Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Early countermeasures to COVID-19 at long-term care facilities in Gwangju Metropolitan City, Republic of Korea
- Hye-Jin Kim, Jieun Kim, Yoon Suk Jang, Hanul Park, Jong Mu Kim, Young Joon Park, So-Yeon Ryu, Jun Hwi Cho, So Yeong Park, Sang-Eun Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(1):59-65. Published online February 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0293
- 1,918 View
- 79 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 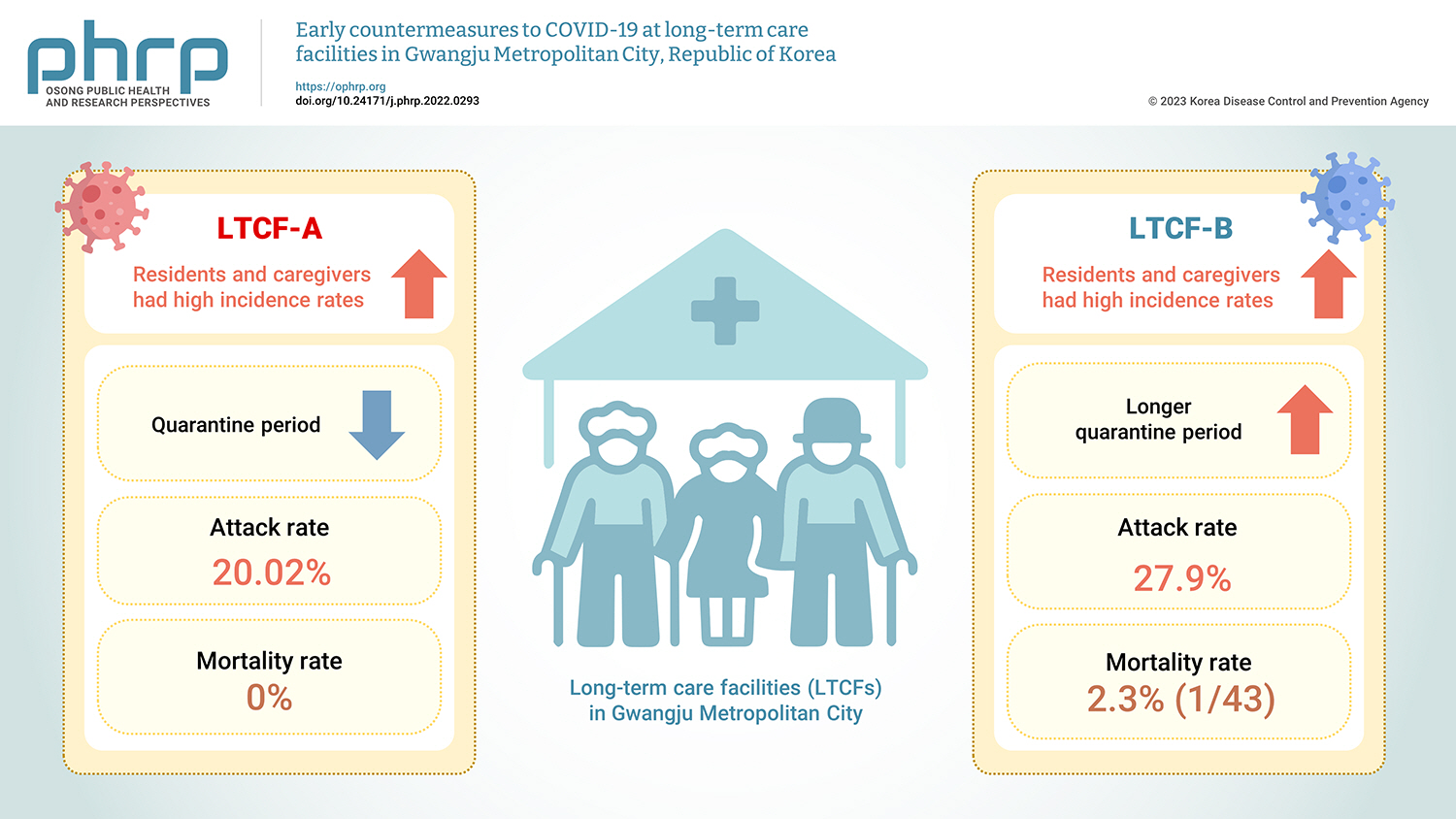
- Objectives
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has continued since its first detection in the Republic of Korea on January 20, 2020. This study describes the early countermeasures used to minimize the risk of COVID-19 outbreaks during cohort quarantine and compares the epidemiological characteristics of 2 outbreaks in long-term care facilities (LTCFs) in Gwangju Metropolitan City in summer 2020. Methods: An epidemiological investigation was conducted via direct visits. We investigated epidemiological characteristics, including incidence, morbidity, and mortality rates, for all residents and staff members. Demographic characteristics were analyzed using a statistical program. Additionally, the method of managing infection in LTCFs is described. Results: Residents and caregivers had high incidence rates in LTCF-A and LTCF-B, respectively. LTCF-B had a longer quarantine period than LTCF-A. The attack rate was 20.02% in LTCF-A and 27.9% in LTCF-B. The mortality rate was 2.3% (1/43) in LTCF-B, the only facility in which a COVID-19 death occurred. Conclusion: Extensive management requires contact minimization, which involves testing all contacts to mitigate further transmission in the early stages of LTCF outbreaks. The findings of this study can help inform and prepare public health authorities for COVID-19 outbreaks, particularly for early control in vulnerable facilities.
- Early Intervention Reduces the Spread of COVID-19 in Long-Term Care Facilities in the Republic of Korea
- Shin Young Park, Gawon Choi, Hyeyoung Lee, Na-young Kim, Seon-young Lee, Kyungnam Kim, Soyoung Shin, Eunsu Jang, YoungSin Moon, KwangHwan Oh, JaeRin Choi, Sangeun Lee, Young-Man Kim, Jieun Kim, Seonju Yi, Jin Gwack, Ok Park, Young Joon Park
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2020;11(4):259-264. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2020.11.4.16
- 6,507 View
- 148 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study describes the epidemiological characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) based on reported cases from long-term care facilities. As of April 20th, 2020, 3 long-term care facilities in a metropolitan area of South Korea had reported cases of COVID-19. These facilities’ employees were presumed to be the sources of infection. There were 2 nursing hospitals that did not report any additional cases. One nursing home had a total of 25 cases, with an attack rate of 51.4% (95% CI 35.6–67.0), and a fatality rate of 38.9% (95% CI 20.3–61.4) among residents. The results from this study suggest that early detection and maintenance of infection control minimizes the risk of rapid transmission.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and corresponding control measures on long-term care facilities: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Jun Zhang, Yushan Yu, Mirko Petrovic, Xiaomei Pei, Qing-Bao Tian, Lei Zhang, Wei-Hong Zhang
Age and Ageing.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A scoping review of the impacts of COVID-19 physical distancing measures on vulnerable population groups
Lili Li, Araz Taeihagh, Si Ying Tan
Nature Communications.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of Concentrated COVID-19 Outbreaks in Elderly Facilities in Suita City, Osaka Prefecture, Japan
Toshiyuki Shibata, Sawa Okano, Daisuke Onozuka, Etsuko Ohta, Satoshi Kutsuna
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2023; 20(20): 6926. CrossRef - Factors relating to intention of use non-face-to-face services among family caregivers of persons with dementia: A cross-sectional study
Myonghwa Park, Jinju Kim, Jihye Jung, Seonhwa Kim, Jinhee Lee, Dongyoung Lee
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2023; 25(4): 377. CrossRef - Staffing Levels and COVID-19 Infections and Deaths in Korean Nursing Homes
Jiyeon Lee, Juh Hyun Shin, Kyeong Hun Lee, Charlene A. Harrington, Sun Ok Jung
Policy, Politics, & Nursing Practice.2022; 23(1): 15. CrossRef - An Experience of the Early Stage of COVID-19 Outbreak in Nursing Homes in Gyeonggi Province, Korea
Gawon Choi, Na-young Kim, Seon-young Lee, Hae Deun Noh, Heeyoung Lee
Korean Journal of Clinical Geriatrics.2022; 23(1): 27. CrossRef - The implications of the COVID-19 pandemic for long term care facilities
Muh-Yong Yen, Jonathan Schwartz, Po-Ren Hsueh
Current Opinion in Infectious Diseases.2022; 35(4): 370. CrossRef - Health impact of the first and second wave of COVID-19 and related restrictive measures among nursing home residents: a scoping review
Marjolein E. A. Verbiest, Annerieke Stoop, Aukelien Scheffelaar, Meriam M. Janssen, Leonieke C. van Boekel, Katrien G. Luijkx
BMC Health Services Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Epidemiology and clinical features of COVID-19 outbreaks in aged care facilities: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Mohammad Rashidul Hashan, Nicolas Smoll, Catherine King, Hannah Ockenden-Muldoon, Jacina Walker, Andre Wattiaux, Julieanne Graham, Robert Booy, Gulam Khandaker
EClinicalMedicine.2021; 33: 100771. CrossRef - Protecting Nursing Homes and Long-Term Care Facilities From COVID-19: A Rapid Review of International Evidence
Sally Hall Dykgraaf, Sethunya Matenge, Jane Desborough, Elizabeth Sturgiss, Garang Dut, Leslee Roberts, Alison McMillan, Michael Kidd
Journal of the American Medical Directors Associat.2021; 22(10): 1969. CrossRef - Dementia Risk among Coronavirus Disease Survivors: A Nationwide Cohort Study in South Korea
Hye-Yoon Park, In-Ae Song, Tak-Kyu Oh
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2021; 11(10): 1015. CrossRef
- Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and corresponding control measures on long-term care facilities: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Factors Related to Healthcare Service Quality in Long-term Care Hospitals in South Korea: A Mixed-methods Study
- Minsung Sohn, Mankyu Choi
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2017;8(5):332-341. Published online October 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2017.8.5.07
- 4,012 View
- 31 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Objectives The environment of long-term care hospitals (LTCHs) is critical to the management of the quality of their services and to patient safety, as highlighted by international studies. However, there is a lack of evidence on this topic in South Korea. This study aimed to examine the factors affecting healthcare quality in LTCHs and to explore the effectiveness of their quality management.
Methods This study used a mixed methods approach with quantitative data collected in a national survey and qualitative data from semi-structured interviews with practice-based managers. The samples included 725 nationally representative LTCHs in South Korea for the quantitative analysis and 15 administrators for the in-depth interviews.
Results A higher installation rate of patient-safety and hygiene-related facilities and staff with longer-tenures, especially nurses, were more likely to have better healthcare quality and education for both employees and patients.
Conclusion The need for patient-safety- and hygiene-related facilities in LTCHs that serve older adults reflects their vulnerability to certain adverse events (e.g., infections). Consistent and skillful nursing care to improve the quality of LTCHs can be achieved by developing relevant educational programs for staff and patients, thereby strengthening the relationships between them.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Improving Preparedness for and Response to Coronavirus Disease 19 (COVID-19) in Long-Term Care Hospitals in Korea
Tark Kim
Infection & Chemotherapy.2020; 52(2): 133. CrossRef - Identifying Potentially Avoidable Emergency Department Visits of Long-Term Care Hospital Residents in Korea: A Multicenter Retrospective Cohort Study
Keon Kim, Dong Hoon Lee, Ho Young Yune, Jung Hee Wee, Duk Ho Kim, Eui Chung Kim, Jee Yong Lim, Seung Pil Choi
BioMed Research International.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef
- Improving Preparedness for and Response to Coronavirus Disease 19 (COVID-19) in Long-Term Care Hospitals in Korea
- Community-Based Home Healthcare Project for Korean Older Adults
- TaeBum Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2013;4(5):233-239. Published online October 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2013.09.002
- 2,870 View
- 15 Download
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
The aim of this study was to identify the effects of community-based home healthcare projects that influence service performances with regard to Korean national long-term care insurance services in older adults.
Methods
The project's applicants were 18 operational agencies in national long-term care institutions in Korea, and participants were care recipients (n = 2263) registered in long-term care institutions. We applied our healthcare system to the recruited participants for a 3-month period from October 2012 to December 2012. We measured the community-based home healthcare services such as long-term care, health and medical service, and welfare and leisure service prior to and after applying the community-based home healthcare system.
Results
After the implementation of community-based home healthcare project, all community-based home healthcare services showed an increase than prior to the project implementation. The nutrition management service was the most increased and its increase rate was 628.6%. A comparison between the long-term care insurance beneficiaries and nonbeneficiaries showed that health and medical services’ increase rate of nonbeneficiaries was significantly higher than beneficiaries (p < 0.001).
Conclusion
Our community-based home healthcare project might improve the service implementation for older adults and there was a difference in the increase rate of health and medical services between Korean national long-term care insurance beneficiaries and nonbeneficiaries. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Perceived availability of home‐ and community‐based services and self‐reported depression among Chinese older adults: A cross‐sectional study
Yushan Yu, Jun Zhang, Chao Song, Mirko Petrovic, Xiaomei Pei, Wei‐Hong Zhang
Health & Social Care in the Community.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Community-based health financing: empirical evaluation of the socio-demographic factors determining its uptake in Awka, Anambra state, Nigeria
Felix O. Iyalomhe, Paul O. Adekola, Giuseppe T. Cirella
International Journal for Equity in Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Influencing Burnout in Primary Family Caregivers of Hospital-based Home Care Patients
Ju Ok Yang, Hye Kyung Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nurs.2018; 29(1): 54. CrossRef - A Systematic Literature Review Comparing Primary and Community Health Care Indicators and Measurement Frameworks
Nour El Kadri, Liam Peyton
Procedia Computer Science.2017; 113: 384. CrossRef - Economic Effect of Home Health Care Services for Community-dwelling Vulnerable Populations
Eunhee Lee, Jinhyun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2016; 46(4): 562. CrossRef
- Perceived availability of home‐ and community‐based services and self‐reported depression among Chinese older adults: A cross‐sectional study
- Improving Service Quality in Long-term Care Hospitals: National Evaluation on Long-term Care Hospitals and Employees Perception of Quality Dimensions
- Jinkyung Kim, Woosok Han
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2012;3(2):94-99. Published online June 30, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2012.04.005
- 2,778 View
- 16 Download
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
To investigate predictors for specific dimensions of service quality perceived by hospital employees in long-term care hospitals.
Methods
Data collected from a survey of 298 hospital employees in 18 long-term care hospitals were analysed. Multivariate ordinary least squares regression analysis with hospital fixed effects was used to determine the predictors of service quality using respondents’ and organizational characteristics.
Results
The most significant predictors of employee-perceived service quality were job satisfaction and degree of consent on national evaluation criteria. National evaluation results on long-term care hospitals and work environment also had positive effects on service quality.
Conclusion
The findings of the study show that organizational characteristics are significant determinants of service quality in long-term care hospitals. Assessment of the extent to which hospitals address factors related to employeeperceived quality of services could be the first step in quality improvement activities. Results have implications for efforts to improve service quality in longterm care hospitals and designing more comprehensive national evaluation criteria. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The assessment of quality of care in the Indian healthcare industry: the employees’ and patients’ perspectives
Karthik Padamata, Rama Devi Vangapandu
Benchmarking: An International Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The perception of health care quality by primary health care managers in Ukraine
Valentyna Anufriyeva, Milena Pavlova, Tetiana Stepurko, Wim Groot
BMC Health Services Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Primary Health Institutions and Service Quality in China: Implications for Health Policy
Junfang Xu, Yuyin Zhou, Ruyu Liu, Feng Cheng, Wannian Liang
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2022; 19(19): 12063. CrossRef - Lean Healthcare Readiness Evaluation among Staff in Private Hospital
Nihayatul Munaa, Faizatul Ummah, M.I. Kartasurya, N. Lisnawati, A.F. Asna, N. Handayani, D.Z. Nuridzin
BIO Web of Conferences.2022; 54: 00015. CrossRef - A tool to assess the quality perception of healthcare employees
Ajayan Kamalasanan, Gurumoorthy Sathiyamurthi, Arun Vijay Subbarayalu
International Journal of Health Care Quality Assur.2020; 33(4/5): 291. CrossRef - Dimensions of service quality in healthcare: a systematic review of literature
Iram Fatima, Ayesha Humayun, Usman Iqbal, Muhammad Shafiq
International Journal for Quality in Health Care.2019; 31(1): 11. CrossRef - Using the Importance–Satisfaction Model and Service Quality Performance Matrix to Improve Long-Term Care Service Quality in Taiwan
Shun-Hsing Chen, Fan-Yun Pai, Tsu-Ming Yeh
Applied Sciences.2019; 10(1): 85. CrossRef - Jurnal Kualitas Pelayanan Kesehatan (Studi Analitik Terhadap Pasien Rawat Jalan di RSUD Makassar)
Andi Alim, Novagita Tangdilambi, Adam Badwi
Jurnal Manajemen Kesehatan Yayasan RS.Dr. Soetomo.2019; 5(2): 165. CrossRef - Manufacturers’ perceived quality of electricity service and organizational performance in Nigeria
Abdulrahman Muhammed, Lamidi Yusuf
Journal of Transportation and Logistics.2016; 1(2): 143. CrossRef - Public Health Services for Foreign Workers in Malaysia
Normah Awang Noh, Haris Abd. Wahab, Siti Hajar Abu Bakar Ah, M. Rezaul Islam
Social Work in Public Health.2016; 31(5): 419. CrossRef
- The assessment of quality of care in the Indian healthcare industry: the employees’ and patients’ perspectives



 First
First Prev
Prev


