Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Zika virus as an emerging arbovirus of international public health concern
- Samira Vaziri, Siavash Hamzeh Pour, Fateme Akrami-Mohajeri
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2022;13(5):341-351. Published online October 12, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0101
- 2,405 View
- 130 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Zika virus (ZIKV) was identified in 1947 in a rhesus monkey during an investigation of the yellow fever virus in the Zika Forest of Uganda; it was also isolated later from humans in Nigeria. The main distribution areas of ZIKV were the African mainland and South-East Asia in the 1980s, Micronesia in 2007, and more recently the Americas in 2014. ZIKV belongs to the Flaviviridae family and Flavivirus genus. ZIKV infection, which is transmitted by Aedes mosquitoes, is an emerging arbovirus disease. The clinical symptoms of ZIKV infection are fever, headache, rashes, arthralgia, and conjunctivitis, which clinically resemble dengue fever syndrome. Sometimes, ZIKV infection has been associated with Guillain-Barré syndrome and microcephaly. At the end of 2015, following an increase in cases of ZIKV infection associated with Guillain-Barré syndrome and microcephaly in newborns in Brazil, the World Health Organization declared a global emergency. Therefore, considering the global distribution and pathogenic nature of this virus, the current study aimed at reviewing the virologic features, transmission patterns, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of ZIKV infection.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Review on The Pathogenesis of Cardiovascular Disease of Flaviviridea Viruses Infection
Tie-Hua Yang, Wen-Cong Gao, Xin Ma, Qian Liu, Pan-Pan Pang, Yong-Tang Zheng, Yinnong Jia, Chang-Bo Zheng
Viruses.2024; 16(3): 365. CrossRef - The race against time: Zika virus on the horizon in Pakistan
Moiz Ahmed Khan, Summaiya Zafar
Tropical Doctor.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Zika virus disease: an alarming situation resurfacing on the radar – a short communication
Sanobar Shariff, Burhan Kantawala, Nakyanzi Hamiidah, Tularam Yadav, Abubakar Nazir, Olivier Uwishema
Annals of Medicine & Surgery.2023; 85(10): 5294. CrossRef
- A Review on The Pathogenesis of Cardiovascular Disease of Flaviviridea Viruses Infection
- The role of lipids in the pathophysiology of coronavirus infections
- Milad Zandi, Parastoo Hosseini, Saber Soltani, Azadeh Rasooli, Mona Moghadami, Sepideh Nasimzadeh, Farzane Behnezhad
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2021;12(5):278-285. Published online October 15, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.0153
- 5,585 View
- 166 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 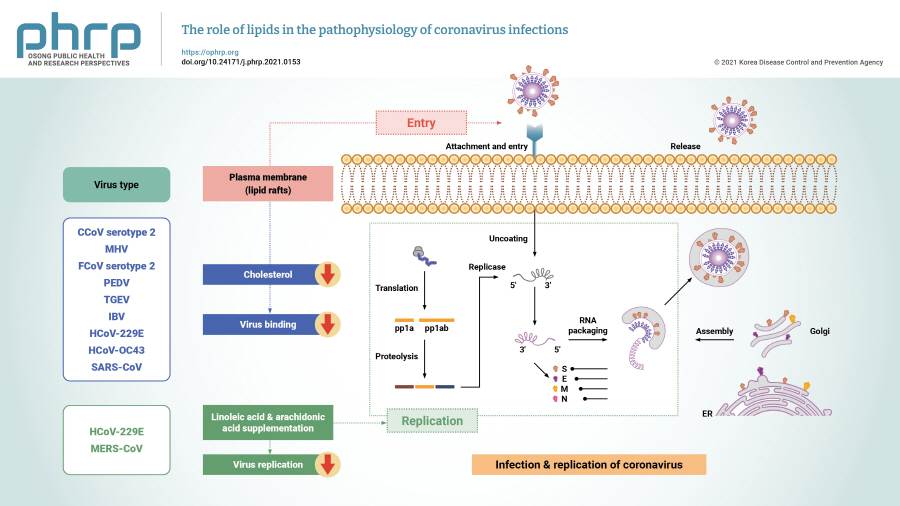
- Coronaviruses, which have been known to cause diseases in animals since the 1930s, utilize cellular components during their replication cycle. Lipids play important roles in viral infection, as coronaviruses target cellular lipids and lipid metabolism to modify their host cells to become an optimal environment for viral replication. Therefore, lipids can be considered as potential targets for the development of antiviral agents. This review provides an overview of the roles of cellular lipids in different stages of the life cycle of coronaviruses.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- PEDV inhibits HNRNPA3 expression by miR-218-5p to enhance cellular lipid accumulation and promote viral replication
Xiaojie Shi, Qi Zhang, Naling Yang, Quanqiong Wang, Yanxia Zhang, Xingang Xu, Xiang-Jin Meng, Ying Fang
mBio.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Orsay Virus Infection of Caenorhabditis elegans Is Modulated by Zinc and Dependent on Lipids
Luis Alberto Casorla-Perez, Ranya Guennoun, Ciro Cubillas, Bo Peng, Kerry Kornfeld, David Wang, Rebecca Ellis Dutch
Journal of Virology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- PEDV inhibits HNRNPA3 expression by miR-218-5p to enhance cellular lipid accumulation and promote viral replication
- Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 and respiratory syncytial virus coinfection in children
- Milad Zandi, Saber Soltani, Mona Fani, Samaneh Abbasi, Saeedeh Ebrahimi, Ali Ramezani
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2021;12(5):286-292. Published online October 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.0140
- 6,696 View
- 158 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), which has infected many people around the world. Children are considered an important target group for SARS-CoV-2, as well as other viral infections such as respiratory syncytial virus infection. Both SARS-CoV-2 and respiratory syncytial virus can affect the respiratory tract. Coinfection of SARS-CoV-2 and respiratory syncytial virus can pose significant challenges in terms of diagnosis and treatment in children. This review compares the symptoms, diagnostic methods, and treatment of COVID-19 and respiratory syncytial virus infection in children.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Results from the second WHO external quality assessment for the molecular detection of respiratory syncytial virus, 2019–2020
Thomas Williams, Sandra Jackson, Ian Barr, Shabana Bi, Jinal Bhiman, Joanna Ellis, Anne von Gottberg, Stephen Lindstrom, Teresa Peret, Sanjiv Rughooputh, Mariana Viegas, Siddhivinayak Hirve, Maria Zambon, Wenqing Zhang
Influenza and Other Respiratory Viruses.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Impact of Coronavirus Disease 2019 on Viral, Bacterial, and Fungal Respiratory Infections
Ashley Losier, Gayatri Gupta, Mario Caldararo, Charles S. Dela Cruz
Clinics in Chest Medicine.2023; 44(2): 407. CrossRef - Viral Coinfection of Children Hospitalized with Severe Acute Respiratory Infections during COVID-19 Pandemic
Célia Regina Malveste Ito, André Luís Elias Moreira, Paulo Alex Neves da Silva, Mônica de Oliveira Santos, Adailton Pereira dos Santos, Geovana Sôffa Rézio, Pollyanna Neta de Brito, Alana Parreira Costa Rezende, Jakeline Godinho Fonseca, Fernanda Aparecid
Biomedicines.2023; 11(5): 1402. CrossRef - Clinical Relevance of RSV and SARS-CoV-2 Coinfections in Infants and Young Children
Rosa Rodriguez-Fernandez, Felipe González-Martínez, Jimena Perez-Moreno, María Isabel González-Sánchez, Blanca Toledo del Castillo, Irene Mingueza de la Paz, Laura Diaz Pozo, Asuncion Mejias, Octavio Ramilo
Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal.2023; 42(12): e473. CrossRef - Targeting host calcium channels and viroporins: a promising strategy for SARS-CoV-2 therapy
Mona Fani, Maryam Moossavi, Hasan Bakhshi, Abozar Nasiri Jahrodi, Mohammad Reza Khazdair, Amir Hossein Zardast, Shokouh Ghafari
Future Virology.2023; 18(12): 797. CrossRef - Respiratory syncytial virus, recurrent wheeze and asthma: A narrative review of pathophysiology, prevention and future directions
Elly Binns, Jane Tuckerman, Paul V Licciardi, Danielle Wurzel
Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health.2022; 58(10): 1741. CrossRef - Impact of genetic polymorphisms related to innate immune response on respiratory syncytial virus infection in children
Laura Elena Córdova-Dávalos, Alicia Hernández-Mercado, Claudia Berenice Barrón-García, Augusto Rojas-Martínez, Mariela Jiménez, Eva Salinas, Daniel Cervantes-García
Virus Genes.2022; 58(6): 501. CrossRef - Clinical and epidemiological characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 virus in ambulatory children under 2 years old
Carolina A. Perez, Ivana Ormazabal, Javier Pérez-Valenzuela, Andrea Araya, Rafael A. Medina, Cecilia Perret
Frontiers in Pediatrics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Results from the second WHO external quality assessment for the molecular detection of respiratory syncytial virus, 2019–2020
- Cell Death Mechanisms in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Induced by Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Matrix Protein
- Yousef Douzandegan, Alireza Tahamtan, Zahra Gray, Hadi Razavi Nikoo, Alijan Tabarraei, Abdolvahab Moradi
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2019;10(4):246-252. Published online August 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2019.10.4.08
- 6,513 View
- 144 Download
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives Vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) is under development as an oncolytic virus due to its preferential replication in cancer cells and oncolytic activity, however the viral components responsible have not yet been determined. In this study the effects of VSV wild-type (wt) and M51R-mutant matrix proteins (M51R-mMP) on apoptosis, pyroptosis, necroptosis, and autophagy pathways, in an esophagus cancer cell line (KYSE-30) were investigated.
Methods The KYSE-30 cells were transfected with pcDNA3.1 plasmids encoding wt or M51R-mMP, and apoptosis, pyroptosis, necroptosis, and autophagy were evaluated 48 and 72 hours after transfection.
Results KYSE-30 cells transfected with VSV wt and M51R-mMPs significantly reduced cell viability to < 50% at 72 hours post-transfection. M51R-MP significantly increased the concentration of caspase-8 and caspase-9 at 48 and 72 hours post-transfection, respectively (
p < 0.05). In contrast, no significant changes were detected following transfection with the VSV wt plasmid. Moreover, VSV wt and M51R-mMP transfected cells did not change the expression of caspase-3. VSV wt and M51R-mMPs did not mMP change caspase-1 expression (a marker of pyroptosis) at 48 and 72 hours post-transfection. However, M51R-mMP and VSV wt transfected cells significantly increased RIP-1 (a marker of necroptosis) expression at 72 hours post-infection (p < 0.05). Beclin-1, a biomarker of autophagy, was also induced by transfection with VSV wt or M51R-mMPs at 48 hours post-transfection.Conclusion The results in this study indicated that VSV exerts oncolytic activity in KYSE-30 tumor cells through different cell death pathways, suggesting that M51R-mMP may potentially be used to enhance oncolysis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evoking pyroptosis with nanomaterials for cancer immunotherapy: Current boom and novel outlook
Wen-Da Wang, Zhi-Jun Sun
Nano TransMed.2022; 1(1): 9130001. CrossRef - Biological causes of immunogenic cancer cell death (ICD) and anti-tumor therapy; Combination of Oncolytic virus-based immunotherapy and CAR T-cell therapy for ICD induction
Amirhossein Mardi, Anastasia V. Shirokova, Rebar N. Mohammed, Ali Keshavarz, Angelina O. Zekiy, Lakshmi Thangavelu, Talar Ahmad Merza Mohamad, Faroogh Marofi, Navid Shomali, Amir Zamani, Morteza Akbari
Cancer Cell International.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Oncolytic Viruses: Immunotherapy Drugs for Gastrointestinal Malignant Tumors
Qingbo Li, Patrick Kwabena Oduro, Rui Guo, Ruiqiao Li, Ling Leng, Xianbin Kong, Qilong Wang, Long Yang
Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Live-attenuated poliovirus-induced extrinsic apoptosis through Caspase 8 within breast cancer cell lines expressing CD155
Hossein Vazeh, Emad Behboudi, Anahita Hashemzadeh-Omran, Abdolvahab Moradi
Breast Cancer.2022; 29(5): 899. CrossRef - Exogenous expression of both matrix protein and glycoprotein facilitates infectious viral particle production of Borna disease virus 1
Takehiro Kanda, Madoka Sakai, Akiko Makino, Keizo Tomonaga
Journal of General Virology .2022;[Epub] CrossRef - La herencia de Prometeo. Las enfermedades ocupacionales en el Corpus Hippocraticum
César Sierra Martín
Asclepio.2022; 74(1): p587. CrossRef - Analyses of cell death mechanisms related to amino acid substitution at position 95 in the rabies virus matrix protein
Isshu Kojima, Fumiki Izumi, Makoto Ozawa, Yoshikazu Fujimoto, Misuzu Okajima, Naoto Ito, Makoto Sugiyama, Tatsunori Masatani
Journal of General Virology .2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The role of non-apoptotic cell death in the treatment and drug-resistance of digestive tumors
Yang Yang, LiangLiang Bai, Weiting Liao, Mingyang Feng, Mengxi Zhang, Qiuji Wu, Kexun Zhou, Feng Wen, Wanting Lei, Nan Zhang, Jiaxing Huang, Qiu Li
Experimental Cell Research.2021; 405(2): 112678. CrossRef - NEBL and AKT1 maybe new targets to eliminate the colorectal cancer cells resistance to oncolytic effect of vesicular stomatitis virus M-protein
Zoleikha Mamizadeh, Mohamad Reza Kalani, Masoud Parsania, Mohammad Mehdi Soltan Dallal, Abdolvahab Moradi
Molecular Therapy - Oncolytics.2021; 23: 593. CrossRef
- Evoking pyroptosis with nanomaterials for cancer immunotherapy: Current boom and novel outlook
- Antiviral Activity of Itraconazole against Echovirus 30 Infection
In Vitro - Jae-Sug Lee, Hwa-Jung Choi, Jae-Hyoung Song, Hyun-Jeong Ko, Kyungah Yoon, Jeong-Min Seong
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2017;8(5):318-324. Published online October 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2017.8.5.05
- 4,351 View
- 28 Download
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives Echovirus 30 is a major cause of meningitis in children and adults. The aim of this study was to investigate whether the antifungal drug itraconazole could exhibit antiviral activity against echovirus 30.
Methods The cytopathic effect and viral RNA levels were assessed in RD cells as indicators of viral replication. The effects of itraconazole were compared to those of two known antiviral drugs, rupintrivir and pleconaril. The time course and time-of-addition assays were used to approximate the time at which itraconazole exerts its activity in the viral cycle.
Results Itraconazole and rupintrivir demonstrated the greatest potency against echovirus 30, demonstrating concentration-dependent activity, whereas pleconaril showed no antiviral activity. Itraconazole did not directly inactivate echovirus 30 particles or impede viral uptake into RD cells, but did affect the initial stages of echovirus 30 infection through interference with viral replication.
Conclusion Itraconazole can be considered a lead candidate for the development of antiviral drugs against echovirus 30 that may be used during the early stages of echovirus 30 replication.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Direct-Acting Antivirals and Host-Targeting Approaches against Enterovirus B Infections: Recent Advances
Chiara Tammaro, Michela Guida, Federico Appetecchia, Mariangela Biava, Sara Consalvi, Giovanna Poce
Pharmaceuticals.2023; 16(2): 203. CrossRef - Antiviral Activity of Approved Antibacterial, Antifungal, Antiprotozoal and Anthelmintic Drugs: Chances for Drug Repurposing for Antiviral Drug Discovery
Leena Abdulaziz, Esraa Elhadi, Ejlal A Abdallah, Fadlalbaseer A Alnoor, Bashir A Yousef
Journal of Experimental Pharmacology.2022; Volume 14: 97. CrossRef - Identification of novel Ebola virus inhibitors using biologically contained virus
Bert Vanmechelen, Joren Stroobants, Winston Chiu, Joost Schepers, Arnaud Marchand, Patrick Chaltin, Kurt Vermeire, Piet Maes
Antiviral Research.2022; 200: 105294. CrossRef - The Antifungal Itraconazole Is a Potent Inhibitor of Chikungunya Virus Replication
Lucca Policastro, Isabela Dolci, Andre Godoy, José Silva Júnior, Uriel Ruiz, Igor Santos, Ana Jardim, Kirandeep Samby, Jeremy Burrows, Timothy Wells, Laura Gil, Glaucius Oliva, Rafaela Fernandes
Viruses.2022; 14(7): 1351. CrossRef - Antifungal Triazole Posaconazole Targets an Early Stage of the Parechovirus A3 Life Cycle
Eric Rhoden, Terry Fei Fan Ng, Ray Campagnoli, W. Allan Nix, Jennifer Konopka-Anstadt, Rangaraj Selvarangan, Laurence Briesach, M. Steven Oberste, William C. Weldon
Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Potential antiviral properties of antifungal drugs
FalahH.O Al-Khikani, HudaA.S Almosawey, YounusJ Abdullah, AtyafA Al-Asadi, RaghdahM Hameed, NoorF Hasan, MohanadK.M Al-Ibraheemi
Journal of the Egyptian Women's Dermatologic Socie.2020; 17(3): 185. CrossRef - Repurposing approach identifies new treatment options for invasive fungal disease
Isis Regina Grenier Capoci, Daniella Renata Faria, Karina Mayumi Sakita, Franciele Abigail Vilugron Rodrigues-Vendramini, Patricia de Souza Bonfim-Mendonça, Tania Cristina Alexandrino Becker, Érika Seki Kioshima, Terezinha Inez Estivalet Svidzinski, Berna
Bioorganic Chemistry.2019; 84: 87. CrossRef
- Direct-Acting Antivirals and Host-Targeting Approaches against Enterovirus B Infections: Recent Advances
- Traditional and Modern Cell Culture in Virus Diagnosis
- Ali Hematian, Nourkhoda Sadeghifard, Reza Mohebi, Morovat Taherikalani, Abbas Nasrolahi, Mansour Amraei, Sobhan Ghafourian
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2016;7(2):77-82. Published online April 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2015.11.011
- Correction in: Osong Public Health Res Perspect 2020;11(4):266
- 6,172 View
- 100 Download
- 60 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Cell cultures are developed from tissue samples and then disaggregated by mechanical, chemical, and enzymatic methods to extract cells suitable for isolation of viruses. With the recent advances in technology, cell culture is considered a gold standard for virus isolation. This paper reviews the evolution of cell culture methods and demonstrates why cell culture is a preferred method for identification of viruses. In addition, the advantages and disadvantages of both traditional and modern cell culture methods for diagnosis of each type of virus are discussed. Detection of viruses by the novel cell culture methods is considered more accurate and sensitive. However, there is a need to include some more accurate methods such as molecular methods in cell culture for precise identification of viruses.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The cell cultures in virology: from the past to the future
Tatyana A. Kuznetsova, Natalia N. Besednova, Maxim R. Aliev, Michail Y. Shchelkanov
Journal of microbiology, epidemiology and immunobi.2024; 101(1): 143. CrossRef - Smartphone recognition-based immune microparticles for rapid on-site visual data-sharing detection of Newcastle disease virus
Shenjunjie Lu, Binglin Ma, Haoran Zhou, Yayang Li, Zhihao Qiao, Tong Xiao, Husheng Li, Baijie Wang, Meihui Cui, Shufang Zhang, Jin Chang, Taofeng Du, Jing Liu, Hanjie Wang
Talanta.2023; 252: 123845. CrossRef - Microbiological quality of irrigation water for cultivation of fruits and vegetables: An overview of available guidelines, water testing strategies and some factors that influence compliance.
Oluwadara Alegbeleye, Anderson S. Sant’Ana
Environmental Research.2023; 220: 114771. CrossRef - Raman spectroscopy for viral diagnostics
Jijo Lukose, Ajaya Kumar Barik, Mithun N, Sanoop Pavithran M, Sajan D. George, V. M. Murukeshan, Santhosh Chidangil
Biophysical Reviews.2023; 15(2): 199. CrossRef - Characterisation of new animal cell cultures’ sensitivity to Coxsackievirus B5 and Herpes simplex virus‑1
Yu. A. Zakharova, A. V. Ostapchuk, W. W. Wasielewski, O. S. Fedotova, N. A. Shmeleva
Biological Products. Prevention, Diagnosis, Treatm.2023; 23(1): 102. CrossRef - Paper-based diagnostic chips for viral detection
Srividya Oruganti, Sai Lakshmi Gundimeda, Viswanath Buddolla, Buddolla Anantha Lakshmi, Young-Joon Kim
Clinica Chimica Acta.2023; 546: 117413. CrossRef - Automated System for Multiplexing Detection of COVID-19 and Other Respiratory Pathogens
Parker Y. L. Tsang, Sunny L. H. Chu, Libby C. W. Li, Deborah M. S. Tai, Berry K. C. Cheung, Firaol Tamiru Kebede, Pete Y. M. Leung, Winston Wong, Teresa Chung, Cyril C. Y. Yip, Rosana W. S. Poon, Jonathan H. K. Chen, Kwok-Yung Yuen, Manson Fok, Johnson Y.
IEEE Journal of Translational Engineering in Healt.2023; 11: 424. CrossRef - The Role of Viral Infection in the Pathogenesis of Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome
Jia-Fong Jhang, Hann-Chorng Kuo
Current Bladder Dysfunction Reports.2023; 18(4): 374. CrossRef - Isolation and pathogenic characterization of duck adenovirus 3 mutant circulating in China
Xinjin Shi, Xinyu Zhang, Haiwei Sun, Changqing Wei, Yingnan Liu, Jiguan Luo, Xuebo Wang, Zongyan Chen, Hongjun Chen
Poultry Science.2022; 101(1): 101564. CrossRef - Nanotechnology: A Potential Weapon to Fight against COVID‐19
Atul K. Tiwari, Anupa Mishra, Govind Pandey, Munesh K. Gupta, Prem C. Pandey
Particle & Particle Systems Characterization.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Establishment and characterization of a cell line from ictalurid catfish
Suja Aarattuthodi, Vandana Dharan, Lester Khoo, Brian Bosworth
Journal of the World Aquaculture Society.2022; 53(3): 620. CrossRef - Canine parvovirology – A brief updated review on structural biology, occurrence, pathogenesis, clinical diagnosis, treatment and prevention
Deepika Tuteja, Kauser Banu, Bhairab Mondal
Comparative Immunology, Microbiology and Infectiou.2022; 82: 101765. CrossRef - A review on the contamination of SARS-CoV-2 in water bodies: Transmission route, virus recovery and recent biosensor detection techniques
Siti Adibah Zamhuri, Chin Fhong Soon, Anis Nurashikin Nordin, Rosminazuin Ab Rahim, Naznin Sultana, Muhammad Arif Khan, Gim Pao Lim, Kian Sek Tee
Sensing and Bio-Sensing Research.2022; 36: 100482. CrossRef - State-of-the-art nanotechnologies used in the development of SARS-CoV-2 biosensors: a review
Dongtak Lee, Taeha Lee, Ji Hye Hong, Hyo Gi Jung, Sang Won Lee, Gyudo Lee, Dae Sung Yoon
Measurement Science and Technology.2022; 33(6): 062002. CrossRef - Viral culture and immunofluorescence for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 infectivity in RT-PCR positive respiratory samples
Carla Berengua, Marina López, Montserrat Esteban, Pilar Marín, Paula Ramos, Margarita del Cuerpo, Ignasi Gich, Ferran Navarro, Elisenda Miró, Núria Rabella
Journal of Clinical Virology.2022; 152: 105167. CrossRef - Genome-Wide Analysis and Molecular Characterization of Orf Virus Strain UPM/HSN-20 Isolated From Goat in Malaysia
Hassana Kyari Mangga, Jamilu Abubakar Bala, Krishnan Nair Balakrishnan, Alhaji Modu Bukar, Zaharaddeen Lawan, Auwal Gambo, Faez Firdaus Abdullah Jesse, Mustapha M. Noordin, Mohd-Lila Mohd-Azmi
Frontiers in Microbiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Non-invasive detection of COVID-19 using a microfluidic-based colorimetric sensor array sensitive to urinary metabolites
Mohammad Mahdi Bordbar, Hosein Samadinia, Azarmidokht Sheini, Jasem Aboonajmi, Mohammad Javid, Hashem Sharghi, Mostafa Ghanei, Hasan Bagheri
Microchimica Acta.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - How Metagenomics Has Transformed Our Understanding of Bacteriophages in Microbiome Research
Laura K. Inglis, Robert A. Edwards
Microorganisms.2022; 10(8): 1671. CrossRef - Emergence of infectious diseases and role of advanced nanomaterials in point-of-care diagnostics: a review
Kalaimani Markandan, Yong Wei Tiong, Revathy Sankaran, Sakthinathan Subramanian, Uma Devi Markandan, Vishal Chaudhary, Arshid Numan, Mohammad Khalid, Rashmi Walvekar
Biotechnology and Genetic Engineering Reviews.2022; : 1. CrossRef - Respiratory Tract Infections and Laboratory Diagnostic Methods: A Review with A Focus on Syndromic Panel-Based Assays
Adriana Calderaro, Mirko Buttrini, Benedetta Farina, Sara Montecchini, Flora De Conto, Carlo Chezzi
Microorganisms.2022; 10(9): 1856. CrossRef - Viral Coinfections
Yanting Du, Chen Wang, Ying Zhang
Viruses.2022; 14(12): 2645. CrossRef - An Overview of Laboratory Diagnosis of Central Nervous System Viral Infections
Sharifah Aliah Diyanah Syed Hussin, Ang-Lim Chua, Hassanain Al-Talib, Shamala Devi Sekaran, Seok Mui Wang
Journal of Pure and Applied Microbiology.2022; 16(4): 2225. CrossRef - Multiplex detection of meningitis and encephalitis pathogens: A study from laboratory to clinic
Yanjun Si, Weijun He, Shuo Guo, Xiaohui Wang, Meng Tang, Binwu Ying, Minjin Wang
Frontiers in Neurology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) microfluidic modifications for cell-based immunofluorescence assay
Numfon Khemthongcharoen, Panapat Uawithya, Mayuree Chanasakulniyom, Montri Yasawong, Wutthinan Jeamsaksiri, Witsaroot Sripumkhai, Pattaraluck Pattamang, Ekachai Juntasaro, Nongluck Houngkamhang, Therdthai Thienthong, Chamras Promptmas
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2021; 35(9): 955. CrossRef - Pathogenic Virus Detection by Optical Nanobiosensors
Menglin Song, Mo Yang, Jianhua Hao
Cell Reports Physical Science.2021; 2(1): 100288. CrossRef - Emerging antiviral therapeutics for human adenovirus infection: Recent developments and novel strategies
Mackenzie J. Dodge, Katelyn M. MacNeil, Tanner M. Tessier, Jason B. Weinberg, Joe S. Mymryk
Antiviral Research.2021; 188: 105034. CrossRef - Magnetic Nanomaterials in Microfluidic Sensors for Virus Detection: A Review
Nahid Rezvani Jalal, Parvaneh Mehrbod, Shahla Shojaei, Hagar Ibrahim Labouta, Pooneh Mokarram, Abbas Afkhami, Tayyebeh Madrakian, Marek J. Los, Dedmer Schaafsma, Michael Giersig, Mazaher Ahmadi, Saeid Ghavami
ACS Applied Nano Materials.2021; 4(5): 4307. CrossRef - Virus Detection: A Review of the Current and Emerging Molecular and Immunological Methods
A. Cassedy, A. Parle-McDermott, R. O’Kennedy
Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Nanobased Platforms for Diagnosis and Treatment of COVID-19: From Benchtop to Bedside
Elham Bidram, Yasaman Esmaeili, Abbas Amini, Rossella Sartorius, Franklin R. Tay, Laleh Shariati, Pooyan Makvandi
ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering.2021; 7(6): 2150. CrossRef - Contagious ecthyma: how serious is the disease worldwide?
Zaharaddeen Lawan, Jamilu Abubakar Bala, Alhaji Modu Bukar, Krishnan Nair Balakrishnan, Hassana Kyari Mangga, Faez Firdaus Jesse Abdullah, Mustapha Mohamed Noordin, Mohd Lila Mohd-Azmi
Animal Health Research Reviews.2021; 22(1): 40. CrossRef - Recent Advances in Two-Dimensional Transition Metal Dichalcogenide Nanocomposites Biosensors for Virus Detection before and during COVID-19 Outbreak
Ching Ying Katherine Lam, Qin Zhang, Bohan Yin, Yingying Huang, Hui Wang, Mo Yang, Siu Hong Dexter Wong
Journal of Composites Science.2021; 5(7): 190. CrossRef - Viral Cultures for Coronavirus Disease 2019 Infectivity Assessment: A Systematic Review
Tom Jefferson, Elisabeth A Spencer, Jon Brassey, Carl Heneghan
Clinical Infectious Diseases.2021; 73(11): e3884. CrossRef - Severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus 2 in domesticated animals and its potential of transmission: A meta-analysis
Yos Adi Prakoso, Chylen Setiyo Rini, Yuli Purwandari Kristianingrum, Nurul Hidayah, Dyah Widhowati, Miarsono Sigit
Veterinary World.2021; : 2782. CrossRef - Nucleic Acids Analytical Methods for Viral Infection Diagnosis: State-of-the-Art and Future Perspectives
Emanuele Luigi Sciuto, Antonio Alessio Leonardi, Giovanna Calabrese, Giovanna De Luca, Maria Anna Coniglio, Alessia Irrera, Sabrina Conoci
Biomolecules.2021; 11(11): 1585. CrossRef - ATeam technology for detecting early signs of viral cytopathic effect
Karla Cristine C. DOYSABAS, Mami OBA, Tomoki ISHIBASHI, Hideki SHIBATA, Hitoshi TAKEMAE, Hiroshi SHIMODA, Ronald TARIGAN, Tetsuya MIZUTANI, Atsuo IIDA, Eiichi HONDO
Journal of Veterinary Medical Science.2020; 82(3): 387. CrossRef - Advanced “lab-on-a-chip” to detect viruses – Current challenges and future perspectives
Jianjian Zhuang, Juxin Yin, Shaowu Lv, Ben Wang, Ying Mu
Biosensors and Bioelectronics.2020; 163: 112291. CrossRef - Bee Viruses: Routes of Infection in Hymenoptera
Orlando Yañez, Niels Piot, Anne Dalmon, Joachim R. de Miranda, Panuwan Chantawannakul, Delphine Panziera, Esmaeil Amiri, Guy Smagghe, Declan Schroeder, Nor Chejanovsky
Frontiers in Microbiology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef Study on Adenovirus Infection in vitro with Nanoself-Assembling Peptide as Scaffolds for 3D Culture
Di-Shu Ao, Lu-Yao Gao, Jing-Han Gu, Jun-Hua Qiao, Huan Wang, Yan-Fei Liu, Hong Song
International Journal of Nanomedicine.2020; Volume 15: 6327. CrossRef- Determining sensitivity of novel animal-derived cell cultures to clinical isolates of human enterovirus Echovirus 11 and Coxsackievirus B5
A. V. Alimov, O. S. Fedotova, N. A. Shmelyova, A. A. Bakharev, A. V. Rezaykin, P. S. Usoltseva, B. S. Imangaliyev, T. L. Bakhareva
Medical alphabet.2020; (18): 17. CrossRef -
Strength and Weakness of Molecular Identification Strategies Against Causative Viral Agent from Emerging COVID-19
Chunguang Cui, Kisoon Kim
Journal of Bacteriology and Virology.2020; 50(2): 65. CrossRef - Isolation and characterization of duck adenovirus 3 circulating in China
Shaohua Shi, Rongchang Liu, Chunhe Wan, Longfei Cheng, Zhen Chen, Guanghua Fu, Hongmei Chen, Qiuling Fu, Yu Huang
Archives of Virology.2019; 164(3): 847. CrossRef - Bibliometric mapping of microbiology research topics (2012–16): a comparison by socioeconomic development and infectious disease vulnerability values
Tahereh Dehdarirad, Hajar Sotudeh, Jonathan Freer
FEMS Microbiology Letters.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Advances in Diagnostic Approaches for Viral Etiologies of Diarrhea: From the Lab to the Field
Yashpal Singh Malik, Atul Kumar Verma, Naveen Kumar, Nadia Touil, Kumaragurubaran Karthik, Ruchi Tiwari, Durlav Prasad Bora, Kuldeep Dhama, Souvik Ghosh, Maged Gomaa Hemida, Ahmed S. Abdel-Moneim, Krisztián Bányai, Anastasia N. Vlasova, Nobumichi Kobayash
Frontiers in Microbiology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Nanoparticle-Based LDI-MS Immunoassay for the Multiple Diagnosis of Viral Infections
Han-Wei Chu, Chao-Sung Lai, Jo-Yun Ko, Scott G. Harroun, Chiao-I Chuang, Robert Y. L. Wang, Binesh Unnikrishnan, Chih-Ching Huang
ACS Sensors.2019; 4(6): 1543. CrossRef - Development of conventional and real time PCR assays for rapid species authentication of mammalian cell lines commonly used in veterinary diagnostic laboratories
Amaresh Das, Lizhe Xu, Wei Jia
Research in Veterinary Science.2019; 126: 170. CrossRef - Development of an in-situ hybridization assay using riboprobes for detection of viral haemorrhagic septicemia virus (VHSV) mRNAs in a cell culture model
Syed Shariq Nazir Qadiri, Soo-Jin Kim, Rahul Krishnan, Jae-Ok Kim, Wi-Sik Kim, Myung-Joo Oh
Journal of Virological Methods.2019; 264: 1. CrossRef - Real-time PCR versus shell vial culture on urine of patients with suspected congenital cytomegalovirus infection
Luana Coltella, Stefania Ranno, Giuseppe Pizzichemi, Livia Piccioni, Stefano Chiavelli, Andrea Onetti Muda, Carlo Concato
Future Virology.2019; 14(9): 585. CrossRef - Isolation of the Human Cytomegalovirus from bodily fluids
Sigrid Johanna Camacho Ortega, Sonia Del Pilar Bohorquez Avila, Myriam Lucia Velandia Romero, Jaime Eduardo Castellanos Parra
Acta Biológica Colombiana.2019; 24(3): 520. CrossRef - Parechovirus a Detection by a Comprehensive Approach in a Clinical Laboratory
Bao-Chen Chen, Jenn-Tzong Chang, Tsi-Shu Huang, Jih-Jung Chen, Yao-Shen Chen, Ming-Wei Jan, Tsung-Hsien Chang
Viruses.2018; 10(12): 711. CrossRef - Aptamer immobilization on amino-functionalized metal–organic frameworks: an ultrasensitive platform for the electrochemical diagnostic of Escherichia coli O157:H7
Saeed Shahrokhian, Saba Ranjbar
The Analyst.2018; 143(13): 3191. CrossRef - Development and evaluation of a nested-PCR assay for Senecavirus A diagnosis
Cesar Feronato, Raquel A. Leme, Jaqueline A. Diniz, Alais Maria Dall Agnol, Alice F. Alfieri, Amauri A. Alfieri
Tropical Animal Health and Production.2018; 50(2): 337. CrossRef - Diagnosis of Viral Infection Using Real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction
Kyung-Ah Hwang, Ji Hoon Ahn, Jae-Hwan Nam
Journal of Bacteriology and Virology.2018; 48(1): 1. CrossRef - Virological and Immunological Outcomes of Coinfections
Naveen Kumar, Shalini Sharma, Sanjay Barua, Bhupendra N. Tripathi, Barry T. Rouse
Clinical Microbiology Reviews.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Laboratory Diagnosis of Respiratory Tract Infections in Children – the State of the Art
Shubhagata Das, Sherry Dunbar, Yi-Wei Tang
Frontiers in Microbiology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic Testing of Neurologic Infections
Prashanth S. Ramachandran, Michael R. Wilson
Neurologic Clinics.2018; 36(4): 687. CrossRef - Overview of Trends in the Application of Metagenomic Techniques in the Analysis of Human Enteric Viral Diversity in Africa’s Environmental Regimes
Cecilia Osunmakinde, Ramganesh Selvarajan, Timothy Sibanda, Bhekie Mamba, Titus Msagati
Viruses.2018; 10(8): 429. CrossRef - Nanomaterial-based biosensors for detection of pathogenic virus
Ahad Mokhtarzadeh, Reza Eivazzadeh-Keihan, Paria Pashazadeh, Maryam Hejazi, Nasrin Gharaatifar, Mohammad Hasanzadeh, Behzad Baradaran, Miguel de la Guardia
TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry.2017; 97: 445. CrossRef - Plasma assisted surface treatments of biomaterials
L. Minati, C. Migliaresi, L. Lunelli, G. Viero, M. Dalla Serra, G. Speranza
Biophysical Chemistry.2017; 229: 151. CrossRef - Combined Proteomics/Genomics Approach Reveals Proteomic Changes of Mature Virions as a Novel Poxvirus Adaptation Mechanism
Marica Grossegesse, Joerg Doellinger, Alona Tyshaieva, Lars Schaade, Andreas Nitsche
Viruses.2017; 9(11): 337. CrossRef - A Lipidomics Approach in the Characterization of Zika-Infected Mosquito Cells: Potential Targets for Breaking the Transmission Cycle
Carlos Fernando Odir Rodrigues Melo, Diogo Noin de Oliveira, Estela de Oliveira Lima, Tatiane Melina Guerreiro, Cibele Zanardi Esteves, Raissa Marques Beck, Marina Aiello Padilla, Guilherme Paier Milanez, Clarice Weis Arns, José Luiz Proença-Modena, Jayme
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(10): e0164377. CrossRef
- The cell cultures in virology: from the past to the future



 First
First Prev
Prev


