Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Factors affecting depression and health-related quality of life in the elderly during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Deok-Ju Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(6):520-529. Published online November 16, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2023.0166
- 853 View
- 42 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 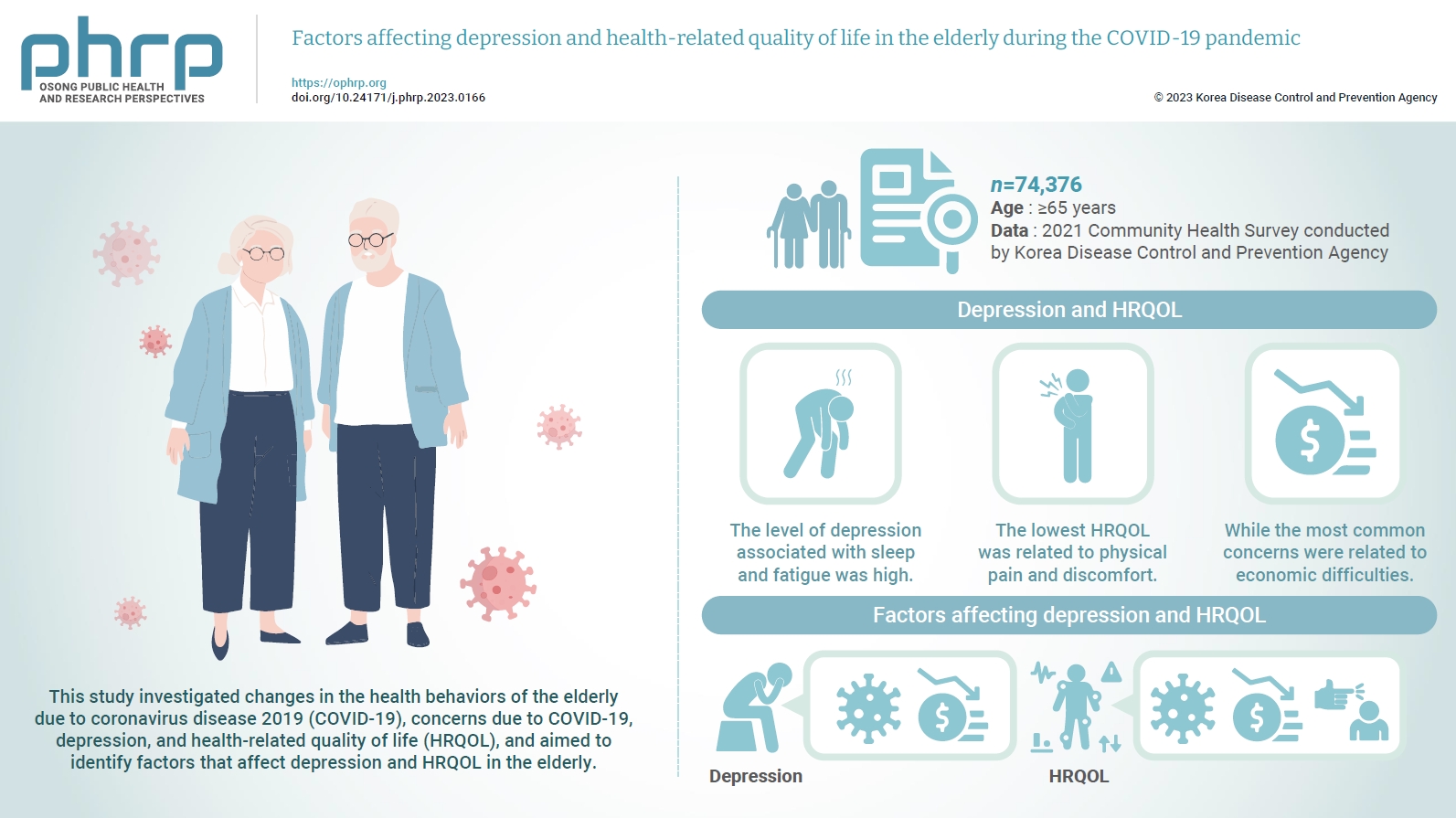
- Objectives
This study investigated changes in the health behaviors of the elderly due to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), concerns due to COVID-19, depression, and healthrelated quality of life (HRQOL), and aimed to identify factors that affect depression and HRQOL in the elderly. Methods: This study was conducted using data from the 2021 Community Health Survey of the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency. From a total sample size of 229,242 individuals, 74,376 elderly people aged 65 or older were selected as subjects, and changes in health behaviors, concerns due to COVID-19, depression, and HRQOL were measured and analyzed. Results: The level of depression associated with sleep and fatigue was high. The lowest HRQOL was related to physical pain and discomfort, while the most common concerns were related to economic difficulties. Factors influencing depression included worries about infection and economic harm, while factors impacting HRQOL encompassed concerns about infection, economic harm, and criticism from others. Conclusion: If an infectious disease situation such as COVID-19 reoccurs in the future, it will be necessary to encourage participation in hybrid online and offline programs at senior welfare centers. This should also extend to community counseling institutions like mental health welfare centers. Additionally, establishing connections with stable senior job projects can help to mitigate the effects of social interaction restrictions, physical and psychological health issues, and economic difficulties experienced by the elderly.
- The role of risk perception, risk communication, and demographic factors in COVID-19 preventive behaviors: an online survey in Iran
- Mansour Rezaei, Nader Rajabi Gilan, Ali Almasi, Mehdi Khezeli, Fatemeh Jamshidi Nazar, Zahra Jorjoran Shushtari, Yahya Salimi, Farid Najafi, Neda Sarabi, Shahram Saeidi, Saeid Saeidi
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(4):282-289. Published online August 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.0345
- 2,843 View
- 57 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study investigated preventive behaviors toward coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and related factors in a Kurdish Iranian sample.
Methods
This online survey was conducted among the population aged 18 and above in Kermanshah Province, in western Iran, in April 2020. Samples were invited and recruited through social media. Data were collected using a questionnaire consisting of 4 sections (questions on demographic variables, risk perception, risk communication, and COVID-19 preventive behaviors) and analyzed using Stata ver. 8.
Results
The Pearson correlation test showed that risk communication was significantly correlated with COVID-19 preventive behaviors (r=0.320, p<0.01). In the final model, where the explanatory power increased with the entry of the risk communication variable, the variables explained a total of 14% of variance in COVID-19 preventive behaviors. Sex (β=−0.482), risk perception (β=0.047), and risk communication (β=0.662) were significant determinants.
Conclusion
Risk communication and risk perception related to COVID-19, as well as being a woman, were determinants of COVID-19 preventive behaviors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Understanding Australian Government Risk Communication Early in the COVID-19 Pandemic: Sociodemographics, Risk Attitudes and Media Consumption
Yiyun Shou, Louise M. Farrer, Amelia Gulliver, Eryn Newman, Philip J. Batterham, Michael Smithson
Journal of Health Communication.2023; 28(4): 254. CrossRef - Risk perception and avoidance of preventive behavior on the COVID‐19 among cancer patients
Mehdi Khezeli, Asghar Tavan, Sajjad Narimani, Vahideh Hoseini, Elham Zare Hosseinzadeh, Parisa Motamedi
Health Science Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Role of Risk Communication in Shaping Health-Protective Behavior Amid the COVID-19 Pandemic in Thailand
Suphunnika Termmee, Bing Wang
Social Sciences.2023; 12(10): 551. CrossRef
- Understanding Australian Government Risk Communication Early in the COVID-19 Pandemic: Sociodemographics, Risk Attitudes and Media Consumption
- Sex differences in factors associated with prediabetes in Korean adults
- Jin Suk Ra
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(2):142-152. Published online April 22, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0053
- 4,039 View
- 61 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Identifying the factors associated with prediabetes is necessary for the early detection and management of high-risk individuals with prediabetes. The purpose of this study was to identify the factors associated with prediabetes according to sex in Korean adults. Methods: Using the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey from 2015 to 2019, a total of 13,595 adults (5,565 males and 8,030 females) aged ≥20 years were included in the data analysis. Logistic regression analysis was performed to identify the factors associated with prediabetes according to sex in Korean adults. Results: In both males and females, age and a family history of type 2 diabetes were associated with prediabetes. In males, current and past smoking habits were associated with increased prediabetes. In addition, low-intensity physical activity and prolonged sedentary behavior were associated with a higher prevalence of prediabetes. Females with a lower education level (less than middle school graduation) showed a higher risk of prediabetes. Conclusion: Sex-specific prevention strategies for prediabetes should be developed. In addition, older individuals and those with a family history of type 2 diabetes should be screened for prediabetes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of a nutrition program based on the Health Behavior Interaction Model on primary school students’ nutritional attitudes and behaviors
Ayşe Burcu Başçı, Oya Nuran Emiroğlu, Bilge Kalanlar
Journal of Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors associated with the combination of general and abdominal obesity in middle-aged and older Korean women: a cross-sectional study
Jin Suk Ra
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2023; 14(5): 379. CrossRef
- The effect of a nutrition program based on the Health Behavior Interaction Model on primary school students’ nutritional attitudes and behaviors
- Social determinants of adherence to COVID-19 preventive guidelines: a comprehensive review
- Zahra Jorjoran Shushtari, Yahya Salimi, Sina Ahmadi, Nader Rajabi-Gilan, Marzieh Shirazikhah, Akbar Biglarian, Ali Almasi, Mohammad Ali Mohammadi Gharehghani
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2021;12(6):346-360. Published online December 21, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.0180
- 7,432 View
- 161 Download
- 19 Web of Science
- 20 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material 
- Adherence to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) preventive guidelines (ACPG) is an important strategy to control the COVID-19 pandemic effectively. The present study aimed to identify and summarize the social determinants of ACPG among the general population. A comprehensive review was performed from December 2019 to February 2021 through searching electronic databases. Two independent reviewers assessed and selected relevant studies. Next, the characteristics and main findings of the included studies were summarized. Finally, the World Health Organization’s conceptual framework of social determinants of health was used to synthesize the identified social determinants of ACPG. Forty-one of 453 retrieved articles met the inclusion criteria. The study results showed different patterns of ACPG among various communities. Furthermore, 84 social determinants were identified and categorized into structural and intermediary determinants. ACPG is a set of complex behaviors associated with different individual sociodemographic and behavioral characteristics; living and working conditions; COVID-19 knowledge, attitudes, and risk perceptions; exposure to sources and information level; leisure activities; social support; trust; social norms; psychosocial well-being; socio-economic position; and the socio-economic and political context. Interventions to promote ACPG among the general population should consider the identified social determinants of ACPG.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- ISO 50001 based energy management system: a bibliometric perspective
Marlina Pandin, Sik Sumaedi, Aris Yaman, Meilinda Ayundyahrini, Nina Konitat Supriatna, Nurry Widya Hesty
International Journal of Energy Sector Management.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of long COVID-19 on posttraumatic stress disorder as modified by health literacy: an observational study in Vietnam
Han Thi Vo, Tien Duc Dao, Tuyen Van Duong, Tan Thanh Nguyen, Binh Nhu Do, Tinh Xuan Do, Khue Minh Pham, Vinh Hai Vu, Linh Van Pham, Lien Thi Hong Nguyen, Lan Thi Huong Le, Hoang Cong Nguyen, Nga Hoang Dang, Trung Huu Nguyen, Anh The Nguyen, Hoan Van Nguye
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2024; 15(1): 33. CrossRef - Cognitive predictors of COVID-19 mitigation behaviors in vaccinated and unvaccinated general population members
Anna Hudson, Peter A. Hall, Sara C. Hitchman, Gang Meng, Geoffrey T. Fong
Vaccine.2023; 41(27): 4019. CrossRef - Utilisation of rehabilitation due to mental disorders during the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic: a difference-in-differences analysis
Matthias Bethge, David Fauser, Pia Zollmann, Marco Streibelt
BMC Psychiatry.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Perceptions about COVID-19 preventive measures among Ghanaian women
Frank Kyei-Arthur, Martin Wiredu Agyekum, Grace Frempong Afrifa-Anane, Reuben Tete Larbi, Peter Kisaakye, Dario Ummarino
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(4): e0284362. CrossRef - Cognitive and Emotional Motivation to Explain Infection-Prevention Behaviors with Social Support as a Mediator During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Nationwide Cross-Sectional Study in Korea
Myonghwa Park, Keunyeob Oh, Hyungjun Kim, Xing Fan, Thi-Thanh-Thnh Giap, Rhayun Song
Patient Preference and Adherence.2023; Volume 17: 1063. CrossRef - Factors Influencing COVID-19 Prevention Behavior: A Community-based Cross-sectional Study
Ernawaty Ernawaty, Nabilla Belqys Dherindri
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2023; 11(E): 191. CrossRef - The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Outcomes in Acute Pancreatitis: A Propensity Score Matched Study Comparing before and during the Pandemic
Patricia Mihaela Rădulescu, Elena Irina Căluianu, Emil Tiberius Traşcă, Dorin Mercuţ, Ion Georgescu, Eugen Florin Georgescu, Eleonora Daniela Ciupeanu-Călugăru, Maria Filoftea Mercuţ, Răzvan Mercuţ, Vlad Padureanu, Costin Teodor Streba, Cristina Călăraşu,
Diagnostics.2023; 13(14): 2446. CrossRef - COVID-19 in social networks: unravelling its impact on youth risk perception, motivations and protective behaviours during the initial stages of the pandemic
Marta Anson, Ksenia Eritsyan
International Journal of Adolescence and Youth.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Bi-directional associations between mask usage and beliefs about reasons for masking before and after the downgrading of the legal status of COVID-19 in Japan: A longitudinal study
Michio Murakami
International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction.2023; 97: 104072. CrossRef - Geoepidemiological perspective on COVID-19 pandemic review, an insight into the global impact
Alexandre Vallée
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of COVID-19 Pandemic on Using CTS and MRI in Iran: Evidence from an Interrupted Time Series Analysis
Monireh Mahmood Pour-Azari, Nasim Badiee, Ali Kazemi Karyani, Shahin Soltani, Satar Rezaei
Journal of Health Reports and Technology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between social isolation and loneliness with COVID-19 vaccine uptake in Japan: a nationwide cross-sectional internet survey
Tomohiko Ukai, Takahiro Tabuchi
BMJ Open.2023; 13(11): e073008. CrossRef - Exploration of factors associated with mask-wearing and hand disinfection in Japan after the coronavirus disease outbreak: A longitudinal study
Michio Murakami, Mei Yamagata, Asako Miura
International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction.2023; 98: 104107. CrossRef - Social Determinants of Adherence to COVID-19 Preventive Guidelines in Iran: A Qualitative Study
Sina Ahmadi, Zahra Jorjoran Shushtari, Marzieh Shirazikhah, Akbar Biglarian, Seyed Fahim Irandoost, Toktam Paykani, Ali Almasi, Nader Rajabi-Gilan, Nafiul Mehedi, Yahya Salimi
INQUIRY: The Journal of Health Care Organization, .2022; 59: 004695802210841. CrossRef - Determinants of observing health protocols related to preventing COVID-19 in adult women: A qualitative study in Iran
Javad Yoosefi Lebni, Saeede Pavee, Mandana Saki, Arash Ziapour, Ahmad Ahmadi, Mehdi Khezeli
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Adherence to Coronavirus Disease 2019 Preventive Measures in a Representative Sample of the Population of the Canton of Vaud, Switzerland
Audrey Butty, Nolwenn Bühler, Jérôme Pasquier, Julien Dupraz, Vincent Faivre, Sandrine Estoppey, Cloé Rawlinson, Semira Gonseth Nusslé, Murielle Bochud, Valérie D’Acremont
International Journal of Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Quarantine preparedness – the missing factor in COVID-19 behaviour change? Qualitative insights from Australia
Angela Davis, Stephanie Munari, Joseph Doyle, Brett Sutton, Allen Cheng, Margaret Hellard, Lisa Gibbs
BMC Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The impact of COVID-19 pandemic on hospital admissions for nine diseases in Iran: insight from an interrupted time series analysis
Sina Ahmadi, Ali Kazemi-Karyani, Nasim Badiee, Sarah Byford, Ali Mohammadi, Bakhtiar Piroozi, Satar Rezaei
Cost Effectiveness and Resource Allocation.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychosocial Determinants of Hand Hygiene, Facemask Wearing, and Physical Distancing During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Wei Liang, Yanping Duan, Feifei Li, Ryan E Rhodes, Xiang Wang, Dehiwala Liyanage Ishanka Harshani Kusum Peiris, Lin Zhou, Borui Shang, Yide Yang, Julien S Baker, Jiao Jiao, Wei Han
Annals of Behavioral Medicine.2022; 56(11): 1174. CrossRef
- ISO 50001 based energy management system: a bibliometric perspective
- Prevalence and correlates of highly caffeinated beverage consumption among Korean adolescents
- Ho-Kyung Kwak, Jaesin Sa, Siyoung Choe, Jean-Philippe Chaput, Joon Chung, Gayle Cummings, Jounghee Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2021;12(6):374-384. Published online November 23, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.0013
- 10,147 View
- 94 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The purposes of this study were to (1) examine the multi-year prevalence of highly caffeinated beverage (HCB) consumption, (2) identify sex differences in the prevalence, and (3) investigate relationships between HCB consumption and behavioral characteristics in a nationally representative sample of Korean adolescents.
Methods
Data from the Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web-based Survey (2014–2017) were analyzed.
Results
HCB consumption was higher in 2017 than 2014 (23.9% vs. 12.0%), and higher among boys than girls (17.2% vs. 13.1%). HCB drinkers were more likely to (1) be boys, (2) be overweight or obese, (3) use alcohol and tobacco, (4) consume soda at least once per week, (5) consume sweetened beverages at least once per week, (6) have seriously considered suicide during the past 12 months, and (7) have attempted suicide during the past 12 months (p<0.05 for all).
Conclusion
Effective programs to curb HCB consumption among Korean adolescents need to be established. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Secondary School Students and Caffeine: Consumption Habits, Motivations, and Experiences
Sophie Turner, Ajmol Ali, Carol Wham, Kay Rutherfurd-Markwick
Nutrients.2023; 15(4): 1011. CrossRef
- Secondary School Students and Caffeine: Consumption Habits, Motivations, and Experiences
- Behavioral therapy and pharmacotherapy for relapse prevention in abstinent smokers: a rapid review and meta-analysis for the Korea Preventive Service Task Force
- Naae Lee, Eon Sook Lee, Jae Moon Yun, Cheol Min Lee, Seung-Won Oh, Younglee Choi, Belong Cho
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2021;12(4):244-253. Published online July 6, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.0017
- 5,946 View
- 94 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Objectives
This study aimed to assess the effectiveness of relapse prevention interventions involving behavioral and pharmacological treatment among abstinent smokers.
Methods
This rapid review was conducted using MEDLINE, Cochrane CENTRAL, CINAHL, Embase, KMbase, and KoreaMed to identify studies published until June 20, 2020. The participants were abstinent smokers who quit smoking on their own, due to pregnancy, hospitalization, or by participating in a smoking cessation program. We found a systematic review that fit the objective of this study and included 81 randomized controlled trials (RCTs). Studies that did not present information on smoking cessation status, had no control group, or used reward-based interventions were excluded. Random effect and fixed effect meta-analyses were used to estimate the relative risk (RR) and 95% confidence interval (CI). In subgroup analyses, differences between subgroups were verified based on the participant setting, characteristics, intervention type, and intensity.
Results
Following screening, 44 RCTs were included in the meta-analysis. The review reported no differences in the success rate of relapse prevention between the behavioral interventions. Pharmacotherapy interventions showed higher success rates (RR, 1.15; 95% CI, 1.05−1.26; I2=40.71%), depending on prior abstinence duration and the drug type. Conclusions: The results indicated that pharmacotherapy has a significant effect on preventing relapse among abstinent smokers. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Survey of the Clinical Practice of Korean Medicine for Smoking Cessation in Public Health Centers: A Web-Based Survey of Public Health Doctors of Korean Medicine
Gyoungeun Park, Jeong-Hyun Moon, Eun-Jung Kim, Byung-Kwan Seo, Yong-Hyeon Baek, Won-Suk Sung
Perspectives on Integrative Medicine.2024; 3(1): 45. CrossRef
- A Survey of the Clinical Practice of Korean Medicine for Smoking Cessation in Public Health Centers: A Web-Based Survey of Public Health Doctors of Korean Medicine
- Behavioral interventions for smoking cessation among adolescents: a rapid review and meta-analysis for the Korea Preventive Services Task Force
- Younglee Choi, Cheol Min Lee, Belong Cho, Eon Sook Lee, Seung-Won Oh, Naae Lee, Jae Moon Yun
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2021;12(3):177-186. Published online June 2, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.0018
- 9,378 View
- 162 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Objectives
The aim of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of behavioral smoking cessation interventions among adolescents.
Methods
MEDLINE, CENTRAL, Embase, CINAHL, KoreaMed, and KMbase were searched from inception to June 2020. Systematic reviews (SRs) or meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) were initially searched to perform a rapid SR. After selecting the final SR, RCTs after the publication year of the selected SR were searched. The primary outcome was smoking status after at least 6 months of follow-up, and the secondary outcome was smoking status at 4 weeks. Two reviewers independently assessed the selected studies’ quality using the Cochrane risk of bias tool. The meta-analysis utilized a Mantel-Haenszel fixed-effect model reporting the relative risk (RR) and 95% confidence interval (CI). The subgroup analysis utilized Cochrane’s Q.
Results
Thirty-two RCTs (11,637 participants) from a single SR were meta-analyzed. After 6 months of follow-up, the intervention group had significantly higher abstinence rates (RR, 1.30; 95% CI, 1.20−1.41; I2=26.46%). At 4 weeks of follow-up, the intervention group also had significantly higher abstinence rates (RR, 1.92; 95% CI, 1.49–2.47; I2=0.00%). The subgroup analysis indicated a significant difference in the abstinence rate according to the study setting and the period between intervention completion and follow-up.
Conclusion
This review showed that adolescent behavioral smoking cessation intervention programs significantly increased abstinence rates compared to the usual care. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of Healthcare Interventions on Smoking Cessation in Adolescents in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: A Narrative Review
Janhvi Thakur, Sonali G Choudhari
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Non-pharmacological interventions for smoking cessation: analysis of systematic reviews and meta-analyses
Tao Nian, Kangle Guo, Wendi Liu, Xinxin Deng, Xiaoye Hu, Meng Xu, Fenfen E, Ziyi Wang, Guihang Song, Kehu Yang, Xiuxia Li, Wenru Shang
BMC Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Behavioral Interventions for Smoking Cessation in Adolescents: Korea Preventive Services Task Force Guidance
Younglee Choi, Cheol Min Lee, Jae Moon Yun, Eon Sook Lee, Seung-Won Oh, Naae Lee, Belong Cho
Journal of the Korean Society for Research on Nico.2021; 12(1): 1. CrossRef - Tobacco Control Policy in Period of Epidemic “COVID 19”
Eon Sook Lee
Journal of the Korean Society for Research on Nico.2021; 12(1): 34. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of Healthcare Interventions on Smoking Cessation in Adolescents in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: A Narrative Review
- Relationship Between Assertion and Aggression with Addiction Potential: A Cross-Sectional Study in 2019
- Mohammad Amiri, Zakieh Sadeghi, Elham Sadeghi, Ahmad Khosravi
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2020;11(4):231-238. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2020.11.4.12
- 6,173 View
- 88 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives This study aimed to determine the relationship between assertion and aggression with addiction potential among students in Shahroud University of Medical Sciences.
Methods In this cross-sectional study conducted in 2019, 500 students of Shahroud University of Medical Sciences, were selected by multistage random sampling, for a study using the Addiction Potential Scale, and Assertion and Aggression Questionnaires. Data were analyzed using ANOVA, Chi-square,
t test, Pearson’s correlation coefficient, and the linear regression model.Results The mean scores of addiction potential, aggression, and assertion were 32.7 ± 17.2, 41.5 ± 12.9 and 139.4 ± 22.3, respectively. In this study, 38.8% (
N = 194) of students had high aggression and 76.8% (N = 384) had high assertion. In the regression model, aggression, history of drug and addictive substances abuse, history of tobacco use, and history of alcohol abuse were significantly related to addiction potential (p ≤ 0.05). There was a negative relationship between assertion and addiction potential so that with one-unit increase in the assertion score, the addiction potential score decreased by −0.11.Conclusion Given the direct relationship between aggression and addiction potential, and since more than three-quarters of the students had moderate to high aggression, it is necessary to pay more attention to this issue. Interventions may play an important role in improving the current situation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Perceived personality traits and parenting styles on addiction potentiality among nursing students
Sabah AliMohammed Elsisi, MonaHamdy Mostafa, Mohamed AbdEl-Fattah Khalil, Sayeda Mohamed
Egyptian Nursing Journal.2023; 20(1): 138. CrossRef - From emotional intelligence to suicidality: a mediation analysis in patients with borderline personality disorder
Mohsen Khosravi, Fahimeh Hassani
BMC Psychiatry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Addiction Potential and its Correlates Among Medical Students
Mohammad Amiri, Ahmad Khosravi, Reza Chaman, Zakieh Sadeghi, Elham Sadeghi, Mehdi Raei
The Open Public Health Journal.2021; 14(1): 32. CrossRef - Exploring the Influence of Parenting Style on Adolescents’ Maladaptive Game Use through Aggression and Self-Control
Hyeon Gyu Jeon, Sung Je Lee, Jeong Ae Kim, Gyoung Mo Kim, Eui Jun Jeong
Sustainability.2021; 13(8): 4589. CrossRef
- Perceived personality traits and parenting styles on addiction potentiality among nursing students
- The Effects of the Korean Medicine Health Care Program on Stroke-Related Factors and Self-Care Enhancement
- Kyoung-Oh Chang, Jung-Hye Lim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2019;10(5):307-314. Published online October 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2019.10.5.07
- 4,929 View
- 180 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives This study was performed to examine the effects of the Korean medicine healthcare program on stroke-related factors and self-care enhancement.
Methods This study was a quasi-experimental, pretest-posttest nonequivalent control group design study (
N = 58 participants), with 28 in the treatment group (Korean medicine health care program) and 30 in the control group (no intervention). The program was conducted twice a week for 2 hours, for a total of 12 weeks.Results There were statistically significant differences in systolic (
p = 0.005) and diastolic blood pressure (p = 0.006), cholesterol (p < 0.001), blood glucose (p < 0.001), self-esteem (p = 0.001), self-efficacy (p < 0.001), health perception (p < 0.001), and the health behavior (p < 0.001) between the experimental group and the control group.Conclusion Thus, the Korean medicine healthcare program was effective in managing stroke-related factors and enhancing self-care, and should be actively used to develop community health promotion strategies to prevent strokes and prepare long-term measures.
- Interaction Between Smoking Cigarettes and Alcohol Consumption on Sexual Experience in High School Students
- Soo Jeong Kim, Kyoung Won Cho
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2019;10(5):274-280. Published online October 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2019.10.5.03
- 8,836 View
- 52 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives This study aimed to analyze nationwide representative data from the 11th Korean Youth Health Risk Behavior Web-Based Survey to determine whether factors including socio-demographics, smoking and alcohol consumption, were factors related to high school students that had experienced sexual intercourse.
Methods A total of 33,744 students (17,346 boys and 16,398 girls) in 1st, 2nd, and 3rd grade at high school were analyzed. SPSS complex samples methods were used for analyses. Socio-demographic and health risk behaviors (type of region of residence, family structure, and economic status, student academic achievement, gender, high school grade, pocket money, student smoking, alcohol consumption, and having engaged in sexual intercourse) were considered as independent variables.
Results There were 3.6% of girls and 9.9% of boys in high school that were sexually active. This behavior and the average number of cigarettes smoked daily, and alcohol consumed weekly, represented a dose-response relationship, after considering confounding factors. Compared with students that did not smoke or consume alcohol, smoking 1–9 cigarettes per day and consuming 1–6 cups of alcohol and group “smoking more than 10 cigarettes per day and consuming more than 7 cups of alcohol, had a 5.94 and 22.25 higher risk of having had sexual intercourse, respectively.
Conclusion Cigarette smoking and alcohol consumption were associated with an increased likelihood of high school students engaging in sexual intercourse.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors associated with adolescents’ sexual experience based on the biopsychosocial model: a cross-sectional study using the Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web-based Survey (KYRBS)
Ka Young Kim, Hye Young Shin
BMJ Open.2022; 12(11): e066307. CrossRef - DETERMINANTS OF PREMARITAL SEXUAL BEHAVIOR AMONGST ADOLESCENTS IN INDONESIA
Nadhirul Mundhiro, Ridhwan Fauzi, Mohammad Ainul Maruf, Nurfadhilah Nurfadhilah
Jurnal Biometrika dan Kependudukan.2021; 10(1): 86. CrossRef
- Factors associated with adolescents’ sexual experience based on the biopsychosocial model: a cross-sectional study using the Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web-based Survey (KYRBS)
- Designing and Evaluating Educational Intervention to Improve Preventive Behavior Against Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in Endemic Areas in Iran
- Musalreza Ghodsi, Mina Maheri, Hamid Joveini, Mohammad Hassan Rakhshani, Ali Mehri
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2019;10(4):253-262. Published online August 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2019.10.4.09
- 8,805 View
- 109 Download
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives Health education programs are one of the most important strategies for controlling cutaneous leishmaniasis (CL) in endemic areas such as Neshabur city. This study aimed to develop and evaluate a comprehensive health education program to improve preventive behaviors for CL.
Methods This was an interventional study conducted on 136 high school students in Neishabur city. Data collection instruments included a demographic questionnaire and a researcher-made questionnaire based on the “Health Belief Model” and “Beliefs, Attitudes, Subjective Norms and Enabling Factors Model” constructs. The control and intervention groups completed the questionnaires before and 2 months after the intervention. The intervention was conducted in 6, 1-hour educational sessions for the intervention group students and 2, 1-hour sessions for school administrators, teachers, and students’ parents.
Results There was no significant difference between the 2 groups in the pre-intervention phase. However, in the post-intervention phase, there were significant differences between the 2 groups for mean scores of knowledge, perceived susceptibility, perceived severity, perceived benefits, cues to action, self-efficacy, attitude, subjective norms, behavioral intention, enabling factors, and behavior associated with CL.
Conclusion Health education program based on the “Health Belief Model” and the “Beliefs, Attitudes, Subjective Norms and Enabling Factors Model” model constructs may be a comprehensive and effective educational program to improve preventive behaviors against CL in students.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Antiparasitic activity of the iron-containing milk protein lactoferrin and its potential derivatives against human intestinal and blood parasites
Namrata Anand
Frontiers in Parasitology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Cutaneous leishmaniasis situation analysis in the Islamic Republic of Iran in preparation for an elimination plan
Iraj Sharifi, Ahmad Khosravi, Mohammad Reza Aflatoonian, Ehsan Salarkia, Mehdi Bamorovat, Ali Karamoozian, Mahmoud Nekoei Moghadam, Fatemeh Sharifi, Abbas Aghaei Afshar, Setareh Agha Kuchak Afshari, Faranak Gharachorloo, Mohammad Reza Shirzadi, Behzad Ami
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Mutual Role of Patients and the Healthcare System in the Control of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis
Mehdi Bamorovat, Iraj Sharifi, Setareh Agha Kuchak Afshari, Pooya Ghasemi Nejad Almani, Fedor Korennoy
Transboundary and Emerging Diseases.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Knowledge, perceptions and practices of health students and professionals regarding leishmaniasis in Portugal: a cross-sectional study
Rafael Rocha, Cláudia Conceição, Luzia Gonçalves, Carla Maia
Parasites & Vectors.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Investigating Iranians’ Attitude, Practice, and Perceived Self-Efficacy towards COVID-19 Preventive Behaviors
Hamid Joveini, Zahra Zare, Masoumeh Hashemian, Ali Mehri, Reza Shahrabadi, Neda Mahdavifar, Hamideh Ebrahimi Aval
The Open Public Health Journal.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Şark çıbanı vakalarında bilgi ve farkındalık düzeyini artırmaya yönelik müdahale çalışması: Şanlıurfa örneği
Burcu BEYAZGÜL, İbrahim KORUK, Rüstem KUZAN, Şule ALLAHVERDİ
Mersin Üniversitesi Sağlık Bilimleri Dergisi.2022; 15(2): 188. CrossRef - Congregational Worshiping and Implementation of the COVID-19 Preventive Behavioral Measures During the Re-opening Phase of Worship Places Among Indonesian Muslims
Mochamad Iqbal Nurmansyah, Sarah Handayani, Deni Wahyudi Kurniawan, Emma Rachmawati, Hidayati, Ahmad Muttaqin Alim
Journal of Religion and Health.2022; 61(5): 4169. CrossRef - Development and psychometric assessment of cutaneous leishmaniasis prevention behaviors questionnaire in adolescent female students: Application of integration of cultural model and extended parallel process model
Masoumeh Alidosti, Hossein Shahnazi, Zahra Heidari, Fereshteh Zamani-Alavijeh, Mona Dür
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(8): e0273400. CrossRef - Community-Based Interventions for the Prevention and Control of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis: A Systematic Review
Kay Polidano, Brianne Wenning, Alejandra Ruiz-Cadavid, Baheya Dawaishan, Jay Panchal, Sonali Gunasekara, Haftom Abebe, Marciglei Morais, Helen Price, Lisa Dikomitis
Social Sciences.2022; 11(10): 490. CrossRef - Design and evaluation of two educational media in the form of animation and games to promote the cutaneous leishmaniasis prevention behaviors in adolescent female
Masoumeh Alidosti, Hossein Shahnazi, Zahra Heidari, Fereshteh Zamani-Alavijeh
BMC Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Knowledge, attitude, and practice toward Zika virus among staff of comprehensive health services centers affiliated with Tehran University of Medical Sciences in 2020
Hamidreza Farrokh‐Eslamlou, Mina Maheri
Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research.2021; 47(6): 2204. CrossRef - Behaviors and Perceptions Related to Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in Endemic Areas of the World: A Review
Masoumeh Alidosti, Zahra Heidari, Hossein Shahnazi, Fereshteh Zamani-Alavijeh
Acta Tropica.2021; 223: 106090. CrossRef - Application of BASNEF model in students training regarding cutaneous leishmaniasis prevention behaviors: a school-based quasi experimental study
Gholamreza Alizadeh, Hossein Shahnazi, Akbar Hassanzadeh
BMC Infectious Diseases.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Predicting the Preventive Behaviors of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in families with Children Under 10 Years, Applied the Precede Model
Hosein Jajarmi, Mahdi Gholian-Aval, Asma pourtaheri, Habibollah Esmaily, Hamid Hosseini, Rezvan Rajabzadeh, Hadi Tehrani
ranian Journal of Health Education and Health Prom.2021; 9(4): 360. CrossRef - Effects of an Educational Intervention on Male Students’ Intention to Quit Water Pipe Smoking: an Application of the Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB) and Health Action Process Approach (HAPA)
Hamid Joveini, Tahereh Dehdari, Masoumeh Hashemian, Mina Maheri, Reza Shahrabadi, Alireza Rohban, Ali Mehri, Hasan Eftekhar Ardebili
Journal of Education and Community Health.2020; 7(2): 73. CrossRef
- Antiparasitic activity of the iron-containing milk protein lactoferrin and its potential derivatives against human intestinal and blood parasites
- Army Soldiers’ Knowledge of, Attitude Towards, and Preventive Behavior Towards Tuberculosis in Korea
- Yun Choi, Geum Hee Jeong
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2018;9(5):269-277. Published online October 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2018.9.5.09
- 6,341 View
- 150 Download
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives The aim of this study was to gather information about Korean Army soldiers’ attitude towards tuberculosis to enable the development of an informed educational program and potential intervention plans.
Methods There were 500 male soldiers serving in the Korean Army who responded to questionnaires regarding knowledge of, attitudes towards, and preventive behavior towards tuberculosis. The questionnaires were collected between September 10 until October 1, 2014. Participants’ characteristic that influenced differences in knowledge, attitudes, and preventive behavior towards tuberculosis were compared by
t test. Variables that influenced preventive behavior were identified by multiple regression analysis.Results The mean scores assessing knowledge of, attitude, and preventive behavior towards tuberculosis were 11.64 (± 4.03) out of 20 points, 3.21 (± 0.38) out of 4 points, and 2.88 (± 0.42) out of 4 points, respectively. Non-smokers were more knowledgeable about tuberculosis than smokers. Participants who had family or friends with tuberculosis had better knowledge and a more productive attitude to tuberculosis. Participants who were educated or obtained information about tuberculosis, received better scores in all areas of knowledge, attitude and preventive behavior compared to other participants. Non-smoking, family or friends who have had tuberculosis, obtaining information about tuberculosis, and positive attitudes towards treatment and preventive education had an explanatory power of 24.6% with regard to preventive behavior against tuberculosis.
Conclusion More relatable, systemized education should be provided regularly to improve soldiers’ knowledge of, attitudes towards, and prevention against tuberculosis in the Republic of Korea Army.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Tingkat Pengetahuan Keluarga Tinggal Serumah Tentang Pencegahan Penularan Pasien Tuberkulosis Paru
Komang Yuliani, I Dewa Agung Ketut Sudarsana
Journal Nursing Research Publication Media (NURSEP.2023; 2(1): 47. CrossRef - Knowledge, Attitudes, and Preventative Behavior Toward Tuberculosis in University Students in Indonesia
Irma Melyani Puspitasari, Rano Kurnia Sinuraya, Arini Nurhaqiqi Aminudin, Rika Rahmi Kamilah
Infection and Drug Resistance.2022; Volume 15: 4721. CrossRef - The Relationship between Health Literacy and Preventive Behaviors of Soldiers
Javad Azimzadeh, Maryam Nezamzadeh, Fatemeh Kalroozi, Seyyed Amir Hossein Pishgooie
Military Caring Sciences.2021; 8(2): 109. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Preventive Behavior related to Tuberculosis among University Students in Korea: Focused on Knowledge, Attitude and Optimistic Bias related to Tuberculosis
Myung Soon Kwon, Yun Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursi.2020; 27(3): 236. CrossRef - Assessment of knowledge, attitude and practice on tuberculosis among teacher trainees of Samtse College of Education, Bhutan
Thinley Dorji, Tandin Tshering, Kinley Wangdi, Ritesh G. Menezes
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(11): e0241923. CrossRef - The Infectivity of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Korean Army Units: Evidence from Outbreak Investigations
Chang-gyo Yoon, Dong Yoon Kang, Jaehun Jung, Soo Yon Oh, Jin Beom Lee, Mi-Hyun Kim, Younsuk Seo, Hee-Jin Kim
Tuberculosis and Respiratory Diseases.2019; 82(4): 298. CrossRef
- Tingkat Pengetahuan Keluarga Tinggal Serumah Tentang Pencegahan Penularan Pasien Tuberkulosis Paru
- Multilevel Analysis of the Risk Factors in High-Risk Health Behavior among Korean Adolescents
- Eun Gyeong Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2018;9(1):3-8. Published online December 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2018.9.1.02
- 5,204 View
- 77 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives To examine health behaviors among Korean adolescents with a focus on both individual and school-based factors, specifically in relation to predictors of high-risk groups.
Methods Secondary data analysis was conducted with data from the 8th Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web-Based Survey, using descriptive statistics, t tests, χ2 test, and multilevel logistic regression analysis. Health Practice Index was calculated and a range of 0 to 2 was classified as a high-risk group.
Results The results revealed that the individual-level variables of sex, age, stress, depression, subjective health status, school performance, health education, father’s level of education, and living situation were significant predictors of high-risk behaviors. The risk was greater in girls, greater with higher age and higher stress scores, greater in adolescents with depression, greater with lower paternal educational level, and greater in adolescents who did not live with both parents, as were the school-level variables of school grade and school affluence score. The possibility of being in the high-risk group in health behavior was greater if a student attended a school where the Family Affluence Score (FAS) was lower.
Conclusion School health education should be expanded to manage students’ high-risk health behaviors, especially in schools that have many students from families with a low affluence status.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mental health and its determinants among adolescents living in families with separated or divorced parents in an urban area of Vietnam
Binh Thang Tran, Minh Tu Nguyen, Minh Tam Nguyen, Thanh Gia Nguyen, Vo Nu Hong Duc, Thi Tra My Tran
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2023; 14(4): 300. CrossRef - Prevalence of and Factors Associated with Club Drug Use among Secondary Vocational Students in China
Jincong Yu, Qingfeng Wu, Yuqin Wu, Jiang Li, Qinxuan Wu, Huiping Cao, Zengzhen Wang
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2021; 18(19): 10408. CrossRef - Problematic Gaming Is Associated with Some Health-Related Behaviors Among Finnish Vocational School Students
Niko Männikkö, Heidi Ruotsalainen, Asko Tolvanen, Maria Kääriäinen
International Journal of Mental Health and Addicti.2020; 18(4): 993. CrossRef - The relationship between social participation and self-rated health in persons with psychiatric disabilities: Is the health behavior mediation model useful
Ji Hye Park, Sun Hae Lee
Korean Journal of Health Education and Promotion.2020; 37(2): 69. CrossRef
- Mental health and its determinants among adolescents living in families with separated or divorced parents in an urban area of Vietnam
- Korean Adolescents’ Health Behavior and Psychological Status according to Their Mother’s Nationality
- Yunjeong Yi, Ji-Soo Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2017;8(6):377-383. Published online December 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2017.8.6.04
- 4,303 View
- 24 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives This study was conducted to compare adolescents’ health behaviors and psychological status according to whether or not their mother was born in Korea.
Methods This secondary analysis used nationally representative data from the 2015 Korean Youth Risk Behavior Web-based Survey. The self-administered questionnaire included computer measured socio-demographic variables, 15 health behaviors, and psychological status. Data from 65,426 middle school and high school students were analyzed. Multiple logistic regression, adjusting for socio-demographic variables, was used to analyze differences in health behaviors and psychological status between adolescents with a foreign-born mother and those with a Korean mother.
Results Adolescents who have foreign-born mothers had a lower level of current drinking and subjective happiness, but a higher stress level.
Conclusion The stress levels of the adolescents with foreign-born mothers could be affected by their multicultural background. It is necessary to analyze stress-influencing factors of multicultural adolescents by comparing them to adolescents from Korean parents. Additionally, our society should pay more attention to the mental health of multicultural adolescents. Schools should also make various efforts to protect multicultural adolescents by adopting mental health management programs led by school nurses and counselors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Measuring Happiness in Adolescent Samples: A Systematic Review
Justė Lukoševičiūtė, Gita Argustaitė-Zailskienė, Kastytis Šmigelskas
Children.2022; 9(2): 227. CrossRef - Factors Related to Depressive Symptoms Among Multicultural Adolescents in Korea
Kyoung Hwa Joung, Sung Suk Chung
The Journal of School Nursing.2022; 38(2): 138. CrossRef - The Mental Health of Ethnic Minority Youths in South Korea and Its Related Environmental Factors: A Literature Review
Yeeun Lee, Minji Lee, Subin Park
Journal of the Korean Academy of Child and Adolesc.2019; 30(3): 88. CrossRef - Adolescents in Multi-Ethnic Families under Korean Ethnic Nationalism
Hae-Wol Cho, Chaeshin Chu
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2017; 8(6): 367. CrossRef
- Measuring Happiness in Adolescent Samples: A Systematic Review
- Does Skipping Breakfast and Being Overweight Influence Academic Achievement Among Korean Adolescents?
- Yang Wha Kang, Jong-Hyock Park
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2016;7(4):220-227. Published online August 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2016.05.004
- 2,859 View
- 26 Download
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
Health status and health behaviors are associated with academic achievement in children and adolescents. The purpose of this study was to investigate whether skipping breakfast and being overweight are related to academic achievement of Korean adolescents.
Methods
Cross-sectional data on a sample of 1,652 high-school seniors (942 males and 710 females) drawn from the 2004 Korea Education Employment Panel were analyzed.
Results
A higher proportion of males (15.3%) than females (6.1%) was overweight (p < 0.001); 37% of males and 41% of females reported skipping breakfast. Overall test scores were significantly higher for females than males (p < 0.05), and in language and foreign language subjects. However, both males and females who reported skipping breakfast had significantly lower scores in language, mathematics, and foreign language than those who did not report skipping breakfast. Overweight males had a lower probability than normal-weight males of having the highest language scores (OR = 0.52, p < 0.05), but there was no difference among females. Females who skipped breakfast had a lower probability of having the highest scores in language (OR = 0.41, p < 0.05), mathematics (OR = 0.24, p < 0.01), or foreign language (OR = 0.18, p < 0.01), while males had a lower probability of having the highest scores in language only (OR = 0.46, p < 0.05).
Conclusion
Skipping breakfast and being overweight are associated with poor academic achievement in Korean adolescents. Eating breakfast and weight control is being discussed as the overlooked factors that may influence better academic achievement. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- İstanbul ili Silivri ilçesi lise öğrencilerinde depresyon sıklığı ve ilişkili risk faktörleri
Gülver GÜLEN, Ethem ERGİNÖZ, Cemal KOÇAK
Türkiye Halk Sağlığı Dergisi.2022; 20(1): 90. CrossRef - Predicting the academic performance of middle- and high-school students using machine learning algorithms
Suchithra Rajendran, S Chamundeswari, Akhouri Amitanand Sinha
Social Sciences & Humanities Open.2022; 6(1): 100357. CrossRef - Predicting the Academic Performance of Middle- and High-School Students Using Machine Learning Algorithms
Suchithra Rajendran, Akhouri Sinha, Chamundeswari Rajendran
SSRN Electronic Journal .2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Sociodemographic and clinical factors associated with breakfast skipping among high school students
Ju‐Yeon Lee, Dahye Ban, Honey Kim, Seon‐Young Kim, Jae‐Min Kim, Il‐Seon Shin, Sung‐Wan Kim
Nutrition & Dietetics.2021; 78(4): 442. CrossRef - Effect of a nutritional education intervention on breakfast consumption among preparatory school students in Egypt
Omnia S. Elseifi, Doaa M. Abdelrahman, Eman M. Mortada
International Journal of Public Health.2020; 65(6): 893. CrossRef - Impact of Dietary Patterns and Nutritional Status on the Academic Performance of Omani School Students
Laila S. Al-Saadi , Amanat Ali , Mostafa I. Waly , K.M. Al-Zuhaibi
Journal of Pharmacy and Nutrition Sciences .2020; 10(3): 74. CrossRef - Predictors of breakfast skipping among 14 to 16 years old adolescents in Jordan: The influential role of mothers
Reem A. Ali, Nadin M. Abdel Razeq, Manal I. Al‐Kloub, Fatmeh A. Alzoubi
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Association among Executive Function, Physical Activity, and Weight Status in Youth
Vaida Borkertienė, Arvydas Stasiulis, Birutė Zacharienė, Laura Kyguolienė, Rasa Bacevičienė
Medicina.2019; 55(10): 677. CrossRef - SOCIAL SUPPORT TO TEENAGER BREAKFAST BEHAVIOR (Study at Sidoarjo Islamic State Senior High School)
Angga Satria Prayogo, Muji Sulistyowati
Jurnal PROMKES.2019; 7(1): 105. CrossRef - The association between obesity and academic performance in youth: a systematic review
C. C. A. Santana, J. O. Hill, L. B. Azevedo, T. Gunnarsdottir, W. L. Prado
Obesity Reviews.2017; 18(10): 1191. CrossRef - Effects of Reading a Picture Leaflet on Rhythm for Enhancement of Morning-Typed Life in Japanese Infants
Misako Kawamata, Ryota Kawasumi, Fujiko Tsuji, Nozomi Taniwaki, Takahiro Kawada, Teruki Noji, Milada Krejci, Miyo Nakade, Hitomi Takeuchi, Tetsuo Harada
Psychology.2017; 08(11): 1621. CrossRef - Study on Skipping Breakfast in Adolescents Classified by Household Type
Jaehong Park, Soye You
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2017; 28(2): 329. CrossRef
- İstanbul ili Silivri ilçesi lise öğrencilerinde depresyon sıklığı ve ilişkili risk faktörleri



 First
First Prev
Prev


