants were observed with appropriate knowledge regarding HIV/AIDS. Bivariate and multivariate analysis revealed significant variation in the proportion of participants with appropriate knowledge with age and educational status.
Conclusion
Overall, the knowledge of the fishermen community in the present study was evidenced to be poor creating an alarming situation demanding educative interventions as a part of AIDS control programs. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prolonged Release of Anti-Retroviral Efavirenz From System Using ZIF-8 as Carrier
Alinne Élida Gonçalves Alves Tabosa, Aline Silva Ferreira, Natália Millena da Silva, Débora Dolores Souza da Silva Nascimento, Leslie Raphael de Moura Ferraz, José Yago Rodrigues Silva, Severino Alves Junior, Rosali Maria Ferreira da Silva, Larissa Araúj
Current HIV Research.2020; 18(6): 396. CrossRef - Prevalence of HIV infection and uptake of HIV/AIDS services among fisherfolk in landing Islands of Lake Victoria, north western Tanzania
Anthony Kapesa, Namanya Basinda, Elias C. Nyanza, Martha F. Mushi, Ola Jahanpour, Sospatro E. Ngallaba
BMC Health Services Research.2018;[Epub] CrossRef
- Prolonged Release of Anti-Retroviral Efavirenz From System Using ZIF-8 as Carrier
- Prevalence of Dyslipidemia and Hypertension in Indian Type 2 Diabetic Patients with Metabolic Syndrome and its Clinical Significance
- Dhananjay Yadav, Meerambika Mishra, Arvind Tiwari, Prakash Singh Bisen, Hari Mohan Goswamy, G.B.K.S. Prasad
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2014;5(3):169-175. Published online June 30, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2014.04.009
- 2,901 View
- 26 Download
- 16 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The present study was designed to estimate the prevalence of dyslipidemia and hypertension based on the National Cholesterol Educational Programme Adult Treatment Panel III definition of metabolic syndrome (MetS). The study also focuses on prevalence for MetS with respect to the duration of disease in Gwalior–Chambal region of Madhya Pradesh, India.
Methods
Type 2 diabetic patients (n = 700) were selected from a cross-sectional study that is regularly being conducted in the School of Studies in Biochemistry, Jiwaji University Gwalior, India. The period of our study was from January 2007 to October 2009. Dyslipidemia and hypertension were determined in type 2 diabetic patients with MetS as per National Cholesterol Educational Programme Adult Treatment Panel III criteria.
Results
The mean age of the study population was 54 ± 9.3 years with 504 (72%) males and 196 (28%) females. The prevalence of MetS increased with increased duration of diabetes in females; however, almost constant prevalence was seen in the males. Notable increase in the dyslipidemia (64.1%) and hypertension (49%) in type 2 diabetic patients were seen. The steep increase in dyslipidemia and hypertension could be the reason for the growing prevalence of diabetes worldwide. The study also noted a close association between age and occurrence of MetS.
Conclusion
Individual variable of MetS appears to be highly rampant in diabetic population. Despite treatment, almost half of patients still met the criteria for MetS. Effective treatment of MetS components is required to reduce cardiovascular risk in diabetes mellitus hence accurate and early diagnosis to induce effective treatment of MetS in Indian population will be pivotal in the prevention of cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Complete blood count inflammation derived indexes as predictors of metabolic syndrome in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Almir Fajkić, Rijad Jahić, Edin Begić, Amela Dervišević, Avdo Kurtović, Orhan Lepara
Technology and Health Care.2024; : 1. CrossRef - Mapping multimorbidity from diabetes mellitus and its association with depressive symptoms among older people of India: a cross-sectional study from a nationally representative survey
Gayatri Khanal, Y. Selvamani, J. Kezia Angeline
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Co.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Utilization of Hypolipidemic Drugs, Patterns, and Factors Affecting Dyslipidemia Among Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus at a Tertiary Care Teaching Hospital in South India
Sandeep Khot, Ananya Chakraborty, Savitha Vijaykumar
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Real-World Observational Study on Vildagliptin With Insulin (VIL-INS) or Vildagliptin and Metformin With Insulin (VIL-MET-INS) Therapy in Indian Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
P Panneerselvam, Dibakar Biswas, Hema Singh, K Dilip Kumar, P Ravi Kumar, Pramila Kalra, Santosh Revankar, Sona Warrier
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Magnitude and Determinants of Diabetic Retinopathy Among Indian Diabetic Patients Undergoing Telescreening in India
Rajiv Khandekar, Tamilarasan Senthil, Malathi Nainappan, Deepak P. Edward
Telemedicine and e-Health.2022; 28(2): 176. CrossRef - An experimental study of rosuvastatin’s analgesic effect and its interaction with etoricoxib, tramadol, amlodipine, and amitriptytline in albino mice
Prafull Mohan, Ashok Kumar Sharma, Sharmila Sinha, R. Sabarad
Medical Journal Armed Forces India.2022; 78: S61. CrossRef - Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Product, Organ Crosstalk, and Pathomechanism Targets for Comprehensive Molecular Therapeutics in Diabetic Ischemic Stroke
Nivedita L. Rao, Greeshma B. Kotian, Jeevan K. Shetty, Bhaskara P. Shelley, Mackwin Kenwood Dmello, Eric C. Lobo, Suchetha Padar Shankar, Shellette D. Almeida, Saiqa R. Shah
Biomolecules.2022; 12(11): 1712. CrossRef - Metabolic and Energy Imbalance in Dysglycemia-Based Chronic Disease
Sanjay Kalra, Ambika Gopalakrishnan Unnikrishnan, Manash P Baruah, Rakesh Sahay, Ganapathi Bantwal
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets .2021; Volume 14: 165. CrossRef - Association between diet quality scores, adiposity, glycemic status and nutritional biomarkers among Indian population with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A cross-sectional study
Aamir Bashir, Krishna Pandey, Md Azharuddin, Anjali Kumari, Ishfaq Rashid, N.A. Siddiqui, Chandra Shekhar Lal, Krishna Murti
Clinical Epidemiology and Global Health.2020; 8(1): 53. CrossRef The Impact of BMI Categories on Metabolic Abnormality Development in Chinese Adults Who are Metabolically Healthy: A 7-Year Prospective Study
Xiangtong Liu, Jingbo Zhang, Jingwei Wu, Xiaolin Xu, Lixin Tao, Yue Sun, Shuo Chen, Yumei Han, Yanxia Luo, Xinghua Yang, Xiuhua Guo
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets .2020; Volume 13: 819. CrossRef- Metabolic syndrome in north Indian type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: A comparison of four different diagnostic criteria of metabolic syndrome
Deepak Gahlan, Rajesh Rajput, Vandana Singh
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research &.2019; 13(1): 356. CrossRef - Prevalence of Type 2 Diabetes and Prediabetes in the Gwalior-Chambal Region of Central India
Senthil Kumar Subramani, Dhananjay Yadav, Meerambika Mishra, Umamaheswari Pakkirisamy, Prakesh Mathiyalagen, GBKS Prasad
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2019; 16(23): 4708. CrossRef - A PROSPECTIVE STUDY OF DYSLIPIDAEMIA AND OBESITY IN HYPERTENSION PATIENTS
Ponnana Raja Kumar, Siripurapu Sasikala
Journal of Evidence Based Medicine and Healthcare.2018; 5(1): 43. CrossRef - Prevalence and pattern of co morbidity among type2 diabetics attending urban primary healthcare centers at Bhubaneswar (India)
Sandipana Pati, F. G. Schellevis, Alessandra Marengoni
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(8): e0181661. CrossRef - Dyslipidemia Prevalence in Iranian Adult Men: The Impact of Population-Based Screening on the Detection of Undiagnosed Patients
Abolfazl Mohammadbeigi, Esamil Moshiri, Narges Mohammadsalehi, Hossein Ansari, Ali Ahmadi
The World Journal of Men's Health.2015; 33(3): 167. CrossRef - Association of high-density lipoprotein with development of metabolic syndrome components: a five-year follow-up in adults
Xiangtong Liu, Lixin Tao, Kai Cao, Zhaoping Wang, Dongning Chen, Jin Guo, Huiping Zhu, Xinghua Yang, Youxin Wang, Jingjing Wang, Chao Wang, Long Liu, Xiuhua Guo
BMC Public Health.2015;[Epub] CrossRef
- Complete blood count inflammation derived indexes as predictors of metabolic syndrome in type 2 diabetes mellitus



 First
First Prev
Prev


